Android 15 平台包含可能對應用程式造成影響的行為變更。無論 targetSdkVersion 為何,當應用程式在 Android 15 上執行時,下列行為變更將會套用至所有應用程式。您應測試應用程式,並視需要修改,以便在適當情況下支援新版本功能。
另請務必查看僅對指定 Android 15 為目標版本的應用程式造成影響的行為變更。
核心功能
Android 15 會修改或擴充 Android 系統的各種核心功能。
套件停止狀態的變更
套件 FLAG_STOPPED 狀態的意圖 (使用者可以透過長按應用程式圖示並選取「強制停止」來啟用 AOSP 版本) 一向是讓應用程式維持在這個狀態,直到使用者透過直接啟動應用程式或間接與應用程式互動 (透過分享畫面或小工具,將應用程式選做動態桌布等) 明確將應用程式移除為止。在 Android 15 中,我們已更新系統行為,以符合這項預期行為。應用程式應僅透過直接或間接的使用者操作,從停止狀態移除。
為了支援預期的行為,除了現有的限制之外,當應用程式在執行 Android 15 的裝置上進入已停止狀態時,系統也會取消所有待處理意圖。當使用者的動作將應用程式從已停止狀態移除時,系統會將 ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED 廣播傳送至應用程式,讓應用程式有機會重新註冊任何待處理的意圖。
您可以呼叫新的 ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped() 方法,確認應用程式是否已進入停止狀態。
支援 16 KB 分頁大小
過去 Android 僅支援 4 KB 的記憶體分頁大小,這已針對 Android 裝置通常擁有的平均總記憶體量,最佳化系統記憶體效能。從 Android 15 開始,AOSP 支援設定為使用 16 KB 頁面大小的裝置 (16 KB 裝置)。如果應用程式使用任何 NDK 程式庫 (直接或透過 SDK 間接使用),您必須重建應用程式,才能在這些 16 KB 裝置上運作。
隨著裝置製造商持續打造實體記憶體 (RAM) 容量更大的裝置,許多裝置將採用 16 KB (最終會更大) 的分頁大小,以最佳化裝置效能。為 16 KB 頁面大小的裝置新增支援功能,可讓應用程式在這些裝置上執行,並享有相關的效能提升優勢。如果沒有重新編譯,應用程式就無法在日後的 Android 版本中,於 16 KB 裝置上運作。
為協助您為應用程式新增支援功能,我們提供了相關指南,說明如何檢查應用程式是否受到影響、如何重建應用程式 (如適用),以及如何使用模擬器 (包括 Android Emulator 的 Android 15 系統映像檔),在 16 KB 環境中測試應用程式。
優點和效能提升
以 16 KB 頁面大小設定的裝置平均會耗用較多記憶體,但系統和應用程式也能獲得各種效能改善:
- 系統面臨記憶體壓力時,應用程式啟動時間越短:平均低 3.16%,部分受測的應用程式還大幅改善 (最多提升 30%)
- 應用程式啟動期間的耗電量降幅:平均減少 4.56%
- 相機啟動速度更快:熱啟動速度平均快了 4.48%,冷啟動速度平均快了 6.60%
- 縮短系統啟動時間:縮短 8% (平均約 950 毫秒)
這些改善項目是根據初步測試結果而來,實際裝置上的結果可能會有所不同。我們會在持續測試的過程中,針對應用程式可能獲得的效益提供額外分析。
確認應用程式是否受到影響
如果應用程式使用任何原生程式碼,請重新建構應用程式,支援 16 KB 裝置。如果您不確定應用程式是否使用原生程式碼,可以使用 APK 分析工具找出是否有任何原生程式碼,然後檢查找到的任何共用程式庫的 ELF 區段是否對齊。Android Studio 也提供相關功能,可協助您自動偵測對齊問題。
如果應用程式只使用以 Java 程式設計語言或 Kotlin 編寫的程式碼 (包括所有程式庫或 SDK),則應用程式已可支援 16 KB 裝置。不過,我們建議您在 16 KB 環境中測試應用程式,確認應用程式行為沒有發生非預期的迴歸。
部分應用程式必須進行變更,才能支援私人空間
私人空間是 Android 15 的新功能,可讓使用者在裝置上建立獨立空間,在額外的驗證機制下,隱藏敏感應用程式,防止他人查看。由於私人空間中的應用程式可見度受限,某些類型的應用程式需要採取額外步驟,才能查看及與使用者私人空間中的應用程式互動。
所有應用程式
由於私人空間中的應用程式會保存在獨立的使用者資料夾中 (類似工作資料夾),因此應用程式不應假設任何未位於主要資料夾中的應用程式副本,都位於工作資料夾中。如果您的應用程式包含與工作資料夾應用程式相關的邏輯,且會做出這項假設,您就需要調整這項邏輯。
醫療應用程式
使用者鎖定私人空間後,私人空間中的所有應用程式都會停止,這些應用程式無法執行前景或背景活動,包括顯示通知。這項行為可能會嚴重影響安裝在私人空間中的醫療應用程式使用方式和功能。
私人空間設定體驗會警告使用者,私人空間不適用於需要執行重要前景或背景活動的應用程式,例如顯示醫療應用程式通知。不過,應用程式無法判斷是否在私人空間中使用,因此無法針對這種情況向使用者顯示警告。
基於這些原因,如果您開發醫療應用程式,請查看這項功能可能對應用程式造成的影響,並採取適當行動,例如告知使用者不要在私人空間安裝應用程式,以免中斷重要應用程式功能。
啟動器應用程式
如果您要開發啟動器應用程式,則必須先執行下列操作,才能顯示私人空間中的應用程式:
- 您的應用程式必須指派為裝置的預設啟動器應用程式,也就是擁有
ROLE_HOME角色。 - 應用程式必須在應用程式的資訊清單檔案中宣告
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES一般權限。
宣告 ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES 權限的啟動器應用程式必須處理下列私人空間用途:
- 您的應用程式必須有獨立的啟動器容器,用於安裝在私人空間中的應用程式。使用
getLauncherUserInfo()方法,判斷要處理哪種類型的使用者設定檔。 - 使用者必須能夠隱藏及顯示私人空間容器。
- 使用者必須能夠鎖定及解鎖私人空間容器。使用
requestQuietModeEnabled()方法鎖定 (傳遞true) 或解鎖 (傳遞false) 私人空間。 在鎖定狀態下,私人空間容器中的應用程式不得顯示或透過搜尋等機制發現。應用程式應為
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLE和ACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLE廣播訊息註冊接收器,並在私人空間容器的鎖定或解鎖狀態變更時更新應用程式中的 UI。這兩種廣播都包含EXTRA_USER,可讓應用程式參照私人設定檔使用者。您也可以使用
isQuietModeEnabled()方法,檢查私人空間設定檔是否已鎖定。
應用程式商店應用程式
私人空間包含「安裝應用程式」按鈕,可啟動隱含意圖,將應用程式安裝至使用者的私人空間。為了讓應用程式接收這項隱含意圖,請在應用程式資訊清單檔案中宣告 <intent-filter>,並使用 CATEGORY_APP_MARKET 的 <category>。
移除以 PNG 為基礎的表情符號字型
舊版的 PNG 表情符號字型檔案 (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf) 已移除,只保留以向量為基礎的檔案。自 Android 13 (API 級別 33) 起,系統表情符號轉譯器使用的表情符號字型檔案已從以 PNG 為基礎的檔案變更為以向量為基礎的檔案。基於相容性考量,系統會保留 Android 13 和 14 中的舊版字型檔案,讓自有字型轉譯器的應用程式在升級前,可以繼續使用舊版字型檔案。
如要確認您的應用程式是否受到影響,請搜尋應用程式程式碼中是否有 NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf 檔案的參照。
您可以透過多種方式調整應用程式:
- 使用平台 API 轉譯文字。您可以將文字算繪至以位圖為後端的
Canvas,並視需要使用該圖片取得原始圖片。 - 為應用程式新增 COLRv1 字型支援功能。FreeType 開放原始碼程式庫在 2.13.0 以上版本中支援 COLRv1。
- 如非萬不得已,您可以將舊版表情符號字型檔案 (
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) 整合至 APK,但這樣一來,您的應用程式就會缺少最新的表情符號更新。詳情請參閱 Noto Emoji GitHub 專案頁面。
目標 SDK 最低版本從 23 提高至 24
Android 15 採用
Android 14 所做的變更,並將這項做法
在 Android 15 中,
24 以下版本的 targetSdkVersion 無法安裝。
要求應用程式符合現代 API 級別,有助於提供更完善的安全防護和
隱私權。
為了規避 Android 較新版本的安全性和隱私權保護措施,惡意軟體通常會鎖定較低的 API 級別。例如:
部分惡意軟體應用程式會使用 22 的 targetSdkVersion,以免受到
Android 6.0 Marshmallow (API) 在 2015 年推出的執行階段權限模型
第 23 級)。這項 Android 15 變更會讓惡意軟體更難躲過更嚴謹的安全性和隱私權措施。嘗試安裝以較低 API 為目標的應用程式
level 會導致安裝失敗,並顯示以下訊息:
出現在 Logcat 中:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
在升級至 Android 15 的裝置上,targetSdkVersion 較低的所有應用程式
仍未解除安裝。
如要測試以舊版 API 級別為目標的應用程式,請使用下列 ADB 指令:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
安全性和隱私權
Android 15 推出了可有效防範一次性密碼 (OTP) 詐欺行為的強大措施,並保護使用者的敏感內容,重點是強化通知事件監聽器服務和螢幕分享保護機制。主要強化功能包括從可供不受信任的應用程式存取的通知中遮蓋 OTP、在螢幕分享期間隱藏通知,以及在發布 OTP 時保護應用程式活動。這些異動旨在保護使用者的機密內容,避免遭到未經授權的人士存取。
開發人員需要注意下列事項,確保應用程式與 Android 15 的變更相容:
動態密碼遮蓋
Android 會停止未受信任的應用程式,避免其在偵測到 OTP 時,從通知中讀取未經遮蓋的內容。NotificationListenerService信任的應用程式 (例如隨附裝置管理員關聯) 不受這些限制。
螢幕分享保護功能
- 為保護使用者隱私,系統會在螢幕分享工作階段中隱藏通知內容。如果應用程式實作
setPublicVersion(),Android 會顯示通知的公開版本,這可在非安全環境中做為替換通知。否則,通知內容會遭到遮蓋,且不會提供任何其他背景資訊。 - 遠端觀眾無法看到密碼輸入內容等機密內容,以免洩漏使用者的機密資訊。
- 在偵測到 OTP 的螢幕分享期間,系統會隱藏發布通知的應用程式活動。應用程式內容在啟動時會隱藏在遠端檢視器中。
- 除了 Android 自動辨識敏感欄位之外,開發人員也可以使用
setContentSensitivity手動將應用程式的部分內容標示為敏感內容,這樣在螢幕分享期間,遠端觀眾就不會看到這些內容。 - 開發人員可以選擇切換「開發人員選項」下方的「停用螢幕畫面分享防護」選項,為示範或測試目的,免除螢幕畫面分享防護。預設的系統螢幕錄影工具不受這些變更影響,因為錄影內容會保留在裝置上。
相機和媒體
Android 15 對所有應用程式的相機和媒體行為進行下列變更。
如果達到資源限制,直接和卸載音訊播放作業會使先前開啟的直接或卸載音軌失效
在 Android 15 之前,如果應用程式在其他應用程式播放音訊時要求直接或卸載音訊播放,且已達到資源限制,應用程式就會無法開啟新的 AudioTrack。
自 Android 15 起,當應用程式要求直接或卸載播放功能,且已達到資源限制時,系統會使任何目前開啟的 AudioTrack 物件失效,以免無法滿足新曲目要求。
(直接和卸載音訊音軌通常會在播放壓縮音訊格式時開啟。直接播放音訊的常見用途包括透過 HDMI 將編碼音訊串流至電視。卸載音軌通常用於在行動裝置上播放經過壓縮的音訊,並使用硬體 DSP 加速功能。
使用者體驗和系統 UI
Android 15 包含一些變更,旨在打造更一致、直覺的使用者體驗。
為已選擇加入的應用程式啟用預測返回動畫
從 Android 15 開始,預測返回動畫的開發人員選項已遭移除。對於已全面或在活動層級啟用預測返回手勢功能的應用程式,現在會顯示返回首頁、跨工作和跨活動等系統動畫。如果您的應用程式受到影響,請採取下列行動:
- 請確認應用程式已正確遷移,可使用預測返回手勢。
- 確保片段轉場效果可與預測返回導覽功能搭配運作。
- 請移除動畫和架構轉場效果,改用動畫器和 androidx 轉場效果。
- 從
FragmentManager不瞭解的返回堆疊中移除。請改用由FragmentManager或 Navigation 元件管理的返回堆疊。
使用者強制停止應用程式時,小工具會停用
如果使用者在搭載 Android 15 的裝置上強制停止應用程式,系統會暫時停用所有應用程式小工具。小工具會顯示為灰色,使用者無法與其互動。這是因為從 Android 15 開始,系統會在應用程式強制停止時取消所有應用程式的待處理意圖。
系統會在使用者下次啟動應用程式時,重新啟用這些小工具。
詳情請參閱「套件停止狀態的變更」。
媒體投影狀態列晶片會提醒使用者分享螢幕畫面、投放及錄製畫面
螢幕投影漏洞會洩漏使用者的私人資料,例如財務資訊,因為使用者不會察覺自己的裝置螢幕正在分享。
如果應用程式在搭載 Android 15 QPR1 以上版本的裝置上執行,狀態列的方塊會以大而醒目的方式,提醒使用者任何進行中的螢幕投影作業。使用者可以輕觸方塊,停止分享、投放或錄製螢幕畫面。此外,裝置螢幕鎖定時,螢幕投放功能也會自動停止。
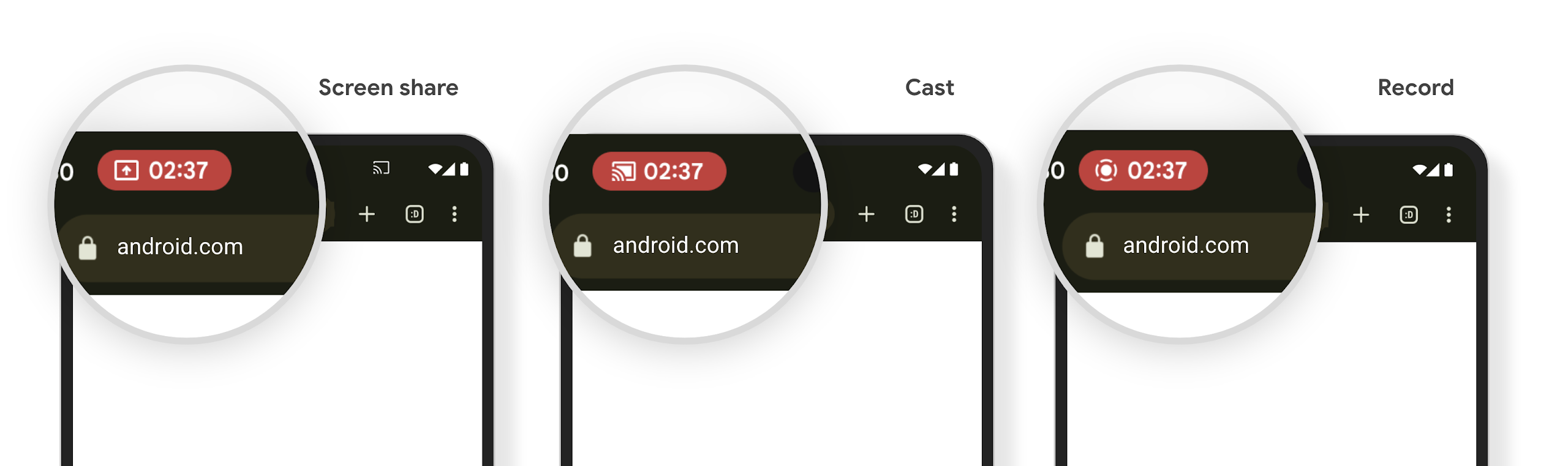
確認應用程式是否受到影響
根據預設,應用程式會包含狀態列方塊,並在螢幕鎖定畫面啟用時自動暫停投放螢幕畫面。
如要進一步瞭解如何針對這些用途測試應用程式,請參閱「狀態列方塊和自動停止」。
背景網路存取權限制
在 Android 15 中,如果應用程式在有效的程序生命週期之外啟動網路要求,就會收到例外狀況。通常是 UnknownHostException 或其他與 Socket 相關的 IOException。在有效生命週期以外發生的網路要求,通常是因為應用程式在不再處於活動狀態後,仍不知情地繼續網路要求。
為減少這種例外狀況,請使用生命週期感知元件,確保網路要求具備生命週期感知功能,並在離開有效程序生命週期時取消。如果您認為網路要求必須在使用者離開應用程式後繼續執行,建議您使用 WorkManager 排程網路要求,或是使用前景服務繼續執行使用者可見的工作。
淘汰項目
每次發布新版本時,特定 Android API 可能會過時,或需要重構,才能提供更優質的開發人員體驗或支援新的平台功能。在這種情況下,我們會正式淘汰舊版 API,並引導開發人員改用其他 API。
淘汰表示我們已終止對 API 的官方支援,但開發人員仍可繼續使用。如要進一步瞭解 Android 這個版本的重要淘汰項目,請參閱淘汰項目頁面。
