Android 15 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่อาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณเช่นเดียวกับรุ่นก่อนหน้า การเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานต่อไปนี้จะมีผลกับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ขึ้นไปเท่านั้น หากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ขึ้นไป คุณควรแก้ไขแอปให้รองรับลักษณะการทำงานเหล่านี้อย่างเหมาะสมในกรณีที่ เกี่ยวข้อง
นอกจากนี้ โปรดตรวจสอบรายการการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่มีผลกับแอปทั้งหมด
ที่ทำงานบน Android 15 ไม่ว่า targetSdkVersion ของแอปจะเป็นอย่างไร
ฟังก์ชันหลัก
Android 15 จะแก้ไขหรือขยายความสามารถหลักต่างๆ ของระบบ Android
การเปลี่ยนแปลงบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า
We are making the following changes to foreground services with Android 15.
- Data sync foreground service timeout behavior
- New media processing foreground service type
- Restrictions on
BOOT_COMPLETEDbroadcast receivers launching foreground services - Restrictions on starting foreground services while an app holds the
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOWpermission
Data sync foreground service timeout behavior
Android 15 introduces a new timeout behavior to dataSync for apps targeting
Android 15 (API level 35) or higher. This behavior also applies to the new
mediaProcessing foreground service type.
The system permits an app's dataSync services to run for a total of 6 hours
in a 24-hour period, after which the system calls the running service's
Service.onTimeout(int, int) method (introduced in Android
15). At this time, the service has a few seconds to call
Service.stopSelf(). When Service.onTimeout() is called, the
service is no longer considered a foreground service. If the service does not
call Service.stopSelf(), the system throws an internal exception. The
exception is logged in Logcat with the following message:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
To avoid problems with this behavior change, you can do one or more of the following:
- Have your service implement the new
Service.onTimeout(int, int)method. When your app receives the callback, make sure to callstopSelf()within a few seconds. (If you don't stop the app right away, the system generates a failure.) - Make sure your app's
dataSyncservices don't run for more than a total of 6 hours in any 24-hour period (unless the user interacts with the app, resetting the timer). - Only start
dataSyncforeground services as a result of direct user interaction; since your app is in the foreground when the service starts, your service has the full six hours after the app goes to the background. - Instead of using a
dataSyncforeground service, use an alternative API.
If your app's dataSync foreground services have run for 6 hours in the last
24, you cannot start another dataSync foreground service unless the user
has brought your app to the foreground (which resets the timer). If you try to
start another dataSync foreground service, the system throws
ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
with an error message like "Time limit already exhausted for foreground service
type dataSync".
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable data sync timeouts even if your app
is not targeting Android 15 (as long as the app is running on an Android 15
device). To enable timeouts, run the following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
You can also adjust the timeout period, to make it easier to test how your
app behaves when the limit is reached. To set a new timeout period, run the
following adb command:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
New media processing foreground service type
Android 15 introduces a new foreground service type, mediaProcessing. This
service type is appropriate for operations like transcoding media files. For
example, a media app might download an audio file and need to convert it to a
different format before playing it. You can use a mediaProcessing foreground
service to make sure the conversion continues even while the app is in the
background.
The system permits an app's mediaProcessing services to run for a total of 6
hours in a 24-hour period, after which the system calls the running service's
Service.onTimeout(int, int) method (introduced in Android
15). At this time, the service has a few seconds to call
Service.stopSelf(). If the service does not
call Service.stopSelf(), the system throws an internal exception. The
exception is logged in Logcat with the following message:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
To avoid having the exception, you can do one of the following:
- Have your service implement the new
Service.onTimeout(int, int)method. When your app receives the callback, make sure to callstopSelf()within a few seconds. (If you don't stop the app right away, the system generates a failure.) - Make sure your app's
mediaProcessingservices don't run for more than a total of 6 hours in any 24-hour period (unless the user interacts with the app, resetting the timer). - Only start
mediaProcessingforeground services as a result of direct user interaction; since your app is in the foreground when the service starts, your service has the full six hours after the app goes to the background. - Instead of using a
mediaProcessingforeground service, use an alternative API, like WorkManager.
If your app's mediaProcessing foreground services have run for 6 hours in the
last 24, you cannot start another mediaProcessing foreground service unless
the user has brought your app to the foreground (which resets the timer). If you
try to start another mediaProcessing foreground service, the system throws
ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
with an error message like "Time limit already exhausted for foreground service
type mediaProcessing".
For more information about the mediaProcessing service type, see Changes to
foreground service types for Android 15: Media processing.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable media processing timeouts even if
your app is not targeting Android 15 (as long as the app is running on an
Android 15 device). To enable timeouts, run the following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
You can also adjust the timeout period, to make it easier to test how your
app behaves when the limit is reached. To set a new timeout period, run the
following adb command:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Restrictions on BOOT_COMPLETED broadcast receivers launching foreground services
มีข้อจำกัดใหม่ในการเปิดตัว Broadcast Receiver ของ BOOT_COMPLETED
บริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า ระบบไม่อนุญาตให้ Receiver BOOT_COMPLETED เปิดบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าประเภทต่อไปนี้
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(ข้อจำกัดนี้มีการใช้มาเป็นเวลาmicrophoneตั้งแต่ Android 14)
หากตัวรับสัญญาณ BOOT_COMPLETED พยายามเปิดเบื้องหน้าประเภทใดก็ตามเหล่านี้
ระบบอาจไม่แสดง ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
การทดสอบ
หากต้องการทดสอบลักษณะการทำงานของแอป คุณสามารถเปิดใช้ข้อจำกัดใหม่เหล่านี้ได้ แม้ว่า
แอปไม่ได้กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (ตราบใดที่แอปยังทํางานอยู่ใน Android 15
อุปกรณ์) เรียกใช้คำสั่ง adb ต่อไปนี้
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
หากต้องการส่งประกาศBOOT_COMPLETEDโดยไม่ต้องรีสตาร์ทอุปกรณ์ ให้ทำดังนี้
เรียกใช้คำสั่ง adb ต่อไปนี้
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
Restrictions on starting foreground services while an app holds the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission
Previously, if an app held the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission, it could launch
a foreground service even if the app was currently in the background (as
discussed in exemptions from background start restrictions).
If an app targets Android 15, this exemption is now narrower. The app now needs
to have the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission and also have a visible overlay
window. That is, the app needs to first launch a
TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY window and the window
needs to be visible before you start a foreground service.
If your app attempts to start a foreground service from the background without
meeting these new requirements (and it does not have some other exemption), the
system throws ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
If your app declares the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission
and launches foreground services from the background, it may be affected by this
change. If your app gets a ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException, check
your app's order of operations and make sure your app already has an active
overlay window before it attempts to start a foreground service from the
background. You can check if your overlay window is currently visible
by calling View.getWindowVisibility(), or you
can override View.onWindowVisibilityChanged()
to get notified whenever the visibility changes.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable these new restrictions even if your
app is not targeting Android 15 (as long as the app is running on an Android 15
device). To enable these new restrictions on starting foreground services
from the background, run the following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
การเปลี่ยนแปลงเวลาที่แอปจะแก้ไขสถานะส่วนกลางของโหมดห้ามรบกวนได้
Apps that target Android 15 (API level 35) and higher can no longer change the
global state or policy of Do Not Disturb (DND) on a device (either by modifying
user settings, or turning off DND mode). Instead, apps must contribute an
AutomaticZenRule, which the system combines into a global policy with the
existing most-restrictive-policy-wins scheme. Calls to existing APIs that
previously affected global state (setInterruptionFilter,
setNotificationPolicy) result in the creation or update of an implicit
AutomaticZenRule, which is toggled on and off depending on the call-cycle of
those API calls.
Note that this change only affects observable behavior if the app is calling
setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) and expects that call to
deactivate an AutomaticZenRule that was previously activated by their owners.
การเปลี่ยนแปลง API ของ OpenJDK
Android 15 จะยังคงปรับปรุงไลบรารีหลักของ Android ให้สอดคล้องกับฟีเจอร์ใน OpenJDK LTS เวอร์ชันล่าสุด
การเปลี่ยนแปลงบางอย่างเหล่านี้อาจส่งผลต่อความเข้ากันได้ของแอปสำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ดังนี้
การเปลี่ยนแปลง API การจัดรูปแบบสตริง: ตอนนี้การตรวจสอบดัชนีอาร์กิวเมนต์ แฟล็ก ความกว้าง และความแม่นยำจะเข้มงวดมากขึ้นเมื่อใช้ API
String.format()และFormatter.format()ต่อไปนี้String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
ตัวอย่างเช่น ระบบจะแสดงข้อยกเว้นต่อไปนี้เมื่อใช้อาร์กิวเมนต์ดัชนี 0 (
%0ในสตริงรูปแบบ)IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0ในกรณีนี้ คุณสามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้โดยใช้อาร์กิวเมนต์ดัชนี 1 (
%1ในสตริงรูปแบบ)การเปลี่ยนแปลงประเภทคอมโพเนนต์ของ
Arrays.asList(...).toArray(): เมื่อใช้Arrays.asList(...).toArray()ประเภทคอมโพเนนต์ของอาร์เรย์ผลลัพธ์จะเป็นObjectไม่ใช่ประเภทขององค์ประกอบของอาร์เรย์พื้นฐาน ดังนั้นโค้ดต่อไปนี้จะแสดงClassCastExceptionString[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();ในกรณีนี้ หากต้องการเก็บรักษา
Stringเป็นประเภทคอมโพเนนต์ในอาร์เรย์ผลลัพธ์ คุณสามารถใช้Collection.toArray(Object[])แทนได้String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);การเปลี่ยนแปลงการจัดการรหัสภาษา: เมื่อใช้
LocaleAPI ระบบจะไม่แปลงรหัสภาษาสำหรับภาษาฮีบรู ยิดดิช และอินโดนีเซีย เป็นรูปแบบที่ล้าสมัยอีกต่อไป (ฮีบรู:iw, ยิดดิช:jiและอินโดนีเซีย:in) เมื่อระบุรหัสภาษาสำหรับภาษาใดภาษาหนึ่งเหล่านี้ ให้ใช้รหัส จาก ISO 639-1 แทน (ฮีบรู:he, ยิดดิช:yiและอินโดนีเซีย:id)การเปลี่ยนแปลงลำดับ int แบบสุ่ม: ตามการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ทำใน https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574 ตอนนี้เมธอดต่อไปนี้
Random.ints()จะแสดงลำดับตัวเลขที่แตกต่างจากเมธอดRandom.nextInt()โดยทั่วไปแล้ว การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ไม่น่าจะส่งผลให้แอปทำงานผิดปกติ แต่โค้ดของคุณไม่ควรคาดหวังว่าลำดับที่สร้างจากเมธอด
Random.ints()จะตรงกับRandom.nextInt()
API SequencedCollection ใหม่นี้อาจส่งผลต่อความเข้ากันได้ของแอป
หลังจากที่คุณอัปเดต compileSdk ในการกำหนดค่าบิลด์ของแอปเพื่อใช้
Android 15 (API ระดับ 35)
การชนกันกับฟังก์ชันส่วนขยาย
MutableList.removeFirst()และMutableList.removeLast()ในkotlin-stdlibประเภท
Listใน Java จะแมปกับประเภทMutableListใน Kotlin เนื่องจากมีการเปิดตัว APIList.removeFirst()และList.removeLast()ใน Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) คอมไพเลอร์ Kotlin จึงแก้ไขการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน เช่นlist.removeFirst()แบบคงที่ไปยัง APIListใหม่แทนที่จะเป็นฟังก์ชันส่วนขยายในkotlin-stdlibหากมีการคอมไพล์แอปอีกครั้งโดยตั้งค่า
compileSdkเป็น35และตั้งค่าminSdkเป็น34หรือต่ำกว่า จากนั้นเรียกใช้แอปใน Android 14 และต่ำกว่า ระบบจะแสดงข้อผิดพลาดรันไทม์java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;NewApiตัวเลือก lint ที่มีอยู่ในปลั๊กอิน Android Gradle สามารถตรวจพบการใช้ API ใหม่เหล่านี้ได้./gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()หากต้องการแก้ไขข้อยกเว้นรันไทม์และข้อผิดพลาดของ Lint คุณสามารถแทนที่การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
removeFirst()และremoveLast()ด้วยremoveAt(0)และremoveAt(list.lastIndex)ตามลำดับใน Kotlin หากคุณใช้ Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 ขึ้นไป ก็จะมีตัวเลือกการแก้ไขด่วน สำหรับข้อผิดพลาดเหล่านี้ด้วยลองนำ
@SuppressLint("NewApi")และlintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }ออกหากปิดใช้ตัวเลือกการตรวจสอบแล้วการชนกันกับเมธอดอื่นๆ ใน Java
เราได้เพิ่มวิธีการใหม่ๆ ลงในประเภทที่มีอยู่แล้ว เช่น
ListและDequeวิธีการใหม่เหล่านี้อาจใช้ร่วมกับวิธีการที่มีชื่อและประเภทอาร์กิวเมนต์เดียวกันในอินเทอร์เฟซและคลาสอื่นๆ ไม่ได้ ในกรณีที่ลายเซ็นของเมธอดชนกันกับความไม่เข้ากัน คอมไพเลอร์javacจะแสดงข้อผิดพลาดขณะสร้าง เช่นตัวอย่างข้อผิดพลาด 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface Listตัวอย่างข้อผิดพลาด 2
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorตัวอย่างข้อผิดพลาด 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorหากต้องการแก้ไขข้อผิดพลาดในการบิลด์เหล่านี้ คลาสที่ใช้การติดตั้งอินเทอร์เฟซเหล่านี้ควร ลบล้างเมธอดด้วยประเภทการคืนค่าที่เข้ากันได้ เช่น
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
ความปลอดภัย
Android 15 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ส่งเสริมความปลอดภัยของระบบเพื่อช่วยปกป้องแอป และผู้ใช้จากแอปที่เป็นอันตราย
เวอร์ชัน TLS ที่ถูกจำกัด
Android 15 จำกัดการใช้ TLS เวอร์ชัน 1.0 และ 1.1 ก่อนหน้านี้ Android ได้เลิกใช้งานเวอร์ชันเหล่านี้แล้ว แต่ตอนนี้ไม่อนุญาตให้แอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ใช้เวอร์ชันดังกล่าว
เปิดใช้กิจกรรมในเบื้องหลังที่ปลอดภัย
Android 15 protects users from malicious apps and gives them more control over their devices by adding changes that prevent malicious background apps from bringing other apps to the foreground, elevating their privileges, and abusing user interaction. Background activity launches have been restricted since Android 10 (API level 29).
Other changes
In addition to the restriction for UID matching, these other changes are also included:
- Change
PendingIntentcreators to block background activity launches by default. This helps prevent apps from accidentally creating aPendingIntentthat could be abused by malicious actors. - Don't bring an app to the foreground unless the
PendingIntentsender allows it. This change aims to prevent malicious apps from abusing the ability to start activities in the background. By default, apps are not allowed to bring the task stack to the foreground unless the creator allows background activity launch privileges or the sender has background activity launch privileges. - Control how the top activity of a task stack can finish its task. If the top activity finishes a task, Android will go back to whichever task was last active. Moreover, if a non-top activity finishes its task, Android will go back to the home screen; it won't block the finish of this non-top activity.
- Prevent launching arbitrary activities from other apps into your own task. This change prevents malicious apps from phishing users by creating activities that appear to be from other apps.
- Block non-visible windows from being considered for background activity launches. This helps prevent malicious apps from abusing background activity launches to display unwanted or malicious content to users.
Intent ที่ปลอดภัยกว่า
Android 15 เพิ่มมาตรการรักษาความปลอดภัยที่ไม่บังคับแบบใหม่เพื่อให้ความตั้งใจปลอดภัยมากขึ้น และมีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้น การเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้มีจุดประสงค์เพื่อป้องกันช่องโหว่ที่อาจเกิดขึ้นและการใช้ Intent ในทางที่ผิดซึ่งแอปที่เป็นอันตรายอาจใช้ประโยชน์ได้ มี 2 แบบ การปรับปรุงหลักด้านความปลอดภัยของ Intent ใน Android 15 มีดังนี้
- จับคู่ตัวกรอง Intent เป้าหมาย: Intent ที่กำหนดเป้าหมายคอมโพเนนต์ที่เฉพาะเจาะจงจะต้อง ตรงกับข้อกำหนดตัวกรอง Intent ของเป้าหมายอย่างถูกต้อง หากคุณส่ง Intent เพื่อเปิดใช้งาน Activity ของแอปอื่น คอมโพเนนต์ Intent เป้าหมายต้องสอดคล้องกับ Intent-Filter ที่ประกาศไว้ของ Activity ที่รับ
- Intent ต้องมีการดำเนินการ: Intent ที่ไม่มีการดำเนินการจะไม่จับคู่กับตัวกรอง Intent อีกต่อไป ซึ่งหมายความว่า Intent ที่ใช้เพื่อเริ่มกิจกรรมหรือบริการต้องมีการดำเนินการที่ระบุไว้อย่างชัดเจน
หากต้องการตรวจสอบว่าแอปของคุณตอบสนองต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้อย่างไร ให้ใช้ StrictMode ในแอป หากต้องการดูบันทึกโดยละเอียดเกี่ยวกับการละเมิดการใช้งาน Intent ให้เพิ่มเมธอดต่อไปนี้
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้และ UI ของระบบ
Android 15 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงบางอย่างที่มุ่งสร้างประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้ที่สอดคล้องกันมากขึ้น และใช้งานง่าย
การเปลี่ยนแปลงส่วนที่เว้นไว้ในหน้าต่าง
การเปลี่ยนแปลงที่เกี่ยวข้องกับส่วนแทรกของหน้าต่างใน Android 15 มี 2 อย่าง ได้แก่ ระบบจะบังคับใช้การแสดงผลแบบเต็มหน้าจอโดยค่าเริ่มต้น และยังมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงการกำหนดค่า เช่น การกําหนดค่าเริ่มต้นของแถบระบบ
Edge-to-edge enforcement
Apps are edge-to-edge by default on devices running Android 15 if the app is targeting Android 15 (API level 35).
This is a breaking change that might negatively impact your app's UI. The changes affect the following UI areas:
- Gesture handle navigation bar
- Transparent by default.
- Bottom offset is disabled so content draws behind the system navigation bar unless insets are applied.
setNavigationBarColorandR.attr#navigationBarColorare deprecated and don't affect gesture navigation.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedcontinue to have no effect on gesture navigation.
- 3-button navigation
- Opacity set to 80% by default, with color possibly matching the window background.
- Bottom offset disabled so content draws behind the system navigation bar unless insets are applied.
setNavigationBarColorandR.attr#navigationBarColorare set to match the window background by default. The window background must be a color drawable for this default to apply. This API is deprecated but continues to affect 3-button navigation.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedis true by default, which adds an 80% opaque background across 3-button navigation.
- Status bar
- Transparent by default.
- The top offset is disabled so content draws behind the status bar unless insets are applied.
setStatusBarColorandR.attr#statusBarColorare deprecated and have no effect on Android 15.setStatusBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedare deprecated but still have an effect on Android 15.
- Display cutout
layoutInDisplayCutoutModeof non-floating windows must beLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS.SHORT_EDGES,NEVER, andDEFAULTare interpreted asALWAYSso that users don't see a black bar caused by the display cutout and appear edge-to-edge.
The following example shows an app before and after targeting Android 15 (API level 35), and before and after applying insets. This example is not comprehensive, this might appear differently on Android Auto.

What to check if your app is already edge-to-edge
If your app is already edge-to-edge and applies insets, you are mostly unimpacted, except in the following scenarios. However, even if you think you aren't impacted, we recommend you test your app.
- You have a non-floating window, such as an
Activitythat usesSHORT_EDGES,NEVERorDEFAULTinstead ofLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS. If your app crashes on launch, this might be due to your splashscreen. You can either upgrade the core splashscreen dependency to 1.2.0-alpha01 or later or setwindow.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always. - There might be lower-traffic screens with occluded UI. Verify these
less-visited screens don't have occluded UI. Lower-traffic screens include:
- Onboarding or sign-in screens
- Settings pages
What to check if your app is not already edge-to-edge
If your app is not already edge-to-edge, you are most likely impacted. In addition to the scenarios for apps that are already edge-to-edge, you should consider the following:
- If your app uses Material 3 Components (
androidx.compose.material3) in compose, such asTopAppBar,BottomAppBar, andNavigationBar, these components are likely not impacted because they automatically handle insets. - If your app is using Material 2 Components (
androidx.compose.material) in Compose, these components don't automatically handle insets. However, you can get access to the insets and apply them manually. In androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 and later, use thewindowInsetsparameter to apply the insets manually forBottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigation, andNavigationRail. Likewise, use thecontentWindowInsetsparameter forScaffold. - If your app uses views and Material Components
(
com.google.android.material), most views-based Material Components such asBottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar,NavigationRailView, orNavigationView, handle insets and require no additional work. However, you need to addandroid:fitsSystemWindows="true"if usingAppBarLayout. - For custom composables, apply the insets manually as padding. If your
content is within a
Scaffold, you can consume insets using theScaffoldpadding values. Otherwise, apply padding using one of theWindowInsets. - If your app is using views and
BottomSheet,SideSheetor custom containers, apply padding usingViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener. ForRecyclerView, apply padding using this listener and also addclipToPadding="false".
What to check if your app must offer custom background protection
If your app must offer custom background protection to 3-button navigation or
the status bar, your app should place a composable or view behind the system bar
using WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() to get the 3-button
navigation bar height or WindowInsets.Type#statusBars.
Additional edge-to-edge resources
See the Edge to Edge Views and Edge to Edge Compose guides for additional considerations on applying insets.
Deprecated APIs
The following APIs are deprecated but not disabled:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(for 3 button navigation, with 80% alpha)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(for 3 button navigation, with 80% alpha)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
The following APIs are deprecated and disabled:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(for gesture navigation)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(for gesture navigation)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
Stable configuration
หากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ขึ้นไป Configuration จะไม่
รวมแถบระบบอีกต่อไป หากคุณใช้ขนาดหน้าจอในคลาส Configuration เพื่อคำนวณเลย์เอาต์ คุณควรแทนที่ด้วยตัวเลือกอื่นที่ดีกว่า เช่น ViewGroup, WindowInsets หรือ WindowMetricsCalculator ที่เหมาะสม ทั้งนี้ขึ้นอยู่กับความต้องการของคุณ
Configuration พร้อมใช้งานตั้งแต่ API 1 โดยปกติแล้วจะได้รับจาก
Activity.onConfigurationChanged โดยจะให้ข้อมูล เช่น ความหนาแน่นของหน้าต่าง
การวางแนว และขนาด ลักษณะสำคัญอย่างหนึ่งเกี่ยวกับขนาดหน้าต่างที่ส่งคืนจาก Configuration คือก่อนหน้านี้จะไม่รวมแถบระบบ
โดยปกติแล้ว ขนาดการกำหนดค่าจะใช้สำหรับการเลือกทรัพยากร เช่น
/res/layout-h500dp และนี่ก็ยังคงเป็น Use Case ที่ถูกต้อง อย่างไรก็ตาม เราไม่แนะนำให้ใช้สำหรับ
การคำนวณเลย์เอาต์มาโดยตลอด หากคุณกำลังทำเช่นนั้น คุณควรหยุด
ทำทันที คุณควรแทนที่การใช้ Configuration ด้วยสิ่งอื่นที่เหมาะสมกว่าตามกรณีการใช้งาน
หากใช้เพื่อคำนวณเลย์เอาต์ ให้ใช้ ViewGroup ที่เหมาะสม เช่น
CoordinatorLayout หรือ ConstraintLayout หากคุณใช้เพื่อกำหนดความสูง
ของแถบนำทางของระบบ ให้ใช้ WindowInsets หากต้องการทราบขนาดปัจจุบัน
ของหน้าต่างแอป ให้ใช้ computeCurrentWindowMetrics
รายการต่อไปนี้อธิบายฟิลด์ที่ได้รับผลกระทบจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้
- ขนาด
Configuration.screenWidthDpและscreenHeightDpจะไม่ รวมแถบระบบอีกต่อไป Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpได้รับผลกระทบโดยอ้อมจากการเปลี่ยนแปลง ในscreenWidthDpและscreenHeightDpConfiguration.orientationได้รับผลกระทบโดยอ้อมจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงในscreenWidthDpและscreenHeightDpในอุปกรณ์ที่มีสัดส่วนใกล้เคียงกับสี่เหลี่ยมจัตุรัสDisplay.getSize(Point)ได้รับผลกระทบโดยอ้อมจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงในConfigurationซึ่งเลิกใช้งานแล้วตั้งแต่ API ระดับ 30 เป็นต้นไปDisplay.getMetrics()ทำงานในลักษณะนี้มาตั้งแต่ API ระดับ 33 แล้ว
แอตทริบิวต์ elegantTextHeight จะมีค่าเริ่มต้นเป็น true
สําหรับแอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) แอตทริบิวต์ elegantTextHeight TextView จะเปลี่ยนเป็น true โดยค่าเริ่มต้น โดยแทนที่แบบอักษรแบบกะทัดรัดที่ใช้โดยค่าเริ่มต้นด้วยสคริปต์บางรายการที่มีเมตริกแนวตั้งขนาดใหญ่ด้วยแบบอักษรที่อ่านง่ายกว่ามาก
แบบอักษรแบบกะทัดรัดมีไว้เพื่อป้องกันการแบ่งเลย์เอาต์ Android 13 (API ระดับ 33) ป้องกันปัญหาการแบ่งเลย์เอาต์เหล่านี้ได้หลายอย่างโดยอนุญาตให้เลย์เอาต์ข้อความยืดความสูงแนวตั้งโดยใช้แอตทริบิวต์ fallbackLineSpacing
ใน Android 15 ฟอนต์แบบกะทัดรัดจะยังคงอยู่ในระบบ แอปของคุณจึงตั้งค่า elegantTextHeight เป็น false เพื่อให้มีลักษณะการทำงานเหมือนเดิมได้ แต่ไม่น่าจะได้รับการสนับสนุนในรุ่นที่กำลังจะเปิดตัว ดังนั้น หากแอปของคุณรองรับสคริปต์ต่อไปนี้ อาหรับ ลาว พม่า ทมิฬ คุชราต กันนาดา มาลายาลัม โอเดีย เตลูกู หรือไทย ให้ทดสอบแอปโดยตั้งค่า elegantTextHeight เป็น true
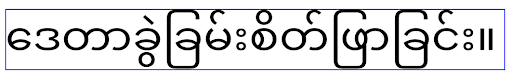 ลักษณะการทํางานของ
ลักษณะการทํางานของ elegantTextHeight สําหรับแอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 14 (API ระดับ 34) และต่ำกว่า ลักษณะการทํางานของ
ลักษณะการทํางานของ elegantTextHeight สําหรับแอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15การเปลี่ยนแปลงความกว้างของ TextView สำหรับรูปร่างตัวอักษรที่ซับซ้อน
In previous versions of Android, some cursive fonts or languages that have
complex shaping might draw the letters in the previous or next character's area.
In some cases, such letters were clipped at the beginning or ending position.
Starting in Android 15, a TextView allocates width for drawing enough space
for such letters and allows apps to request extra paddings to the left to
prevent clipping.
Because this change affects how a TextView decides the width, TextView
allocates more width by default if the app targets Android 15 (API level 35) or
higher. You can enable or disable this behavior by calling the
setUseBoundsForWidth API on TextView.
Because adding left padding might cause a misalignment for existing layouts, the
padding is not added by default even for apps that target Android 15 or higher.
However, you can add extra padding to preventing clipping by calling
setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang.
The following examples show how these changes can improve text layout for some fonts and languages.

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
ความสูงของบรรทัดเริ่มต้นที่รับรู้ภาษาสำหรับ EditText
In previous versions of Android, the text layout stretched the height of the
text to meet the line height of the font that matched the current locale. For
example, if the content was in Japanese, because the line height of the Japanese
font is slightly larger than the one of a Latin font, the height of the text
became slightly larger. However, despite these differences in line heights, the
EditText element was sized uniformly, regardless
of the locale being used, as illustrated in the following image:

EditText elements that
can contain text from English (en), Japanese (ja), and Burmese (my). The
height of the EditText is the same, even though these languages
have different line heights from each other.For apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35), a minimum line height is now
reserved for EditText to match the reference font for the specified Locale, as
shown in the following image:

EditText elements that
can contain text from English (en), Japanese (ja), and Burmese (my). The
height of the EditText now includes space to accommodate the
default line height for these languages' fonts.If needed, your app can restore the previous behavior by specifying the
useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum attribute
to false, and your app can set custom minimum vertical metrics using the
setMinimumFontMetrics API in Kotlin and Java.
กล้องและสื่อ
Android 15 จะทำการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานของกล้องและสื่อสำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ขึ้นไปดังนี้
ข้อจำกัดในการขอโฟกัสเสียง
แอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ต้องเป็นแอปที่ทำงานอยู่ด้านบนหรือกำลังใช้บริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าเพื่อขอโฟกัสเสียง หากแอปพยายามขอโฟกัสเมื่อไม่เป็นไปตามข้อกำหนดข้อใดข้อหนึ่งเหล่านี้ การเรียกใช้จะแสดงผลเป็น AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับโหมดโฟกัสเสียงได้ที่จัดการโหมดโฟกัสเสียง
ข้อจำกัดที่ไม่ใช่ SDK ที่อัปเดตแล้ว
Android 15 includes updated lists of restricted non-SDK interfaces based on collaboration with Android developers and the latest internal testing. Whenever possible, we make sure that public alternatives are available before we restrict non-SDK interfaces.
If your app does not target Android 15, some of these changes might not immediately affect you. However, while it's possible for your app to access some non-SDK interfaces depending on your app's target API level, using any non-SDK method or field always carries a high risk of breaking your app.
If you are unsure if your app uses non-SDK interfaces, you can test your app to find out. If your app relies on non-SDK interfaces, you should begin planning a migration to SDK alternatives. Nevertheless, we understand that some apps have valid use cases for using non-SDK interfaces. If you can't find an alternative to using a non-SDK interface for a feature in your app, you should request a new public API.
To learn more about the changes in this release of Android, see Updates to non-SDK interface restrictions in Android 15. To learn more about non-SDK interfaces generally, see Restrictions on non-SDK interfaces.

