Android 15 में कुछ ऐसे बदलाव किए गए हैं जिनका असर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन पर पड़ सकता है.
Android 15 पर चलने वाले सभी ऐप्लिकेशन पर, यहां दिए गए बदलाव लागू होते हैं. भले ही, targetSdkVersion कुछ भी हो. आपको अपने ऐप्लिकेशन की जांच करनी चाहिए. इसके बाद, जहां ज़रूरी हो वहां इन सुविधाओं को सही तरीके से काम करने के लिए, ऐप्लिकेशन में बदलाव करना चाहिए.
Android 15 को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन पर असर डालने वाले बदलावों की सूची भी ज़रूर देखें.
मुख्य फ़ंक्शन
Android 15, Android सिस्टम की कई मुख्य सुविधाओं में बदलाव करता है या उन्हें बेहतर बनाता है.
पैकेज के बंद होने की स्थिति में बदलाव
पैकेज FLAG_STOPPED की स्थिति का मकसद, ऐप्लिकेशन को तब तक इस स्थिति में रखना है, जब तक उपयोगकर्ता सीधे तौर पर ऐप्लिकेशन को लॉन्च करके या शेयरशीट या विजेट के ज़रिए ऐप्लिकेशन के साथ इंटरैक्ट करके (ऐप्लिकेशन को लाइव वॉलपेपर के तौर पर चुनना वगैरह) ऐप्लिकेशन को इस स्थिति से हटा न दे. उपयोगकर्ता, AOSP बिल्ड में ऐप्लिकेशन आइकॉन को दबाकर रखकर और "ज़बरदस्ती बंद करें" को चुनकर, पैकेज FLAG_STOPPED की स्थिति में ऐप्लिकेशन को डाल सकता है. Android 15 में, हमने सिस्टम के व्यवहार को अपडेट किया है, ताकि यह इस मकसद के मुताबिक काम करे. ऐप्लिकेशन को 'रोका गया' स्थिति से सिर्फ़ तब हटाया जाना चाहिए, जब उपयोगकर्ता ने सीधे तौर पर या किसी अन्य तरीके से ऐसा किया हो.
ऐप्लिकेशन को Android 15 वाले डिवाइस पर बंद होने पर, सिस्टम सभी मंज़ूरी बाकी इंटेंट को रद्द कर देता है. ऐसा, ऐप्लिकेशन के सही तरीके से काम करने के लिए, मौजूदा पाबंदियों के साथ-साथ किया जाता है. जब उपयोगकर्ता की कार्रवाइयों से ऐप्लिकेशन को 'बंद है' स्थिति से हटाया जाता है, तो ऐप्लिकेशन पर ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED ब्रॉडकास्ट डिलीवर किया जाता है. इससे, किसी भी लंबित इंटेंट को फिर से रजिस्टर करने का मौका मिलता है.
ऐप्लिकेशन को बंद किया गया है या नहीं, इसकी पुष्टि करने के लिए, नए ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped() तरीके का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है.
16 केबी वाले पेज साइज़ के साथ काम करने की सुविधा
Android पर, अब तक सिर्फ़ 4 केबी मेमोरी वाले पेज साइज़ का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता था. इससे, Android डिवाइसों में आम तौर पर मौजूद कुल मेमोरी के लिए, सिस्टम मेमोरी की परफ़ॉर्मेंस को ऑप्टिमाइज़ किया जाता था. Android 15 से, AOSP उन डिवाइसों के साथ काम करता है जिन्हें 16 केबी (16 केबी डिवाइस) के पेज साइज़ का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए कॉन्फ़िगर किया गया है. अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन, सीधे तौर पर या किसी SDK टूल के ज़रिए, NDK लाइब्रेरी का इस्तेमाल करता है, तो आपको अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को फिर से बनाना होगा, ताकि वह 16 केबी वाले डिवाइसों पर काम कर सके.
डिवाइस बनाने वाली कंपनियां, ज़्यादा फ़िज़िकल मेमोरी (रैम) वाले डिवाइस बना रही हैं. इसलिए, इनमें से कई डिवाइसों पर 16 केबी (और बाद में ज़्यादा) पेज साइज़ का इस्तेमाल किया जाएगा, ताकि डिवाइस की परफ़ॉर्मेंस को ऑप्टिमाइज़ किया जा सके. 16 केबी वाले पेज साइज़ वाले डिवाइसों के लिए, ऐप्लिकेशन को चलाने की सुविधा जोड़ने पर, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन इन डिवाइसों पर चल पाएगा. साथ ही, इससे आपके ऐप्लिकेशन की परफ़ॉर्मेंस में हुई सुधारों का फ़ायदा भी मिलेगा. फिर से कंपाइल किए बिना, ऐप्लिकेशन Android के आने वाले वर्शन में 16 KB वाले डिवाइसों पर काम नहीं करेंगे.
अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए सहायता जोड़ने में आपकी मदद करने के लिए, हमने यह देखने का तरीका बताया है कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन पर असर पड़ा है या नहीं. साथ ही, अगर लागू हो, तो अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को फिर से बनाने का तरीका और 16 केबी वाले एनवायरमेंट में अपने ऐप्लिकेशन की जांच करने का तरीका भी बताया है. इसके लिए, हमने Android 15 के सिस्टम इमेज वाले Android एमुलेटर का इस्तेमाल करने का तरीका भी बताया है.
फ़ायदे और परफ़ॉर्मेंस में बढ़ोतरी
16 केबी वाले पेज साइज़ के साथ कॉन्फ़िगर किए गए डिवाइस औसतन थोड़ी ज़्यादा मेमोरी का इस्तेमाल करते हैं, लेकिन इससे सिस्टम और ऐप्लिकेशन, दोनों के लिए परफ़ॉर्मेंस में कई सुधार भी होते हैं:
- सिस्टम में मेमोरी कम होने पर, ऐप्लिकेशन लॉन्च होने में लगने वाला समय कम हो गया है: औसतन 3.16% कम, जिन ऐप्लिकेशन की हमने जांच की है उनमें 30% तक का सुधार हुआ है
- ऐप्लिकेशन के लॉन्च के दौरान, पावर सप्लाई में कमी: औसतन 4.56% की कमी
- कैमरे को तेज़ी से लॉन्च करने की सुविधा: औसतन 4.48% ज़्यादा तेज़ी से हॉट स्टार्ट और 6.60% ज़्यादा तेज़ी से कोल्ड स्टार्ट
- सिस्टम बूट होने का समय बेहतर हुआ: औसतन 8% (करीब 950 मिलीसेकंड) की बढ़ोतरी हुई
ये सुधार, हमारी शुरुआती जांच पर आधारित हैं. इसलिए, हो सकता है कि असल डिवाइसों पर नतीजे अलग हों. जैसे-जैसे हम अपनी टेस्टिंग को जारी रखेंगे, वैसे-वैसे हम ऐप्लिकेशन को मिलने वाले संभावित फ़ायदों का अतिरिक्त विश्लेषण देंगे.
देखें कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन पर इसका असर पड़ा है या नहीं
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन किसी नेटिव कोड का इस्तेमाल करता है, तो आपको अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को 16 केबी वाले डिवाइसों के लिए फिर से बनाना होगा. अगर आपको नहीं पता कि आपका ऐप्लिकेशन नेटिव कोड का इस्तेमाल करता है या नहीं, तो APK विश्लेषक का इस्तेमाल करके यह पता लगाया जा सकता है कि कोई नेटिव कोड मौजूद है या नहीं. इसके बाद, आपको जो शेयर की गई लाइब्रेरी मिलती हैं उनके ELF सेगमेंट के अलाइनमेंट की जांच करें. Android Studio में ऐसी सुविधाएं भी होती हैं जिनकी मदद से, अलाइनमेंट से जुड़ी समस्याओं का पता अपने-आप चल जाता है.
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन सिर्फ़ Java प्रोग्रामिंग भाषा या Kotlin में लिखे गए कोड का इस्तेमाल करता है, तो इसका मतलब है कि आपका ऐप्लिकेशन पहले से ही 16 केबी वाले डिवाइसों पर काम करता है. इसमें सभी लाइब्रेरी या SDK टूल भी शामिल हैं. इसके बावजूद, हमारा सुझाव है कि आप अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को 16 केबी वाले एनवायरमेंट में टेस्ट करें. इससे यह पक्का किया जा सकेगा कि ऐप्लिकेशन के काम करने के तरीके में कोई अनचाहा बदलाव नहीं हुआ है.
प्राइवेट स्पेस की सुविधा के साथ काम करने के लिए, कुछ ऐप्लिकेशन में ज़रूरी बदलाव
प्राइवेट स्पेस, Android 15 की एक नई सुविधा है. इसकी मदद से, उपयोगकर्ता अपने डिवाइस पर एक अलग स्पेस बना सकते हैं. इस स्पेस में, वे संवेदनशील ऐप्लिकेशन को छिपाकर रख सकते हैं. इसके लिए, उन्हें पुष्टि करने की एक अतिरिक्त लेयर से गुज़रना होगा. प्राइवेट स्पेस में मौजूद ऐप्लिकेशन, सभी को नहीं दिखते. इसलिए, कुछ ऐप्लिकेशन को उपयोगकर्ता के प्राइवेट स्पेस में मौजूद ऐप्लिकेशन देखने और उनसे इंटरैक्ट करने के लिए, कुछ और कार्रवाइयां करनी पड़ती हैं.
सभी ऐप्लिकेशन
प्राइवेट स्पेस में मौजूद ऐप्लिकेशन, वर्क प्रोफ़ाइल की तरह ही एक अलग उपयोगकर्ता प्रोफ़ाइल में रखे जाते हैं. इसलिए, ऐप्लिकेशन को यह नहीं मानना चाहिए कि उनके ऐप्लिकेशन की इंस्टॉल की गई ऐसी कॉपी जो मुख्य प्रोफ़ाइल में नहीं हैं वे वर्क प्रोफ़ाइल में मौजूद हैं. अगर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन में वर्क प्रोफ़ाइल वाले ऐप्लिकेशन से जुड़ा लॉजिक है, जो यह अनुमान लगाता है, तो आपको इस लॉजिक में बदलाव करना होगा.
चिकित्सा से जुड़े ऐप्लिकेशन
जब कोई उपयोगकर्ता प्राइवेट स्पेस को लॉक करता है, तो प्राइवेट स्पेस में मौजूद सभी ऐप्लिकेशन बंद हो जाते हैं. साथ ही, वे ऐप्लिकेशन फ़ोरग्राउंड या बैकग्राउंड में कोई गतिविधि नहीं कर सकते. जैसे, सूचनाएं दिखाना. इस वजह से, प्राइवेट स्पेस में इंस्टॉल किए गए मेडिकल ऐप्लिकेशन के इस्तेमाल और काम करने के तरीके पर काफ़ी असर पड़ सकता है.
प्राइवेट स्पेस सेट अप करने के दौरान, उपयोगकर्ताओं को चेतावनी दी जाती है कि प्राइवेट स्पेस का इस्तेमाल, फ़ोरग्राउंड या बैकग्राउंड में ज़रूरी गतिविधियां करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए नहीं किया जा सकता. जैसे, चिकित्सा से जुड़े ऐप्लिकेशन से सूचनाएं दिखाना. हालांकि, ऐप्लिकेशन यह पता नहीं लगा सकते कि उनका इस्तेमाल प्राइवेट स्पेस में किया जा रहा है या नहीं. इसलिए, वे इस मामले में उपयोगकर्ता को चेतावनी नहीं दिखा सकते.
इन वजहों से, अगर आपने कोई मेडिकल ऐप्लिकेशन डेवलप किया है, तो देखें कि इस सुविधा से आपके ऐप्लिकेशन पर क्या असर पड़ सकता है. साथ ही, ज़रूरी कार्रवाइयां करें. जैसे, अपने उपयोगकर्ताओं को बताएं कि वे आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को प्राइवेट स्पेस में इंस्टॉल न करें. इससे, ऐप्लिकेशन की मुख्य सुविधाओं के काम करने में आने वाली रुकावटों से बचा जा सकता है.
लॉन्चर ऐप्लिकेशन
अगर आपने कोई लॉन्चर ऐप्लिकेशन डेवलप किया है, तो निजी स्पेस में ऐप्लिकेशन दिखने से पहले, आपको ये काम करने होंगे:
- आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को डिवाइस के लिए डिफ़ॉल्ट लॉन्चर ऐप्लिकेशन के तौर पर असाइन किया जाना चाहिए. इसका मतलब है कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन के पास
ROLE_HOMEभूमिका होनी चाहिए. - आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILESसामान्य अनुमति का एलान करना होगा. यह एलान, आपके ऐप्लिकेशन की मेनिफ़ेस्ट फ़ाइल में करना होगा.
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES अनुमति का एलान करने वाले लॉन्चर ऐप्लिकेशन को, प्राइवेट स्पेस के इस्तेमाल के इन उदाहरणों को मैनेज करना होगा:
- आपके ऐप्लिकेशन में, प्राइवेट स्पेस में इंस्टॉल किए गए ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, अलग लॉन्चर कंटेनर होना चाहिए.
getLauncherUserInfo()तरीके का इस्तेमाल करके, यह पता लगाएं कि किस तरह की उपयोगकर्ता प्रोफ़ाइल मैनेज की जा रही है. - उपयोगकर्ता के पास प्राइवेट स्पेस कंटेनर को छिपाने और दिखाने का विकल्प होना चाहिए.
- उपयोगकर्ता के पास प्राइवेट स्पेस कंटेनर को लॉक और अनलॉक करने का विकल्प होना चाहिए. प्राइवेट स्पेस को लॉक करने (
trueपास करके) या अनलॉक करने (falseपास करके) के लिए,requestQuietModeEnabled()तरीके का इस्तेमाल करें. लॉक होने पर, प्राइवेट स्पेस कंटेनर में मौजूद कोई भी ऐप्लिकेशन न दिखे या खोज जैसे तरीकों से न खोजा जा सके. आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLEऔरACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLEब्रॉडकास्ट के लिए एक रिसीवर रजिस्टर करना चाहिए. साथ ही, प्राइवेट स्पेस कंटेनर की लॉक या अनलॉक की गई स्थिति में बदलाव होने पर, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन में यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) को अपडेट करना चाहिए. इन दोनों ब्रॉडकास्ट मेंEXTRA_USERशामिल होता है. आपका ऐप्लिकेशन, निजी प्रोफ़ाइल के उपयोगकर्ता को रेफ़र करने के लिए इसका इस्तेमाल कर सकता है.isQuietModeEnabled()तरीके का इस्तेमाल करके भी यह देखा जा सकता है कि प्राइवेट स्पेस प्रोफ़ाइल लॉक है या नहीं.
ऐप स्टोर के ऐप्लिकेशन
प्राइवेट स्पेस में "ऐप्लिकेशन इंस्टॉल करें" बटन होता है. इस बटन पर टैप करने से, उपयोगकर्ता के प्राइवेट स्पेस में ऐप्लिकेशन इंस्टॉल करने के लिए, एक इंटेंट शुरू होता है. आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को यह इंप्लिसिट इंटेंट पाने के लिए, अपनी ऐप्लिकेशन मेनिफ़ेस्ट फ़ाइल में <intent-filter> का एलान करें. साथ ही, CATEGORY_APP_MARKET के <category> का इस्तेमाल करें.
PNG पर आधारित इमोजी फ़ॉन्ट हटाया गया
लेगसी, PNG-आधारित इमोजी फ़ॉन्ट फ़ाइल (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf) को हटा दिया गया है. अब सिर्फ़ वेक्टर-आधारित फ़ाइल ही उपलब्ध है. Android 13 (एपीआई लेवल 33) से, सिस्टम इमोजी रेंडरर का इस्तेमाल करने वाली इमोजी फ़ॉन्ट फ़ाइल PNG फ़ाइल से वेक्टर फ़ाइल में बदल गई. सिस्टम ने Android 13 और 14 में, काम करने की सुविधा के लिए लेगसी फ़ॉन्ट फ़ाइल को बनाए रखा, ताकि अपने फ़ॉन्ट रेंडरर वाले ऐप्लिकेशन, अपग्रेड होने तक लेगसी फ़ॉन्ट फ़ाइल का इस्तेमाल कर सकें.
यह देखने के लिए कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन पर असर पड़ा है या नहीं, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के कोड में NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf फ़ाइल के रेफ़रंस खोजें.
अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को कई तरीकों से अडैप्ट किया जा सकता है:
- टेक्स्ट रेंडर करने के लिए, प्लैटफ़ॉर्म एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करें. टेक्स्ट को बिटमैप के साथ रेंडर किया जा सकता है
Canvasऔर ज़रूरत पड़ने पर, रॉ इमेज पाने के लिए उसका इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. - अपने ऐप्लिकेशन में COLRv1 फ़ॉन्ट का इस्तेमाल करने की सुविधा जोड़ें. FreeType ओपन सोर्स लाइब्रेरी, 2.13.0 और उसके बाद के वर्शन में COLRv1 के साथ काम करती है.
- आखिरी विकल्प के तौर पर, अपने APK में लेगसी इमोजी फ़ॉन्ट फ़ाइल (
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) को बंडल किया जा सकता है. हालांकि, ऐसा करने पर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन में इमोजी के नए अपडेट नहीं दिखेंगे. ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, Noto Emoji GitHub प्रोजेक्ट का पेज देखें.
एसडीके के टारगेट वर्शन को 23 से बढ़ाकर 24 किया गया
Android 15, Android 15 के साथ
Android 14 में किए गए बदलावों को ध्यान में रखते हुए बनाया गया है.
सुरक्षा को बेहतर किया है. Android 15 में, 24 से कम targetSdkVersion वाले ऐप्लिकेशन इंस्टॉल नहीं किए जा सकते.
आधुनिक एपीआई लेवल को पूरा करने के लिए ऐप्लिकेशन की ज़रूरत, बेहतर सुरक्षा और
निजता.
मैलवेयर, सुरक्षा और निजता को बायपास करने के लिए, अक्सर एपीआई लेवल के निचले हिस्से को टारगेट करता है
सुरक्षा से जुड़ी सुविधाएं मौजूद हैं जो Android के नए वर्शन में उपलब्ध कराई गई हैं. उदाहरण के लिए,
कुछ मैलवेयर ऐप्लिकेशनtargetSdkVersion
रनटाइम अनुमति मॉडल को 2015 में Android 6.0 Marshmallow (एपीआई) ने लॉन्च किया था
लेवल 23). Android 15 में किए गए इस बदलाव की वजह से, मैलवेयर से सुरक्षा को रोकना मुश्किल हो गया है
और निजता में सुधार किए गए हैं. कम एपीआई को टारगेट करने वाला ऐप्लिकेशन इंस्टॉल करने की कोशिश
के स्तर के कारण इंस्टॉलेशन विफल हो जाता है, जिसमें ऐसा मैसेज दिखाई देता है
Logcat में दिखाई दे रहा है:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
Android 15 पर अपग्रेड करने वाले डिवाइसों पर, targetSdkVersion 24 से कम वाले सभी ऐप्लिकेशन इंस्टॉल रहेंगे.
अगर आपको पुराने एपीआई लेवल को टारगेट करने वाले किसी ऐप्लिकेशन की जांच करनी है, तो यहां दिए गए ADB का इस्तेमाल करें आदेश:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
सुरक्षा और निजता
Android 15 में, एक बार इस्तेमाल होने वाले पासवर्ड (ओटीपी) से जुड़े धोखाधड़ी के मामलों को रोकने और उपयोगकर्ता के संवेदनशील कॉन्टेंट को सुरक्षित रखने के लिए, बेहतर उपाय किए गए हैं. इन उपायों में, सूचना सुनने वाली सेवा और स्क्रीन शेयर करने की सुविधा को ज़्यादा सुरक्षित बनाने पर फ़ोकस किया गया है. इसमें कई अहम बदलाव किए गए हैं. जैसे, अविश्वसनीय ऐप्लिकेशन के ऐक्सेस वाली सूचनाओं से ओटीपी हटाना, स्क्रीन शेयर करने के दौरान सूचनाएं छिपाना, और ओटीपी पोस्ट करने पर ऐप्लिकेशन की गतिविधियों को सुरक्षित रखना. इन बदलावों का मकसद, उपयोगकर्ता के संवेदनशील कॉन्टेंट को बिना अनुमति वाले लोगों से सुरक्षित रखना है.
डेवलपर को इन बातों का ध्यान रखना चाहिए, ताकि यह पक्का किया जा सके कि उनके ऐप्लिकेशन, Android 15 में किए गए बदलावों के साथ काम करते हों:
ओटीपी छिपाना
Android, NotificationListenerService को लागू करने वाले गैर-भरोसेमंद ऐप्लिकेशन को, सूचनाओं में मौजूद ओटीपी को छिपाए बिना पढ़ने से रोक देगा. भरोसेमंद ऐप्लिकेशन, जैसे कि साथी डिवाइस मैनेजर असोसिएशन को इन पाबंदियों से छूट मिली है.
स्क्रीन शेयर करने की सुविधा को सुरक्षित करना
- स्क्रीन शेयर करने के दौरान, सूचनाओं का कॉन्टेंट छिपा दिया जाता है, ताकि उपयोगकर्ता की निजता को बनाए रखा जा सके. अगर ऐप्लिकेशन में
setPublicVersion()लागू किया जाता है, तो Android सूचना का सार्वजनिक वर्शन दिखाता है. यह सूचना, असुरक्षित कॉन्टेक्स्ट में सूचना की जगह काम करती है. ऐसा न होने पर, सूचना के कॉन्टेंट को बिना किसी और जानकारी के बदल दिया जाता है. - पासवर्ड डालने जैसा संवेदनशील कॉन्टेंट, दर्शकों से छिपाकर रखा जाता है, ताकि उपयोगकर्ता की संवेदनशील जानकारी ज़ाहिर न हो.
- स्क्रीन शेयर करने के दौरान, जिन ऐप्लिकेशन से सूचनाएं पोस्ट की जाती हैं और जिनमें ओटीपी का पता चलता है उनकी गतिविधियां छिपी होंगी. ऐप्लिकेशन लॉन्च करने पर, उसका कॉन्टेंट रिमोट व्यूअर से छिप जाता है.
- Android, संवेदनशील फ़ील्ड की अपने-आप पहचान करता है. इसके अलावा, डेवलपर
setContentSensitivityका इस्तेमाल करके, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के कुछ हिस्सों को मैन्युअल तौर पर संवेदनशील के तौर पर मार्क कर सकते हैं. स्क्रीन शेयर करने के दौरान, ये हिस्से रीमोट दर्शकों से छिपे रहते हैं. - डेवलपर, डेवलपर के लिए विकल्प में जाकर, स्क्रीन शेयर करने से जुड़ी सुरक्षा सुविधाएं बंद करें विकल्प को टॉगल कर सकते हैं. इससे, डेमो या टेस्टिंग के लिए, स्क्रीन शेयर करने से जुड़ी सुरक्षा सुविधाओं से छूट मिलती है. डिफ़ॉल्ट सिस्टम स्क्रीन रिकॉर्डर को इन बदलावों से छूट मिली है, क्योंकि रिकॉर्डिंग डिवाइस पर ही सेव रहती हैं.
कैमरा और मीडिया
Android 15 में, सभी ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए कैमरे और मीडिया के व्यवहार में ये बदलाव किए गए हैं.
ऑडियो को सीधे तौर पर चलाने और ऑफ़लोड करने की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करने पर, संसाधन की सीमाएं पूरी होने पर, सीधे तौर पर चलाए गए या ऑफ़लोड किए गए ऑडियो ट्रैक अमान्य हो जाते हैं
Android 15 से पहले, अगर कोई ऐप्लिकेशन सीधे तौर पर या ऑफ़लोड करके ऑडियो चलाने का अनुरोध करता था, तो जब कोई दूसरा ऐप्लिकेशन ऑडियो चला रहा होता था और रिसॉर्स की सीमा पूरी हो जाती थी, तो वह ऐप्लिकेशन नया AudioTrack नहीं खोल पाता था.
Android 15 से, जब कोई ऐप्लिकेशन सीधे या ऑफ़लोड किए गए वीडियो को चलाने का अनुरोध करता है और संसाधन की सीमाएं पूरी हो जाती हैं, तो सिस्टम उन सभी AudioTrack ऑब्जेक्ट को अमान्य कर देता है जो नए ट्रैक के अनुरोध को पूरा करने से रोकते हैं.
(डायरेक्ट और ऑफ़लोड किए गए ऑडियो ट्रैक, आम तौर पर संपीड़ित ऑडियो फ़ॉर्मैट चलाने के लिए खोले जाते हैं. डायरेक्ट ऑडियो चलाने के सामान्य इस्तेमाल के उदाहरणों में, एचडीएमआई के ज़रिए टीवी पर एन्क्रिप्ट किए गए ऑडियो को स्ट्रीम करना शामिल है. आम तौर पर, ऑफ़लोड किए गए ट्रैक का इस्तेमाल, हार्डवेयर डीएसपी ऐक्सेलरेशन वाले मोबाइल डिवाइस पर, संकुचित किए गए ऑडियो को चलाने के लिए किया जाता है.)
उपयोगकर्ता अनुभव और सिस्टम यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई)
Android 15 में कुछ ऐसे बदलाव किए गए हैं जिनसे उपयोगकर्ता को बेहतर अनुभव मिलेगा.
जिन ऐप्लिकेशन ने ऑप्ट-इन किया है उनके लिए, प्रिडिक्टिव बैक ऐनिमेशन की सुविधा चालू की गई
Android 15 में, प्रिडिक्टिव बैक ऐनिमेशन के लिए डेवलपर का विकल्प हटा दिया गया है. होम स्क्रीन पर वापस जाने, एक टास्क से दूसरे टास्क पर जाने, और एक गतिविधि से दूसरी गतिविधि पर जाने जैसे सिस्टम ऐनिमेशन, अब उन ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए दिखेंगे जिन्होंने पूरी तरह से या किसी गतिविधि के लेवल पर, 'वापस जाने के लिए जेस्चर का सुझाव' सुविधा के लिए ऑप्ट इन किया है. अगर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन पर असर पड़ा है, तो ये कार्रवाइयां करें:
- पक्का करें कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को, अनुमानित बैक जेस्चर का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए सही तरीके से माइग्रेट किया गया हो.
- पक्का करें कि आपके फ़्रैगमेंट ट्रांज़िशन, अनुमानित बैक नेविगेशन के साथ काम करते हों.
- ऐनिमेशन और फ़्रेमवर्क ट्रांज़िशन से माइग्रेट करें. इसके बजाय, ऐनिमेशन और androidx ट्रांज़िशन का इस्तेमाल करें.
- उन बैक स्टैक से माइग्रेट करें जिनके बारे में
FragmentManagerको नहीं पता. इसके बजाय,FragmentManagerया नेविगेशन कॉम्पोनेंट से मैनेज किए जाने वाले बैक स्टैक का इस्तेमाल करें.
जब कोई उपयोगकर्ता किसी ऐप्लिकेशन को ज़बरदस्ती बंद करता है, तब विजेट बंद हो जाते हैं
अगर कोई उपयोगकर्ता Android 15 वाले डिवाइस पर किसी ऐप्लिकेशन को जबरदस्ती बंद करता है, तो सिस्टम ऐप्लिकेशन के सभी विजेट को कुछ समय के लिए बंद कर देता है. विजेट धूसर हो जाते हैं और उपयोगकर्ता उनसे इंटरैक्ट नहीं कर सकता. ऐसा इसलिए है, क्योंकि Android 15 से, ऐप्लिकेशन को जबरन बंद करने पर, सिस्टम उस ऐप्लिकेशन के सभी इंटेंट रद्द कर देता है.
जब उपयोगकर्ता अगली बार ऐप्लिकेशन लॉन्च करता है, तो सिस्टम उन विजेट को फिर से चालू कर देता है.
ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, पैकेज के बंद होने की स्थिति में हुए बदलाव लेख पढ़ें.
मीडिया प्रोजेक्शन स्टेटस बार चिप, उपयोगकर्ताओं को स्क्रीन शेयर करने, कास्ट करने, और रिकॉर्ड करने के बारे में सूचनाएं देता है
स्क्रीन प्रोजेक्शन का गलत इस्तेमाल करने पर, उपयोगकर्ताओं का निजी डेटा, जैसे कि वित्तीय जानकारी ज़ाहिर हो जाती है. ऐसा इसलिए होता है, क्योंकि उपयोगकर्ताओं को पता नहीं चलता कि उनकी डिवाइस की स्क्रीन शेयर की जा रही है.
Android 15 QPR1 या इसके बाद के वर्शन वाले डिवाइसों पर चलने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, स्टेटस बार में एक बड़ा और प्रमुख चिप दिखता है. इससे, उपयोगकर्ताओं को स्क्रीन प्रोजेक्शन के दौरान सूचना मिलती है. उपयोगकर्ता, अपनी स्क्रीन को शेयर, कास्ट या रिकॉर्ड किए जाने से रोकने के लिए, चिप पर टैप कर सकते हैं. साथ ही, डिवाइस की स्क्रीन लॉक होने पर, स्क्रीन प्रोजेक्शन अपने-आप बंद हो जाता है.
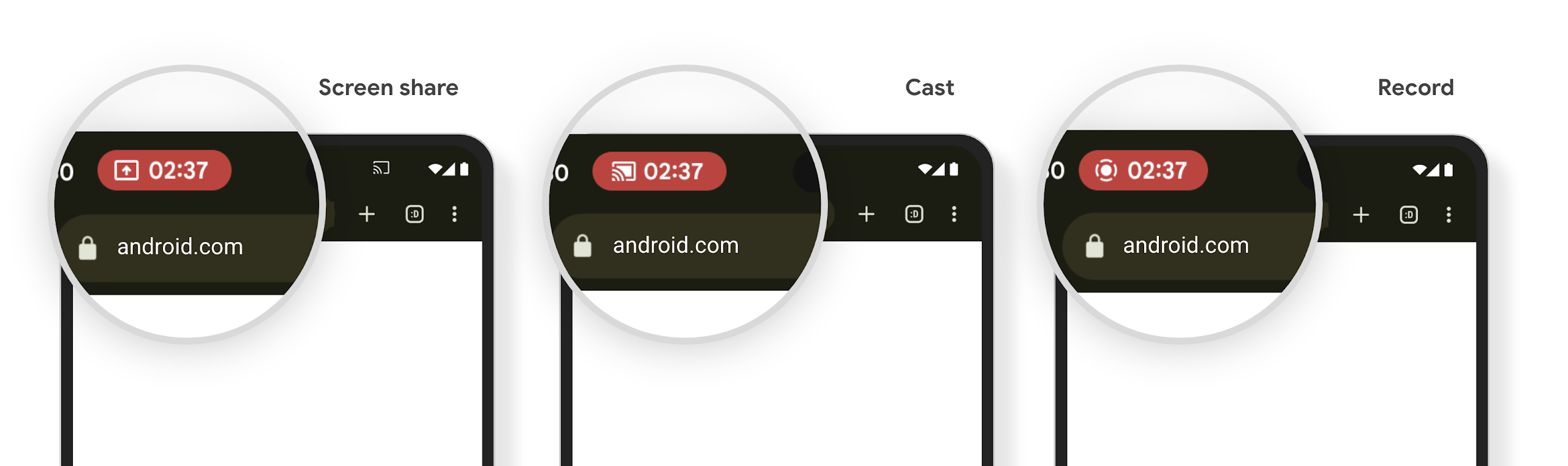
देखें कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन पर इसका असर पड़ा है या नहीं
डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से, आपके ऐप्लिकेशन में स्टेटस बार चिप शामिल होता है. साथ ही, लॉक स्क्रीन चालू होने पर, स्क्रीन प्रोजेक्शन अपने-आप निलंबित हो जाता है.
इस्तेमाल के इन उदाहरणों के लिए, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन की जांच करने के तरीके के बारे में ज़्यादा जानने के लिए, स्टेटस बार के चिप और अपने-आप बंद होने की सुविधा लेख पढ़ें.
बैकग्राउंड में नेटवर्क ऐक्सेस करने से जुड़ी पाबंदियां
Android 15 में, ऐसे ऐप्लिकेशन को अपवाद मिलता है जो मान्य प्रोसेस के लाइफ़साइकल के बाहर नेटवर्क अनुरोध शुरू करते हैं. आम तौर पर, एक
UnknownHostException या सॉकेट से जुड़ा कोई अन्य
IOException. मान्य लाइफ़साइकल के बाहर होने वाले नेटवर्क अनुरोध, आम तौर पर तब होते हैं, जब ऐप्लिकेशन बंद होने के बाद भी, अनजाने में नेटवर्क अनुरोध जारी रहता है.
इस अपवाद को कम करने के लिए, पक्का करें कि आपके नेटवर्क अनुरोध, लाइफ़साइकल के बारे में जानकारी रखते हों और लाइफ़साइकल के बारे में जानकारी देने वाले कॉम्पोनेंट का इस्तेमाल करके, किसी मान्य प्रोसेस के लाइफ़साइकल को छोड़ने पर रद्द हो जाएं. अगर यह ज़रूरी है कि उपयोगकर्ता के ऐप्लिकेशन से बाहर निकलने के बाद भी नेटवर्क अनुरोध किया जाए, तो WorkManager का इस्तेमाल करके नेटवर्क अनुरोध को शेड्यूल करें या फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा का इस्तेमाल करके, उपयोगकर्ता को दिखने वाले टास्क को जारी रखें.
बंद की गई सेवाएं/सुविधाएं
हर रिलीज़ के साथ, Android के कुछ एपीआई पुराने हो सकते हैं या डेवलपर को बेहतर अनुभव देने या नए प्लैटफ़ॉर्म की सुविधाओं के साथ काम करने के लिए, उन्हें फिर से तैयार करना पड़ सकता है. ऐसे मामलों में, हम पुराने एपीआई को आधिकारिक तौर पर बंद कर देते हैं. साथ ही, डेवलपर को अन्य एपीआई इस्तेमाल करने का सुझाव देते हैं.
बंद करने का मतलब है कि हमने एपीआई के लिए आधिकारिक सहायता बंद कर दी है. हालांकि, डेवलपर के लिए ये एपीआई उपलब्ध रहेंगे. Android के इस वर्शन में बंद किए गए कुछ एपीआई के बारे में ज़्यादा जानने के लिए, बंद किए गए एपीआई के बारे में जानकारी देने वाला पेज देखें.
