Android 15 플랫폼에는 앱에 영향을 줄 수 있는 동작 변경사항이 있습니다. targetSdkVersion과 관계없이 Android 15에서 실행되는 모든 앱에 적용되는 동작 변경사항은 다음과 같습니다. 이러한 변경사항을 적절히 지원해야 하는 경우 앱을 테스트한 후 필요에 따라 수정해야 합니다.
또한 Android 15를 타겟팅하는 앱에만 영향을 주는 동작 변경사항 목록을 검토해야 합니다.
핵심 기능
Android 15는 Android 시스템의 다양한 핵심 기능을 수정하거나 확장합니다.
패키지 중지 상태 변경
패키지 FLAG_STOPPED 상태 (사용자가 앱 아이콘을 길게 누르고 '강제 종료'를 선택하여 AOSP 빌드에서 참여할 수 있음)의 의도는 항상 사용자가 앱을 직접 실행하거나 공유 시트 또는 위젯을 통해 앱과 간접적으로 상호작용 (앱을 라이브 배경화면으로 선택 등)하여 이 상태에서 앱을 명시적으로 삭제할 때까지 앱을 이 상태로 유지하는 것이었습니다. Android 15에서는 의도된 동작에 맞게 시스템 동작을 업데이트했습니다. 앱은 직접 또는 간접적인 사용자 작업을 통해서만 중지된 상태에서 삭제되어야 합니다.
의도한 동작을 지원하기 위해 시스템은 기존 제한사항 외에도 앱이 Android 15를 실행하는 기기에서 중지된 상태가 되면 모든 대기 중인 인텐트를 취소합니다. 사용자 작업으로 인해 앱이 중지된 상태에서 삭제되면 ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED 브로드캐스트가 앱에 전송되어 대기 중인 인텐트를 다시 등록할 수 있는 기회를 제공합니다.
새 ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped() 메서드를 호출하여 앱이 중지 상태인지 확인할 수 있습니다.
16KB 페이지 크기 지원
이전에는 Android에서 4KB 메모리 페이지 크기만 지원하여 Android 기기가 일반적으로 보유한 평균 총 메모리에 맞게 시스템 메모리 성능을 최적화했습니다. Android 15부터 AOSP는 페이지 크기 16KB (16KB 기기)를 사용하도록 구성된 기기를 지원합니다. 앱이 NDK 라이브러리를 직접 또는 SDK를 통해 간접적으로 사용하는 경우 이러한 16KB 기기에서 작동하도록 앱을 다시 빌드해야 합니다.
기기 제조업체가 더 많은 실제 메모리 (RAM)가 있는 기기를 계속 빌드함에 따라 이러한 기기 중 다수가 기기 성능을 최적화하기 위해 16KB (결국 더 큰) 페이지 크기를 채택할 것입니다. 16KB 페이지 크기 기기에 대한 지원을 추가하면 앱이 이러한 기기에서 실행될 수 있으며 앱이 관련 성능 개선의 이점을 누릴 수 있습니다. 다시 컴파일하지 않으면 앱이 향후 Android 출시에서 16KB 기기에서 작동하지 않습니다.
앱 지원을 추가할 수 있도록 앱이 영향을 받는지 확인하는 방법, 앱을 다시 빌드하는 방법 (해당하는 경우), 에뮬레이터 (Android Emulator용 Android 15 시스템 이미지 포함)를 사용하여 16KB 환경에서 앱을 테스트하는 방법에 관한 안내를 제공해 드렸습니다.
이점 및 성능 향상
16KB 페이지 크기로 구성된 기기는 평균적으로 약간 더 많은 메모리를 사용하지만 시스템과 앱 모두에서 다양한 성능이 개선됩니다.
- 시스템에 메모리 문제가 있는 동안 앱 실행 시간 단축: 평균 3.16% 감소, 테스트한 일부 앱의 경우 더 큰 개선 (최대 30%)
- 앱 실행 중 전원 소모 감소: 평균 4.56% 감소
- 카메라 실행 속도 향상: 평균 핫 스타트 속도가 4.48%, 콜드 스타트 속도가 6.60% 빨라짐
- 시스템 부팅 시간 개선: 평균 8% (약 950밀리초) 개선됨
이러한 개선사항은 초기 테스트를 기반으로 하며 실제 기기의 결과는 다를 수 있습니다. 테스트를 계속하면서 앱의 잠재적 이점에 관한 추가 분석을 제공할 예정입니다.
앱이 영향을 받는지 확인하기
앱에서 네이티브 코드를 사용하는 경우 16KB 기기를 지원하도록 앱을 다시 빌드해야 합니다. 앱에서 네이티브 코드를 사용하는지 확실히 알 수 없는 경우 APK 분석기를 사용하여 네이티브 코드가 있는지 확인한 다음 찾은 공유 라이브러리의 ELF 세그먼트 정렬을 확인하면 됩니다. Android 스튜디오는 정렬 문제를 자동으로 감지하는 데 도움이 되는 기능도 제공합니다.
앱에서 모든 라이브러리나 SDK를 비롯하여 Java 프로그래밍 언어나 Kotlin으로 작성된 코드만 사용한다면 이미 16KB 기기를 지원하는 것입니다. 하지만 16KB 환경에서 앱을 테스트하여 앱 동작에 예기치 않은 회귀가 없는지 확인하는 것이 좋습니다.
일부 앱이 비공개 스페이스를 지원하는 데 필요한 변경사항
비공개 스페이스는 Android 15의 새로운 기능으로, 사용자가 기기에 별도의 공간을 만들어 민감한 앱을 다른 사람이 보지 못하도록 추가 인증 레이어로 보관할 수 있습니다. 비공개 스페이스의 앱은 공개 범위가 제한되어 있으므로 일부 유형의 앱은 사용자의 비공개 스페이스에 있는 앱을 보고 상호작용하려면 추가 단계를 수행해야 합니다.
모든 앱
비공개 공간의 앱은 직장 프로필과 마찬가지로 별도의 사용자 프로필에 보관되므로 앱은 기본 프로필에 없는 설치된 앱 사본이 직장 프로필에 있다고 가정해서는 안 됩니다. 앱에 이러한 가정을 하는 직장 프로필 앱과 관련된 로직이 있는 경우 이 로직을 조정해야 합니다.
의료 앱
사용자가 비공개 스페이스를 잠그면 비공개 스페이스의 모든 앱이 중지되며 이러한 앱은 알림 표시를 비롯한 포그라운드 또는 백그라운드 활동을 실행할 수 없습니다. 이 동작은 비공개 스페이스에 설치된 의료 앱의 사용 및 기능에 심각한 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
비공개 스페이스 설정 환경은 의료 앱의 알림 표시와 같이 중요한 포그라운드 또는 백그라운드 활동을 실행해야 하는 앱에는 비공개 스페이스가 적합하지 않다고 사용자에게 경고합니다. 그러나 앱은 비공개 스페이스에서 사용 중인지 여부를 확인할 수 없으므로 이 경우 사용자에게 경고를 표시할 수 없습니다.
따라서 의료 앱을 개발하는 경우 이 기능이 앱에 미칠 수 있는 영향을 검토하고 중요한 앱 기능이 중단되지 않도록 사용자에게 비공개 스페이스에 앱을 설치하지 말라고 알리는 등 적절한 조치를 취하세요.
런처 앱
런처 앱을 개발하는 경우 비공개 공간의 앱이 표시되기 전에 다음을 실행해야 합니다.
- 앱이 기기의 기본 런처 앱으로 할당되어야 합니다. 즉,
ROLE_HOME역할을 보유해야 합니다. - 앱은
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES일반 권한을 앱의 매니페스트 파일에서 선언해야 합니다.
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES 권한을 선언하는 런처 앱은 다음과 같은 비공개 공간 사용 사례를 처리해야 합니다.
- 앱에는 비공개 스페이스에 설치된 앱을 위한 별도의 런처 컨테이너가 있어야 합니다.
getLauncherUserInfo()메서드를 사용하여 처리 중인 사용자 프로필 유형을 확인합니다. - 사용자가 비공개 스페이스 컨테이너를 숨기고 표시할 수 있어야 합니다.
- 사용자는 비공개 스페이스 컨테이너를 잠그고 잠금 해제할 수 있어야 합니다.
requestQuietModeEnabled()메서드를 사용하여 비공개 스페이스를 잠그거나 (true전달) 잠금 해제합니다 (false전달). 잠겨 있는 동안 비공개 스페이스 컨테이너의 앱은 검색과 같은 메커니즘을 통해 표시되거나 검색될 수 없어야 합니다. 앱은
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLE및ACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLE브로드캐스트에 수신기를 등록하고 비공개 스페이스 컨테이너의 잠금 또는 잠금 해제 상태가 변경될 때 앱의 UI를 업데이트해야 합니다. 두 브로드캐스트 모두 앱에서 비공개 프로필 사용자를 참조하는 데 사용할 수 있는EXTRA_USER를 포함합니다.isQuietModeEnabled()메서드를 사용하여 비공개 스페이스 프로필이 잠겨 있는지 확인할 수도 있습니다.
앱 스토어 앱
비공개 스페이스에는 사용자의 비공개 스페이스에 앱을 설치하기 위한 암시적 인텐트를 실행하는 '앱 설치' 버튼이 포함되어 있습니다. 앱이 이 암시적 인텐트를 수신하려면 앱의 매니페스트 파일에서 CATEGORY_APP_MARKET의 <category>로 <intent-filter>를 선언합니다.
PNG 기반 그림 이모티콘 글꼴 삭제됨
기존의 PNG 기반 그림 이모티콘 글꼴 파일 (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf)이 삭제되고 벡터 기반 파일만 남았습니다. Android 13 (API 수준 33)부터 시스템 그림 이모티콘 렌더러에서 사용하는 그림 이모티콘 글꼴 파일이 PNG 기반 파일에서 벡터 기반 파일로 변경되었습니다. 시스템은 호환성 문제로 인해 Android 13 및 14에서 기존 글꼴 파일을 유지했습니다. 따라서 자체 글꼴 렌더러가 있는 앱은 업그레이드할 수 있을 때까지 기존 글꼴 파일을 계속 사용할 수 있었습니다.
앱이 영향을 받는지 확인하려면 앱 코드에서 NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf 파일에 대한 참조를 검색합니다.
다음과 같은 여러 가지 방법으로 앱을 조정할 수 있습니다.
- 텍스트 렌더링에 플랫폼 API를 사용합니다. 텍스트를 비트맵 지원
Canvas로 렌더링하고 필요한 경우 이를 사용하여 원시 이미지를 가져올 수 있습니다. - 앱에 COLRv1 글꼴 지원을 추가합니다. FreeType 오픈소스 라이브러리는 버전 2.13.0 이상에서 COLRv1을 지원합니다.
- 최후의 수단으로 기존 그림 이모티콘 글꼴 파일(
NotoColorEmoji.ttf)을 APK에 번들로 묶을 수 있습니다. 단, 이 경우 앱에서 최신 그림 이모티콘 업데이트를 놓치게 됩니다. 자세한 내용은 Noto Emoji GitHub 프로젝트 페이지를 참고하세요.
최소 타겟 SDK 버전이 23에서 24로 상향됨
Android 15는
Android 14에 적용된 변경사항을 살펴보고
보안을 한층 더 강화합니다 Android 15에서는 targetSdkVersion이 24 미만인 앱을 설치할 수 없습니다.
앱이 최신 API 수준을 충족하도록 요구하면 더 나은 보안과
있습니다.
멀웨어는 최신 Android 버전에 도입된 보안 및 개인 정보 보호 기능을 우회하기 위해 낮은 API 수준을 타겟팅하는 경우가 많습니다. 예를 들어 일부 멀웨어 앱은 targetSdkVersion 22를 사용하여 2015년 Android 6.0 Marshmallow(API 수준 23)에서 도입된 런타임 권한 모델이 적용되지 않도록 합니다. 이러한 Android 15 변경사항으로 인해 멀웨어가 보안 문제를 피하기가 더 어려워짐
개인 정보 보호 개선 더 낮은 API를 대상으로 하는 앱 설치 시도
설치에 실패하며 다음과 같은 메시지가 표시됩니다.
Logcat에 나타날 수 있습니다.
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
Android 15로 업그레이드하는 기기에서 targetSdkVersion이 더 낮은 모든 앱
설치된 상태로 유지됩니다.
이전 API 수준을 타겟팅하는 앱을 테스트해야 한다면 다음 ADB 명령어를 사용합니다.
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
보안 및 개인 정보 보호
Android 15에서는 일회용 비밀번호 (OTP) 사기를 방지하고 사용자의 민감한 콘텐츠를 보호하기 위한 강력한 조치를 도입하여 알림 리스너 서비스 및 화면 공유 보호를 강화하는 데 중점을 둡니다. 주요 개선사항에는 신뢰할 수 없는 앱에서 액세스할 수 있는 알림에서 OTP 삭제, 화면 공유 중에 알림 숨기기, OTP가 게시될 때 앱 활동 보호 등이 있습니다. 이번 변경사항은 승인되지 않은 행위자로부터 사용자의 민감한 콘텐츠를 안전하게 보호하기 위한 것입니다.
앱이 Android 15의 변경사항과 호환되도록 하려면 개발자는 다음 사항을 알아야 합니다.
OTP 수정
Android에서는 NotificationListenerService를 구현하는 신뢰할 수 없는 앱이 OTP가 감지된 알림에서 수정되지 않은 콘텐츠를 읽지 못하도록 합니다. 호환 기기 관리자 연결과 같은 신뢰할 수 있는 앱에는 이러한 제한사항이 적용되지 않습니다.
화면 공유 보호
- 사용자의 개인 정보를 보호하기 위해 화면 공유 세션 중에 알림 콘텐츠가 숨겨집니다. 앱이
setPublicVersion()를 구현하는 경우 Android는 안전하지 않은 컨텍스트에서 대체 알림 역할을 하는 알림의 공개 버전을 표시합니다. 그렇지 않으면 추가 컨텍스트 없이 알림 콘텐츠가 수정됩니다. - 비밀번호 입력과 같은 민감한 콘텐츠는 사용자의 민감한 정보가 노출되지 않도록 원격 시청자에게 표시되지 않습니다.
- OTP가 감지된 화면 공유 중에 알림을 게시하는 앱의 활동이 숨겨집니다. 앱 콘텐츠가 실행되면 원격 뷰어에서 숨겨집니다.
- Android에서 민감한 입력란을 자동으로 식별하는 것 외에도 개발자는
setContentSensitivity를 사용하여 앱의 일부를 수동으로 민감한 정보로 표시할 수 있습니다. 이 입력란은 화면 공유 중에 원격 시청자에게 표시되지 않습니다. - 개발자는 개발자 옵션에서 화면 공유 보호 기능 사용 안함 옵션을 전환하여 데모 또는 테스트 목적으로 화면 공유 보호 기능을 제외할 수 있습니다. 녹화 파일이 기기에 남아 있으므로 기본 시스템 화면 녹화기는 이러한 변경사항에서 제외됩니다.
카메라 및 미디어
Android 15에서는 모든 앱의 카메라 및 미디어 동작이 다음과 같이 변경됩니다.
리소스 한도에 도달하면 직접 및 오프로드 오디오 재생으로 인해 이전에 열린 직접 또는 오프로드 오디오 트랙이 무효화됨
Android 15 이전에는 다른 앱에서 오디오를 재생하고 리소스 한도에 도달한 동안 앱이 직접 또는 오프로드 오디오 재생을 요청하면 앱이 새 AudioTrack를 열지 못했습니다.
Android 15부터 앱이 직접 재생 또는 오프로드 재생을 요청하고 리소스 한도에 도달하면 시스템은 새 트랙 요청을 처리하지 못하게 하는 현재 열려 있는 모든 AudioTrack 객체를 무효화합니다.
직접 및 오프로드 오디오 트랙은 일반적으로 압축된 오디오 형식을 재생하기 위해 열립니다. 직접 오디오를 재생하는 일반적인 사용 사례로는 HDMI를 통해 인코딩된 오디오를 TV로 스트리밍하는 것이 있습니다. 오프로드 트랙은 일반적으로 하드웨어 DSP 가속이 있는 휴대기기에서 압축된 오디오를 재생하는 데 사용됩니다.)
사용자 환경 및 시스템 UI
Android 15에는 더 일관되고 직관적인 사용자 환경을 만들기 위한 몇 가지 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
선택한 앱에 뒤로 탐색 예측 애니메이션 사용 설정
Android 15부터 뒤로 탐색 예측 애니메이션의 개발자 옵션이 삭제되었습니다. 이제 홈으로 돌아가기, 교차 작업, 교차 활동과 같은 시스템 애니메이션이 전체적으로 또는 활동 수준에서 뒤로 탐색 예측 동작을 선택한 앱에 표시됩니다. 앱이 영향을 받는 경우 다음 작업을 실행합니다.
- 뒤로 탐색 예측 동작을 사용하도록 앱이 올바르게 이전되었는지 확인합니다.
- 프래그먼트 전환이 뒤로 탐색 예측 탐색과 함께 작동하는지 확인합니다.
- 애니메이션 및 프레임워크 전환에서 이전하고 대신 애니메이터 및 androidx 전환을 사용하세요.
FragmentManager가 알지 못하는 백 스택에서 이전합니다. 대신FragmentManager또는 탐색 구성요소에서 관리하는 백 스택을 사용하세요.
사용자가 앱을 강제 종료하면 위젯이 사용 중지됨
사용자가 Android 15를 실행하는 기기에서 앱을 강제 종료하면 시스템은 일시적으로 앱의 모든 위젯을 사용 중지합니다. 위젯이 비활성화되어 있고 사용자는 위젯과 상호작용할 수 없습니다. Android 15부터 시스템은 앱이 강제 종료될 때 앱의 대기 중인 인텐트를 모두 취소하기 때문입니다.
시스템은 사용자가 다음에 앱을 실행할 때 이러한 위젯을 다시 사용 설정합니다.
자세한 내용은 패키지 중지 상태 변경사항을 참고하세요.
미디어 프로젝션 상태 표시줄 칩은 사용자에게 화면 공유, 전송, 녹화를 알립니다.
화면 프로젝션 악용은 사용자가 기기 화면이 공유되고 있다는 사실을 모르기 때문에 금융 정보와 같은 민감한 사용자 데이터를 노출합니다.
Android 15 QPR1 이상을 실행하는 기기에서 실행되는 앱의 경우 크고 눈에 잘 띄는 상태 표시줄 칩이 진행 중인 화면 프로젝션을 사용자에게 알립니다. 사용자는 칩을 탭하여 화면 공유, 전송, 녹화를 중지할 수 있습니다. 또한 기기 화면이 잠기면 화면 프로젝션이 자동으로 중지됩니다.
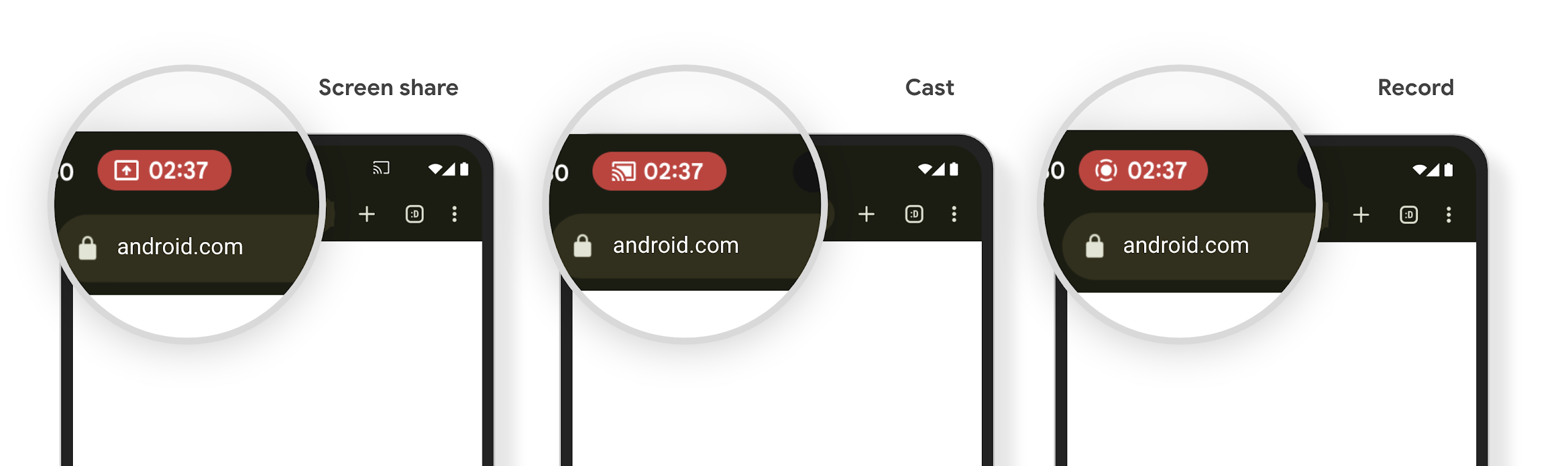
앱이 영향을 받는지 확인하기
기본적으로 앱에는 상태 표시줄 칩이 포함되며 잠금 화면이 활성화되면 화면 프로젝션이 자동으로 일시중지됩니다.
이러한 사용 사례에 맞게 앱을 테스트하는 방법을 자세히 알아보려면 상태 표시줄 칩 및 자동 중지를 참고하세요.
백그라운드 네트워크 액세스 제한
Android 15에서는 유효한 프로세스 수명 주기 외부에서 네트워크 요청을 시작하는 앱에 예외가 발생합니다. 일반적으로 UnknownHostException 또는 기타 소켓 관련 IOException입니다. 유효한 수명 주기 외부에서 발생하는 네트워크 요청은 일반적으로 앱이 더 이상 활성 상태가 아님에도 앱이 모르는 사이에 네트워크 요청을 계속하기 때문에 발생합니다.
이 예외를 완화하려면 수명 주기 인식 구성요소를 사용하여 네트워크 요청이 수명 주기를 인식하고 유효한 프로세스 수명 주기를 종료할 때 취소되도록 합니다. 사용자가 애플리케이션을 종료해도 네트워크 요청이 실행되어야 하는 경우 WorkManager를 사용하여 네트워크 요청을 예약하거나 포그라운드 서비스를 사용하여 사용자에게 표시되는 작업을 계속하는 것이 좋습니다.
지원 중단
각 출시에서 특정 Android API는 더 이상 사용되지 않거나 더 나은 개발자 환경 제공이나 새 플랫폼 기능 지원을 위해 리팩터링해야 할 수 있습니다. 이 경우 Google은 더 이상 사용되지 않는 API를 공식적으로 지원 중단하고 개발자에게 대신 사용할 대체 API를 안내합니다.
지원 중단이란 API에 관한 공식 지원은 종료되나 개발자는 계속 사용할 수 있다는 의미입니다. 이번 Android 출시에서 주목할 만한 지원 중단에 대해 자세히 알아보려면 지원 중단 페이지를 참고하세요.

