Android 15 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่อาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณเช่นเดียวกับรุ่นก่อนหน้า การเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานต่อไปนี้จะมีผลกับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ขึ้นไปเท่านั้น หากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ขึ้นไป คุณควรแก้ไขแอปให้รองรับลักษณะการทำงานเหล่านี้อย่างเหมาะสมในกรณีที่ เกี่ยวข้อง
นอกจากนี้ โปรดตรวจสอบรายการการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่มีผลกับแอปทั้งหมด
ที่ทำงานบน Android 15 ไม่ว่า targetSdkVersion ของแอปจะเป็นอย่างไร
ฟังก์ชันหลัก
Android 15 จะแก้ไขหรือขยายความสามารถหลักต่างๆ ของระบบ Android
การเปลี่ยนแปลงบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า
เราจะทำการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้กับบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าใน Android 15
- ลักษณะการหมดเวลาของบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าของการซิงค์ข้อมูล
- ประเภทบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าสำหรับการประมวลผลสื่อแบบใหม่
- ข้อจำกัดเกี่ยวกับ
BOOT_COMPLETEDBroadcast Receiver ที่เปิดบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า - ข้อจำกัดในการเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าขณะที่แอปมีสิทธิ์
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
ลักษณะการหมดเวลาของบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าของการซิงค์ข้อมูล
Android 15 introduces a new timeout behavior to dataSync for apps targeting
Android 15 (API level 35) or higher. This behavior also applies to the new
mediaProcessing foreground service type.
The system permits an app's dataSync services to run for a total of 6 hours
in a 24-hour period, after which the system calls the running service's
Service.onTimeout(int, int) method (introduced in Android
15). At this time, the service has a few seconds to call
Service.stopSelf(). When Service.onTimeout() is called, the
service is no longer considered a foreground service. If the service does not
call Service.stopSelf(), the system throws an internal exception. The
exception is logged in Logcat with the following message:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
To avoid problems with this behavior change, you can do one or more of the following:
- Have your service implement the new
Service.onTimeout(int, int)method. When your app receives the callback, make sure to callstopSelf()within a few seconds. (If you don't stop the app right away, the system generates a failure.) - Make sure your app's
dataSyncservices don't run for more than a total of 6 hours in any 24-hour period (unless the user interacts with the app, resetting the timer). - Only start
dataSyncforeground services as a result of direct user interaction; since your app is in the foreground when the service starts, your service has the full six hours after the app goes to the background. - Instead of using a
dataSyncforeground service, use an alternative API.
If your app's dataSync foreground services have run for 6 hours in the last
24, you cannot start another dataSync foreground service unless the user
has brought your app to the foreground (which resets the timer). If you try to
start another dataSync foreground service, the system throws
ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
with an error message like "Time limit already exhausted for foreground service
type dataSync".
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable data sync timeouts even if your app
is not targeting Android 15 (as long as the app is running on an Android 15
device). To enable timeouts, run the following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
You can also adjust the timeout period, to make it easier to test how your
app behaves when the limit is reached. To set a new timeout period, run the
following adb command:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
ประเภทบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าใหม่สำหรับการประมวลผลสื่อ
Android 15 introduces a new foreground service type, mediaProcessing. This
service type is appropriate for operations like transcoding media files. For
example, a media app might download an audio file and need to convert it to a
different format before playing it. You can use a mediaProcessing foreground
service to make sure the conversion continues even while the app is in the
background.
The system permits an app's mediaProcessing services to run for a total of 6
hours in a 24-hour period, after which the system calls the running service's
Service.onTimeout(int, int) method (introduced in Android
15). At this time, the service has a few seconds to call
Service.stopSelf(). If the service does not
call Service.stopSelf(), the system throws an internal exception. The
exception is logged in Logcat with the following message:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
To avoid having the exception, you can do one of the following:
- Have your service implement the new
Service.onTimeout(int, int)method. When your app receives the callback, make sure to callstopSelf()within a few seconds. (If you don't stop the app right away, the system generates a failure.) - Make sure your app's
mediaProcessingservices don't run for more than a total of 6 hours in any 24-hour period (unless the user interacts with the app, resetting the timer). - Only start
mediaProcessingforeground services as a result of direct user interaction; since your app is in the foreground when the service starts, your service has the full six hours after the app goes to the background. - Instead of using a
mediaProcessingforeground service, use an alternative API, like WorkManager.
If your app's mediaProcessing foreground services have run for 6 hours in the
last 24, you cannot start another mediaProcessing foreground service unless
the user has brought your app to the foreground (which resets the timer). If you
try to start another mediaProcessing foreground service, the system throws
ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
with an error message like "Time limit already exhausted for foreground service
type mediaProcessing".
For more information about the mediaProcessing service type, see Changes to
foreground service types for Android 15: Media processing.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable media processing timeouts even if
your app is not targeting Android 15 (as long as the app is running on an
Android 15 device). To enable timeouts, run the following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
You can also adjust the timeout period, to make it easier to test how your
app behaves when the limit is reached. To set a new timeout period, run the
following adb command:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
ข้อจำกัดเกี่ยวกับ Broadcast Receiver BOOT_COMPLETED ที่เปิดบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า
มีข้อจำกัดใหม่ในการเปิดตัว Broadcast Receiver ของ BOOT_COMPLETED
บริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า ระบบไม่อนุญาตให้ Receiver BOOT_COMPLETED เปิดบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าประเภทต่อไปนี้
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(ข้อจำกัดนี้มีการใช้มาเป็นเวลาmicrophoneตั้งแต่ Android 14)
หากตัวรับสัญญาณ BOOT_COMPLETED พยายามเปิดเบื้องหน้าประเภทใดก็ตามเหล่านี้
ระบบอาจไม่แสดง ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
การทดสอบ
หากต้องการทดสอบลักษณะการทำงานของแอป คุณสามารถเปิดใช้ข้อจำกัดใหม่เหล่านี้ได้ แม้ว่า
แอปไม่ได้กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (ตราบใดที่แอปยังทํางานอยู่ใน Android 15
อุปกรณ์) เรียกใช้คำสั่ง adb ต่อไปนี้
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
หากต้องการส่งประกาศBOOT_COMPLETEDโดยไม่ต้องรีสตาร์ทอุปกรณ์ ให้ทำดังนี้
เรียกใช้คำสั่ง adb ต่อไปนี้
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
ข้อจำกัดในการเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าขณะที่แอปมีสิทธิ์ SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
ก่อนหน้านี้ หากแอปมีสิทธิ์ SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW แอปจะเปิดบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าได้แม้ว่าในขณะนั้นแอปจะทำงานอยู่เบื้องหลังก็ตาม (ตามที่ได้อธิบายไว้ในการยกเว้นจากการจำกัดการเริ่มทำงานในเบื้องหลัง)
หากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 การยกเว้นนี้จะแคบลงแล้ว ตอนนี้แอปต้องมีสิทธิ์ SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW และต้องมีหน้าต่างวางซ้อนที่มองเห็นได้ กล่าวคือ แอปต้องเปิดหน้าต่าง TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY ก่อน และหน้าต่างต้องปรากฏขึ้นก่อนที่คุณจะเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า
หากแอปพยายามเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าจากเบื้องหลังโดยไม่เป็นไปตามข้อกำหนดใหม่เหล่านี้ (และไม่มีข้อยกเว้นอื่นๆ) ระบบจะแสดงข้อผิดพลาด ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
หากแอปประกาศสิทธิ์ SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW และเปิดบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าจากเบื้องหลัง แอปอาจได้รับผลกระทบจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ หากแอปได้รับ ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException ให้ตรวจสอบลําดับการทํางานของแอปและตรวจสอบว่าแอปมีหน้าต่างวางซ้อนที่ใช้งานอยู่ก่อนที่จะพยายามเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าจากเบื้องหลัง คุณสามารถตรวจสอบว่าขณะนี้หน้าต่างวางซ้อนแสดงอยู่หรือไม่โดยเรียกใช้ View.getWindowVisibility() หรือจะลบล้าง View.onWindowVisibilityChanged() เพื่อรับการแจ้งเตือนทุกครั้งที่ระดับการแชร์มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงก็ได้
การทดสอบ
หากต้องการทดสอบลักษณะการทํางานของแอป คุณสามารถเปิดใช้ข้อจํากัดใหม่เหล่านี้ได้แม้ว่าแอปของคุณจะไม่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ก็ตาม (ตราบใดที่แอปทํางานบนอุปกรณ์ Android 15) หากต้องการเปิดใช้ข้อจำกัดใหม่เหล่านี้เกี่ยวกับการเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าจากเบื้องหลัง ให้เรียกใช้คำสั่ง adb ต่อไปนี้
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
การเปลี่ยนแปลงเวลาที่แอปจะแก้ไขสถานะส่วนกลางของโหมดห้ามรบกวนได้
แอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ขึ้นไปจะไม่สามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงสถานะหรือนโยบายแบบรวมของโหมดห้ามรบกวน (DND) ในอุปกรณ์ได้อีกต่อไป (ไม่ว่าจะแก้ไขการตั้งค่าของผู้ใช้หรือปิดโหมด DND) แต่แอปต้องส่งAutomaticZenRule ซึ่งระบบจะรวมเข้ากับนโยบายส่วนกลางโดยใช้รูปแบบ "นโยบายที่เข้มงวดที่สุดจะชนะ" ที่มีอยู่ การเรียก API ที่มีอยู่ซึ่งก่อนหน้านี้ส่งผลต่อสถานะส่วนกลาง (setInterruptionFilter,
setNotificationPolicy) จะส่งผลให้มีการสร้างหรืออัปเดต AutomaticZenRule ที่ไม่ชัดแจ้ง ซึ่งจะเปิดและปิดอยู่โดยขึ้นอยู่กับรอบการเรียกของ API เหล่านั้น
โปรดทราบว่าการเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้มีผลต่อลักษณะการทำงานที่สังเกตได้เฉพาะในกรณีที่แอปเรียกใช้ setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) และคาดว่าการเรียกใช้ดังกล่าวจะปิดใช้งาน AutomaticZenRule ที่เจ้าของเปิดใช้งานไว้ก่อนหน้านี้
การเปลี่ยนแปลง API ของ OpenJDK
Android 15 จะยังคงปรับปรุงไลบรารีหลักของ Android ให้สอดคล้องกับฟีเจอร์ใน OpenJDK LTS เวอร์ชันล่าสุด
การเปลี่ยนแปลงบางอย่างเหล่านี้อาจส่งผลต่อความเข้ากันได้ของแอปสำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ดังนี้
การเปลี่ยนแปลง API การจัดรูปแบบสตริง: ตอนนี้การตรวจสอบดัชนีอาร์กิวเมนต์ แฟล็ก ความกว้าง และความแม่นยำจะเข้มงวดมากขึ้นเมื่อใช้ API
String.format()และFormatter.format()ต่อไปนี้String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
ตัวอย่างเช่น ระบบจะแสดงข้อยกเว้นต่อไปนี้เมื่อใช้อาร์กิวเมนต์ดัชนี 0 (
%0ในสตริงรูปแบบ)IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0ในกรณีนี้ คุณสามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้โดยใช้อาร์กิวเมนต์ดัชนี 1 (
%1ในสตริงรูปแบบ)การเปลี่ยนแปลงประเภทคอมโพเนนต์ของ
Arrays.asList(...).toArray(): เมื่อใช้Arrays.asList(...).toArray()ประเภทคอมโพเนนต์ของอาร์เรย์ผลลัพธ์จะเป็นObjectไม่ใช่ประเภทขององค์ประกอบของอาร์เรย์พื้นฐาน ดังนั้นโค้ดต่อไปนี้จะแสดงClassCastExceptionString[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();ในกรณีนี้ หากต้องการเก็บรักษา
Stringเป็นประเภทคอมโพเนนต์ในอาร์เรย์ผลลัพธ์ คุณสามารถใช้Collection.toArray(Object[])แทนได้String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);การเปลี่ยนแปลงการจัดการรหัสภาษา: เมื่อใช้
LocaleAPI ระบบจะไม่แปลงรหัสภาษาสำหรับภาษาฮีบรู ยิดดิช และอินโดนีเซีย เป็นรูปแบบที่ล้าสมัยอีกต่อไป (ฮีบรู:iw, ยิดดิช:jiและอินโดนีเซีย:in) เมื่อระบุรหัสภาษาสำหรับภาษาใดภาษาหนึ่งเหล่านี้ ให้ใช้รหัส จาก ISO 639-1 แทน (ฮีบรู:he, ยิดดิช:yiและอินโดนีเซีย:id)การเปลี่ยนแปลงลำดับ int แบบสุ่ม: ตามการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ทำใน https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574 ตอนนี้เมธอดต่อไปนี้
Random.ints()จะแสดงลำดับตัวเลขที่แตกต่างจากเมธอดRandom.nextInt()โดยทั่วไปแล้ว การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ไม่น่าจะส่งผลให้แอปทำงานผิดปกติ แต่โค้ดของคุณไม่ควรคาดหวังว่าลำดับที่สร้างจากเมธอด
Random.ints()จะตรงกับRandom.nextInt()
API SequencedCollection ใหม่นี้อาจส่งผลต่อความเข้ากันได้ของแอป
หลังจากที่คุณอัปเดต compileSdk ในการกำหนดค่าบิลด์ของแอปเพื่อใช้
Android 15 (API ระดับ 35)
การชนกันกับฟังก์ชันส่วนขยาย
MutableList.removeFirst()และMutableList.removeLast()ในkotlin-stdlibประเภท
Listใน Java จะแมปกับประเภทMutableListใน Kotlin เนื่องจากมีการเปิดตัว APIList.removeFirst()และList.removeLast()ใน Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) คอมไพเลอร์ Kotlin จึงแก้ไขการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน เช่นlist.removeFirst()แบบคงที่ไปยัง APIListใหม่แทนที่จะเป็นฟังก์ชันส่วนขยายในkotlin-stdlibหากมีการคอมไพล์แอปอีกครั้งโดยตั้งค่า
compileSdkเป็น35และตั้งค่าminSdkเป็น34หรือต่ำกว่า จากนั้นเรียกใช้แอปใน Android 14 และต่ำกว่า ระบบจะแสดงข้อผิดพลาดรันไทม์java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;NewApiตัวเลือก lint ที่มีอยู่ในปลั๊กอิน Android Gradle สามารถตรวจพบการใช้ API ใหม่เหล่านี้ได้./gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()หากต้องการแก้ไขข้อยกเว้นรันไทม์และข้อผิดพลาดของ Lint คุณสามารถแทนที่การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
removeFirst()และremoveLast()ด้วยremoveAt(0)และremoveAt(list.lastIndex)ตามลำดับใน Kotlin หากคุณใช้ Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 ขึ้นไป ก็จะมีตัวเลือกการแก้ไขด่วน สำหรับข้อผิดพลาดเหล่านี้ด้วยลองนำ
@SuppressLint("NewApi")และlintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }ออกหากปิดใช้ตัวเลือกการตรวจสอบแล้วการชนกันกับเมธอดอื่นๆ ใน Java
เราได้เพิ่มวิธีการใหม่ๆ ลงในประเภทที่มีอยู่แล้ว เช่น
ListและDequeวิธีการใหม่เหล่านี้อาจใช้ร่วมกับวิธีการที่มีชื่อและประเภทอาร์กิวเมนต์เดียวกันในอินเทอร์เฟซและคลาสอื่นๆ ไม่ได้ ในกรณีที่ลายเซ็นของเมธอดชนกันกับความไม่เข้ากัน คอมไพเลอร์javacจะแสดงข้อผิดพลาดขณะสร้าง เช่นตัวอย่างข้อผิดพลาด 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface Listตัวอย่างข้อผิดพลาด 2
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorตัวอย่างข้อผิดพลาด 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorหากต้องการแก้ไขข้อผิดพลาดในการบิลด์เหล่านี้ คลาสที่ใช้การติดตั้งอินเทอร์เฟซเหล่านี้ควร ลบล้างเมธอดด้วยประเภทการคืนค่าที่เข้ากันได้ เช่น
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
ความปลอดภัย
Android 15 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ส่งเสริมความปลอดภัยของระบบเพื่อช่วยปกป้องแอป และผู้ใช้จากแอปที่เป็นอันตราย
เวอร์ชัน TLS ที่ถูกจำกัด
Android 15 จำกัดการใช้ TLS เวอร์ชัน 1.0 และ 1.1 ก่อนหน้านี้ Android ได้เลิกใช้งานเวอร์ชันเหล่านี้แล้ว แต่ตอนนี้ไม่อนุญาตให้แอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ใช้เวอร์ชันดังกล่าว
เปิดใช้กิจกรรมในเบื้องหลังที่ปลอดภัย
Android 15 ปกป้องผู้ใช้จากแอปที่เป็นอันตรายและช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ควบคุมอุปกรณ์ได้มากขึ้นด้วยการเพิ่มการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ป้องกันไม่ให้แอปที่เป็นอันตรายซึ่งทำงานอยู่เบื้องหลังแสดงแอปอื่นๆ ขึ้นเบื้องหน้า ยกระดับสิทธิ์ และละเมิดการโต้ตอบของผู้ใช้ การเปิดตัวกิจกรรมในเบื้องหลังถูกจำกัดตั้งแต่ Android 10 (API ระดับ 29)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงอื่นๆ
นอกจากข้อจำกัดสำหรับการจับคู่ UID แล้ว การเปลี่ยนแปลงอื่นๆ เหล่านี้ยัง รวม:
- เปลี่ยนครีเอเตอร์
PendingIntentรายให้บล็อกการเปิดตัวกิจกรรมในเบื้องหลังโดย ค่าเริ่มต้น ซึ่งช่วยป้องกันไม่ให้แอปสร้างPendingIntentโดยไม่ได้ตั้งใจ ซึ่งผู้ไม่ประสงค์ดีอาจนำไปใช้ในทางที่ผิดได้ - อย่าดึงแอปมาไว้ที่เบื้องหน้า เว้นแต่ว่า
PendingIntentผู้ส่งจะอนุญาต การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้มีจุดประสงค์เพื่อป้องกันไม่ให้แอปที่เป็นอันตรายละเมิดความสามารถในการเริ่มกิจกรรมในเบื้องหลัง โดยค่าเริ่มต้น แอปไม่ได้รับอนุญาตให้นำกองงานมาไว้ที่เบื้องหน้า เว้นแต่ครีเอเตอร์จะอนุญาตให้มีสิทธิ์เปิดกิจกรรมเบื้องหลัง หรือผู้ส่งมีสิทธิ์เปิดกิจกรรมเบื้องหลัง - ควบคุมวิธีที่กิจกรรมยอดนิยมของสแต็กงานจะทำงานให้เสร็จสิ้น หากกิจกรรมบนสุดทำงานเสร็จแล้ว Android จะกลับไปที่งานที่ใช้งานล่าสุด นอกจากนี้ หากกิจกรรมที่ไม่ใช่กิจกรรมบนสุดทำงานเสร็จแล้ว Android จะกลับไปที่หน้าจอหลัก โดยไม่บล็อกไม่ให้กิจกรรมที่ไม่ใช่กิจกรรมบนสุดนี้ทำงานเสร็จ
- ป้องกันไม่ให้เปิดกิจกรรมที่ไม่ได้รับอนุญาตจากแอปอื่นๆ ไปยังงานของคุณเอง การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะป้องกันแอปที่เป็นอันตรายจากผู้ใช้ฟิชชิงด้วยการสร้าง กิจกรรมที่ดูเหมือนว่ามาจากแอปอื่นๆ
- บล็อกหน้าต่างที่มองไม่เห็นไม่ให้มีการพิจารณาสำหรับกิจกรรมในเบื้องหลัง เปิดตัว วิธีนี้จะช่วยป้องกันไม่ให้แอปที่เป็นอันตรายใช้พื้นหลังในทางที่ผิด เพื่อแสดงเนื้อหาที่ไม่ต้องการหรือเป็นอันตรายแก่ผู้ใช้
Intent ที่ปลอดภัยกว่า
Android 15 introduces new optional security measures to make intents safer and more robust. These changes are aimed at preventing potential vulnerabilities and misuse of intents that can be exploited by malicious apps. There are two main improvements to the security of intents in Android 15:
- Match target intent-filters: Intents that target specific components must accurately match the target's intent-filter specifications. If you send an intent to launch another app's activity, the target intent component needs to align with the receiving activity's declared intent-filters.
- Intents must have actions: Intents without an action will no longer match any intent-filters. This means that intents used to start activities or services must have a clearly defined action.
In order to check how your app responds to these changes, use
StrictMode in your app. To see detailed
logs about Intent usage violations, add the following method:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้และ UI ของระบบ
Android 15 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงบางอย่างที่มุ่งสร้างประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้ที่สอดคล้องกันมากขึ้น และใช้งานง่าย
การเปลี่ยนแปลงส่วนที่เว้นไว้ในหน้าต่าง
การเปลี่ยนแปลงที่เกี่ยวข้องกับส่วนแทรกของหน้าต่างใน Android 15 มี 2 อย่าง ได้แก่ ระบบจะบังคับใช้การแสดงผลแบบเต็มหน้าจอโดยค่าเริ่มต้น และยังมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงการกำหนดค่า เช่น การกําหนดค่าเริ่มต้นของแถบระบบ
Edge-to-edge enforcement
Apps are edge-to-edge by default on devices running Android 15 if the app is targeting Android 15 (API level 35).
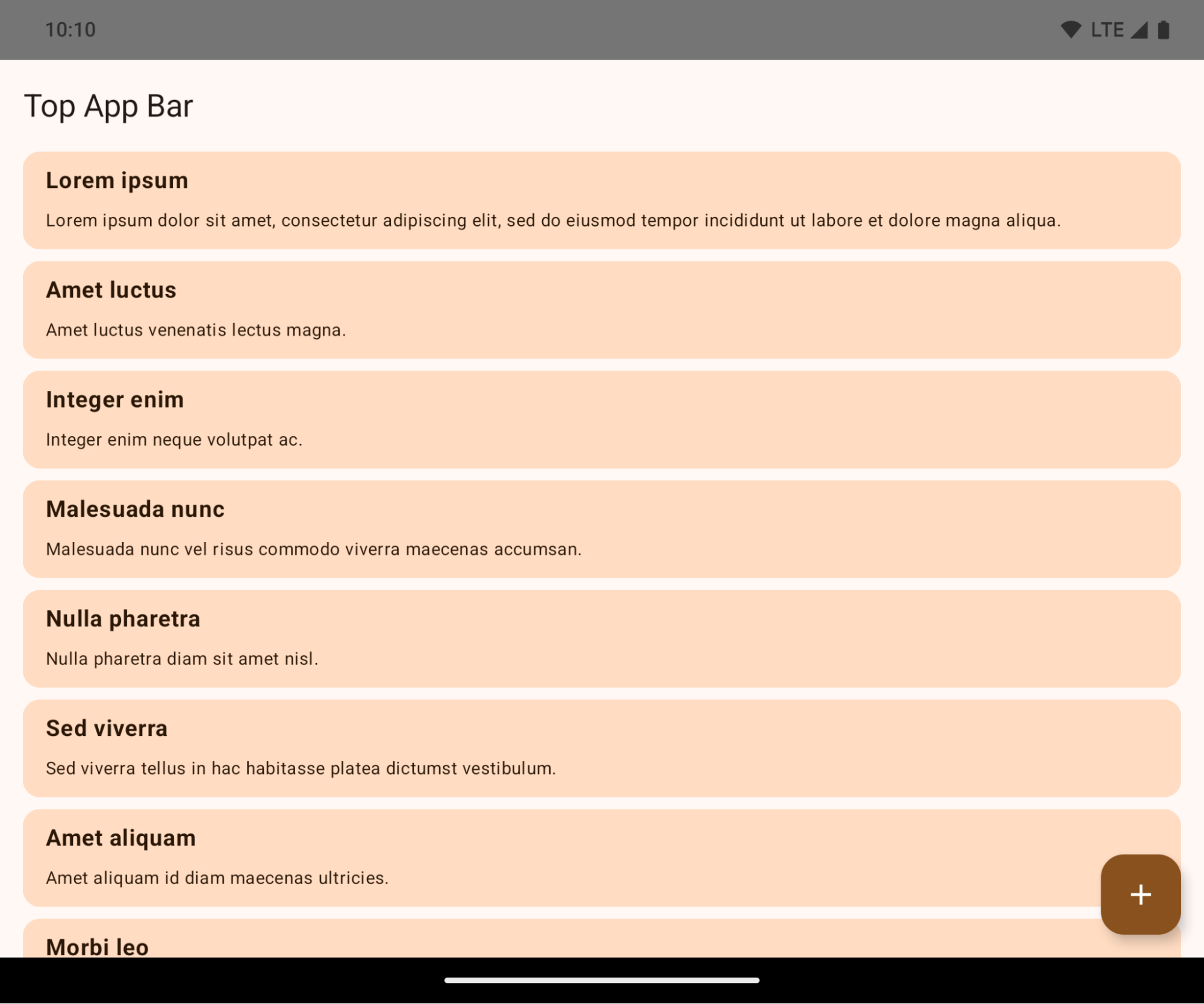
This is a breaking change that might negatively impact your app's UI. The changes affect the following UI areas:
- Gesture handle navigation bar
- Transparent by default.
- Bottom offset is disabled so content draws behind the system navigation bar unless insets are applied.
setNavigationBarColorandR.attr#navigationBarColorare deprecated and don't affect gesture navigation.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedcontinue to have no effect on gesture navigation.
- 3-button navigation
- Opacity set to 80% by default, with color possibly matching the window background.
- Bottom offset disabled so content draws behind the system navigation bar unless insets are applied.
setNavigationBarColorandR.attr#navigationBarColorare set to match the window background by default. The window background must be a color drawable for this default to apply. This API is deprecated but continues to affect 3-button navigation.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedis true by default, which adds an 80% opaque background across 3-button navigation.
- Status bar
- Transparent by default.
- The top offset is disabled so content draws behind the status bar unless insets are applied.
setStatusBarColorandR.attr#statusBarColorare deprecated and have no effect on Android 15.setStatusBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedare deprecated but still have an effect on Android 15.
- Display cutout
layoutInDisplayCutoutModeof non-floating windows must beLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS.SHORT_EDGES,NEVER, andDEFAULTare interpreted asALWAYSso that users don't see a black bar caused by the display cutout and appear edge-to-edge.
The following example shows an app before and after targeting Android 15 (API level 35), and before and after applying insets. This example is not comprehensive, this might appear differently on Android Auto.
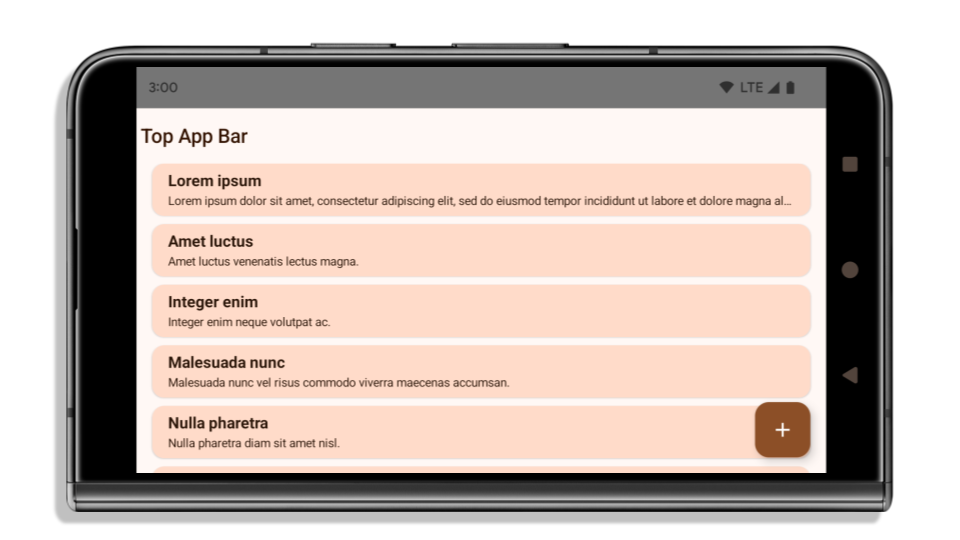

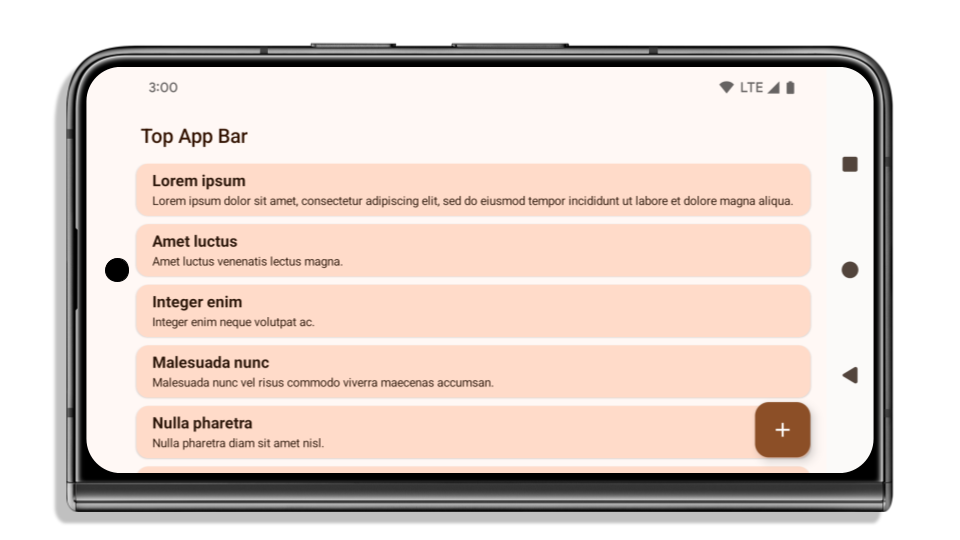
What to check if your app is already edge-to-edge
If your app is already edge-to-edge and applies insets, you are mostly unimpacted, except in the following scenarios. However, even if you think you aren't impacted, we recommend you test your app.
- You have a non-floating window, such as an
Activitythat usesSHORT_EDGES,NEVERorDEFAULTinstead ofLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS. If your app crashes on launch, this might be due to your splashscreen. You can either upgrade the core splashscreen dependency to 1.2.0-alpha01 or later or setwindow.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always. - There might be lower-traffic screens with occluded UI. Verify these
less-visited screens don't have occluded UI. Lower-traffic screens include:
- Onboarding or sign-in screens
- Settings pages
What to check if your app is not already edge-to-edge
If your app is not already edge-to-edge, you are most likely impacted. In addition to the scenarios for apps that are already edge-to-edge, you should consider the following:
- If your app uses Material 3 Components (
androidx.compose.material3) in compose, such asTopAppBar,BottomAppBar, andNavigationBar, these components are likely not impacted because they automatically handle insets. - If your app is using Material 2 Components (
androidx.compose.material) in Compose, these components don't automatically handle insets. However, you can get access to the insets and apply them manually. In androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 and later, use thewindowInsetsparameter to apply the insets manually forBottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigation, andNavigationRail. Likewise, use thecontentWindowInsetsparameter forScaffold. - If your app uses views and Material Components
(
com.google.android.material), most views-based Material Components such asBottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar,NavigationRailView, orNavigationView, handle insets and require no additional work. However, you need to addandroid:fitsSystemWindows="true"if usingAppBarLayout. - For custom composables, apply the insets manually as padding. If your
content is within a
Scaffold, you can consume insets using theScaffoldpadding values. Otherwise, apply padding using one of theWindowInsets. - If your app is using views and
BottomSheet,SideSheetor custom containers, apply padding usingViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener. ForRecyclerView, apply padding using this listener and also addclipToPadding="false".
What to check if your app must offer custom background protection
If your app must offer custom background protection to 3-button navigation or
the status bar, your app should place a composable or view behind the system bar
using WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() to get the 3-button
navigation bar height or WindowInsets.Type#statusBars.
Additional edge-to-edge resources
See the Edge to Edge Views and Edge to Edge Compose guides for additional considerations on applying insets.
Deprecated APIs
The following APIs are deprecated but not disabled:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(for 3 button navigation, with 80% alpha)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(for 3 button navigation, with 80% alpha)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
The following APIs are deprecated and disabled:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(for gesture navigation)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(for gesture navigation)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
Stable configuration
หากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ขึ้นไป Configuration จะไม่
รวมแถบระบบอีกต่อไป หากคุณใช้ขนาดหน้าจอในคลาส Configuration เพื่อคำนวณเลย์เอาต์ คุณควรแทนที่ด้วยตัวเลือกอื่นที่ดีกว่า เช่น ViewGroup, WindowInsets หรือ WindowMetricsCalculator ที่เหมาะสม ทั้งนี้ขึ้นอยู่กับความต้องการของคุณ
Configuration พร้อมใช้งานตั้งแต่ API 1 โดยปกติแล้วจะได้รับจาก
Activity.onConfigurationChanged โดยจะให้ข้อมูล เช่น ความหนาแน่นของหน้าต่าง
การวางแนว และขนาด ลักษณะสำคัญอย่างหนึ่งเกี่ยวกับขนาดหน้าต่างที่ส่งคืนจาก Configuration คือก่อนหน้านี้จะไม่รวมแถบระบบ
โดยปกติแล้ว ขนาดการกำหนดค่าจะใช้สำหรับการเลือกทรัพยากร เช่น
/res/layout-h500dp และนี่ก็ยังคงเป็น Use Case ที่ถูกต้อง อย่างไรก็ตาม เราไม่แนะนำให้ใช้สำหรับ
การคำนวณเลย์เอาต์มาโดยตลอด หากคุณกำลังทำเช่นนั้น คุณควรหยุด
ทำทันที คุณควรแทนที่การใช้ Configuration ด้วยสิ่งอื่นที่เหมาะสมกว่าตามกรณีการใช้งาน
หากใช้เพื่อคำนวณเลย์เอาต์ ให้ใช้ ViewGroup ที่เหมาะสม เช่น
CoordinatorLayout หรือ ConstraintLayout หากคุณใช้เพื่อกำหนดความสูง
ของแถบนำทางของระบบ ให้ใช้ WindowInsets หากต้องการทราบขนาดปัจจุบัน
ของหน้าต่างแอป ให้ใช้ computeCurrentWindowMetrics
รายการต่อไปนี้อธิบายฟิลด์ที่ได้รับผลกระทบจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้
- ขนาด
Configuration.screenWidthDpและscreenHeightDpจะไม่ รวมแถบระบบอีกต่อไป Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpได้รับผลกระทบโดยอ้อมจากการเปลี่ยนแปลง ในscreenWidthDpและscreenHeightDpConfiguration.orientationได้รับผลกระทบโดยอ้อมจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงในscreenWidthDpและscreenHeightDpในอุปกรณ์ที่มีสัดส่วนใกล้เคียงกับสี่เหลี่ยมจัตุรัสDisplay.getSize(Point)ได้รับผลกระทบโดยอ้อมจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงในConfigurationซึ่งเลิกใช้งานแล้วตั้งแต่ API ระดับ 30 เป็นต้นไปDisplay.getMetrics()ทำงานในลักษณะนี้มาตั้งแต่ API ระดับ 33 แล้ว
แอตทริบิวต์ elegantTextHeight จะมีค่าเริ่มต้นเป็น true
For apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35), the
elegantTextHeight TextView attribute
becomes true by default, replacing the compact font used by default with some
scripts that have large vertical metrics with one that is much more readable.
The compact font was introduced to prevent breaking layouts; Android 13 (API
level 33) prevents many of these breakages by allowing the text layout to
stretch the vertical height utilizing the fallbackLineSpacing
attribute.
In Android 15, the compact font still remains in the system, so your app can set
elegantTextHeight to false to get the same behavior as before, but it is
unlikely to be supported in upcoming releases. So, if your app supports the
following scripts: Arabic, Lao, Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam,
Odia, Telugu or Thai, test your app by setting elegantTextHeight to true.
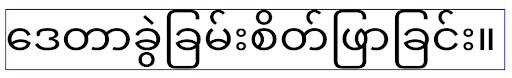
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android 14 (API level 34) and lower.
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android 15.การเปลี่ยนแปลงความกว้างของ TextView สำหรับรูปร่างตัวอักษรที่ซับซ้อน
In previous versions of Android, some cursive fonts or languages that have
complex shaping might draw the letters in the previous or next character's area.
In some cases, such letters were clipped at the beginning or ending position.
Starting in Android 15, a TextView allocates width for drawing enough space
for such letters and allows apps to request extra paddings to the left to
prevent clipping.
Because this change affects how a TextView decides the width, TextView
allocates more width by default if the app targets Android 15 (API level 35) or
higher. You can enable or disable this behavior by calling the
setUseBoundsForWidth API on TextView.
Because adding left padding might cause a misalignment for existing layouts, the
padding is not added by default even for apps that target Android 15 or higher.
However, you can add extra padding to preventing clipping by calling
setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang.
The following examples show how these changes can improve text layout for some fonts and languages.

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
ความสูงของบรรทัดเริ่มต้นที่รับรู้ภาษาสำหรับ EditText
ใน Android เวอร์ชันก่อนหน้า เลย์เอาต์ข้อความจะยืดความสูงของข้อความให้เท่ากับความสูงของบรรทัดแบบอักษรที่ตรงกับภาษาปัจจุบัน เช่น หากเนื้อหาเป็นภาษาญี่ปุ่น ความสูงของบรรทัดของแบบอักษรญี่ปุ่นจะสูงกว่าแบบอักษรละตินเล็กน้อย ความสูงของข้อความจึงเพิ่มขึ้นเล็กน้อย อย่างไรก็ตาม แม้ความสูงของบรรทัดจะแตกต่างกัน แต่องค์ประกอบ EditText ก็มีการปรับขนาดให้เหมือนกัน โดยไม่คำนึงถึงภาษาที่ใช้ ดังที่แสดงในภาพต่อไปนี้

EditText ซึ่งอาจมีข้อความจากภาษาอังกฤษ (en), ญี่ปุ่น (ja) และพม่า (my) ความสูงของ EditText เหมือนกัน แม้ว่าภาษาเหล่านี้จะมีความสูงของบรรทัดต่างกันสำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ระบบจะสงวนความสูงบรรทัดขั้นต่ำไว้สำหรับ EditText เพื่อให้ตรงกับแบบอักษรอ้างอิงสำหรับภาษาที่ระบุ ดังที่แสดงในภาพต่อไปนี้

EditText ซึ่งอาจมีข้อความจากภาษาอังกฤษ (en), ญี่ปุ่น (ja) และพม่า (my) ตอนนี้ความสูงของ EditText จะรวมช่องว่างไว้เพื่อรองรับความสูงของบรรทัดเริ่มต้นสำหรับแบบอักษรของภาษาเหล่านี้หากจําเป็น แอปจะกู้คืนลักษณะการทํางานก่อนหน้าได้โดยระบุแอตทริบิวต์ useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum เป็น false และแอปจะตั้งค่าเมตริกแนวตั้งขั้นต่ำที่กําหนดเองได้โดยใช้ setMinimumFontMetrics API ใน Kotlin และ Java
กล้องและสื่อ
Android 15 จะทำการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานของกล้องและสื่อสำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ขึ้นไปดังนี้
ข้อจำกัดในการขอโฟกัสเสียง
แอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ต้องเป็นแอปที่ทำงานอยู่ด้านบนหรือกำลังใช้บริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าเพื่อขอโฟกัสเสียง หากแอปพยายามขอโฟกัสเมื่อไม่เป็นไปตามข้อกำหนดข้อใดข้อหนึ่งเหล่านี้ การเรียกใช้จะแสดงผลเป็น AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับโหมดโฟกัสเสียงได้ที่จัดการโหมดโฟกัสเสียง
ข้อจำกัดที่ไม่ใช่ SDK ที่อัปเดตแล้ว
Android 15 มีรายการอินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK ที่ถูกจำกัดซึ่งอัปเดตแล้วโดยอิงตามการทำงานร่วมกับนักพัฒนาแอป Android และการทดสอบภายในล่าสุด เราจะตรวจสอบว่ามีทางเลือกสาธารณะ พร้อมใช้งานก่อนที่จะจำกัดอินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK ทุกครั้งที่ทำได้
หากแอปไม่ได้กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 การเปลี่ยนแปลงบางอย่างเหล่านี้ อาจไม่มีผลกับคุณในทันที อย่างไรก็ตาม แม้ว่าแอปของคุณจะ เข้าถึงอินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK บางรายการได้ ขึ้นอยู่กับระดับ API เป้าหมายของแอป แต่การใช้วิธีการหรือฟิลด์ที่ไม่ใช่ SDK ใดๆ ก็ตามมีความเสี่ยงสูงที่จะทำให้แอปของคุณใช้งานไม่ได้
หากไม่แน่ใจว่าแอปใช้อินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK หรือไม่ คุณสามารถทดสอบแอปเพื่อดูได้ หากแอปของคุณใช้ อินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK คุณควรเริ่มวางแผนการย้ายข้อมูลไปยังทางเลือกอื่นของ SDK อย่างไรก็ตาม เราเข้าใจว่าแอปบางแอปมี Use Case ที่ถูกต้องสำหรับการใช้อินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK หากไม่พบวิธีอื่นในการใช้อินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK สำหรับฟีเจอร์ในแอป คุณควรขอ API สาธารณะใหม่
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการเปลี่ยนแปลงใน Android เวอร์ชันนี้ได้ที่การอัปเดตข้อจำกัดของอินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK ใน Android 15 ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับอินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK โดยทั่วไปได้ที่ข้อจำกัดเกี่ยวกับอินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK

