La piattaforma Android 15 include modifiche al comportamento che potrebbero influire sulla tua app.
Le seguenti modifiche al comportamento si applicano a tutte le app quando vengono eseguite su Android 15,
indipendentemente dal targetSdkVersion. Devi testare la tua app e poi modificarla
in base alle esigenze per supportare correttamente questi comportamenti, ove applicabile.
Assicurati di esaminare anche l'elenco delle modifiche al comportamento che interessano solo le app che hanno come target Android 15.
Funzionalità di base
Android 15 modifica o espande varie funzionalità di base del sistema Android.
Modifiche allo stato interrotto del pacchetto
L'intenzione dello stato del pacchetto FLAG_STOPPED (che gli utenti possono attivare nelle build AOSP premendo a lungo l'icona di un'app e selezionando "Forza interruzione") è sempre stata quella di mantenere le app in questo stato finché l'utente non le rimuove esplicitamente da questo stato avviandole direttamente o interagendo indirettamente con l'app (tramite la scheda di condivisione o un widget, selezionando l'app come sfondo animato e così via). In Android 15, abbiamo aggiornato il comportamento del sistema in modo che sia in linea con questo comportamento previsto. Le app devono essere rimosse
dallo stato di interruzione solo tramite un'azione diretta o indiretta dell'utente.
Per supportare il comportamento previsto, oltre alle limitazioni esistenti, il sistema annulla anche tutti gli intent in attesa quando l'app entra nello stato di fermata su un dispositivo con Android 15. Quando le azioni dell'utente rimuovono l'app dallo stato di fermata, il broadcast ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED viene inviato all'app, offrendo la possibilità di registrare nuovamente gli intent in attesa.
Puoi chiamare il nuovo metodo
ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped()
per verificare se l'app è stata messa in stato di arresto.
Supporto delle dimensioni delle pagine di 16 kB
Storicamente, Android ha supportato solo dimensioni delle pagine di memoria di 4 KB, il che ha ottimizzato le prestazioni della memoria di sistema per la quantità media di memoria totale che i dispositivi Android hanno in genere avuto. A partire da Android 15, AOSP supporta i dispositivi configurati per utilizzare una dimensione pagina di 16 KB (dispositivi da 16 KB). Se la tua app utilizza librerie NDK, direttamente o indirettamente tramite un SDK, dovrai ricompilare l'app per farla funzionare su questi dispositivi da 16 KB.
Man mano che i produttori di dispositivi continuano a creare dispositivi con quantità maggiori di memoria fisica (RAM), molti di questi dispositivi adotteranno dimensioni delle pagine di 16 KB (e alla fine maggiori) per ottimizzare le prestazioni del dispositivo. L'aggiunta del supporto per i dispositivi con dimensioni di pagina di 16 kB consente alla tua app di essere eseguita su questi dispositivi e di sfruttare i miglioramenti delle prestazioni associati. Senza ricompilazione, le app non funzioneranno sui dispositivi da 16 KB nelle versioni future di Android.
Per aiutarti ad aggiungere il supporto per la tua app, abbiamo fornito indicazioni su come verificare se la tua app è interessata, su come ricompilare l'app (se applicabile) e su come testarla in un ambiente da 16 kB utilizzando emulatori (incluse le immagini di sistema Android 15 per Android Emulator).
Vantaggi e miglioramenti delle prestazioni
I dispositivi configurati con dimensioni di pagina di 16 KB in media utilizzano un po' più di memoria, ma ottengono anche vari miglioramenti delle prestazioni sia per il sistema sia per le app:
- Tempi di avvio delle app più ridotti quando il sistema è sotto pressione di memoria: in media il 3,16% meno, con miglioramenti più significativi (fino al 30%) per alcune app che abbiamo testato
- Assorbimento di corrente ridotto durante l'avvio dell'app: riduzione media del 4,56%
- Avvio più rapido della fotocamera: in media gli avvii a caldo più veloci del 4,48% e degli avvii a freddo del 6,60% più velocemente
- Tempo di avvio del sistema migliorato: miglioramento medio dell'8% (circa 950 millisecondi)
Questi miglioramenti si basano sui nostri test iniziali e i risultati sui dispositivi effettivi potrebbero essere diversi. Forniremo ulteriori analisi dei potenziali guadagni per le app man mano che continuiamo i test.
Controllare se la tua app è interessata
Se la tua app utilizza codice nativo, devi ricompilarla con il supporto per i dispositivi da 16 kB. Se non sai con certezza se la tua app utilizza codice nativo, puoi utilizzare APK Analyzer per identificare se è presente codice nativo e poi controllare l'allineamento dei segmenti ELF per le librerie condivise che trovi. Android Studio offre anche funzionalità che ti aiutano a rilevare automaticamente i problemi di allineamento.
Se la tua app utilizza solo codice scritto nel linguaggio di programmazione Java o in Kotlin, incluse tutte le librerie o gli SDK, allora la tua app supporta già dispositivi da 16 KB. Tuttavia, ti consigliamo di testare l'app in un ambiente da 16 KB per verificare che non si verifichino regressioni impreviste nel comportamento dell'app.
Modifiche necessarie per alcune app per supportare lo spazio privato
Spazio privato è una nuova funzionalità di Android 15 che consente agli utenti di creare uno spazio separato sul proprio dispositivo in cui possono proteggere le app sensibili da occhi indiscreti mediante un ulteriore livello di autenticazione. Poiché le app nello spazio privato hanno visibilità limitata, alcuni tipi di app devono eseguire passaggi aggiuntivi per poter vedere e interagire con le app nello spazio privato di un utente.
Tutte le app
Poiché le app nello spazio privato vengono conservate in un profilo utente separato, simile ai profili di lavoro, le app non devono presumere che le eventuali copie installate della loro app che non si trovano nel profilo principale siano nel profilo di lavoro. Se la tua app ha una logica relativa alle app del profilo di lavoro che fa questa supposizione, dovrai modificarla.
App di medicina
Quando un utente blocca lo spazio privato, tutte le app al suo interno vengono interrotte e non possono eseguire attività in primo piano o in background, inclusa la visualizzazione delle notifiche. Questo comportamento potrebbe influire in modo significativo sull'utilizzo e sul funzionamento delle app mediche installate nello spazio privato.
L'esperienza di configurazione dello spazio privato avvisa gli utenti che lo spazio privato non è adatto per le app che devono eseguire attività in primo piano o in background critiche, ad esempio la visualizzazione di notifiche di app mediche. Tuttavia, le app non possono determinare se vengono utilizzate o meno nello spazio privato, quindi non possono mostrare un avviso all'utente in questo caso.
Per questi motivi, se sviluppi un'app medica, controlla in che modo questa funzionalità potrebbe influire sulla tua app e adotta le misure appropriate, ad esempio informando gli utenti di non installarla nello spazio privato, per evitare di interrompere le funzionalità critiche dell'app.
App di avvio
Se sviluppi un'app Avvio app, devi eseguire le seguenti operazioni prima che le app nello spazio privato siano visibili:
- La tua app deve essere assegnata come app di avvio predefinita per il dispositivo, ovvero deve disporre del ruolo
ROLE_HOME. - L'app deve dichiarare l'autorizzazione normale
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILESnel file manifest dell'app.
Le app di Avvio app che dichiarano l'autorizzazione ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES devono gestire
i seguenti casi d'uso dello spazio privato:
- L'app deve avere un contenitore Avvio app separato per le app installate nello spazio privato. Utilizza il metodo
getLauncherUserInfo()per determinare il tipo di profilo utente gestito. - L'utente deve essere in grado di nascondere e mostrare il contenitore dello spazio privato.
- L'utente deve essere in grado di bloccare e sbloccare il contenitore dello spazio privato. Utilizza il metodo
requestQuietModeEnabled()per bloccare (passandotrue) o sbloccare (passandofalse) lo spazio privato. Quando è bloccato, nessuna app nel contenitore dello spazio privato deve essere visibile o rilevabile tramite meccanismi come la ricerca. L'app deve registrare un transceiver per le trasmissioni
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLEeACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLEe aggiornare l'UI nell'app quando cambia lo stato bloccato o sbloccato del contenitore dello spazio privato. Entrambe le trasmissioni includonoEXTRA_USER, che la tua app può utilizzare per fare riferimento all' utente del profilo privato.Puoi anche utilizzare il metodo
isQuietModeEnabled()per verificare se il profilo dello spazio privato è bloccato o meno.
App dello store
Lo spazio privato include un pulsante "Installa app" che avvia un'intent implicita per installare app nello spazio privato dell'utente. Affinché la tua app possa ricevere questo intent implicito, dichiara un <intent-filter> nel file manifest dell'app con un <category> di CATEGORY_APP_MARKET.
Carattere emoji basato su PNG rimosso
Il file del carattere emoji precedente (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf) basato su PNG è stato
rimosso, lasciando solo il file basato su vettori. A partire da Android 13 (livello API 33), il file del carattere emoji utilizzato dal renderer emoji di sistema è passato da un file basato su PNG a un file basato su vettori. Il sistema ha mantenuto il file dei caratteri legacy in Android 13 e 14 per motivi di compatibilità, in modo che le app con i propri visualizzatori dei caratteri potessero continuare a utilizzarlo fino a quando non fosse stato possibile eseguire l'upgrade.
Per verificare se la tua app è interessata, cerca nel codice riferimenti al
NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf file.
Puoi scegliere di adattare la tua app in diversi modi:
- Utilizza le API di piattaforma per il rendering del testo. Puoi eseguire il rendering del testo in un
Canvasbasato su bitmap e utilizzarlo per ottenere un'immagine non elaborata, se necessario. - Aggiungi il supporto dei caratteri COLRv1 alla tua app. La libreria open source FreeType supporta COLRv1 nella versione 2.13.0 e superiori.
- Come ultima risorsa, puoi includere il file del carattere emoji precedente
(
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) nel tuo APK, anche se in questo caso la tua app non avrà gli aggiornamenti emoji più recenti. Per maggiori informazioni, consulta la pagina del progetto GitHub di Noto Emoji.
Aumento della versione minima dell'SDK target da 23 a 24
Android 15 si basa su
le modifiche apportate in Android 14 ed estende questa
ulteriormente la sicurezza. In Android 15, le app con un
Impossibile installare targetSdkVersion inferiore a 24.
La richiesta di app che soddisfino i livelli API moderni contribuisce a garantire una maggiore sicurezza e
privacy.
Il malware spesso punta a livelli API più bassi per aggirare la sicurezza e la privacy
che sono state introdotte nelle versioni successive di Android. Ad esempio:
alcune app malware utilizzano un valore targetSdkVersion pari a 22 per evitare di essere soggette
di autorizzazione di runtime introdotto nel 2015 da Android 6.0 Marshmallow (API
livello 23). Questa modifica ad Android 15 rende più difficile evitare la sicurezza del malware
e miglioramenti della privacy. Il tentativo di installare un'app che ha come target un livello API inferiore comporta un errore di installazione e in Logcat viene visualizzato un messaggio simile al seguente:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
Sui dispositivi su cui viene eseguito l'upgrade ad Android 15, tutte le app con un targetSdkVersion inferiore
ne rimangono installate più di 24.
Se devi testare un'app che ha come target un livello API precedente, utilizza il seguente comando ADB:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
Sicurezza e privacy
Android 15 introduce misure efficaci per combattere le frodi con passcode una tantum (OTP) e per proteggere i contenuti sensibili dell'utente, concentrandosi sull'aumento della sicurezza del servizio di ascolto delle notifiche e delle protezioni per la condivisione schermo. I miglioramenti principali includono l'oscuramento delle OTP dalle notifiche accessibili ad app non attendibili, la disattivazione delle notifiche durante la condivisione schermo e la protezione delle attività delle app quando vengono pubblicate le OTP. Queste modifiche hanno lo scopo di proteggere i contenuti sensibili dell'utente da soggetti non autorizzati.
Gli sviluppatori devono tenere presente quanto segue per assicurarsi che le loro app siano compatibili con le modifiche di Android 15:
Oscuramento OTP
Android impedirà alle app non attendibili che implementano un
NotificationListenerService di leggere i contenuti non oscurati
delle notifiche in cui è stata rilevata una OTP. Le app attendibili, come le associazioni di gestori dei dispositivi complementari, sono esenti da queste limitazioni.
Protezione Condivisione schermo
- I contenuti delle notifiche vengono nascosti durante le sessioni di condivisione dello schermo per preservare la privacy dell'utente. Se l'app implementa
setPublicVersion(), Android mostra la versione pubblica della notifica che funge da notifica sostitutiva in contesti non sicuri. In caso contrario, i contenuti della notifica vengono oscurati senza alcun ulteriore contesto. - I contenuti sensibili, come l'inserimento della password, vengono nascosti agli spettatori remoti per impedire la divulgazione delle informazioni sensibili dell'utente.
- Le attività delle app che pubblicano notifiche durante la condivisione schermo in cui è stato rilevato un codice OTP verranno nascoste. I contenuti dell'app vengono nascosti all'utente remoto quando l'app viene lanciata.
- Oltre all'identificazione automatica dei campi sensibili da parte di Android, gli sviluppatori possono contrassegnare manualmente parti della propria app come sensibili utilizzando
setContentSensitivity, che viene nascosta agli spettatori remoti durante la condivisione schermo. - Gli sviluppatori possono scegliere di attivare/disattivare l'opzione Disattiva protezioni condivisione schermo nelle Opzioni sviluppatore per essere esentati dalle protezioni della condivisione schermo a scopo di dimostrazione o test. Lo screen recorder di sistema predefinito è esente da queste modifiche, poiché le registrazioni rimangono sul dispositivo.
Fotocamera e contenuti multimediali
Android 15 apporta le seguenti modifiche al comportamento della fotocamera e dei contenuti multimediali per tutte le app.
La riproduzione audio diretta e l'offload invalidano le tracce audio dirette o con offload aperte in precedenza quando vengono raggiunti i limiti delle risorse
Prima di Android 15, se un'app richiedeva la riproduzione audio diretta o di offload mentre un'altra app stava riproducendo audio e i limiti di risorse erano stati raggiunti, l'app non riusciva ad aprire un nuovo AudioTrack.
A partire da Android 15, quando un'app richiede la riproduzione diretta o con offload e vengono raggiunti i limiti di risorse, il sistema invalida tutti gli oggetti AudioTrack attualmente aperti che impediscono di soddisfare la nuova richiesta di traccia.
Le tracce audio dirette e di offload vengono in genere aperte per la riproduzione di formati audio compressi. Casi d'uso comuni per la riproduzione di audio diretto includono lo streaming di audio codificato tramite HDMI su una TV. Le tracce di offload vengono in genere utilizzate per riprodurre audio compresso su un dispositivo mobile con accelerazione DSP hardware.
Esperienza utente e UI di sistema
Android 15 include alcune modifiche volte a creare un'esperienza utente più coerente e intuitiva.
Animazioni predittive per Indietro attivate per le app che hanno eseguito l'opt-in
A partire da Android 15, l'opzione sviluppatore per le animazioni di ritorno predittive è stata rimossa. Le animazioni di sistema, come il ritorno alla schermata Home, il passaggio da un'attività all'altra e il ritorno da un'attività all'altra, ora vengono visualizzate per le app che hanno attivato il gesto di ritorno predittivo, in toto o a livello di attività. Se la tua app è interessata, svolgi le seguenti azioni:
- Assicurati che la migrazione della tua app sia stata eseguita correttamente per utilizzare il gesto di ritorno predetto.
- Assicurati che le transizioni dei frammenti funzionino con la navigazione a ritroso predittiva.
- Esegui la migrazione dalle transizioni di animazione e framework e utilizza invece le transizioni di animator e androidx.
- Esegui la migrazione da stack precedenti non noti a
FragmentManager. Utilizza i frame di ritorno gestiti daFragmentManagero dal componente Navigation.
Widget disattivati quando l'utente arresta forzatamente un'app
Se un utente forza l'interruzione di un'app su un dispositivo con Android 15, il sistema disattiva temporaneamente tutti i widget dell'app. I widget non sono selezionabili e l'utente non può interagire con loro. Questo perché, a partire da Android 15, il sistema annulla tutti gli intent in attesa di un'app quando questa viene interrotta forzatamente.
Il sistema riattiva questi widget alla successiva apertura dell'app da parte dell'utente.
Per ulteriori informazioni, consulta Modifiche allo stato di arresto del pacchetto.
Il chip della barra di stato della proiezione dei contenuti multimediali avvisa gli utenti di condivisione dello schermo, trasmissione e registrazione
Gli exploit di proiezione dello schermo espongono i dati utente privati, come le informazioni finanziarie, perché gli utenti non si rendono conto che lo schermo del loro dispositivo viene condiviso.
Per le app in esecuzione su dispositivi con Android 15 QPR1 o versioni successive, un chip della barra di stato grande e in evidenza avvisa gli utenti di eventuali proiezioni dello schermo in corso. Gli utenti possono toccare il chip per impedire la condivisione, la trasmissione o la registrazione della schermata. Inoltre, la proiezione dello schermo si interrompe automaticamente quando lo schermo del dispositivo è bloccato.
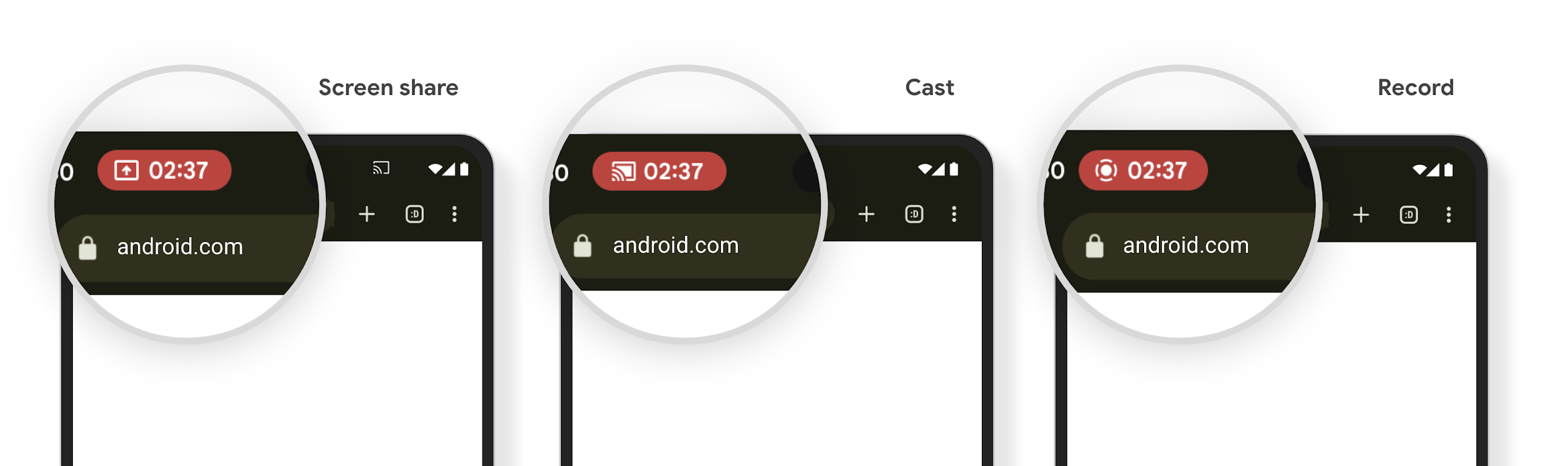
Check if your app is impacted
By default, your app includes the status bar chip and automatically suspends screen projection when the lock screen activates.
To learn more about how to test your app for these use cases, see Status bar chip and auto stop.
Limitazioni di accesso alla rete in background
In Android 15, apps that start a network request outside of a valid process
lifecycle receive an exception. Typically, an
UnknownHostException or other socket-related
IOException. Network requests that happen outside of a valid lifecycle are
usually due to apps unknowingly continuing a network request even after the app
is no longer active.
To mitigate this exception, ensure your network requests are lifecycle aware and cancelled upon leaving a valid process lifecycle by using lifecycle aware components. If it is important that the network request should happen even when the user leaves the application, consider scheduling the network request using WorkManager or continue a user visible task using Foreground Service.
Ritiri
Con ogni release, API Android specifiche potrebbero diventare obsolete o dover essere refattorizzate per offrire una migliore esperienza per gli sviluppatori o supportare nuove funzionalità della piattaforma. In questi casi, ritiriamo ufficialmente le API obsolete e indirizziamo gli sviluppatori verso API alternative da utilizzare.
Il ritiro significa che abbiamo interrotto il supporto ufficiale per le API, ma queste continueranno a rimanere disponibili per gli sviluppatori. Per scoprire di più sui ritiri importanti in questa release di Android, consulta la pagina dei ritiri.
