Al igual que las versiones anteriores, Android 15 incluye cambios de comportamiento que podrían afectar tu app. Los siguientes cambios se aplican exclusivamente a las apps orientadas a Android 15 o versiones posteriores. Si tu app está segmentada para Android 15 o versiones posteriores, debes modificarla para que admita estos comportamientos correctamente, cuando corresponda.
Asegúrate de revisar también la lista de cambios en el comportamiento que afectan a todas las apps que se ejecutan en Android 15, independientemente de targetSdkVersion de tu app.
Funcionalidad principal
Android 15 modifica o expande varias capacidades principales del sistema Android.
Cambios en los servicios en primer plano
We are making the following changes to foreground services with Android 15.
- Data sync foreground service timeout behavior
- New media processing foreground service type
- Restrictions on
BOOT_COMPLETEDbroadcast receivers launching foreground services - Restrictions on starting foreground services while an app holds the
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOWpermission
Data sync foreground service timeout behavior
Android 15 introduces a new timeout behavior to dataSync for apps targeting
Android 15 (API level 35) or higher. This behavior also applies to the new
mediaProcessing foreground service type.
The system permits an app's dataSync services to run for a total of 6 hours
in a 24-hour period, after which the system calls the running service's
Service.onTimeout(int, int) method (introduced in Android
15). At this time, the service has a few seconds to call
Service.stopSelf(). When Service.onTimeout() is called, the
service is no longer considered a foreground service. If the service does not
call Service.stopSelf(), the system throws an internal exception. The
exception is logged in Logcat with the following message:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
To avoid problems with this behavior change, you can do one or more of the following:
- Have your service implement the new
Service.onTimeout(int, int)method. When your app receives the callback, make sure to callstopSelf()within a few seconds. (If you don't stop the app right away, the system generates a failure.) - Make sure your app's
dataSyncservices don't run for more than a total of 6 hours in any 24-hour period (unless the user interacts with the app, resetting the timer). - Only start
dataSyncforeground services as a result of direct user interaction; since your app is in the foreground when the service starts, your service has the full six hours after the app goes to the background. - Instead of using a
dataSyncforeground service, use an alternative API.
If your app's dataSync foreground services have run for 6 hours in the last
24, you cannot start another dataSync foreground service unless the user
has brought your app to the foreground (which resets the timer). If you try to
start another dataSync foreground service, the system throws
ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
with an error message like "Time limit already exhausted for foreground service
type dataSync".
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable data sync timeouts even if your app
is not targeting Android 15 (as long as the app is running on an Android 15
device). To enable timeouts, run the following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
You can also adjust the timeout period, to make it easier to test how your
app behaves when the limit is reached. To set a new timeout period, run the
following adb command:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
New media processing foreground service type
Android 15 presenta un nuevo tipo de servicio en primer plano: mediaProcessing. Este tipo de servicio es adecuado para operaciones como la transcodificación de archivos multimedia. Por ejemplo, una app de música puede descargar un archivo de audio y necesitar convertirlo a un formato diferente antes de reproducirlo. Puedes usar un servicio en primer plano mediaProcessing para asegurarte de que la conversión continúe incluso mientras la app está en segundo plano.
El sistema permite que los servicios mediaProcessing de una app se ejecuten durante un total de 6 horas en un período de 24 horas, después del cual el sistema llama al método Service.onTimeout(int, int) del servicio en ejecución (presentado en Android 15). En este momento, el servicio tiene unos segundos para llamar a Service.stopSelf(). Si el servicio no llama a Service.stopSelf(), el sistema arroja una excepción interna. La excepción se registra en Logcat con el siguiente mensaje:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
Para evitar tener la excepción, puedes realizar una de las siguientes acciones:
- Haz que tu servicio implemente el nuevo método
Service.onTimeout(int, int). Cuando tu app reciba la devolución de llamada, asegúrate de llamar astopSelf()en unos pocos segundos. (Si no detienes la app de inmediato, el sistema genera una falla). - Asegúrate de que los servicios
mediaProcessingde tu app no se ejecuten durante más de un total de 6 horas en cualquier período de 24 horas (a menos que el usuario interactúe con la app y restablezca el temporizador). - Inicia servicios en primer plano de
mediaProcessingsolo como resultado de la interacción directa del usuario. Como tu app está en primer plano cuando se inicia el servicio, este tiene las seis horas completas después de que la app pasa a segundo plano. - En lugar de usar un servicio en primer plano de
mediaProcessing, usa una API alternativa, como WorkManager.
Si los servicios en primer plano de mediaProcessing de tu app se ejecutaron durante 6 horas durante las últimas 24, no puedes iniciar otro servicio mediaProcessing en primer plano, a menos que el usuario haya llevado la app al primer plano (lo que restablece el temporizador). Si intentas iniciar otro servicio en primer plano mediaProcessing, el sistema arroja ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException con un mensaje de error como "Se agotó el tiempo límite para el tipo de servicio en primer plano mediaProcessing".
Para obtener más información sobre el tipo de servicio mediaProcessing, consulta Cambios en los tipos de servicios en primer plano para Android 15: Procesamiento de contenido multimedia.
Prueba
Para probar el comportamiento de tu app, puedes habilitar los tiempos de espera de procesamiento de contenido multimedia, incluso si tu app no está orientada a Android 15 (siempre que se ejecute en un dispositivo con Android 15). Para habilitar los tiempos de espera, ejecuta el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
También puedes ajustar el tiempo de espera para facilitar la prueba del comportamiento de tu app cuando se alcanza el límite. Para establecer un nuevo tiempo de espera, ejecuta el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Restrictions on BOOT_COMPLETED broadcast receivers launching foreground services
Hay nuevas restricciones para los receptores de emisión de BOOT_COMPLETED que se lanzan
servicios en primer plano. Los receptores BOOT_COMPLETED no pueden iniciar los siguientes tipos de servicios en primer plano:
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(esta restricción se aplicó pormicrophonedesde el Android 14)
Si un receptor BOOT_COMPLETED intenta iniciar cualquiera de esos tipos de primer plano.
servicios, el sistema arroja una ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
Prueba
Para probar el comportamiento de tu app, puedes habilitar estas nuevas restricciones, incluso si tu app no está segmentada para Android 15 (siempre que la app se ejecute en un dispositivo con Android 15). Ejecuta el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Para enviar una transmisión de BOOT_COMPLETED sin reiniciar el dispositivo, haz lo siguiente:
Ejecuta el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
Restrictions on starting foreground services while an app holds the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission
Anteriormente, si una app tenía el permiso SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW, podía iniciar un servicio en primer plano, incluso si la app estaba en segundo plano (como se explica en exenciones de las restricciones de inicio en segundo plano).
Si una app está orientada a Android 15, esta exención ahora es más limitada. Ahora, la app debe tener el permiso SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW y también tener una ventana superpuesta visible. Es decir, la app primero debe iniciar una ventana TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY y la ventana debe ser visible antes de iniciar un servicio en primer plano.
Si tu app intenta iniciar un servicio en primer plano desde segundo plano sin cumplir con estos nuevos requisitos (y no tiene otra exención), el sistema arroja ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
Si tu app declara el permiso SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW y, luego, inicia servicios en primer plano desde el segundo plano, es posible que se vea afectada por este cambio. Si tu app obtiene una ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException, verifica el orden de operaciones de tu app y asegúrate de que ya tenga una ventana de superposición activa antes de intentar iniciar un servicio en primer plano desde el segundo plano. Puedes verificar si tu ventana de superposición es visible actualmente llamando a View.getWindowVisibility() o puedes anular View.onWindowVisibilityChanged() para recibir notificaciones cada vez que cambie la visibilidad.
Prueba
Para probar el comportamiento de tu app, puedes habilitar estas nuevas restricciones, incluso si tu app no está segmentada para Android 15 (siempre que la app se ejecute en un dispositivo con Android 15). Para habilitar estas nuevas restricciones para iniciar servicios en primer plano desde segundo plano, ejecuta el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Cambios en el momento en que las apps pueden modificar el estado global del modo No interrumpir
Las apps que se orientan a Android 15 (nivel de API 35) y versiones posteriores ya no pueden cambiar el estado o la política globales de No interrumpir (ND) en un dispositivo (ya sea modificando la configuración del usuario o desactivando el modo ND). En su lugar, las apps deben contribuir con un AutomaticZenRule, que el sistema combina en una política global con el esquema existente de política más restrictiva. Las llamadas a las APIs existentes que antes afectaban el estado global (setInterruptionFilter, setNotificationPolicy) generan la creación o actualización de un AutomaticZenRule implícito, que se activa o desactiva según el ciclo de llamadas de esas llamadas a la API.
Ten en cuenta que este cambio solo afecta el comportamiento observable si la app llama a setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) y espera que esa llamada desactive un AutomaticZenRule que sus propietarios activaron anteriormente.
Cambios en la API de OpenJDK
Android 15 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases.
Some of these changes can affect app compatibility for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35):
Changes to string formatting APIs: Validation of argument index, flags, width, and precision are now more strict when using the following
String.format()andFormatter.format()APIs:String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
For example, the following exception is thrown when an argument index of 0 is used (
%0in the format string):IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0In this case, the issue can be fixed by using an argument index of 1 (
%1in the format string).Changes to component type of
Arrays.asList(...).toArray(): When usingArrays.asList(...).toArray(), the component type of the resulting array is now anObject—not the type of the underlying array's elements. So the following code throws aClassCastException:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();For this case, to preserve
Stringas the component type in the resulting array, you could useCollection.toArray(Object[])instead:String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);Changes to language code handling: When using the
LocaleAPI, language codes for Hebrew, Yiddish, and Indonesian are no longer converted to their obsolete forms (Hebrew:iw, Yiddish:ji, and Indonesian:in). When specifying the language code for one of these locales, use the codes from ISO 639-1 instead (Hebrew:he, Yiddish:yi, and Indonesian:id).Changes to random int sequences: Following the changes made in https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574, the following
Random.ints()methods now return a different sequence of numbers than theRandom.nextInt()methods do:Generally, this change shouldn't result in app-breaking behavior, but your code shouldn't expect the sequence generated from
Random.ints()methods to matchRandom.nextInt().
The new SequencedCollection API can affect your app's compatibility
after you update compileSdk in your app's build configuration to use
Android 15 (API level 35):
Collision with
MutableList.removeFirst()andMutableList.removeLast()extension functions inkotlin-stdlibThe
Listtype in Java is mapped to theMutableListtype in Kotlin. Because theList.removeFirst()andList.removeLast()APIs have been introduced in Android 15 (API level 35), the Kotlin compiler resolves function calls, for examplelist.removeFirst(), statically to the newListAPIs instead of to the extension functions inkotlin-stdlib.If an app is re-compiled with
compileSdkset to35andminSdkset to34or lower, and then the app is run on Android 14 and lower, a runtime error is thrown:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;The existing
NewApilint option in Android Gradle Plugin can catch these new API usages../gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()To fix the runtime exception and lint errors, the
removeFirst()andremoveLast()function calls can be replaced withremoveAt(0)andremoveAt(list.lastIndex)respectively in Kotlin. If you're using Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 or higher, it also provides a quick fix option for these errors.Consider removing
@SuppressLint("NewApi")andlintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }if the lint option has been disabled.Collision with other methods in Java
New methods have been added into the existing types, for example,
ListandDeque. These new methods might not be compatible with the methods with the same name and argument types in other interfaces and classes. In the case of a method signature collision with incompatibility, thejavaccompiler outputs a build-time error. For example:Example error 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface ListExample error 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorExample error 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorTo fix these build errors, the class implementing these interfaces should override the method with a compatible return type. For example:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
Seguridad
Android 15 incluye cambios que promueven la seguridad del sistema para ayudar a proteger las apps y a los usuarios de las apps maliciosas.
Versiones de TLS restringidas
Android 15 restringe el uso de las versiones 1.0 y 1.1 de TLS. Estas versiones ya habían dejado de estar disponibles en Android, pero ahora no se permiten para las apps que se orientan a Android 15.
Inicio seguro de actividades en segundo plano
Android 15 protege a los usuarios de apps maliciosas y les da más control sobre sus dispositivos agregando cambios que eviten que las apps llevar otras apps al primer plano, elevar sus privilegios y fomentar el abuso la interacción del usuario. Los inicios de actividades en segundo plano se restringieron desde Android 10 (nivel de API 29).
Otros cambios
Además de la restricción para la coincidencia de UID, estos otros cambios también se incluidos:
- Cambia los creadores de
PendingIntentpara que bloqueen los inicios de actividades en segundo plano de forma predeterminada. Esto ayuda a evitar que las apps creen accidentalmente unPendingIntentque personas malintencionadas podrían aprovechar. - No lleves una app al primer plano, a menos que el remitente de
PendingIntentlo permita. El objetivo de este cambio es evitar que las apps maliciosas abusen de la capacidad de iniciar actividades en segundo plano. De forma predeterminada, las apps no pueden llevar la pila de actividades al primer plano, a menos que el creador permita privilegios de inicio de actividad en segundo plano o que el remitente tenga privilegios de inicio de actividad en segundo plano. - Controla cómo la actividad principal de una pila de tareas puede finalizar su tarea. Si el botón una actividad principal finaliza una tarea, Android regresará a la tarea que se haya la última vez que estuvo activo. Además, si una actividad que no es de primer nivel finaliza su tarea, Android volverá a la pantalla principal y no bloqueará el final de esta actividad que no es de primer nivel.
- Evita iniciar actividades arbitrarias de otras apps en la tuya tarea. Este cambio evita que las apps maliciosas creen ataques de phishing a través de la creación actividades que parecen ser de otras aplicaciones.
- Bloquea las ventanas no visibles para que no se consideren en los inicios de la actividad en segundo plano. Esto ayuda a evitar que las apps maliciosas abusen de los inicios de actividad en segundo plano para mostrar contenido no deseado o malicioso a los usuarios.
Intents más seguros
Android 15 introduces new optional security measures to make intents safer and more robust. These changes are aimed at preventing potential vulnerabilities and misuse of intents that can be exploited by malicious apps. There are two main improvements to the security of intents in Android 15:
- Match target intent-filters: Intents that target specific components must accurately match the target's intent-filter specifications. If you send an intent to launch another app's activity, the target intent component needs to align with the receiving activity's declared intent-filters.
- Intents must have actions: Intents without an action will no longer match any intent-filters. This means that intents used to start activities or services must have a clearly defined action.
In order to check how your app responds to these changes, use
StrictMode in your app. To see detailed
logs about Intent usage violations, add the following method:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
Experiencia del usuario y la IU del sistema
Android 15 incluye algunos cambios que tienen como objetivo crear una experiencia del usuario más coherente e intuitiva.
Cambios en la inserción de ventana
Hay dos cambios relacionados con los insertos de ventana en Android 15: el modo de pantalla completa se aplica de forma predeterminada y también hay cambios de configuración, como la configuración predeterminada de las barras del sistema.
Edge-to-edge enforcement
Apps are edge-to-edge by default on devices running Android 15 if the app is targeting Android 15 (API level 35).
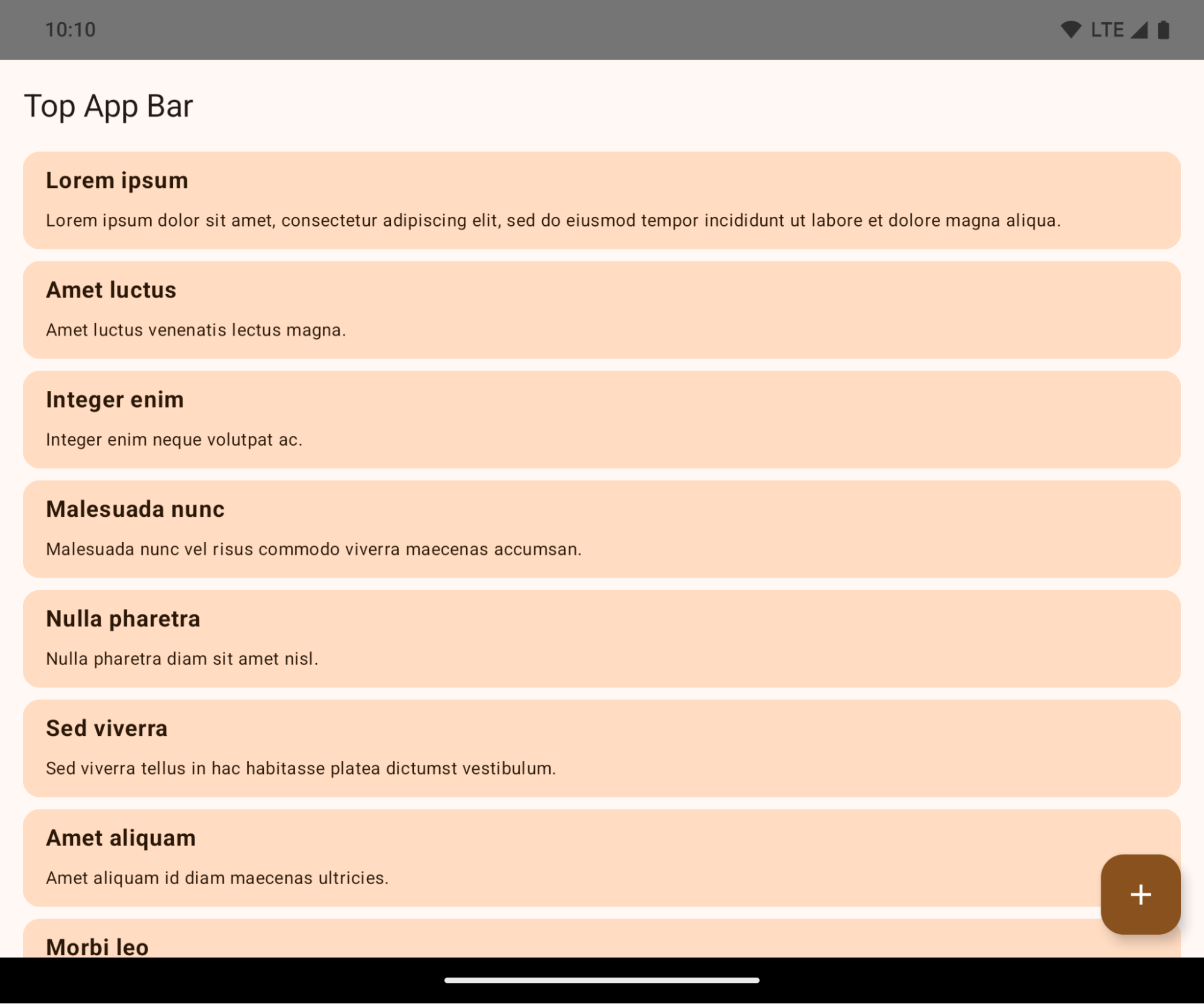
This is a breaking change that might negatively impact your app's UI. The changes affect the following UI areas:
- Gesture handle navigation bar
- Transparent by default.
- Bottom offset is disabled so content draws behind the system navigation bar unless insets are applied.
setNavigationBarColorandR.attr#navigationBarColorare deprecated and don't affect gesture navigation.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedcontinue to have no effect on gesture navigation.
- 3-button navigation
- Opacity set to 80% by default, with color possibly matching the window background.
- Bottom offset disabled so content draws behind the system navigation bar unless insets are applied.
setNavigationBarColorandR.attr#navigationBarColorare set to match the window background by default. The window background must be a color drawable for this default to apply. This API is deprecated but continues to affect 3-button navigation.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedis true by default, which adds an 80% opaque background across 3-button navigation.
- Status bar
- Transparent by default.
- The top offset is disabled so content draws behind the status bar unless insets are applied.
setStatusBarColorandR.attr#statusBarColorare deprecated and have no effect on Android 15.setStatusBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedare deprecated but still have an effect on Android 15.
- Display cutout
layoutInDisplayCutoutModeof non-floating windows must beLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS.SHORT_EDGES,NEVER, andDEFAULTare interpreted asALWAYSso that users don't see a black bar caused by the display cutout and appear edge-to-edge.
The following example shows an app before and after targeting Android 15 (API level 35), and before and after applying insets. This example is not comprehensive, this might appear differently on Android Auto.
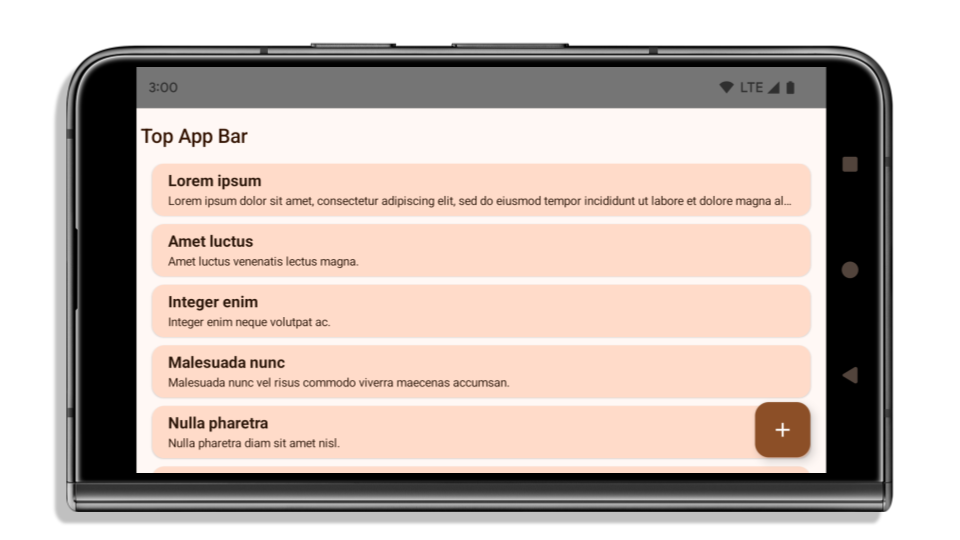

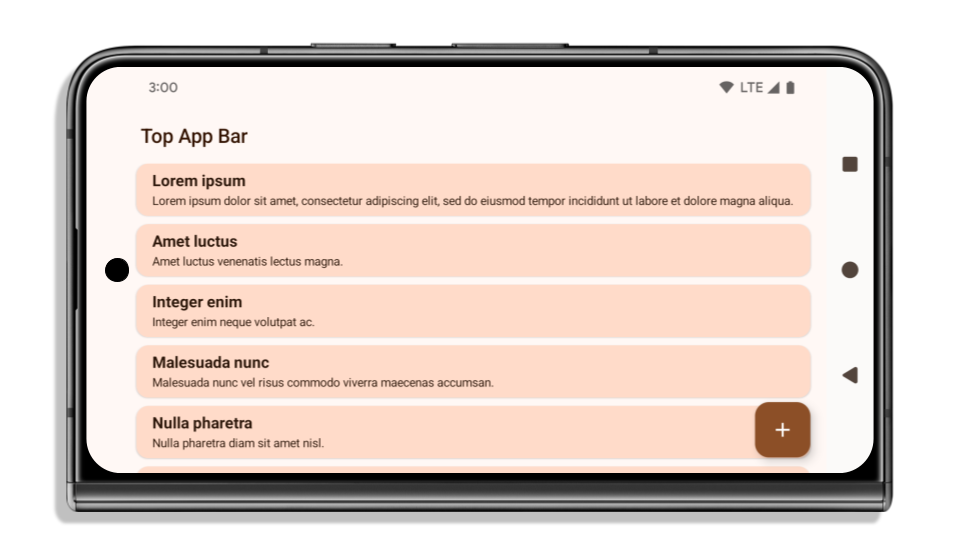
What to check if your app is already edge-to-edge
If your app is already edge-to-edge and applies insets, you are mostly unimpacted, except in the following scenarios. However, even if you think you aren't impacted, we recommend you test your app.
- You have a non-floating window, such as an
Activitythat usesSHORT_EDGES,NEVERorDEFAULTinstead ofLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS. If your app crashes on launch, this might be due to your splashscreen. You can either upgrade the core splashscreen dependency to 1.2.0-alpha01 or later or setwindow.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always. - There might be lower-traffic screens with occluded UI. Verify these
less-visited screens don't have occluded UI. Lower-traffic screens include:
- Onboarding or sign-in screens
- Settings pages
What to check if your app is not already edge-to-edge
If your app is not already edge-to-edge, you are most likely impacted. In addition to the scenarios for apps that are already edge-to-edge, you should consider the following:
- If your app uses Material 3 Components (
androidx.compose.material3) in compose, such asTopAppBar,BottomAppBar, andNavigationBar, these components are likely not impacted because they automatically handle insets. - If your app is using Material 2 Components (
androidx.compose.material) in Compose, these components don't automatically handle insets. However, you can get access to the insets and apply them manually. In androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 and later, use thewindowInsetsparameter to apply the insets manually forBottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigation, andNavigationRail. Likewise, use thecontentWindowInsetsparameter forScaffold. - If your app uses views and Material Components
(
com.google.android.material), most views-based Material Components such asBottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar,NavigationRailView, orNavigationView, handle insets and require no additional work. However, you need to addandroid:fitsSystemWindows="true"if usingAppBarLayout. - For custom composables, apply the insets manually as padding. If your
content is within a
Scaffold, you can consume insets using theScaffoldpadding values. Otherwise, apply padding using one of theWindowInsets. - If your app is using views and
BottomSheet,SideSheetor custom containers, apply padding usingViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener. ForRecyclerView, apply padding using this listener and also addclipToPadding="false".
What to check if your app must offer custom background protection
If your app must offer custom background protection to 3-button navigation or
the status bar, your app should place a composable or view behind the system bar
using WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() to get the 3-button
navigation bar height or WindowInsets.Type#statusBars.
Additional edge-to-edge resources
See the Edge to Edge Views and Edge to Edge Compose guides for additional considerations on applying insets.
Deprecated APIs
The following APIs are deprecated but not disabled:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(for 3 button navigation, with 80% alpha)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(for 3 button navigation, with 80% alpha)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
The following APIs are deprecated and disabled:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(for gesture navigation)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(for gesture navigation)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
Stable configuration
Si tu app se segmenta para Android 15 (nivel de API 35) o versiones posteriores, Configuration ya no excluye las barras del sistema. Si usas el tamaño de pantalla en la clase Configuration para el cálculo del diseño, debes reemplazarlo por mejores alternativas, como un ViewGroup, WindowInsets o WindowMetricsCalculator apropiado, según tus necesidades.
Configuration está disponible desde la API nivel 1. Por lo general, se obtiene de Activity.onConfigurationChanged. Proporciona información como la densidad, la orientación y los tamaños de las ventanas. Una característica importante sobre los tamaños de ventana que devuelve Configuration es que antes excluía las barras del sistema.
El tamaño de la configuración se suele usar para la selección de recursos, como /res/layout-h500dp, y este sigue siendo un caso de uso válido. Sin embargo, siempre se desaconsejó usarlo para el cálculo del diseño. Si es así, debes alejarte de él ahora. Debes reemplazar el uso de Configuration por algo más adecuado según tu caso de uso.
Si lo usas para calcular el diseño, usa un ViewGroup adecuado, como CoordinatorLayout o ConstraintLayout. Si lo usas para determinar la altura de la barra de navegación del sistema, usa WindowInsets. Si quieres conocer el tamaño actual de la ventana de tu app, usa computeCurrentWindowMetrics.
En la siguiente lista, se describen los campos afectados por este cambio:
- Los tamaños
Configuration.screenWidthDpyscreenHeightDpya no excluyen las barras del sistema. Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpse ve afectado indirectamente por los cambios enscreenWidthDpyscreenHeightDp.Configuration.orientationse ve afectado indirectamente por los cambios enscreenWidthDpyscreenHeightDpen dispositivos casi cuadrados.Display.getSize(Point)se ve afectado indirectamente por los cambios enConfiguration. Este método dejó de estar disponible a partir del nivel de API 30.Display.getMetrics()ya funciona de esta manera desde el nivel de API 33.
El atributo elegantTextHeight tiene el valor predeterminado establecido en verdadero.
For apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35), the
elegantTextHeight TextView attribute
becomes true by default, replacing the compact font used by default with some
scripts that have large vertical metrics with one that is much more readable.
The compact font was introduced to prevent breaking layouts; Android 13 (API
level 33) prevents many of these breakages by allowing the text layout to
stretch the vertical height utilizing the fallbackLineSpacing
attribute.
In Android 15, the compact font still remains in the system, so your app can set
elegantTextHeight to false to get the same behavior as before, but it is
unlikely to be supported in upcoming releases. So, if your app supports the
following scripts: Arabic, Lao, Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam,
Odia, Telugu or Thai, test your app by setting elegantTextHeight to true.
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android 14 (API level 34) and lower.
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android 15.El ancho de TextView cambia para formas de letras complejas
En versiones anteriores de Android, algunas fuentes o idiomas en cursiva que tienen formas complejas podrían dibujar las letras en el área del carácter anterior o siguiente.
En algunos casos, esas letras se cortaron al principio o al final.
A partir de Android 15, un TextView asigna ancho para dibujar suficiente espacio para esas letras y permite que las apps soliciten paddings adicionales a la izquierda para evitar los recortes.
Como este cambio afecta la forma en que un TextView decide el ancho, TextView asigna más ancho de forma predeterminada si la app se orienta a Android 15 (nivel de API 35) o versiones posteriores. Para habilitar o inhabilitar este comportamiento, llama a la API de setUseBoundsForWidth en TextView.
Como agregar padding izquierdo puede causar un desajuste en los diseños existentes, el padding no se agrega de forma predeterminada, incluso en el caso de las apps orientadas a Android 15 o versiones posteriores.
Sin embargo, puedes agregar padding adicional para evitar el recorte llamando a setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang.
En los siguientes ejemplos, se muestra cómo estos cambios pueden mejorar el diseño de texto para algunas fuentes y algunos idiomas.

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
Altura de línea predeterminada compatible con la configuración regional para EditText
In previous versions of Android, the text layout stretched the height of the
text to meet the line height of the font that matched the current locale. For
example, if the content was in Japanese, because the line height of the Japanese
font is slightly larger than the one of a Latin font, the height of the text
became slightly larger. However, despite these differences in line heights, the
EditText element was sized uniformly, regardless
of the locale being used, as illustrated in the following image:

EditText elements that
can contain text from English (en), Japanese (ja), and Burmese (my). The
height of the EditText is the same, even though these languages
have different line heights from each other.For apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35), a minimum line height is now
reserved for EditText to match the reference font for the specified Locale, as
shown in the following image:

EditText elements that
can contain text from English (en), Japanese (ja), and Burmese (my). The
height of the EditText now includes space to accommodate the
default line height for these languages' fonts.If needed, your app can restore the previous behavior by specifying the
useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum attribute
to false, and your app can set custom minimum vertical metrics using the
setMinimumFontMetrics API in Kotlin and Java.
Cámara y contenido multimedia
Android 15 realiza los siguientes cambios en el comportamiento de la cámara y los medios para las apps que se segmentan para Android 15 o versiones posteriores.
Restricciones para solicitar el foco de audio
Apps that target Android 15 (API level 35) must be the top app or running a
foreground service in order to request audio focus. If an app
attempts to request focus when it does not meet one of these requirements, the
call returns AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED.
You can learn more about audio focus at Manage audio focus.
Actualización de restricciones que no pertenecen al SDK
Android 15 incluye listas actualizadas de este tipo de interfaces que están basadas en la colaboración con desarrolladores de Android y las pruebas internas más recientes. Siempre que sea posible, nos aseguramos de que las alternativas públicas estén disponibles antes de restringir las interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK.
Si tu app no está segmentada para Android 15, es posible que algunos de estos cambios no te afecten de inmediato. Sin embargo, si bien tu app puede acceder a algunas interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK según el nivel de API objetivo de tu app, usar cualquier método o campo que no pertenezca al SDK siempre implica un gran riesgo de error para tu app.
Si no sabes con seguridad si tu app usa este tipo de interfaces, puedes probarla para verificarlo. Si tu app depende de interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK, deberías planificar una migración hacia otras alternativas SDK. Sin embargo, sabemos que algunas apps tienen casos de uso válidos para usar interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK. Si no encuentras una alternativa al uso de una interfaz que no pertenece al SDK para una función de tu app, deberías solicitar una nueva API pública.
Para obtener más información sobre los cambios implementados en esta versión de Android, consulta Actualizaciones a las restricciones de interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK en Android 15. Para obtener más información sobre interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK en general, consulta Restricciones en interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK.

