يتضمّن الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android تغييرات في السلوك قد تؤثّر في تطبيقك.
تنطبق تغييرات السلوك التالية على جميع التطبيقات عند تشغيلها على الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android،
بغض النظر عن targetSdkVersion. عليك اختبار تطبيقك ثم تعديله حسب الحاجة ليتوافق مع هذه الميزات بشكل سليم، حيثما ينطبق ذلك.
احرص أيضًا على مراجعة قائمة التغييرات في السلوك التي تؤثّر فقط في التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android.
الوظيفة الأساسية
يعدّل نظام التشغيل Android 15 العديد من الإمكانات الأساسية لنظام Android أو يوسّع نطاقها.
التغييرات على حالة إيقاف الحزمة
إنّ الغرض من حالة الحزمة FLAG_STOPPED (التي يمكن للمستخدمين
التفاعل معها في إصدارات AOSP من خلال الضغط مع الاستمرار على رمز التطبيق واختيار "إيقاف
بالقوة") هو إبقاء التطبيقات في هذه الحالة إلى أن يزيل المستخدم
التطبيق من هذه الحالة صراحةً من خلال تشغيل التطبيق مباشرةً أو interacted with the app (من خلال لوحة المشاركة أو التطبيق المصغر، واختيار التطبيق
كخلفية حية، وما إلى ذلك). في Android 15، عدّلنا سلوك
النظام ليتوافق مع هذا السلوك المقصود. يجب عدم إزالة التطبيقات
من حالة الإيقاف إلا من خلال إجراء مباشر أو غير مباشر من المستخدم.
لدعم السلوك المقصود، بالإضافة إلى القيود الحالية، يُلغي
النظام أيضًا جميع الطلبات التي في انتظار المراجعة عندما يدخل التطبيق في حالة
الإيقاف على جهاز يعمل بنظام التشغيل Android 15. عندما تزيل إجراءات المستخدم
التطبيق من الحالة "متوقف"، يتم إرسال البث ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED
إلى التطبيق، ما يمنح التطبيق فرصة لإعادة تسجيل أي
نوايا في انتظار المراجعة.
يمكنك استدعاء الأسلوب الجديد
ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped()
للتأكّد مما إذا تم وضع التطبيق في حالة الإيقاف.
التوافق مع صفحات بحجم 16 كيلوبايت
في السابق، كان نظام التشغيل Android يتيح فقط صفحات الذاكرة بحجم 4 كيلوبايت، ما ساعد في تحسين أداء ذاكرة النظام بما يتناسب مع إجمالي مساحة الذاكرة التي كانت تتوفّر عادةً في أجهزة Android. بدءًا من الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android، يتيح مشروع Android مفتوح المصدر (AOSP) استخدام الأجهزة التي تم ضبطها لاستخدام حجم صفحة يبلغ 16 كيلوبايت (أجهزة 16 كيلوبايت). إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم أي مكتبات NDK، سواء بشكل مباشر أو غير مباشر من خلال حزمة تطوير برامج (SDK)، عليك إعادة إنشاء تطبيقك لكي يعمل على هذه الأجهزة التي تستخدم صفحات ذاكرة بحجم 16 كيلوبايت.
مع استمرار الشركات المصنّعة للأجهزة في تصميم أجهزة تتضمّن كميات أكبر من الذاكرة الفعلية (RAM)، ستستخدم العديد من هذه الأجهزة أحجام صفحات تبلغ 16 كيلوبايت (وأكبر في النهاية) لتحسين أداء الجهاز. تتيح إضافة دعم للأجهزة التي تستخدم صفحات بحجم 16 كيلوبايت تشغيل تطبيقك على هذه الأجهزة، كما تساعد تطبيقك في الاستفادة من التحسينات المرتبطة بالأداء. وبدون إعادة تجميع، لن تعمل التطبيقات على الأجهزة التي تستخدم صفحات الذاكرة بحجم 16 كيلوبايت في إصدارات Android المستقبلية.
لمساعدتك في إضافة إمكانية استخدام تطبيقك، قدّمنا إرشادات حول كيفية التحقّق مما إذا كان تطبيقك سيتأثر، وكيفية إعادة إنشاء تطبيقك (إذا كان ذلك منطبقًا)، وكيفية اختبار تطبيقك في بيئة بحجم 16 كيلوبايت باستخدام المحاكيات (بما في ذلك صور نظام Android 15 لمحاكي Android).
المزايا ومكاسب الأداء
تستهلك الأجهزة التي تم ضبطها على أحجام صفحات تبلغ 16 كيلوبايت مساحة أكبر قليلاً من الذاكرة في المتوسط، لكنها تُجري أيضًا تحسينات متنوعة في الأداء لكل من النظام والتطبيقات:
- أوقات تشغيل التطبيق أقل عندما يكون النظام تحت ضغط الذاكرة: 3.16% انخفاضًا في المتوسط، مع تحسينات أكثر أهمية (تصل إلى %30) لبعض التطبيقات التي اختبرناها
- انخفاض في استهلاك الطاقة أثناء تشغيل التطبيق: انخفاض بنسبة% 4.56 في المتوسّط
- تشغيل أسرع للكاميرا: عمليات تشغيل أسرع بنسبة 4.48% في المتوسط، وعمليات تشغيل على البارد أسرع بنسبة 6.60% في المتوسط
- مدة تشغيل النظام المحسَّنة: تحسّنت بنسبة %8 (950 ملي ثانية تقريبًا) في المتوسّط
تستند هذه التحسينات إلى اختبارنا الأوّلي، ومن المرجّح أن تختلف النتائج على الأجهزة الفعلية. وسنقدّم تحليلاً إضافيًا للفوائد المحتملة للتطبيقات أثناء مواصلة الاختبار.
التحقّق مما إذا كان تطبيقك قد تأثّر
إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم أي رموز برمجية أصلية، عليك إعادة إنشاء تطبيقك ليتوافق مع الأجهزة التي تستخدم صفحات ذاكرة بحجم 16 كيلوبايت. إذا لم تكن متأكدًا مما إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم رمزًا برمجيًا أصليًا، يمكنك استخدام "أداة تحليل حِزم APK" لتحديد ما إذا كان هناك أي رمز برمجي أصلي، ثم التحقّق من توافق أقسام ELF مع أي مكتبات مشتركة تجدها. يوفّر "استوديو Android" أيضًا ميزات تساعدك في رصد مشاكل المحاذاة تلقائيًا.
إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم فقط الرموز البرمجية المكتوبة بلغة البرمجة Java أو Kotlin، بما في ذلك جميع المكتبات أو حِزم تطوير البرامج (SDK)، يكون تطبيقك متوافقًا مع الأجهزة التي تبلغ سعتها 16 كيلوبايت. ومع ذلك، ننصحك باختبار تطبيقك في بيئة بحجم 16 كيلوبايت للتأكّد من عدم حدوث أي تراجع غير متوقّع في سلوك التطبيق.
التغييرات المطلوبة لكي تتوافق بعض التطبيقات مع المساحة الخاصّة
المساحة الخاصة هي ميزة جديدة في Android 15 تتيح للمستخدمين إنشاء مساحة منفصلة على أجهزتهم للحفاظ على خصوصية التطبيقات الحسّاسة من خلال طبقة مصادقة إضافية. بما أنّ التطبيقات في المساحة الخاصة لها إذن وصول محدود، يجب أن تتّخذ بعض أنواع التطبيقات خطوات إضافية لتتمكّن من رؤية التطبيقات في المساحة الخاصة للمستخدم والتفاعل معها.
جميع التطبيقات
بما أنّ التطبيقات في المساحة الخاصة يتم الاحتفاظ بها في ملف شخصي منفصل للمستخدم، على غرار الملفات الشخصية للعمل، يجب ألا تفترض التطبيقات أنّ أي نُسخ مثبَّتة من تطبيقها غير المضمّنة في الملف الشخصي الرئيسي موجودة في الملف الشخصي للعمل. إذا كان تطبيقك يتضمّن منطقًا مرتبطًا بتطبيقات الملف الشخصي للعمل يستند إلى هذا الافتراض، عليك تعديل هذا المنطق.
تطبيقات طبية
عندما يقفل المستخدم المساحة الخاصة، يتم إيقاف جميع التطبيقات في المساحة الخاصة، ولا يمكن لهذه التطبيقات تنفيذ الأنشطة في المقدّمة أو الخلفية، بما في ذلك عرض الإشعارات. قد يؤثر هذا السلوك بشكلٍ كبير في استخدام التطبيقات الطبية المثبَّتة في المساحة الخاصة و عملها.
تُحذّر تجربة إعداد المساحة الخاصة المستخدمين من أنّ المساحة الخاصة ليست مناسبة للتطبيقات التي تحتاج إلى تنفيذ أنشطة مهمة في المقدّمة أو في الخلفية، مثل عرض إشعارات من التطبيقات الطبية. ومع ذلك، لا يمكن للتطبيقات تحديد ما إذا كان يتم استخدامها في المساحة الخاصة أم لا، لذلك لا يمكنها عرض تحذير للمستخدم في هذه الحالة.
لهذه الأسباب، إذا كنت تطوّر تطبيقًا طبيًا، عليك مراجعة كيفية تأثير هذه الميزة في تطبيقك واتّخاذ الإجراءات المناسبة، مثل إبلاغ المستخدمين بعدم تثبيت تطبيقك في المساحة الخاصة، لتجنّب إيقاف وظائف التطبيق الحيوية.
تطبيقات مشغّل التطبيقات
إذا كنت تطوّر تطبيق مشغّل، عليك إجراء ما يلي قبل أن تصبح التطبيقات في المساحة الخاصة مرئية:
- يجب تعيين تطبيقك كتطبيق مشغّل تلقائي للجهاز، أي أن يكون لديه الدور
ROLE_HOME. - يجب أن يُعلن تطبيقك عن
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILESالإذن العادي في ملف بيان تطبيقك.
على تطبيقات المشغّلات التي تذكر إذن ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES التعامل مع
حالات استخدام المساحة الخاصة التالية:
- يجب أن يتضمّن تطبيقك حاوية مشغِّل تطبيقات منفصلة للتطبيقات المثبَّتة في
المساحة الخاصة. استخدِم طريقة
getLauncherUserInfo()لتحديد نوع الملف الشخصي للمستخدم الذي تتم معالجته. - يجب أن يتمكّن المستخدم من إخفاء حاوية المساحة الخاصة وعرضها.
- يجب أن يتمكّن المستخدم من قفل حاوية المساحة الخاصة وفتح قفلها. استخدِم
requestQuietModeEnabled()لقفل المساحة الخاصة (بمروّرtrue) أو فتح قفلها (بمروّرfalse). عندما تكون المساحة الخاصة مقفلة، يجب ألا تظهر أي تطبيقات في حاوية المساحة الخاصة أو يمكن العثور عليها من خلال آليات مثل البحث. يجب أن يُسجِّل تطبيقك جهاز استقبال لبثَّي
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLEوACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLEوتعديل واجهة المستخدم في تطبيقك عند تغيُّر حالة حاوية المساحة الخاصة (مقفلة أو غير مقفلة). يتضمّن كلا البثَّينEXTRA_USER، والذي يمكن لتطبيقك استخدامه للإشارة إلى مستخدم الملف الشخصي الخاص.يمكنك أيضًا استخدام طريقة
isQuietModeEnabled()للتحقّق مما إذا كان الملف الشخصي للمساحة الخاصة مقفلًا أم لا.
تطبيقات متجر التطبيقات
تتضمّن المساحة الخاصة زر "تثبيت التطبيقات" الذي يطلق نية ضمنية
لتثبيت التطبيقات في المساحة الخاصة للمستخدم. لكي يتلقّى تطبيقك
هذا الإجراء الضمني، يجب إدراج <intent-filter>
في ملف بيان تطبيقك مع <category> من
CATEGORY_APP_MARKET.
تمت إزالة خط رموز الإيموجي المستند إلى PNG
تم
إزالة ملف خط الرموز التعبيرية القديم المستنِد إلى تنسيق PNG (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf)، ولم يبق سوى الملف المستنِد إلى تنسيق ملفات المتجهات. بدءًا من الإصدار Android 13 (المستوى 33 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، تغيّر ملف خط الرموز التعبيرية المستخدَم من قِبل أداة عرض الرموز التعبيرية في النظام من ملف يستند إلى PNG إلى ملف يستند إلى شكل مسطّح. احتفظ النظام بملف الخط القديم في Android 13 و14 لأسباب تتعلق بالتوافق، حتى تتمكّن التطبيقات التي تستخدم أدوات عرض الخطوط الخاصة بها من مواصلة استخدام ملف الخط القديم إلى أن تتمكّن من الترقية.
للتحقّق مما إذا كان تطبيقك متأثّرًا، ابحث في رمز تطبيقك عن إشارات إلى ملف
NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf.
يمكنك اختيار تكييف تطبيقك بعدة طرق:
- استخدام واجهات برمجة تطبيقات النظام الأساسي لعرض النص يمكنك عرض النص على
Canvasمستند مستنِد إلى رسومات نقطية، واستخدامه للحصول على صورة أولية إذا لزم الأمر. - أضِف ميزة استخدام خطوط COLRv1 إلى تطبيقك. تتيح مكتبة FreeType المفتوحة المصدر استخدام خطوط COLRv1 في الإصدار 2.13.0 والإصدارات الأحدث.
- كحل أخير، يمكنك تجميع ملف خط الرموز التعبيرية القديم
(
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) في حزمة APK، ولكن في هذه الحالة سيفتقد تطبيقك أحدث تعديلات الرموز التعبيرية. للحصول على مزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على صفحة مشروع Noto Emoji على GitHub.
تمت زيادة الحد الأدنى لإصدار حزمة تطوير البرامج (SDK) المستهدَف من 23 إلى 24
يعتمد Android 15 على
التغييرات التي تمّ إجراؤها في Android 14، وتوسِّع نطاق
لتعزيز الأمان. في نظام التشغيل Android 15، التطبيقات التي تحتوي على
لا يمكن تثبيت targetSdkVersion الأقل من 24.
يمكن أن تساعد المطالبة بتلبية المستويات الحديثة لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات في ضمان مستوى أمان أفضل
الخصوصية.
تستهدف البرامج الضارة غالبًا مستويات أقل من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات لتجاوز الأمان والخصوصية
.أساليب الحماية المُقدمة في الإصدارات الأعلى من Android. على سبيل المثال:
تستخدم بعض التطبيقات الضارة القيمة targetSdkVersion من 22 لتجنُّب تعرُّضها
نموذج إذن وقت التشغيل الذي تم تقديمه في عام 2015 من خلال نظام التشغيل Android 6.0 Marshmallow (واجهة برمجة التطبيقات)
المستوى 23). من خلال هذا التغيير في Android 15، يصعب على البرامج الضارة تجنُّب تحسينات الأمان
والخصوصية. تؤدي محاولة تثبيت تطبيق يستهدف مستوى أقل من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
إلى تعذُّر التثبيت، مع ظهور رسالة مثل الرسالة التالية
في Logcat:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
على الأجهزة التي تتم ترقية نظام التشغيل Android 15 إليه، أي تطبيقات تقلّ قيمتها عن targetSdkVersion
يظل أكثر من 24 مثبّتًا.
إذا كنت بحاجة إلى اختبار تطبيق يستهدف مستوى قديمًا لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات، استخدِم الأمر التالي في أداة ADB:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
الأمان والخصوصية
Android 15 introduces robust measures to combat one-time passcode (OTP) fraud and to protect the user's sensitive content, focusing on hardening the Notification Listener Service and screenshare protections. Key enhancements include redacting OTPs from notifications accessible to untrusted apps, hiding notifications during screenshare, and securing app activities when OTPs are posted. These changes aim to keep the user's sensitive content safe from unauthorized actors.
Developers need to be aware of the following to ensure their apps are compatible with the changes in Android 15:
OTP Redaction
Android will stop untrusted apps that implement a
NotificationListenerService from reading unredacted content
from notifications where an OTP has been detected. Trusted apps such as
companion device manager associations are exempt from these restrictions.
Screenshare Protection
- Notification content is hidden during screen sharing sessions to preserve
the user's privacy. If the app implements
setPublicVersion(), Android shows the public version of the notification which serves as a replacement notification in insecure contexts. Otherwise, the notification content is redacted without any further context. - Sensitive content like password input is hidden from remote viewers to prevent revealing the user's sensitive information.
- Activities from apps that post notifications during screenshare where an OTP has been detected will be hidden. App content is hidden from the remote viewer when launched.
- Beyond Android's automatic identification of sensitive fields, developers
can manually mark parts of their app as sensitive using
setContentSensitivity, which is hidden from remote viewers during screenshare. - Developers can choose to toggle the Disable screen share protections option under Developer Options to be exempted from the screenshare protections for demo or testing purposes. The default system screen recorder is exempted from these changes, since the recordings remain on-device.
الكاميرا والوسائط
يجري نظام التشغيل Android 15 التغييرات التالية على سلوك الكاميرا والوسائط لجميع التطبيقات.
يؤدي تشغيل الصوت مباشرةً أو إيقافه إلى إبطال المقاطع الصوتية التي تم فتحها سابقًا مباشرةً أو إيقافها عند بلوغ حدود الموارد
قبل الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android، إذا طلب تطبيق تشغيل الصوت مباشرةً أو نقله أثناء تشغيل تطبيق آخر للصوت وبلغ الحد الأقصى للموارد، لن يتمكّن التطبيق من فتح AudioTrack جديد.
بدءًا من الإصدار 15 من Android، عندما يطلب أحد التطبيقات تشغيل المحتوى مباشرةً أو من خلال التخزين المؤقت
ويصل إلى حدود موارد
التشغيل، يبطل النظام أي عناصر
AudioTrack مفتوحة حاليًا تمنع تلبية طلب المقطع الصوتي الجديد.
(يتم عادةً فتح المقاطع الصوتية المباشرة والمقاطع الصوتية التي تم نقلها لتشغيل تنسيقات المحتوى الصوتي المضغوط. تشمل حالات الاستخدام الشائعة لتشغيل الصوت المباشر بث محتوى ملف صوتي مُشفَّر عبر HDMI إلى التلفزيون. يتم عادةً استخدام المقاطع الصوتية التي تم نقلها إلى الجهاز لتشغيل ملف صوتي مضغوط على جهاز جوّال مزوّد بتسريع الأجهزة لمعالجة الإشارات الرقمية (DSP).)
تجربة المستخدم وواجهة مستخدم النظام
يتضمّن Android 15 بعض التغييرات التي تهدف إلى توفير تجربة مستخدم أكثر اتساقًا وسهولة.
تفعيل الصور المتحركة لإيماءة الرجوع إلى الخلف التنبؤية للتطبيقات التي فعّلتها
اعتبارًا من الإصدار 15 من Android، تمت إزالة خيار المطوّر المتعلّق بالصور المتحركة التنبؤية للرجوع إلى الخلف. تظهر الآن صور System المتحرّكة، مثل الرجوع إلى الشاشة الرئيسية والتنقّل بين المهام وتنفيذ عدة أنشطة في الوقت نفسه، في التطبيقات التي فعّلت ميزة الإيماءة التوقّعية للرجوع إما بالكامل أو على مستوى نشاط معيّن. إذا كان تطبيقك متأثرًا، اتّخذ الخطوات التالية:
- تأكَّد من نقل بيانات تطبيقك بشكلٍ صحيح لاستخدام لفتة التراجع العميق التوقّعية.
- تأكَّد من أنّ عمليات انتقال الأجزاء تعمل مع ميزة التنقّل التلقائي للخلف.
- توقَّف عن استخدام الرسوم المتحركة وتأثيرات الانتقال في إطار العمل واستخدِم رسوم متحركة وتأثيرات انتقال androidx بدلاً من ذلك.
- نقل البيانات بعيدًا عن الحِزم الخلفية التي لا يعرفها
FragmentManagerاستخدِم بدلاً من ذلك حِزم الخلفية التي تديرهاFragmentManagerأو مكوّن "التنقّل" .
إيقاف التطبيقات المصغّرة عند إيقاف المستخدم تطبيقًا بالقوة
إذا أوقف مستخدم تطبيقًا على جهاز يعمل بنظام Android 15 بشكلٍ قسري، سيؤدي ذلك إلى إيقاف جميع التطبيقات المصغّرة للتطبيق مؤقتًا. تكون التطبيقات المصغّرة غير مفعّلة، ولا يمكن للمستخدِم التفاعل معها. ويعود السبب في ذلك إلى أنّه بدءًا من Android 15، يُلغي النظام جميع نوايا التطبيق التي في انتظار المراجعة عند فرض إغلاق التطبيق.
ويعيد النظام تفعيل هذه التطبيقات المصغّرة في المرة التالية التي يشغّل فيها المستخدم التطبيق.
لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على التغييرات في حالة إيقاف الحزمة.
تنبّه شريحة شريط الحالة الخاصة بعرض الوسائط المستخدمين إلى مشاركة الشاشة وإرسال المحتوى وتسجيله
تؤدي إساءة استخدام ميزة "إلقاء الشاشة" إلى تعريض بيانات المستخدمين الخاصة، مثل معلوماتهم المالية، لأنّ المستخدمين لا يدركون أنّه تتم مشاركة شاشة أجهزتهم.
بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي تعمل على الأجهزة التي تعمل بنظام التشغيل Android 15 QPR1 أو إصدار أحدث، يتم عرض شريحة ملف شخصي كبيرة ومميّزة في شريط الحالة لتنبيه المستخدمين بأي عملية بث شاشة جارية. يمكن للمستخدمين النقر على الشريحة لإيقاف مشاركة الشاشة أو بثها أو تسجيلها. ويتوقف أيضًا عرض الشاشة تلقائيًا عند قفل شاشة الجهاز.
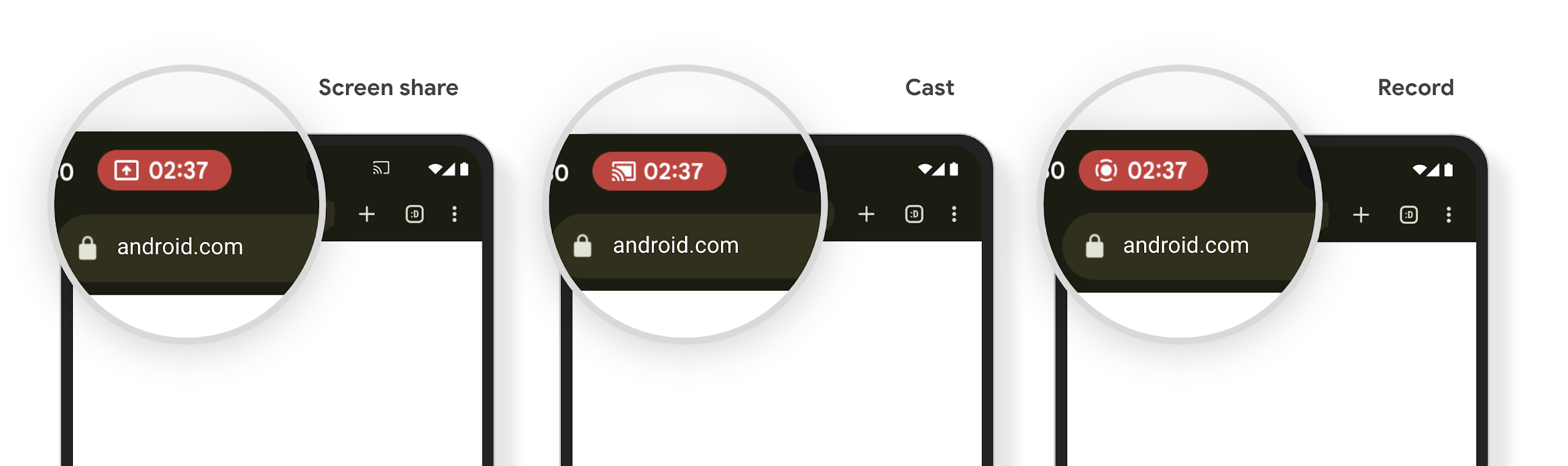
التحقّق مما إذا كان تطبيقك قد تأثّر
يتضمّن تطبيقك تلقائيًا شريحة شريط الحالة ويوقف تلقائيًا إرسال الشاشة عند تفعيل شاشة القفل.
للاطّلاع على مزيد من المعلومات عن كيفية اختبار تطبيقك لاستخدامات هذه الحالات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على شريحة "شريط الحالة" والإيقاف التلقائي.
قيود الوصول إلى الشبكة في الخلفية
في Android 15، تتلقّى التطبيقات التي تبدأ طلب شبكة خارج عملية
دورة حياة صالحة استثناءً. عادةً ما يكون
UnknownHostException أو
IOException آخر مرتبط بمقبس. إنّ طلبات الشبكة التي تحدث خارج دورة حياة صالحة ناتجة عادةً عن مواصلة التطبيقات طلب الشبكة بدون علم حتى بعد أن يصبح التطبيق غير نشط.
للحدّ من هذا الاستثناء، تأكَّد من أنّ طلبات الشبكة على دراية بدورة الحياة وأنّها تُلغى عند مغادرة دورة حياة عملية صالحة باستخدام المكوّنات على دراية بدورة الحياة. إذا كان من المهم أن يتم إرسال طلب الشبكة حتى عندما يغادر المستخدم التطبيق، ننصحك بجدولة طلب الشبكة باستخدام WorkManager أو مواصلة مهمة تظهر للمستخدم باستخدام الخدمة التي تعمل في المقدّمة.
الميزات التي سيتم إيقافها نهائيًا
مع كل إصدار، قد تصبح واجهات برمجة تطبيقات معيّنة في Android قديمة أو تحتاج إلى إعادة تصميم لتوفير تجربة أفضل للمطوّرين أو إتاحة إمكانات جديدة للنظام الأساسي. في هذه الحالات، نوقف رسميًا واجهات برمجة التطبيقات القديمة ونوجّه المطوّرين إلى استخدام واجهات برمجة تطبيقات بديلة.
يعني الإيقاف النهائي أنّنا أوقفنا الدعم الرسمي لواجهات برمجة التطبيقات، ولكن ستظل متاحة للمطوّرين. لمزيد من المعلومات حول عمليات الإيقاف النهائي المهمة في هذا الإصدار من Android، يمكنك الاطّلاع على صفحة عمليات الإيقاف النهائي.
