แพลตฟอร์ม Android 15 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่อาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณ
การเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานต่อไปนี้จะมีผลกับแอปทั้งหมดเมื่อแอปทำงานบน Android 15
ไม่ว่าtargetSdkVersion จะเป็นเวอร์ชันใดก็ตาม คุณควรทดสอบแอป แล้วแก้ไข
ตามความจำเป็นเพื่อรองรับฟีเจอร์เหล่านี้อย่างเหมาะสม (หากมี)
อย่าลืมตรวจสอบรายการการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่มีผลกับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 เท่านั้นด้วย
ฟังก์ชันหลัก
Android 15 จะแก้ไขหรือขยายความสามารถหลักต่างๆ ของระบบ Android
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสถานะของแพ็กเกจเป็นหยุด
The intention of the package FLAG_STOPPED state (which users
can engage in AOSP builds by long-pressing an app icon and selecting "Force
Stop") has always been to keep apps in this state until the user explicitly
removes the app from this state by directly launching the app or indirectly
interacting with the app (through the sharesheet or a widget, selecting the app
as live wallpaper, etc.). In Android 15, we've updated the behavior of the
system to be aligned with this intended behavior. Apps should only be removed
from the stopped state through direct or indirect user action.
To support the intended behavior, in addition to the existing restrictions, the
system also cancels all pending intents when the app enters the
stopped state on a device running Android 15. When the user's actions remove the
app from the stopped state, the ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED
broadcast is delivered to the app providing an opportunity to re-register any
pending intents.
You can call the new
ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped()
method to confirm whether the app was put into the stopped state.
รองรับขนาดหน้าหน่วยความจำขนาด 16 KB
Historically, Android has only supported 4 KB memory page sizes, which has optimized system memory performance for the average amount of total memory that Android devices have typically had. Beginning with Android 15, AOSP supports devices that are configured to use a page size of 16 KB (16 KB devices). If your app uses any NDK libraries, either directly or indirectly through an SDK, then you will need to rebuild your app for it to work on these 16 KB devices.
As device manufacturers continue to build devices with larger amounts of physical memory (RAM), many of these devices will adopt 16 KB (and eventually greater) page sizes to optimize the device's performance. Adding support for 16 KB page size devices enables your app to run on these devices and helps your app benefit from the associated performance improvements. Without recompiling, apps won't work on 16 KB devices in future Android releases.
To help you add support for your app, we've provided guidance on how to check if your app is impacted, how to rebuild your app (if applicable), and how to test your app in a 16 KB environment using emulators (including Android 15 system images for the Android Emulator).
ประโยชน์และประสิทธิภาพที่เพิ่มขึ้น
Devices configured with 16 KB page sizes use slightly more memory on average, but also gain various performance improvements for both the system and apps:
- Lower app launch times while the system is under memory pressure: 3.16% lower on average, with more significant improvements (up to 30%) for some apps that we tested
- Reduced power draw during app launch: 4.56% reduction on average
- Faster camera launch: 4.48% faster hot starts on average, and 6.60% faster cold starts on average
- Improved system boot time: improved by 8% (approximately 950 milliseconds) on average
These improvements are based on our initial testing, and results on actual devices will likely differ. We'll provide additional analysis of potential gains for apps as we continue our testing.
ตรวจสอบว่าแอปของคุณได้รับผลกระทบหรือไม่
If your app uses any native code, then you should rebuild your app with support for 16 KB devices. If you are unsure if your app uses native code, you can use the APK Analyzer to identify whether any native code is present and then check the alignment of ELF segments for any shared libraries that you find. Android Studio also provides features that help you to automatically detect alignment issues.
If your app only uses code written in the Java programming language or in Kotlin, including all libraries or SDKs, then your app already supports 16 KB devices. Nevertheless, we recommend that you test your app in a 16 KB environment to verify that there are no unexpected regressions in app behavior.
การเปลี่ยนแปลงที่จำเป็นสำหรับแอปบางแอปเพื่อให้รองรับพื้นที่ส่วนตัว
Private space is a new feature in Android 15 that lets users create a separate space on their device where they can keep sensitive apps away from prying eyes, under an additional layer of authentication. Because apps in the private space have restricted visibility, some types of apps need to take additional steps to be able to see and interact with apps in a user's private space.
All apps
Because apps in the private space are kept in a separate user profile, similar to work profiles, apps shouldn't assume that any installed copies of their app that aren't in the main profile are in the work profile. If your app has logic related to work profile apps that make this assumption, you'll need to adjust this logic.
Medical apps
When a user locks the private space, all apps in the private space are stopped, and those apps can't perform foreground or background activities, including showing notifications. This behavior might critically impact the use and function of medical apps installed in the private space.
The private space setup experience warns users that the private space is not suitable for apps that need to perform critical foreground or background activities, such as showing notifications from medical apps. However, apps can't determine whether or not they're being used in the private space, so they can't show a warning to the user for this case.
For these reasons, if you develop a medical app, review how this feature might impact your app and take appropriate actions—such as informing your users not to install your app in the private space—to avoid disrupting critical app capabilities.
Launcher apps
If you develop a launcher app, you must do the following before apps in the private space will be visible:
- Your app must be assigned as the default launcher app for the device—that
is, possessing the
ROLE_HOMErole. - Your app must declare the
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILESnormal permission in your app's manifest file.
Launcher apps that declare the ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES permission must handle
the following private space use cases:
- Your app must have a separate launcher container for apps installed in the
private space. Use the
getLauncherUserInfo()method to determine which type of user profile is being handled. - The user must be able to hide and show the private space container.
- The user must be able to lock and unlock the private space container. Use
the
requestQuietModeEnabled()method to lock (by passingtrue) or unlock (by passingfalse) the private space. While locked, no apps in the private space container should be visible or discoverable through mechanisms such as search. Your app should register a receiver for the
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLEandACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLEbroadcasts and update the UI in your app when the locked or unlocked state of the private space container changes. Both of these broadcasts includeEXTRA_USER, which your app can use to refer to the private profile user.You can also use the
isQuietModeEnabled()method to check whether the private space profile is locked or not.
App store apps
The private space includes an "Install Apps" button that launches an implicit
intent to install apps into the user's private space. In order for your app to
receive this implicit intent, declare an <intent-filter>
in your app's manifest file with a <category> of
CATEGORY_APP_MARKET.
นำแบบอักษรอีโมจิที่อิงตาม PNG ออกแล้ว
The legacy, PNG-based emoji font file (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf) has been
removed, leaving just the vector-based file. Beginning with Android 13 (API
level 33), the emoji font file used by the system emoji renderer changed from a
PNG-based file to a vector based file. The system retained
the legacy font file in Android 13 and 14 for compatibility reasons, so that
apps with their own font renderers could continue to use the legacy font file
until they were able to upgrade.
To check if your app is affected, search your app's code for references to the
NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf file.
You can choose to adapt your app in a number of ways:
- Use platform APIs for text rendering. You can render text to a bitmap-backed
Canvasand use that to get a raw image if necessary. - Add COLRv1 font support to your app. The FreeType open source library supports COLRv1 in version 2.13.0 and higher.
- As a last resort, you can bundle the legacy emoji font file
(
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) into your APK, although in that case your app will be missing the latest emoji updates. For more information, see the Noto Emoji GitHub project page.
เพิ่มเวอร์ชัน SDK เป้าหมายขั้นต่ำจาก 23 เป็น 24
Android 15 สร้างขึ้นมาจาก
การเปลี่ยนแปลงที่เกิดขึ้นใน Android 14 และขยายระยะเวลานี้
ด้านความปลอดภัยมากขึ้น ใน Android 15 แอปที่มี
ติดตั้ง targetSdkVersion ที่ต่ำกว่า 24 ไม่ได้
การกําหนดให้แอปเป็นไปตามระดับ API สมัยใหม่จะช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ว่าแอปจะมีความปลอดภัยและความเป็นส่วนตัวที่ดียิ่งขึ้น
มัลแวร์มักกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น API ระดับต่ำกว่าเพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงความปลอดภัยและความเป็นส่วนตัว
ที่เกิดขึ้นใน Android เวอร์ชันที่สูงกว่า ตัวอย่างเช่น
แอปมัลแวร์บางแอปใช้ targetSdkVersion เป็น 22 เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยง
Android 6.0 Marshmallow (API) เปิดตัวโมเดลสิทธิ์รันไทม์ในปี 2015
ระดับ 23) การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ใน Android 15 ทำให้มัลแวร์หลบเลี่ยงการปรับปรุงด้านความปลอดภัยและความเป็นส่วนตัวได้ยากขึ้น การพยายามติดตั้งแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมาย API ที่ต่ำกว่า
จะทำให้การติดตั้งล้มเหลว โดยมีข้อความเหมือนกับข้อความต่อไปนี้
ปรากฏใน Logcat:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
ในอุปกรณ์ที่อัปเกรดเป็น Android 15 แอปที่มี targetSdkVersion ต่ำกว่า 24 จะยังคงติดตั้งอยู่
หากต้องการทดสอบแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น API ระดับเก่า ให้ใช้ ADB ต่อไปนี้ คำสั่ง:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
ความปลอดภัยและความเป็นส่วนตัว
Android 15 introduces robust measures to combat one-time passcode (OTP) fraud and to protect the user's sensitive content, focusing on hardening the Notification Listener Service and screenshare protections. Key enhancements include redacting OTPs from notifications accessible to untrusted apps, hiding notifications during screenshare, and securing app activities when OTPs are posted. These changes aim to keep the user's sensitive content safe from unauthorized actors.
Developers need to be aware of the following to ensure their apps are compatible with the changes in Android 15:
OTP Redaction
Android will stop untrusted apps that implement a
NotificationListenerService from reading unredacted content
from notifications where an OTP has been detected. Trusted apps such as
companion device manager associations are exempt from these restrictions.
Screenshare Protection
- Notification content is hidden during screen sharing sessions to preserve
the user's privacy. If the app implements
setPublicVersion(), Android shows the public version of the notification which serves as a replacement notification in insecure contexts. Otherwise, the notification content is redacted without any further context. - Sensitive content like password input is hidden from remote viewers to prevent revealing the user's sensitive information.
- Activities from apps that post notifications during screenshare where an OTP has been detected will be hidden. App content is hidden from the remote viewer when launched.
- Beyond Android's automatic identification of sensitive fields, developers
can manually mark parts of their app as sensitive using
setContentSensitivity, which is hidden from remote viewers during screenshare. - Developers can choose to toggle the Disable screen share protections option under Developer Options to be exempted from the screenshare protections for demo or testing purposes. The default system screen recorder is exempted from these changes, since the recordings remain on-device.
กล้องและสื่อ
Android 15 จะทำการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานของกล้องและสื่อต่อไปนี้สำหรับแอปทั้งหมด
การเล่นเสียงโดยตรงและการเล่นเสียงที่ออฟโหลดจะทำให้แทร็กเสียงที่เปิดโดยตรงหรือออฟโหลดก่อนหน้านี้ไม่ถูกต้องเมื่อถึงขีดจำกัดของทรัพยากร
Before Android 15, if an app requested direct or offload audio playback while
another app was playing audio and the resource limits were reached, the app
would fail to open a new AudioTrack.
Beginning with Android 15, when an app requests direct or offload
playback and the resource
limits are reached, the system invalidates any currently open
AudioTrack objects which prevent fulfilling the new track request.
(Direct and offload audio tracks are typically opened for playback of compressed audio formats. Common use-cases for playing direct audio include streaming encoded audio over HDMI to a TV. Offload tracks are typically used to play compressed audio on a mobile device with hardware DSP acceleration.)
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้และ UI ของระบบ
Android 15 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงบางอย่างที่มีจุดประสงค์เพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้ที่สอดคล้องกันมากขึ้น และใช้งานง่าย
เปิดใช้ภาพเคลื่อนไหวของการย้อนกลับที่คาดการณ์ได้สำหรับแอปที่เลือกใช้
Beginning in Android 15, the developer option for predictive back animations has been removed. System animations such as back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity now appear for apps that have opted in to the predictive back gesture either entirely or at an activity level. If your app is affected, take the following actions:
- Ensure that your app has been properly migrated to use the predictive back gesture.
- Ensure that your fragment transitions work with predictive back navigation.
- Migrate away from animation and framework transitions and use animator and androidx transitions instead.
- Migrate away from back stacks that
FragmentManagerdoesn't know about. Use back stacks managed byFragmentManageror by the Navigation component instead.
วิดเจ็ตจะปิดใช้เมื่อผู้ใช้บังคับให้แอปหยุด
หากผู้ใช้บังคับหยุดแอปในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 15 ระบบจะปิดใช้วิดเจ็ตทั้งหมดของแอปชั่วคราว วิดเจ็ตจะเป็นสีเทาและผู้ใช้โต้ตอบกับวิดเจ็ตไม่ได้ เนื่องจากตั้งแต่ Android 15 เป็นต้นไป ระบบจะยกเลิก Intent ที่รอดำเนินการทั้งหมดของแอปเมื่อมีการบังคับหยุดแอป
ระบบจะเปิดใช้วิดเจ็ตเหล่านั้นอีกครั้งเมื่อผู้ใช้เปิดแอปในครั้งถัดไป
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่การเปลี่ยนแปลงสถานะ "หยุดแพ็กเกจ"
ชิปแถบสถานะการฉายสื่อจะแจ้งเตือนผู้ใช้เกี่ยวกับการแชร์หน้าจอ การแคสต์ และการบันทึก
Screen projection exploits expose private user data such as financial information because users don't realize their device screen is being shared.
For apps running on devices with Android 15 QPR1 or higher, a status bar chip that is large and prominent alerts users to any in‑progress screen projection. Users can tap the chip to stop their screen from being shared, cast, or recorded. Also, screen projection automatically stops when the device screen is locked.
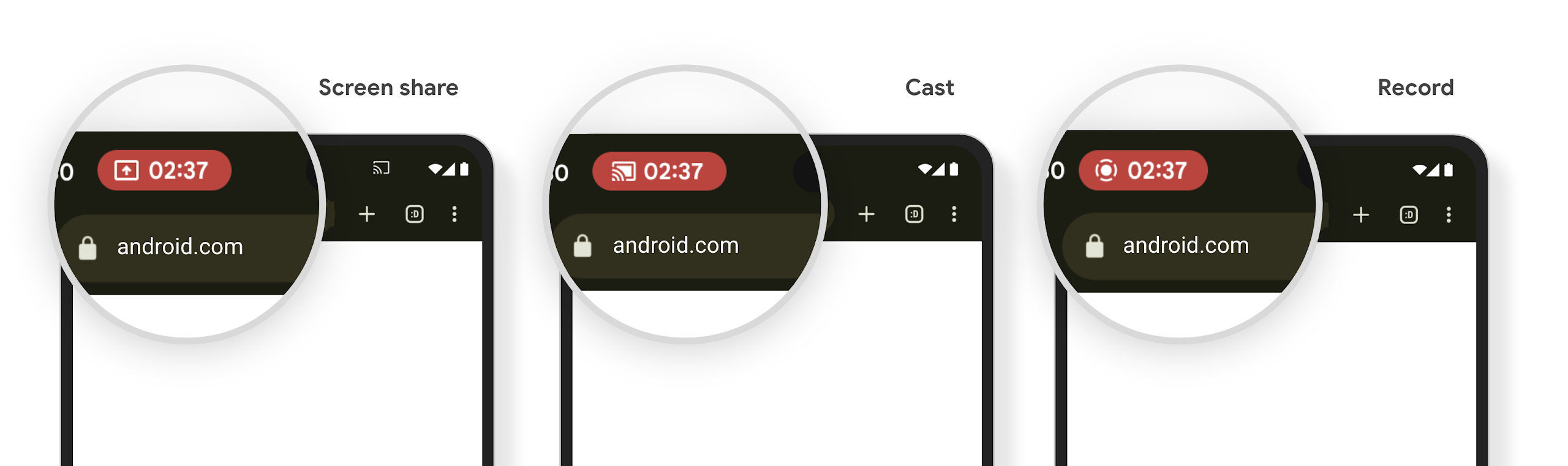
ตรวจสอบว่าแอปของคุณได้รับผลกระทบหรือไม่
โดยค่าเริ่มต้น แอปจะมีชิปแถบสถานะและจะหยุดการฉายหน้าจอโดยอัตโนมัติเมื่อหน้าจอล็อกเปิดใช้งาน
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับวิธีทดสอบแอปสำหรับกรณีการใช้งานเหล่านี้ได้ที่แถบสถานะ ชิปและหยุดอัตโนมัติ
การจำกัดการเข้าถึงเครือข่ายในเบื้องหลัง
ใน Android 15 แอปที่เริ่มคำขอเครือข่ายนอกวงจรของกระบวนการที่ถูกต้องจะได้รับข้อยกเว้น โดยปกติแล้ว จะเป็น UnknownHostException หรือ IOException อื่นๆ ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับซ็อกเก็ต คำขอเครือข่ายที่เกิดขึ้นนอกวงจรที่ถูกต้องมักเกิดจากแอปส่งคำขอเครือข่ายต่อไปโดยไม่รู้ตัว แม้ว่าแอปจะไม่ได้ใช้งานแล้วก็ตาม
หากต้องการลดข้อยกเว้นนี้ ให้ตรวจสอบว่าคำขอเครือข่ายของคุณรับรู้ถึงวงจรของลูกค้าและยกเลิกเมื่อออกจากวงจรกระบวนการที่ถูกต้องโดยใช้คอมโพเนนต์ที่รับรู้ถึงวงจรของลูกค้า หากการขอข้อมูลเครือข่ายต้องเกิดขึ้นแม้ว่าผู้ใช้จะออกจากแอปพลิเคชันแล้ว ให้พิจารณากำหนดเวลาการขอข้อมูลเครือข่ายโดยใช้ WorkManager หรือทำงานที่ผู้ใช้มองเห็นต่อไปโดยใช้บริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า
การเลิกใช้งาน
ในการเปิดตัวแต่ละครั้ง Android API บางรายการอาจล้าสมัยหรือต้อง ปรับโครงสร้างใหม่เพื่อมอบประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่ดียิ่งขึ้นแก่นักพัฒนาแอปหรือรองรับความสามารถใหม่ๆ ของแพลตฟอร์ม ในกรณีเหล่านี้ เราจะเลิกใช้งาน API ที่ล้าสมัยอย่างเป็นทางการและ แนะนำให้นักพัฒนาแอปใช้ API อื่นแทน
การเลิกใช้งานหมายความว่าเราได้สิ้นสุดการสนับสนุน API อย่างเป็นทางการแล้ว แต่ API จะยังคงพร้อมให้บริการแก่นักพัฒนาแอปต่อไป ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการเลิกใช้งานที่สำคัญใน Android รุ่นนี้ได้ที่หน้าการเลิกใช้งาน
