Платформа Android 15 включает изменения поведения, которые могут повлиять на ваше приложение. Следующие изменения поведения применяются ко всем приложениям, работающим на Android 15, независимо от targetSdkVersion . Вам следует протестировать своё приложение и затем внести необходимые изменения для корректной поддержки этих изменений, где это применимо.
Обязательно ознакомьтесь со списком изменений поведения, которые касаются только приложений, предназначенных для Android 15 .
Основная функциональность
Android 15 изменяет или расширяет различные основные возможности системы Android.
Изменения в состоянии остановленного пакета
Целью состояния пакета FLAG_STOPPED (которое пользователи могут использовать в сборках AOSP, нажав и удерживая значок приложения и выбрав «Принудительно остановить») всегда было сохранение приложений в этом состоянии до тех пор, пока пользователь явно не удалит приложение из этого состояния напрямую. запуск приложения или косвенное взаимодействие с приложением (через общий доступ или виджет, выбор приложения в качестве живых обоев и т. д.). В Android 15 мы обновили поведение системы, чтобы оно соответствовало предполагаемому поведению. Приложения следует выводить из остановленного состояния только прямым или косвенным действием пользователя.
Для поддержки предполагаемого поведения, в дополнение к существующим ограничениям, система также отменяет все ожидающие намерения, когда приложение переходит в состояние остановки на устройстве под управлением Android 15. Когда действия пользователя выводят приложение из состояния остановки, трансляция ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED доставлено в приложение, предоставляя возможность перерегистрировать любые ожидающие намерения.
Вы можете вызвать новый метод ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped() , чтобы подтвердить, было ли приложение переведено в состояние остановлено.
Поддержка страниц размером 16 КБ
Исторически Android поддерживал страницы памяти размером всего 4 КБ, что оптимизировало производительность системной памяти для среднего объёма памяти, обычно используемого устройствами Android. Начиная с Android 15, AOSP поддерживает устройства, настроенные на использование страниц размером 16 КБ (устройства с 16 КБ). Если ваше приложение использует библиотеки NDK , напрямую или косвенно через SDK, вам потребуется пересобрать приложение для его работы на устройствах с 16 КБ.
Поскольку производители устройств продолжают выпускать устройства с большим объёмом физической памяти (ОЗУ), многие из них будут использовать размер страницы 16 КБ (а в перспективе и больше) для оптимизации производительности. Добавление поддержки устройств с размером страницы 16 КБ позволит вашему приложению работать на этих устройствах и позволит использовать преимущества, связанные с повышением производительности. Без перекомпиляции приложения не будут работать на устройствах с 16 КБ в будущих версиях Android.
Чтобы помочь вам добавить поддержку для вашего приложения, мы предоставили рекомендации о том, как проверить, затронуто ли ваше приложение , как перестроить ваше приложение (если это применимо) и как протестировать ваше приложение в среде 16 КБ с помощью эмуляторов (включая образы системы Android 15 для эмулятора Android).
Benefits and performance gains
Устройства, настроенные с размером страницы 16 КБ, в среднем используют немного больше памяти, но также получают различные улучшения производительности как для системы, так и для приложений:
- Сокращение времени запуска приложений, когда система испытывает нехватку памяти: в среднем на 3,16 % меньше, с более значительными улучшениями (до 30 %) для некоторых протестированных нами приложений.
- Снижение энергопотребления при запуске приложения: в среднем снижение на 4,56 %.
- Более быстрый запуск камеры: в среднем на 4,48 % более быстрый горячий запуск и в среднем на 6,60 % более быстрый холодный запуск.
- Улучшено время загрузки системы: в среднем улучшено на 8% (приблизительно 950 миллисекунд).
Эти улучшения основаны на нашем первоначальном тестировании, и результаты на реальных устройствах, вероятно, будут отличаться. По мере продолжения тестирования мы предоставим дополнительный анализ потенциальных преимуществ для приложений.
Check if your app is impacted
Если ваше приложение использует нативный код , вам следует пересобрать его с поддержкой устройств с памятью 16 КБ . Если вы не уверены, использует ли ваше приложение нативный код, вы можете использовать APK Analyzer для его определения, а затем проверить выравнивание сегментов ELF для любых обнаруженных общих библиотек . Android Studio также предоставляет функции, помогающие автоматически обнаруживать проблемы выравнивания .
Если ваше приложение использует только код, написанный на языке программирования Java или Kotlin, включая все библиотеки и SDK, то оно уже поддерживает устройства с 16 КБ. Тем не менее, мы рекомендуем протестировать приложение в среде с 16 КБ, чтобы убедиться в отсутствии непредвиденных регрессий в его поведении.
Необходимые изменения для некоторых приложений для поддержки личного пространства
Private space is a new feature in Android 15 that lets users create a separate space on their device where they can keep sensitive apps away from prying eyes, under an additional layer of authentication. Because apps in the private space have restricted visibility, some types of apps need to take additional steps to be able to see and interact with apps in a user's private space.
All apps
Because apps in the private space are kept in a separate user profile, similar to work profiles, apps shouldn't assume that any installed copies of their app that aren't in the main profile are in the work profile. If your app has logic related to work profile apps that make this assumption, you'll need to adjust this logic.
Medical apps
When a user locks the private space, all apps in the private space are stopped, and those apps can't perform foreground or background activities, including showing notifications. This behavior might critically impact the use and function of medical apps installed in the private space.
The private space setup experience warns users that the private space is not suitable for apps that need to perform critical foreground or background activities, such as showing notifications from medical apps. However, apps can't determine whether or not they're being used in the private space, so they can't show a warning to the user for this case.
For these reasons, if you develop a medical app, review how this feature might impact your app and take appropriate actions—such as informing your users not to install your app in the private space—to avoid disrupting critical app capabilities.
Launcher apps
If you develop a launcher app, you must do the following before apps in the private space will be visible:
- Your app must be assigned as the default launcher app for the device—that
is, possessing the
ROLE_HOMErole. - Your app must declare the
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILESnormal permission in your app's manifest file.
Launcher apps that declare the ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES permission must handle
the following private space use cases:
- Your app must have a separate launcher container for apps installed in the
private space. Use the
getLauncherUserInfo()method to determine which type of user profile is being handled. - The user must be able to hide and show the private space container.
- The user must be able to lock and unlock the private space container. Use
the
requestQuietModeEnabled()method to lock (by passingtrue) or unlock (by passingfalse) the private space. While locked, no apps in the private space container should be visible or discoverable through mechanisms such as search. Your app should register a receiver for the
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLEandACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLEbroadcasts and update the UI in your app when the locked or unlocked state of the private space container changes. Both of these broadcasts includeEXTRA_USER, which your app can use to refer to the private profile user.You can also use the
isQuietModeEnabled()method to check whether the private space profile is locked or not.
App store apps
The private space includes an "Install Apps" button that launches an implicit
intent to install apps into the user's private space. In order for your app to
receive this implicit intent, declare an <intent-filter>
in your app's manifest file with a <category> of
CATEGORY_APP_MARKET.
Шрифт эмодзи на основе PNG удален
The legacy, PNG-based emoji font file (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf) has been
removed, leaving just the vector-based file. Beginning with Android 13 (API
level 33), the emoji font file used by the system emoji renderer changed from a
PNG-based file to a vector based file. The system retained
the legacy font file in Android 13 and 14 for compatibility reasons, so that
apps with their own font renderers could continue to use the legacy font file
until they were able to upgrade.
To check if your app is affected, search your app's code for references to the
NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf file.
You can choose to adapt your app in a number of ways:
- Use platform APIs for text rendering. You can render text to a bitmap-backed
Canvasand use that to get a raw image if necessary. - Add COLRv1 font support to your app. The FreeType open source library supports COLRv1 in version 2.13.0 and higher.
- As a last resort, you can bundle the legacy emoji font file
(
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) into your APK, although in that case your app will be missing the latest emoji updates. For more information, see the Noto Emoji GitHub project page.
Минимальная целевая версия SDK увеличена с 23 до 24.
Android 15 основывается на изменениях, внесенных в Android 14, и еще больше расширяет эту безопасность. В Android 15 приложения с targetSdkVersion ниже 24 установить невозможно. Требование, чтобы приложения соответствовали современным уровням API, помогает обеспечить лучшую безопасность и конфиденциальность.
Вредоносное ПО часто нацелено на более низкие уровни API, чтобы обойти защиту безопасности и конфиденциальности, представленную в более поздних версиях Android. Например, некоторые вредоносные приложения используют targetSdkVersion , равный 22, чтобы избежать применения модели разрешений во время выполнения, представленной в 2015 году в Android 6.0 Marshmallow (уровень API 23). Из-за этого изменения в Android 15 вредоносным программам становится сложнее избежать улучшений безопасности и конфиденциальности. Попытка установить приложение, ориентированное на более низкий уровень API, приводит к сбою установки, и в Logcat появляется сообщение, подобное следующему:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
На устройствах, обновляющихся до Android 15, все приложения с targetSdkVersion ниже 24 остаются установленными.
Если вам нужно протестировать приложение, ориентированное на более старый уровень API, используйте следующую команду ADB:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
Безопасность и конфиденциальность
Android 15 introduces robust measures to combat one-time passcode (OTP) fraud and to protect the user's sensitive content, focusing on hardening the Notification Listener Service and screenshare protections. Key enhancements include redacting OTPs from notifications accessible to untrusted apps, hiding notifications during screenshare, and securing app activities when OTPs are posted. These changes aim to keep the user's sensitive content safe from unauthorized actors.
Developers need to be aware of the following to ensure their apps are compatible with the changes in Android 15:
OTP Redaction
Android will stop untrusted apps that implement a
NotificationListenerService from reading unredacted content
from notifications where an OTP has been detected. Trusted apps such as
companion device manager associations are exempt from these restrictions.
Screenshare Protection
- Notification content is hidden during screen sharing sessions to preserve
the user's privacy. If the app implements
setPublicVersion(), Android shows the public version of the notification which serves as a replacement notification in insecure contexts. Otherwise, the notification content is redacted without any further context. - Sensitive content like password input is hidden from remote viewers to prevent revealing the user's sensitive information.
- Activities from apps that post notifications during screenshare where an OTP has been detected will be hidden. App content is hidden from the remote viewer when launched.
- Beyond Android's automatic identification of sensitive fields, developers
can manually mark parts of their app as sensitive using
setContentSensitivity, which is hidden from remote viewers during screenshare. - Developers can choose to toggle the Disable screen share protections option under Developer Options to be exempted from the screenshare protections for demo or testing purposes. The default system screen recorder is exempted from these changes, since the recordings remain on-device.
Камера и медиа
Android 15 вносит следующие изменения в поведение камеры и мультимедиа для всех приложений.
Прямое и выгруженное воспроизведение звука делает недействительными ранее открытые прямые или выгруженные аудиодорожки при достижении ограничений ресурсов.
До Android 15, если приложение запрашивало прямое воспроизведение звука или разгрузку звука, пока другое приложение воспроизводило звук и были достигнуты ограничения ресурсов, приложение не могло открыть новый AudioTrack .
Начиная с Android 15, когда приложение запрашивает прямое воспроизведение или воспроизведение с разгрузкой и достигаются ограничения ресурсов, система аннулирует все открытые в данный момент объекты AudioTrack , которые препятствуют выполнению запроса на новую дорожку.
(Прямая аудиодорожка и аудиодорожки с выгрузкой обычно открываются для воспроизведения сжатых аудиоформатов. Общие случаи использования прямого воспроизведения аудио включают потоковое воспроизведение закодированного звука через HDMI на телевизор. Дорожки с разгрузкой обычно используются для воспроизведения сжатого аудио на мобильном устройстве с аппаратным DSP. ускорение.)
Пользовательский опыт и системный пользовательский интерфейс
В Android 15 внесены некоторые изменения, направленные на создание более последовательного и интуитивно понятного пользовательского опыта.
Предиктивная анимация возврата включена для приложений, которые выбрали эту функцию
Beginning in Android 15, the developer option for predictive back animations has been removed. System animations such as back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity now appear for apps that have opted in to the predictive back gesture either entirely or at an activity level. If your app is affected, take the following actions:
- Ensure that your app has been properly migrated to use the predictive back gesture.
- Ensure that your fragment transitions work with predictive back navigation.
- Migrate away from animation and framework transitions and use animator and androidx transitions instead.
- Migrate away from back stacks that
FragmentManagerdoesn't know about. Use back stacks managed byFragmentManageror by the Navigation component instead.
Виджеты отключаются, когда пользователь принудительно останавливает приложение.
Если пользователь принудительно останавливает приложение на устройстве под управлением Android 15, система временно отключает все виджеты приложения. Виджеты выделены серым цветом, и пользователь не может с ними взаимодействовать. Это связано с тем, что, начиная с Android 15, система отменяет все ожидающие намерения приложения, когда приложение принудительно остановлено.
Система повторно включает эти виджеты при следующем запуске приложения пользователем.
Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Изменения состояния остановки пакета .
Микросхема строки состояния проекции мультимедиа оповещает пользователей о совместном использовании экрана, трансляции и записи
Screen projection exploits expose private user data such as financial information because users don't realize their device screen is being shared.
For apps running on devices with Android 15 QPR1 or higher, a status bar chip that is large and prominent alerts users to any in‑progress screen projection. Users can tap the chip to stop their screen from being shared, cast, or recorded. Also, screen projection automatically stops when the device screen is locked.
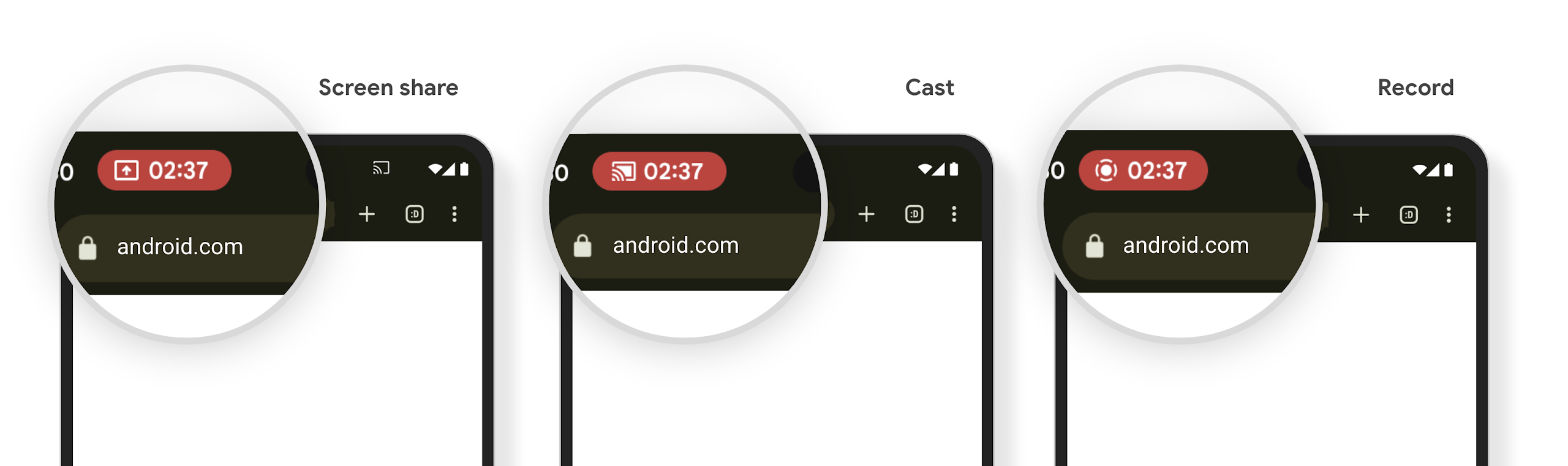
Check if your app is impacted
By default, your app includes the status bar chip and automatically suspends screen projection when the lock screen activates.
To learn more about how to test your app for these use cases, see Status bar chip and auto stop.
Ограничения фонового доступа к сети
In Android 15, apps that start a network request outside of a valid process
lifecycle receive an exception. Typically, an
UnknownHostException or other socket-related
IOException. Network requests that happen outside of a valid lifecycle are
usually due to apps unknowingly continuing a network request even after the app
is no longer active.
To mitigate this exception, ensure your network requests are lifecycle aware and cancelled upon leaving a valid process lifecycle by using lifecycle aware components. If it is important that the network request should happen even when the user leaves the application, consider scheduling the network request using WorkManager or continue a user visible task using Foreground Service.
Устаревания
С каждым релизом некоторые API Android могут устаревать или нуждаться в рефакторинге для улучшения удобства разработки или поддержки новых возможностей платформы. В таких случаях мы официально прекращаем поддержку устаревших API и рекомендуем разработчикам использовать альтернативные API.
Устаревание означает, что мы прекратили официальную поддержку этих API, но они по-прежнему будут доступны разработчикам. Подробнее о важных устарелых функциях в этой версии Android см. на странице «Устаревание» .

