Al igual que las versiones anteriores, Android 15 incluye cambios de comportamiento que podrían afectar tu app. Los siguientes cambios se aplican exclusivamente a las apps orientadas a Android 15 o versiones posteriores. Si tu app está segmentada para Android 15 o versiones posteriores, debes modificarla para que admita estos comportamientos correctamente, cuando corresponda.
Asegúrate de revisar también la lista de cambios en el comportamiento que afectan a todas las apps que se ejecutan en Android 15, independientemente de targetSdkVersion de tu app.
Funcionalidad principal
Android 15 modifica o expande varias capacidades principales del sistema Android.
Cambios en los servicios en primer plano
Realizaremos los siguientes cambios en los servicios en primer plano con Android 15.
- Comportamiento de tiempo de espera del servicio en primer plano de sincronización de datos
- Nuevo tipo de servicio en primer plano de procesamiento de contenido multimedia
- Restricciones para los receptores de emisión
BOOT_COMPLETEDque inician servicios en primer plano - Restricciones para iniciar servicios en primer plano mientras una app tiene el permiso
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
Comportamiento del tiempo de espera del servicio en primer plano de sincronización de datos
Android 15 presenta un nuevo comportamiento de tiempo de espera para dataSync en el caso de las apps que se orientan a Android 15 (nivel de API 35) o versiones posteriores. Este comportamiento también se aplica al nuevo tipo de servicio en primer plano mediaProcessing.
El sistema permite que los servicios dataSync de una app se ejecuten durante un total de 6 horas en un período de 24 horas, después de lo cual el sistema llama al método Service.onTimeout(int, int) del servicio en ejecución (presentado en Android 15). En este momento, el servicio tiene unos segundos para llamar a Service.stopSelf(). Cuando se llama a Service.onTimeout(), el servicio ya no se considera un servicio en primer plano. Si el servicio no llama a Service.stopSelf(), el sistema arroja una excepción interna. La excepción se registra en Logcat con el siguiente mensaje:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
Para evitar problemas con este cambio de comportamiento, puedes realizar una o más de las siguientes acciones:
- Haz que tu servicio implemente el nuevo método
Service.onTimeout(int, int). Cuando tu app reciba la devolución de llamada, asegúrate de llamar astopSelf()en unos pocos segundos. (Si no detienes la app de inmediato, el sistema genera una falla). - Asegúrate de que los servicios
dataSyncde tu app no se ejecuten durante más de un total de 6 horas en cualquier período de 24 horas (a menos que el usuario interactúe con la app y restablezca el temporizador). - Inicia servicios en primer plano de
dataSyncsolo como resultado de la interacción directa del usuario. Como tu app está en primer plano cuando se inicia el servicio, este tiene las seis horas completas después de que la app pasa a segundo plano. - En lugar de usar un servicio en primer plano de
dataSync, usa una API alternativa.
Si los servicios en primer plano dataSync de tu app se ejecutaron durante 6 horas en las últimas 24, no puedes iniciar otro servicio en primer plano dataSync a menos que el usuario haya llevado tu app al primer plano (lo que restablece el temporizador). Si intentas iniciar otro servicio en primer plano dataSync, el sistema arrojará una ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException con un mensaje de error como "El límite de tiempo ya se agotó para el tipo de servicio en primer plano dataSync".
Prueba
Para probar el comportamiento de tu app, puedes habilitar los tiempos de espera de sincronización de datos, incluso si tu app no se orienta a Android 15 (siempre que la app se ejecute en un dispositivo Android 15). Para habilitar los tiempos de espera, ejecuta el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
También puedes ajustar el tiempo de espera para facilitar la prueba del comportamiento de tu app cuando se alcanza el límite. Para establecer un nuevo período de tiempo de espera, ejecuta el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Nuevo tipo de servicio en primer plano de procesamiento de contenido multimedia
Android 15 presenta un nuevo tipo de servicio en primer plano: mediaProcessing. Este tipo de servicio es adecuado para operaciones como la transcodificación de archivos multimedia. Por ejemplo, una app de música puede descargar un archivo de audio y necesitar convertirlo a un formato diferente antes de reproducirlo. Puedes usar un servicio en primer plano mediaProcessing para asegurarte de que la conversión continúe incluso mientras la app está en segundo plano.
El sistema permite que los servicios mediaProcessing de una app se ejecuten durante un total de 6 horas en un período de 24 horas, después del cual el sistema llama al método Service.onTimeout(int, int) del servicio en ejecución (presentado en Android 15). En este momento, el servicio tiene unos segundos para llamar a Service.stopSelf(). Si el servicio no llama a Service.stopSelf(), el sistema arroja una excepción interna. La excepción se registra en Logcat con el siguiente mensaje:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
Para evitar tener la excepción, puedes realizar una de las siguientes acciones:
- Haz que tu servicio implemente el nuevo método
Service.onTimeout(int, int). Cuando tu app reciba la devolución de llamada, asegúrate de llamar astopSelf()en unos pocos segundos. (Si no detienes la app de inmediato, el sistema genera una falla). - Asegúrate de que los servicios
mediaProcessingde tu app no se ejecuten durante más de un total de 6 horas en cualquier período de 24 horas (a menos que el usuario interactúe con la app y restablezca el temporizador). - Inicia servicios en primer plano de
mediaProcessingsolo como resultado de la interacción directa del usuario. Como tu app está en primer plano cuando se inicia el servicio, este tiene las seis horas completas después de que la app pasa a segundo plano. - En lugar de usar un servicio en primer plano de
mediaProcessing, usa una API alternativa, como WorkManager.
Si los servicios en primer plano de mediaProcessing de tu app se ejecutaron durante 6 horas durante las últimas 24, no puedes iniciar otro servicio mediaProcessing en primer plano, a menos que el usuario haya llevado la app al primer plano (lo que restablece el temporizador). Si intentas iniciar otro servicio en primer plano mediaProcessing, el sistema arroja ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException con un mensaje de error como "Se agotó el tiempo límite para el tipo de servicio en primer plano mediaProcessing".
Para obtener más información sobre el tipo de servicio mediaProcessing, consulta Cambios en los tipos de servicios en primer plano para Android 15: Procesamiento de contenido multimedia.
Prueba
Para probar el comportamiento de tu app, puedes habilitar los tiempos de espera de procesamiento de contenido multimedia, incluso si tu app no está orientada a Android 15 (siempre que se ejecute en un dispositivo con Android 15). Para habilitar los tiempos de espera, ejecuta el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
También puedes ajustar el tiempo de espera para facilitar la prueba del comportamiento de tu app cuando se alcanza el límite. Para establecer un nuevo tiempo de espera, ejecuta el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Restricciones para los receptores de emisión BOOT_COMPLETED que inician servicios en primer plano
Hay nuevas restricciones para los receptores de emisión de BOOT_COMPLETED que se lanzan
servicios en primer plano. Los receptores BOOT_COMPLETED no pueden iniciar los siguientes tipos de servicios en primer plano:
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(esta restricción se aplicó pormicrophonedesde el Android 14)
Si un receptor BOOT_COMPLETED intenta iniciar cualquiera de esos tipos de primer plano.
servicios, el sistema arroja una ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
Prueba
Para probar el comportamiento de tu app, puedes habilitar estas nuevas restricciones, incluso si tu app no está segmentada para Android 15 (siempre que la app se ejecute en un dispositivo con Android 15). Ejecuta el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Para enviar una transmisión de BOOT_COMPLETED sin reiniciar el dispositivo, haz lo siguiente:
Ejecuta el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
Restricciones para iniciar servicios en primer plano mientras una app tiene el permiso SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
Anteriormente, si una app tenía el permiso SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW, podía iniciar un servicio en primer plano, incluso si la app estaba en segundo plano (como se explica en exenciones de las restricciones de inicio en segundo plano).
Si una app está orientada a Android 15, esta exención ahora es más limitada. Ahora, la app debe tener el permiso SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW y también tener una ventana superpuesta visible. Es decir, la app primero debe iniciar una ventana TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY y la ventana debe ser visible antes de iniciar un servicio en primer plano.
Si tu app intenta iniciar un servicio en primer plano desde segundo plano sin cumplir con estos nuevos requisitos (y no tiene otra exención), el sistema arroja ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
Si tu app declara el permiso SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW y, luego, inicia servicios en primer plano desde el segundo plano, es posible que se vea afectada por este cambio. Si tu app obtiene una ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException, verifica el orden de operaciones de tu app y asegúrate de que ya tenga una ventana de superposición activa antes de intentar iniciar un servicio en primer plano desde el segundo plano. Puedes verificar si tu ventana de superposición es visible actualmente llamando a View.getWindowVisibility() o puedes anular View.onWindowVisibilityChanged() para recibir notificaciones cada vez que cambie la visibilidad.
Prueba
Para probar el comportamiento de tu app, puedes habilitar estas nuevas restricciones, incluso si tu app no está segmentada para Android 15 (siempre que la app se ejecute en un dispositivo con Android 15). Para habilitar estas nuevas restricciones para iniciar servicios en primer plano desde segundo plano, ejecuta el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Cambios en el momento en que las apps pueden modificar el estado global del modo No interrumpir
Las apps que se orientan a Android 15 (nivel de API 35) y versiones posteriores ya no pueden cambiar el estado o la política globales de No interrumpir (ND) en un dispositivo (ya sea modificando la configuración del usuario o desactivando el modo ND). En su lugar, las apps deben contribuir con un AutomaticZenRule, que el sistema combina en una política global con el esquema existente de política más restrictiva. Las llamadas a las APIs existentes que antes afectaban el estado global (setInterruptionFilter, setNotificationPolicy) generan la creación o actualización de un AutomaticZenRule implícito, que se activa o desactiva según el ciclo de llamadas de esas llamadas a la API.
Ten en cuenta que este cambio solo afecta el comportamiento observable si la app llama a setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) y espera que esa llamada desactive un AutomaticZenRule que sus propietarios activaron anteriormente.
Cambios en la API de OpenJDK
Android 15 continúa la tarea de actualizar las bibliotecas principales de Android para alinearlas con las funciones de las versiones más recientes de LTS de OpenJDK.
Algunos de estos cambios pueden afectar la compatibilidad de las apps que segmentan Android 15 (nivel de API 35):
Cambios en las APIs de formato de cadenas: La validación del índice de argumentos, las marcas, el ancho y la precisión ahora son más estrictos cuando se usan las siguientes APIs de
String.format()yFormatter.format():String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
Por ejemplo, se arroja la siguiente excepción cuando se usa un índice de argumento de 0 (
%0en la cadena de formato):IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0En este caso, el problema se puede solucionar usando un índice de argumento de 1 (
%1en la cadena de formato).Cambios en el tipo de componente de
Arrays.asList(...).toArray(): Cuando se usaArrays.asList(...).toArray(), el tipo de componente del array resultante ahora esObject, no el tipo de los elementos del array subyacente. Por lo tanto, el siguiente código arroja unClassCastException:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();En este caso, para conservar
Stringcomo el tipo de componente en el array resultante, puedes usarCollection.toArray(Object[])en su lugar:String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);Cambios en el manejo de códigos de idioma: Cuando se usa la API de
Locale, los códigos de idioma para hebreo, yidis e indonesio ya no se convierten a sus formas obsoletas (hebreo:iw, yidis:jie indonesio:in). Cuando especifiques el código de idioma para una de estas configuraciones regionales, usa los códigos de ISO 639-1 (hebreo:he, yidis:yie indonesio:id).Cambios en las secuencias de números enteros aleatorios: Después de los cambios realizados en https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574, los siguientes métodos
Random.ints()ahora devuelven una secuencia de números diferente a la que devuelven los métodosRandom.nextInt():En general, este cambio no debería generar un comportamiento que interrumpa la app, pero tu código no debería esperar que la secuencia generada a partir de los métodos
Random.ints()coincida conRandom.nextInt().
La nueva API de SequencedCollection puede afectar la compatibilidad de tu app después de que actualices compileSdk en la configuración de compilación de tu app para usar Android 15 (nivel de API 35):
Colisión con las funciones de extensión
MutableList.removeFirst()yMutableList.removeLast()enkotlin-stdlibEl tipo
Listen Java se asigna al tipoMutableListen Kotlin. Debido a que las APIs deList.removeFirst()yList.removeLast()se introdujeron en Android 15 (nivel de API 35), el compilador de Kotlin resuelve las llamadas a funciones, por ejemplo,list.removeFirst(), de forma estática a las nuevas APIs deListen lugar de a las funciones de extensión enkotlin-stdlib.Si una app se vuelve a compilar con
compileSdkestablecido en35yminSdkestablecido en34o una versión inferior, y luego se ejecuta en Android 14 y versiones anteriores, se arroja un error de tiempo de ejecución:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;La opción
NewApilint existente en el complemento de Android para Gradle puede detectar estos nuevos usos de la API../gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()Para corregir la excepción en tiempo de ejecución y los errores de lint, las llamadas a las funciones
removeFirst()yremoveLast()se pueden reemplazar porremoveAt(0)yremoveAt(list.lastIndex), respectivamente, en Kotlin. Si usas Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 o una versión posterior, también se proporciona una opción de corrección rápida para estos errores.Considera quitar
@SuppressLint("NewApi")ylintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }si se inhabilitó la opción de lint.Colisión con otros métodos en Java
Se agregaron métodos nuevos a los tipos existentes, por ejemplo,
ListyDeque. Es posible que estos métodos nuevos no sean compatibles con los métodos que tienen el mismo nombre y los mismos tipos de argumentos en otras interfaces y clases. En el caso de una colisión de firma de método con incompatibilidad, el compiladorjavacgenera un error en el tiempo de compilación. Por ejemplo:Ejemplo de error 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface ListEjemplo de error 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorEjemplo de error 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorPara corregir estos errores de compilación, la clase que implementa estas interfaces debe anular el método con un tipo de devolución compatible. Por ejemplo:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
Seguridad
Android 15 incluye cambios que promueven la seguridad del sistema para ayudar a proteger las apps y los usuarios de las apps maliciosas.
Versiones de TLS restringidas
Android 15 restringe el uso de las versiones 1.0 y 1.1 de TLS. Estas versiones ya habían dejado de estar disponibles en Android, pero ahora no se permiten para las apps que se orientan a Android 15.
Inicio seguro de actividades en segundo plano
Android 15 protege a los usuarios de las apps maliciosas y les brinda más control sobre sus dispositivos, ya que agrega cambios que impiden que las apps maliciosas en segundo plano lleven otras apps al primer plano, eleven sus privilegios y abusen de la interacción del usuario. Los inicios de actividad en segundo plano están restringidos desde Android 10 (nivel de API 29).
Otros cambios
- Cambia los creadores de
PendingIntentpara bloquear los inicios de actividad en segundo plano de forma predeterminada. Esto ayuda a evitar que las apps creen accidentalmente un objetoPendingIntentque podría ser utilizado de forma abusiva por agentes maliciosos. - No pases una app al primer plano, a menos que el remitente
PendingIntentlo permita. El objetivo de este cambio es evitar que las apps maliciosas abusen de la capacidad de iniciar actividades en segundo plano. De forma predeterminada, las apps no pueden llevar la pila de tareas a primer plano, a menos que el creador permita privilegios de inicio de actividad en segundo plano o el remitente tenga privilegios de inicio de actividad en segundo plano. - Controla cómo la actividad superior de una pila de tareas puede finalizar su tarea. Si la actividad superior finaliza una tarea, Android volverá a la tarea que estuvo activa por última vez. Además, si una actividad que no está en primer plano finaliza su tarea, Android volverá a la pantalla principal y no bloqueará la finalización de esta actividad que no está en primer plano.
- Evita iniciar actividades arbitrarias desde otras apps en tu propia tarea. Este cambio evita que las apps maliciosas realicen phishing a los usuarios creando actividades que parecen ser de otras apps.
- Bloquea las ventanas no visibles para que no se consideren para los inicios de actividad en segundo plano. Esto ayuda a evitar que las apps maliciosas abusen de los inicios de actividad en segundo plano para mostrar contenido no deseado o malicioso a los usuarios.
Intents más seguros
Android 15 introduces StrictMode for
intents.
In order to see detailed logs about Intent usage violations, use following
method:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
Experiencia del usuario y la IU del sistema
Android 15 incluye algunos cambios que tienen como objetivo crear una experiencia del usuario más coherente e intuitiva.
Cambios en la inserción de ventana
Hay dos cambios relacionados con los insertos de ventana en Android 15: el modo de pantalla completa se aplica de forma predeterminada y también hay cambios de configuración, como la configuración predeterminada de las barras del sistema.
Aplicación de borde a borde
Las apps son de borde a borde de forma predeterminada en los dispositivos que ejecutan Android 15 si la app se orienta a Android 15 (nivel de API 35).
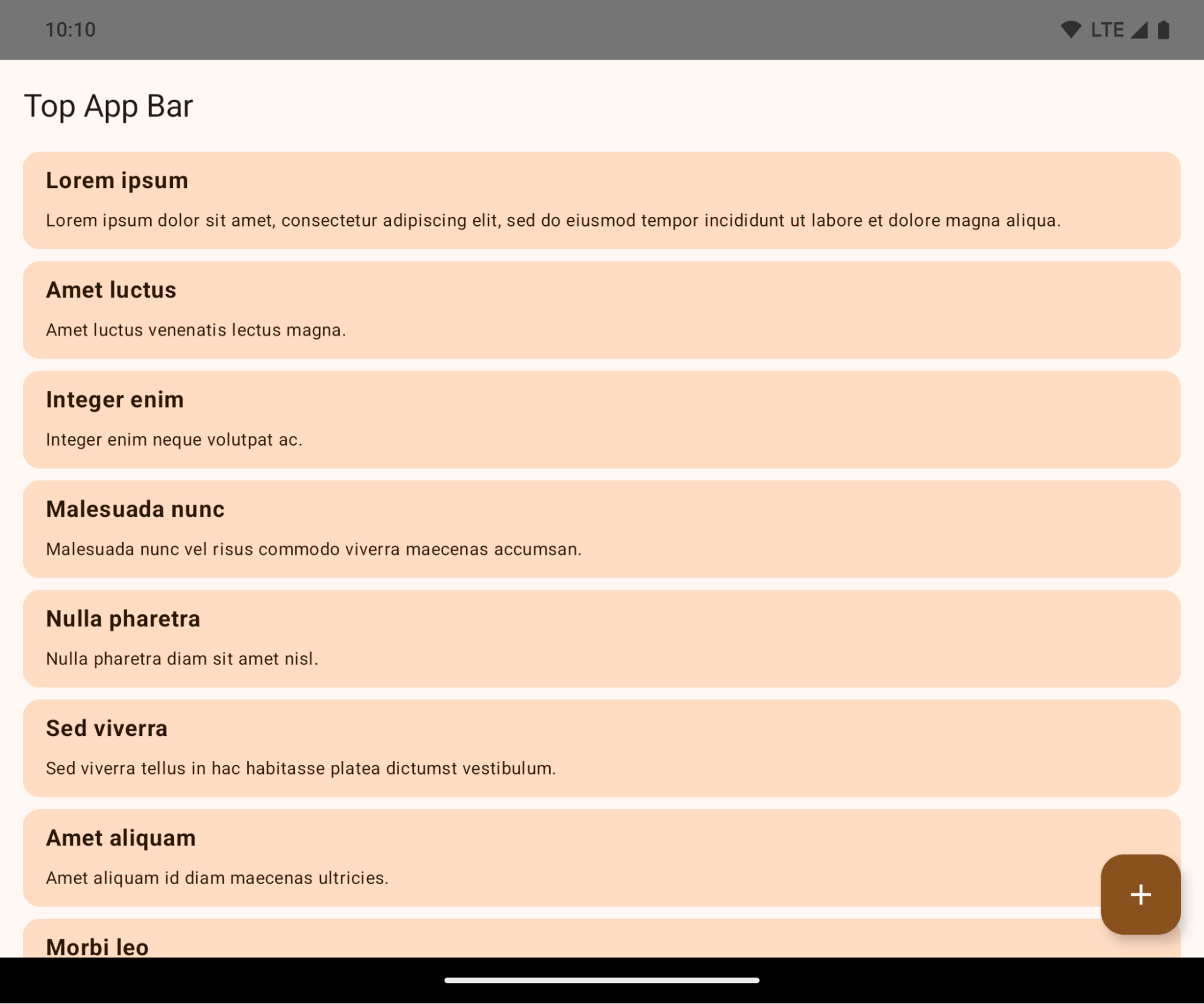
Este es un cambio rotundo que podría afectar negativamente la IU de tu app. Los cambios afectan las siguientes áreas de la IU:
- Barra de navegación con controlador de gestos
- Es transparente de forma predeterminada.
- El desplazamiento inferior está inhabilitado, por lo que el contenido se dibuja detrás de la barra de navegación del sistema, a menos que se apliquen inserciones.
setNavigationBarColoryR.attr#navigationBarColorestán obsoletos y no afectan la navegación por gestos.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedyR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedsiguen sin tener efecto en la navegación por gestos.
- Navegación con 3 botones
- La opacidad se establece en un 80% de forma predeterminada, y el color puede coincidir con el fondo de la ventana.
- Se inhabilitó el desplazamiento inferior para que el contenido se dibuje detrás de la barra de navegación del sistema, a menos que se apliquen inserciones.
setNavigationBarColoryR.attr#navigationBarColorse configuran para que coincidan con el fondo de la ventana de forma predeterminada. El fondo de la ventana debe ser un color de diseño para que se aplique este valor predeterminado. Esta API está obsoleta, pero sigue afectando la navegación con 3 botones.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedyR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedson verdaderos de forma predeterminada, lo que agrega un segundo plano opaco en un 80% en la navegación con 3 botones.
- Barra de estado
- Es transparente de forma predeterminada.
- El desplazamiento superior está inhabilitado, por lo que el contenido se dibuja detrás de la barra de estado, a menos que se apliquen inserciones.
setStatusBarColoryR.attr#statusBarColorestán en desuso y no tienen ningún efecto en Android 15.setStatusBarContrastEnforcedyR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedse dieron de baja, pero aún tienen efecto en Android 15.
- Corte de pantalla
- El
layoutInDisplayCutoutModede las ventanas no flotantes debe serLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS.SHORT_EDGES,NEVERyDEFAULTse interpretan comoALWAYSpara que los usuarios no vean una barra negra causada por el corte de pantalla y aparezcan de borde a borde.
- El
En el siguiente ejemplo, se muestra una app antes y después de segmentar Android 15 (nivel de API 35), y antes y después de aplicar las inserciones. Este ejemplo no es exhaustivo y puede aparecer de manera diferente en Android Auto.
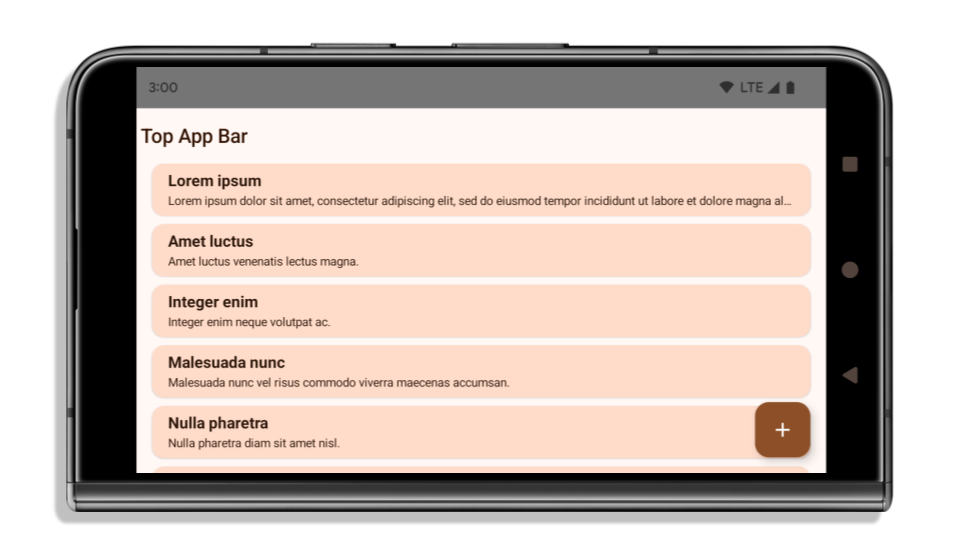

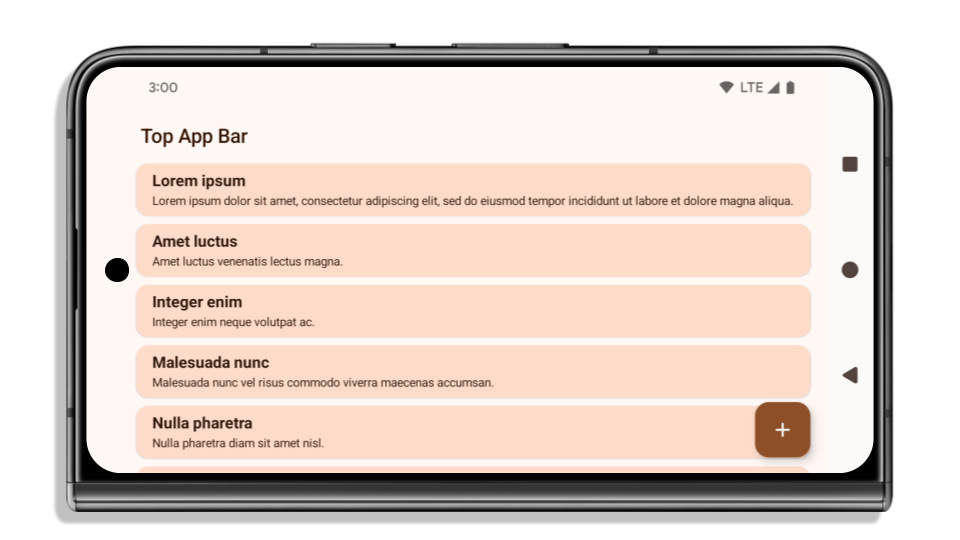
Qué verificar si tu app ya es de borde a borde
Si tu app ya es de borde a borde y aplica inserciones, no se verá afectada en la mayoría de los casos, excepto en las siguientes situaciones. Sin embargo, incluso si crees que no te afecta, te recomendamos que pruebes tu app.
- Tienes una ventana no flotante, como un
Activityque usaSHORT_EDGES,NEVERoDEFAULTen lugar deLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS. Si tu app falla al iniciarse, es posible que se deba a la pantalla de presentación. Puedes actualizar la dependencia de pantalla de presentación principal a 1.2.0-alpha01 o una versión posterior, o bien establecerwindow.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always. - Es posible que haya pantallas con menos tráfico y una IU obstruida. Verifica que estas pantallas menos visitadas no tengan IU obstruida. Las pantallas con menos tráfico incluyen las siguientes:
- Pantallas de acceso o incorporación
- Páginas de configuración
Qué debes verificar si tu app aún no es de borde a borde
Si tu app aún no es de borde a borde, es muy probable que te veas afectado. Además de las situaciones para las apps que ya son de borde a borde, debes tener en cuenta lo siguiente:
- Si tu app usa componentes de Material 3 (
androidx.compose.material3) en Compose, comoTopAppBar,BottomAppBaryNavigationBar, es probable que estos componentes no se vean afectados porque controlan las inserciones automáticamente. - Si tu app usa componentes de Material 2 (
androidx.compose.material) en Compose, estos componentes no controlan las inserciones automáticamente. Sin embargo, puedes obtener acceso a las inserciones y aplicarlas manualmente. En androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 y versiones posteriores, usa el parámetrowindowInsetspara aplicar las inserciones de forma manual paraBottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigationyNavigationRail. De la misma manera, usa el parámetrocontentWindowInsetsparaScaffold. - Si tu app usa vistas y componentes de Material (
com.google.android.material), la mayoría de los componentes de Material basados en vistas, comoBottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar,NavigationRailViewoNavigationView, controlan las inserciones y no requieren trabajo adicional. Sin embargo, debes agregarandroid:fitsSystemWindows="true"si usasAppBarLayout. - En el caso de los elementos componibles personalizados, aplica las inserciones de forma manual como relleno. Si tu contenido se encuentra dentro de un
Scaffold, puedes consumir las inserciones con los valores de paddingScaffold. De lo contrario, aplica padding con uno de losWindowInsets. - Si tu app usa vistas y
BottomSheet,SideSheeto contenedores personalizados, aplica relleno conViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener. ParaRecyclerView, aplica relleno con este objeto de escucha y también agregaclipToPadding="false".
Qué debes verificar si tu app debe ofrecer protección en segundo plano personalizada
Si tu app debe ofrecer protección de fondo personalizada para la navegación con 3 botones o la barra de estado, debe colocar un elemento componible o una vista detrás de la barra del sistema con WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() para obtener la altura de la barra de navegación con 3 botones o WindowInsets.Type#statusBars.
Recursos adicionales de borde a borde
Consulta las guías de Vistas de borde a borde y Edge to Edge Compose para obtener más información sobre cómo aplicar inserciones.
APIs obsoletas
Las siguientes APIs dejaron de estar disponibles, pero no se inhabilitaron:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(para la navegación con 3 botones, con un 80% de alfa)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(para la navegación con 3 botones, con un 80% de alfa)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
Las siguientes APIs están obsoletas y se inhabilitaron:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(para la navegación por gestos)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(para la navegación por gestos)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
Configuración estable
Si tu app se segmenta para Android 15 (nivel de API 35) o versiones posteriores, Configuration ya no excluye las barras del sistema. Si usas el tamaño de pantalla en la clase Configuration para el cálculo del diseño, debes reemplazarlo por mejores alternativas, como un ViewGroup, WindowInsets o WindowMetricsCalculator apropiado según tus necesidades.
Configuration está disponible desde la API 1. Por lo general, se obtiene de Activity.onConfigurationChanged. Proporciona información como la densidad, la orientación y los tamaños de las ventanas. Una característica importante sobre los tamaños de ventana que devuelve Configuration es que antes excluía las barras del sistema.
El tamaño de la configuración se suele usar para la selección de recursos, como /res/layout-h500dp, y este sigue siendo un caso de uso válido. Sin embargo, siempre se desaconsejó usarlo para el cálculo del diseño. Si es así, debes alejarte de él ahora. Debes reemplazar el uso de Configuration por algo más adecuado según tu caso de uso.
Si lo usas para calcular el diseño, usa un ViewGroup adecuado, como CoordinatorLayout o ConstraintLayout. Si lo usas para determinar la altura de la barra de navegación del sistema, usa WindowInsets. Si quieres conocer el tamaño actual de la ventana de tu app, usa computeCurrentWindowMetrics.
En la siguiente lista, se describen los campos afectados por este cambio:
- Los tamaños
Configuration.screenWidthDpyscreenHeightDpya no excluyen las barras del sistema. Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpse ve afectado indirectamente por los cambios enscreenWidthDpyscreenHeightDp.Configuration.orientationse ve afectado indirectamente por los cambios enscreenWidthDpyscreenHeightDpen dispositivos casi cuadrados.Display.getSize(Point)se ve afectado indirectamente por los cambios enConfiguration. Este método dejó de estar disponible a partir del nivel de API 30.Display.getMetrics()ya funciona de esta manera desde el nivel de API 33.
El atributo elegantTextHeight tiene el valor predeterminado establecido en verdadero.
En el caso de las apps orientadas a Android 15 (nivel de API 35), el atributo elegantTextHeight TextView se convierte en true de forma predeterminada, lo que reemplaza la fuente compacta que se usa de forma predeterminada con algunas secuencias de comandos que tienen métricas verticales grandes por una que es mucho más legible.
La fuente compacta se introdujo para evitar que se rompan los diseños. Android 13 (nivel de API 33) evita muchos de estos daños, ya que permite que el diseño de texto estire la altura vertical con el atributo fallbackLineSpacing.
En Android 15, la fuente compacta aún permanece en el sistema, por lo que tu app puede establecer elegantTextHeight en false para obtener el mismo comportamiento que antes, pero es probable que no sea compatible con las próximas versiones. Por lo tanto, si tu app admite las siguientes secuencias de comandos: árabe, lao, birmano, tamil, guyaratí, canarés, malabar, odía, telugu o tailandés, configura elegantTextHeight como true para probarla.
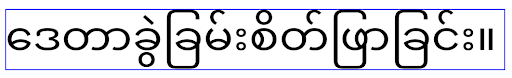
elegantTextHeight para apps orientadas a Android 14 (nivel de API 34) y versiones anteriores.
elegantTextHeight para apps orientadas a Android 15.El ancho de TextView cambia para formas de letras complejas
En versiones anteriores de Android, algunas fuentes o idiomas en cursiva que tienen formas complejas podrían dibujar las letras en el área del carácter anterior o siguiente.
En algunos casos, esas letras se cortaron al principio o al final.
A partir de Android 15, un TextView asigna ancho para dibujar suficiente espacio para esas letras y permite que las apps soliciten paddings adicionales a la izquierda para evitar los recortes.
Como este cambio afecta la forma en que un TextView decide el ancho, TextView asigna más ancho de forma predeterminada si la app se orienta a Android 15 (nivel de API 35) o versiones posteriores. Para habilitar o inhabilitar este comportamiento, llama a la API de setUseBoundsForWidth en TextView.
Como agregar padding izquierdo puede causar un desajuste en los diseños existentes, el padding no se agrega de forma predeterminada, incluso en el caso de las apps orientadas a Android 15 o versiones posteriores.
Sin embargo, puedes agregar padding adicional para evitar el recorte llamando a setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang.
En los siguientes ejemplos, se muestra cómo estos cambios pueden mejorar el diseño de texto para algunas fuentes y algunos idiomas.

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
Altura de línea predeterminada compatible con la configuración regional para EditText
En versiones anteriores de Android, el diseño de texto estiraba la altura del texto para que coincida con la altura de línea de la fuente que coincidía con la configuración regional actual. Por ejemplo, si el contenido estaba en japonés, la altura de la línea de la fuente japonesa es ligeramente mayor que la de una fuente latina, por lo que la altura del texto se hizo un poco más grande. Sin embargo, a pesar de estas diferencias en las alturas de las líneas, el elemento EditText tenía un tamaño uniforme, independientemente de la configuración regional que se usara, como se ilustra en la siguiente imagen:

EditText que pueden contener texto en inglés (en), japonés (ja) y birmano (my). La altura de EditText es la misma, a pesar de que estos lenguajes tienen alturas de línea diferentes entre sí.En el caso de las apps que se orientan a Android 15 (nivel de API 35), ahora se reserva una altura de línea mínima para EditText para que coincida con la fuente de referencia de la configuración regional especificada, como se muestra en la siguiente imagen:

EditText que pueden contener texto en inglés (en), japonés (ja) y birmano (my). La altura de EditText ahora incluye espacio para adaptarse a la altura de línea predeterminada de las fuentes de estos idiomas.Si es necesario, tu app puede restablecer el comportamiento anterior especificando el atributo useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum en false, y puede establecer métricas verticales mínimas personalizadas con la API de setMinimumFontMetrics en Kotlin y Java.
Cámara y contenido multimedia
Android 15 realiza los siguientes cambios en el comportamiento de la cámara y los medios para las apps que se segmentan para Android 15 o versiones posteriores.
Restricciones para solicitar el foco de audio
Las apps que se orientan a Android 15 (nivel de API 35) deben ser la app principal o ejecutar un servicio en primer plano para solicitar el enfoque de audio. Si una app intenta solicitar el enfoque cuando no cumple con uno de estos requisitos, la llamada muestra AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED.
Puedes obtener más información sobre el enfoque de audio en Administra el enfoque de audio.
Actualización de restricciones que no pertenecen al SDK
Android 15 incluye listas actualizadas de este tipo de interfaces que están basadas en la colaboración con desarrolladores de Android y las pruebas internas más recientes. Siempre que sea posible, nos aseguramos de que las alternativas públicas estén disponibles antes de restringir las interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK.
Si tu app no está segmentada para Android 15, es posible que algunos de estos cambios no te afecten de inmediato. Sin embargo, aunque tu app puede acceder a algunas interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK según el nivel de API objetivo de tu app, usar cualquier método o campo que no pertenezca al SDK siempre implica un gran riesgo de error para tu app.
Si no sabes con seguridad si tu app usa este tipo de interfaces, puedes probarla para verificar. Si tu app depende de interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK, deberías planificar una migración hacia otras alternativas SDK. Sin embargo, sabemos que algunas apps tienen casos de uso válidos para usar interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK. Si no encuentras una alternativa al uso de una interfaz que no pertenece al SDK para una función de tu app, deberías solicitar una nueva API pública.
Para obtener más información sobre los cambios implementados en esta versión de Android, consulta Actualizaciones a las restricciones de interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK en Android 15. Para obtener más información sobre interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK en general, consulta Restricciones en interfaces que no pertenecen al SDK.

