كما هو الحال في الإصدارات السابقة، يتضمّن Android 15 تغييرات في السلوك قد تؤثر في تطبيقك. تنطبق تغييرات السلوك التالية حصريًا على التطبيقات التي تستهدف Android 15 أو الإصدارات الأحدث. إذا كان تطبيقك يستهدف الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android أو الإصدارات الأحدث، عليك تعديل تطبيقك ليتوافق مع هذه السلوكيات بشكل سليم، حيثما ينطبق ذلك.
احرص أيضًا على مراجعة قائمة التغييرات في السلوك التي تؤثر في جميع التطبيقات
التي تعمل على Android 15 بغض النظر عن targetSdkVersion لتطبيقك.
الوظيفة الأساسية
يعدّل نظام التشغيل Android 15 العديد من الإمكانات الأساسية لنظام Android أو يوسّع نطاقها.
التغييرات على الخدمات التي تعمل في المقدّمة
نحن بصدد إجراء التغييرات التالية على الخدمات التي تعمل في المقدّمة في Android 15.
- سلوك مهلة الخدمة التي تعمل في المقدّمة لمزامنة البيانات
- نوع الخدمة الجديدة التي تعمل في المقدّمة لمعالجة الوسائط
- القيود المفروضة على
BOOT_COMPLETEDمستقبلات البث التي تبدأ الخدمات التي تعمل في المقدّمة - قيود على بدء الخدمات التي تعمل في المقدّمة عندما يكون لدى التطبيق إذن
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
سلوك مهلة الخدمة التي تعمل في المقدّمة لمزامنة البيانات
Android 15 introduces a new timeout behavior to dataSync for apps targeting
Android 15 (API level 35) or higher. This behavior also applies to the new
mediaProcessing foreground service type.
The system permits an app's dataSync services to run for a total of 6 hours
in a 24-hour period, after which the system calls the running service's
Service.onTimeout(int, int) method (introduced in Android
15). At this time, the service has a few seconds to call
Service.stopSelf(). When Service.onTimeout() is called, the
service is no longer considered a foreground service. If the service does not
call Service.stopSelf(), the system throws an internal exception. The
exception is logged in Logcat with the following message:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
To avoid problems with this behavior change, you can do one or more of the following:
- Have your service implement the new
Service.onTimeout(int, int)method. When your app receives the callback, make sure to callstopSelf()within a few seconds. (If you don't stop the app right away, the system generates a failure.) - Make sure your app's
dataSyncservices don't run for more than a total of 6 hours in any 24-hour period (unless the user interacts with the app, resetting the timer). - Only start
dataSyncforeground services as a result of direct user interaction; since your app is in the foreground when the service starts, your service has the full six hours after the app goes to the background. - Instead of using a
dataSyncforeground service, use an alternative API.
If your app's dataSync foreground services have run for 6 hours in the last
24, you cannot start another dataSync foreground service unless the user
has brought your app to the foreground (which resets the timer). If you try to
start another dataSync foreground service, the system throws
ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
with an error message like "Time limit already exhausted for foreground service
type dataSync".
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable data sync timeouts even if your app
is not targeting Android 15 (as long as the app is running on an Android 15
device). To enable timeouts, run the following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
You can also adjust the timeout period, to make it easier to test how your
app behaves when the limit is reached. To set a new timeout period, run the
following adb command:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
نوع الخدمة الجديدة التي تعمل في المقدّمة لمعالجة الوسائط
Android 15 introduces a new foreground service type, mediaProcessing. This
service type is appropriate for operations like transcoding media files. For
example, a media app might download an audio file and need to convert it to a
different format before playing it. You can use a mediaProcessing foreground
service to make sure the conversion continues even while the app is in the
background.
The system permits an app's mediaProcessing services to run for a total of 6
hours in a 24-hour period, after which the system calls the running service's
Service.onTimeout(int, int) method (introduced in Android
15). At this time, the service has a few seconds to call
Service.stopSelf(). If the service does not
call Service.stopSelf(), the system throws an internal exception. The
exception is logged in Logcat with the following message:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
To avoid having the exception, you can do one of the following:
- Have your service implement the new
Service.onTimeout(int, int)method. When your app receives the callback, make sure to callstopSelf()within a few seconds. (If you don't stop the app right away, the system generates a failure.) - Make sure your app's
mediaProcessingservices don't run for more than a total of 6 hours in any 24-hour period (unless the user interacts with the app, resetting the timer). - Only start
mediaProcessingforeground services as a result of direct user interaction; since your app is in the foreground when the service starts, your service has the full six hours after the app goes to the background. - Instead of using a
mediaProcessingforeground service, use an alternative API, like WorkManager.
If your app's mediaProcessing foreground services have run for 6 hours in the
last 24, you cannot start another mediaProcessing foreground service unless
the user has brought your app to the foreground (which resets the timer). If you
try to start another mediaProcessing foreground service, the system throws
ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
with an error message like "Time limit already exhausted for foreground service
type mediaProcessing".
For more information about the mediaProcessing service type, see Changes to
foreground service types for Android 15: Media processing.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable media processing timeouts even if
your app is not targeting Android 15 (as long as the app is running on an
Android 15 device). To enable timeouts, run the following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
You can also adjust the timeout period, to make it easier to test how your
app behaves when the limit is reached. To set a new timeout period, run the
following adb command:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
القيود المفروضة على تطبيقات BOOT_COMPLETED التي تستخدم مستقبلات البث لتشغيل الخدمات التي تعمل في المقدّمة
هناك قيود جديدة على إطلاق أجهزة استقبال بث BOOT_COMPLETED.
والخدمات التي تعمل في المقدّمة. لا يُسمح لأجهزة استقبال BOOT_COMPLETED بتشغيل
الأنواع التالية من الخدمات التي تعمل في المقدّمة:
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(تم فرض هذا التقييد علىmicrophoneمنذ بدء استخدام الإصدار 14 من نظام التشغيل Android)
إذا حاول مستقبل BOOT_COMPLETED بدء أيّ من هذه الأنواع من الخدمات التي تعمل في
المقدّمة، يُرسِل النظام الخطأ ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
الاختبار
لاختبار سلوك تطبيقك، يمكنك تفعيل هذه القيود الجديدة حتى إذا كان
تطبيقك لا يستهدف الإصدار 15 من Android (ما دام التطبيق يعمل على جهاز يعمل بالإصدار 15 من Android). شغِّل الأمر adb التالي:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
لإرسال بث BOOT_COMPLETED بدون إعادة تشغيل الجهاز، يُرجى اتّباع الخطوات التالية:
شغِّل الأمر adb التالي:
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
القيود المفروضة على بدء الخدمات التي تعمل في المقدّمة عندما يكون لدى التطبيق إذن SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
Previously, if an app held the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission, it could launch
a foreground service even if the app was currently in the background (as
discussed in exemptions from background start restrictions).
If an app targets Android 15, this exemption is now narrower. The app now needs
to have the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission and also have a visible overlay
window. That is, the app needs to first launch a
TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY window and the window
needs to be visible before you start a foreground service.
If your app attempts to start a foreground service from the background without
meeting these new requirements (and it does not have some other exemption), the
system throws ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
If your app declares the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission
and launches foreground services from the background, it may be affected by this
change. If your app gets a ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException, check
your app's order of operations and make sure your app already has an active
overlay window before it attempts to start a foreground service from the
background. You can check if your overlay window is currently visible
by calling View.getWindowVisibility(), or you
can override View.onWindowVisibilityChanged()
to get notified whenever the visibility changes.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable these new restrictions even if your
app is not targeting Android 15 (as long as the app is running on an Android 15
device). To enable these new restrictions on starting foreground services
from the background, run the following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
تغييرات على الأوقات التي يمكن فيها للتطبيقات تعديل الحالة العامة لوضع "عدم الإزعاج"
Apps that target Android 15 (API level 35) and higher can no longer change the
global state or policy of Do Not Disturb (DND) on a device (either by modifying
user settings, or turning off DND mode). Instead, apps must contribute an
AutomaticZenRule, which the system combines into a global policy with the
existing most-restrictive-policy-wins scheme. Calls to existing APIs that
previously affected global state (setInterruptionFilter,
setNotificationPolicy) result in the creation or update of an implicit
AutomaticZenRule, which is toggled on and off depending on the call-cycle of
those API calls.
Note that this change only affects observable behavior if the app is calling
setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) and expects that call to
deactivate an AutomaticZenRule that was previously activated by their owners.
التغييرات في واجهة برمجة التطبيقات OpenJDK
Android 15 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases.
Some of these changes can affect app compatibility for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35):
Changes to string formatting APIs: Validation of argument index, flags, width, and precision are now more strict when using the following
String.format()andFormatter.format()APIs:String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
For example, the following exception is thrown when an argument index of 0 is used (
%0in the format string):IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0In this case, the issue can be fixed by using an argument index of 1 (
%1in the format string).Changes to component type of
Arrays.asList(...).toArray(): When usingArrays.asList(...).toArray(), the component type of the resulting array is now anObject—not the type of the underlying array's elements. So the following code throws aClassCastException:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();For this case, to preserve
Stringas the component type in the resulting array, you could useCollection.toArray(Object[])instead:String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);Changes to language code handling: When using the
LocaleAPI, language codes for Hebrew, Yiddish, and Indonesian are no longer converted to their obsolete forms (Hebrew:iw, Yiddish:ji, and Indonesian:in). When specifying the language code for one of these locales, use the codes from ISO 639-1 instead (Hebrew:he, Yiddish:yi, and Indonesian:id).Changes to random int sequences: Following the changes made in https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574, the following
Random.ints()methods now return a different sequence of numbers than theRandom.nextInt()methods do:Generally, this change shouldn't result in app-breaking behavior, but your code shouldn't expect the sequence generated from
Random.ints()methods to matchRandom.nextInt().
The new SequencedCollection API can affect your app's compatibility
after you update compileSdk in your app's build configuration to use
Android 15 (API level 35):
Collision with
MutableList.removeFirst()andMutableList.removeLast()extension functions inkotlin-stdlibThe
Listtype in Java is mapped to theMutableListtype in Kotlin. Because theList.removeFirst()andList.removeLast()APIs have been introduced in Android 15 (API level 35), the Kotlin compiler resolves function calls, for examplelist.removeFirst(), statically to the newListAPIs instead of to the extension functions inkotlin-stdlib.If an app is re-compiled with
compileSdkset to35andminSdkset to34or lower, and then the app is run on Android 14 and lower, a runtime error is thrown:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;The existing
NewApilint option in Android Gradle Plugin can catch these new API usages../gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()To fix the runtime exception and lint errors, the
removeFirst()andremoveLast()function calls can be replaced withremoveAt(0)andremoveAt(list.lastIndex)respectively in Kotlin. If you're using Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 or higher, it also provides a quick fix option for these errors.Consider removing
@SuppressLint("NewApi")andlintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }if the lint option has been disabled.Collision with other methods in Java
New methods have been added into the existing types, for example,
ListandDeque. These new methods might not be compatible with the methods with the same name and argument types in other interfaces and classes. In the case of a method signature collision with incompatibility, thejavaccompiler outputs a build-time error. For example:Example error 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface ListExample error 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorExample error 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorTo fix these build errors, the class implementing these interfaces should override the method with a compatible return type. For example:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
الأمان
يتضمّن Android 15 تغييرات تعزّز أمان النظام للمساعدة في حماية التطبيقات والمستخدمين من التطبيقات الضارة.
إصدارات TLS المحظورة
Android 15 restricts the usage of TLS versions 1.0 and 1.1. These versions had previously been deprecated in Android, but are now disallowed for apps targeting Android 15.
عمليات إطلاق الأنشطة الآمنة في الخلفية
Android 15 protects users from malicious apps and gives them more control over their devices by adding changes that prevent malicious background apps from bringing other apps to the foreground, elevating their privileges, and abusing user interaction. Background activity launches have been restricted since Android 10 (API level 29).
Other changes
- Change
PendingIntentcreators to block background activity launches by default. This helps prevent apps from accidentally creating aPendingIntentthat could be abused by malicious actors. - Don't bring an app to the foreground unless the
PendingIntentsender allows it. This change aims to prevent malicious apps from abusing the ability to start activities in the background. By default, apps are not allowed to bring the task stack to the foreground unless the creator allows background activity launch privileges or the sender has background activity launch privileges. - Control how the top activity of a task stack can finish its task. If the top activity finishes a task, Android will go back to whichever task was last active. Moreover, if a non-top activity finishes its task, Android will go back to the home screen; it won't block the finish of this non-top activity.
- Prevent launching arbitrary activities from other apps into your own task. This change prevents malicious apps from phishing users by creating activities that appear to be from other apps.
- Block non-visible windows from being considered for background activity launches. This helps prevent malicious apps from abusing background activity launches to display unwanted or malicious content to users.
نوايا أكثر أمانًا
Android 15 introduces StrictMode for
intents.
In order to see detailed logs about Intent usage violations, use following
method:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
تجربة المستخدم وواجهة مستخدم النظام
يتضمّن Android 15 بعض التغييرات التي تهدف إلى توفير تجربة مستخدم أكثر اتساقًا وسهولة.
تغييرات في مساحة العرض داخل النافذة
هناك تغييران مرتبطان بزوايا النافذة في Android 15: يتم تطبيق التمويه من الحافة إلى الحافة تلقائيًا، وهناك أيضًا تغييرات في الإعدادات، مثل الإعدادات التلقائية لأشرطة النظام.
Edge-to-edge enforcement
تكون ميزة "العرض حتى حافة الشاشة" مفعّلة تلقائيًا في التطبيقات على الأجهزة التي تعمل بنظام التشغيل Android 15 إذا كان التطبيق يستهدف الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات).
هذا تغيير غير متوافق قد يؤثر سلبًا في واجهة مستخدم تطبيقك. تؤثّر التغييرات في مناطق واجهة المستخدم التالية:
- شريط التنقل باستخدام مقبض الإيماءات
- تكون شفافة تلقائيًا.
- يتم إيقاف الإزاحة السفلية كي يتم عرض المحتوى خلف شريط التنقّل في النظام ما لم يتم تطبيق هوامش داخلية.
- تم إيقاف
setNavigationBarColorوR.attr#navigationBarColorنهائيًا، ولا يؤثران في التنقّل بالإيماءات. - لن يكون
setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedوR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedأي تأثير على التنقّل بالإيماءات.
- التنقّل باستخدام ثلاثة أزرار
- يتم ضبط مستوى الشفافية على 80% تلقائيًا، وقد يتطابق اللون مع لون خلفية النافذة.
- تم إيقاف الإزاحة السفلية كي يتم عرض المحتوى خلف شريط التنقّل في النظام ما لم يتم تطبيق الحواف الداخلية.
- يتم ضبط
setNavigationBarColorوR.attr#navigationBarColorتلقائيًا ليتطابقا مع خلفية النافذة. يجب أن تكون خلفية النافذة قابلة للرسم بلون حتى يتم تطبيق هذا الإعداد التلقائي. تم إيقاف هذه الواجهة، ولكنها لا تزال تؤثر في التنقّل باستخدام 3 أزرار. - يتم تلقائيًا تفعيل
setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedوR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforced، ما يؤدي إلى إضافة خلفية غير شفافة بنسبة% 80 في جميع أنحاء شاشة التنقّل باستخدام ثلاثة أزرار.
- شريط الحالة
- تكون شفافة تلقائيًا.
- يتم إيقاف الإزاحة العلوية، وبالتالي يتم عرض المحتوى خلف شريط الحالة ما لم يتم تطبيق هوامش داخلية.
- تم إيقاف
setStatusBarColorوR.attr#statusBarColorنهائيًا ولن يكون لهما أي تأثير في Android 15. - تم إيقاف
setStatusBarContrastEnforcedوR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedنهائيًا، ولكن سيظل لهما تأثير على Android 15.
- فتحة الشاشة
- يجب أن تكون قيمة
layoutInDisplayCutoutModeللنوافذ غير العائمةLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS. يتم تفسيرSHORT_EDGESوNEVERوDEFAULTعلى أنّهاALWAYSحتى لا يظهر للمستخدمين شريط أسود بسبب فتحة العرض، ويظهر المحتوى من الحافة إلى الحافة.
- يجب أن تكون قيمة
يوضّح المثال التالي تطبيقًا قبل وبعد استهداف Android 15 (المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، وقبل وبعد تطبيق العناصر المضمّنة. هذا المثال ليس شاملاً، وقد يظهر بشكل مختلف على Android Auto.
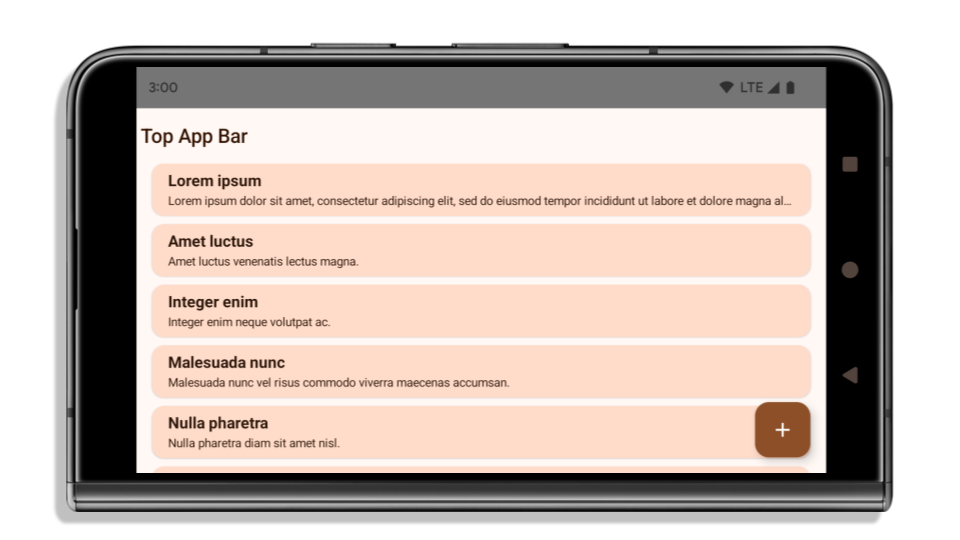

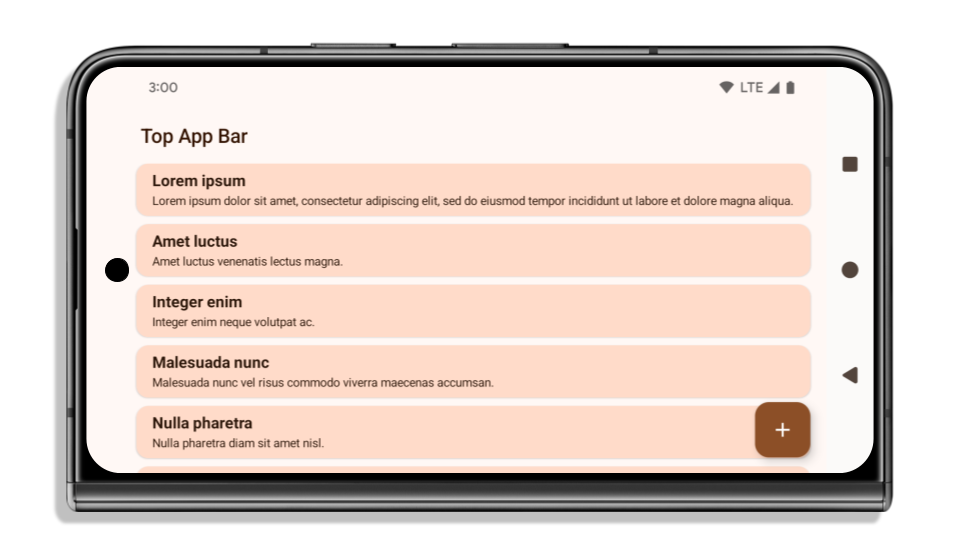
ما يجب التحقّق منه إذا كان تطبيقك معروضًا من الحافة إلى الحافة
إذا كان تطبيقك يعرض المحتوى من الحافة إلى الحافة ويطبّق هوامش داخلية، لن تتأثر في معظم الحالات، باستثناء السيناريوهات التالية. ومع ذلك، حتى إذا كنت تعتقد أنّك لن تتأثر بهذا التغيير، ننصحك باختبار تطبيقك.
- لديك نافذة غير عائمة، مثل
ActivityتستخدمSHORT_EDGESأوNEVERأوDEFAULTبدلاً منLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS. إذا كان تطبيقك يتعطّل عند تشغيله، قد يكون ذلك بسبب شاشة البداية. يمكنك إما ترقية تبعية شاشة البداية الأساسية إلى الإصدار 1.2.0-alpha01 أو إصدار أحدث، أو ضبطwindow.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always. - قد تكون هناك شاشات ذات عدد زيارات أقل مع واجهة مستخدم محجوبة. تأكَّد من أنّ الشاشات الأقل زيارة لا تتضمّن واجهة مستخدم محجوبة. تشمل الشاشات التي تسجّل عددًا أقل من الزيارات ما يلي:
- شاشات الإعداد أو تسجيل الدخول
- صفحات الإعدادات
الإجراءات التي يجب اتّخاذها إذا لم يكن تطبيقك يعرض المحتوى من الحافة إلى الحافة
إذا لم يكن تطبيقك معروضًا من الحافة إلى الحافة، من المرجّح أن تتأثّر بذلك. بالإضافة إلى سيناريوهات التطبيقات التي تعرض المحتوى من الحافة إلى الحافة، يجب مراعاة ما يلي:
- إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم مكوّنات Material 3 (
androidx.compose.material3) في Compose، مثلTopAppBarوBottomAppBarوNavigationBar، من المحتمل أنّ هذه المكوّنات لن تتأثر لأنّها تتعامل تلقائيًا مع الحواف الداخلية. - إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم مكوّنات Material 2 (
androidx.compose.material) في Compose، لن تتعامل هذه المكوّنات تلقائيًا مع الحواف الداخلية. ومع ذلك، يمكنك الوصول إلى الحواف الداخلية وتطبيقها يدويًا. في androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 والإصدارات الأحدث، استخدِم المَعلمةwindowInsetsلتطبيق الهوامش الداخلية يدويًا علىBottomAppBarوTopAppBarوBottomNavigationوNavigationRail. وبالمثل، استخدِم المَعلمةcontentWindowInsetsمعScaffold. - إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم طرق العرض ومكوّنات Material
(
com.google.android.material)، فإنّ معظم مكوّنات Material المستندة إلى طرق العرض، مثلBottomNavigationViewأوBottomAppBarأوNavigationRailViewأوNavigationView، تتعامل مع الحواف الداخلية ولا تتطلّب أي عمل إضافي. ومع ذلك، عليك إضافةandroid:fitsSystemWindows="true"إذا كنت تستخدمAppBarLayout. - بالنسبة إلى العناصر القابلة للإنشاء المخصّصة، طبِّق الحواف الداخلية يدويًا كمسافة بادئة. إذا كان المحتوى الخاص بك ضمن
Scaffold، يمكنك استخدام الحواف الداخلية باستخدام قيم الحشوScaffold. بخلاف ذلك، طبِّق الحشو باستخدام أحدWindowInsets. - إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم طرق العرض و
BottomSheetأوSideSheetأو الحاويات المخصّصة، طبِّق مساحة متروكة باستخدامViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener. بالنسبة إلىRecyclerView، طبِّق المساحة المتروكة باستخدام أداة معالجة الأحداث هذه، وأضِف أيضًاclipToPadding="false".
ما يجب التحقّق منه إذا كان تطبيقك يجب أن يوفّر حماية مخصّصة في الخلفية
إذا كان تطبيقك يوفّر حماية مخصّصة في الخلفية لشريط التنقّل بثلاثة أزرار أو شريط الحالة، يجب أن يضع تطبيقك عنصرًا قابلاً للإنشاء أو عرضًا خلف شريط النظام باستخدام WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() للحصول على ارتفاع شريط التنقّل بثلاثة أزرار أو WindowInsets.Type#statusBars.
مراجع إضافية حول العرض من الحافة إلى الحافة
راجِع الدليلَين طرق العرض من الحافة إلى الحافة وإنشاء محتوى من الحافة إلى الحافة باستخدام Compose للاطّلاع على اعتبارات إضافية بشأن تطبيق عمليات الإزاحة.
واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المتوقّفة نهائيًا
تم إيقاف واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التالية نهائيًا ولكن لم يتم إيقافها:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(للتنقّل باستخدام ثلاثة أزرار، مع قيمة ألفا تبلغ %80)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(للتنقّل باستخدام ثلاثة أزرار، مع قيمة ألفا بنسبة% 80)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
تم إيقاف واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التالية:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(للتنقّل بالإيماءات)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(للتنقّل بالإيماءات)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
Stable configuration
If your app targets Android 15 (API level 35) or higher, Configuration no
longer excludes the system bars. If you use the screen size in the
Configuration class for layout calculation, you should replace it with better
alternatives like an appropriate ViewGroup, WindowInsets, or
WindowMetricsCalculator depending on your need.
Configuration has been available since API 1. It is typically obtained from
Activity.onConfigurationChanged. It provides information like window density,
orientation, and sizes. One important characteristic about the window sizes
returned from Configuration is that it previously excluded the system bars.
The configuration size is typically used for resource selection, such as
/res/layout-h500dp, and this is still a valid use case. However, using it for
layout calculation has always been discouraged. If you do so, you should move
away from it now. You should replace the use of Configuration with something
more suitable depending on your use case.
If you use it to calculate the layout, use an appropriate ViewGroup, such as
CoordinatorLayout or ConstraintLayout. If you use it to determine the height
of the system navbar, use WindowInsets. If you want to know the current size
of your app window, use computeCurrentWindowMetrics.
The following list describes the fields affected by this change:
Configuration.screenWidthDpandscreenHeightDpsizes no longer exclude the system bars.Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpis indirectly affected by changes toscreenWidthDpandscreenHeightDp.Configuration.orientationis indirectly affected by changes toscreenWidthDpandscreenHeightDpon close-to-square devices.Display.getSize(Point)is indirectly affected by the changes inConfiguration. This was deprecated beginning in API level 30.Display.getMetrics()has already worked like this since API level 33.
تكون القيمة التلقائية لسمة elegantTextHeight هي true
For apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35), the
elegantTextHeight TextView attribute
becomes true by default, replacing the compact font used by default with some
scripts that have large vertical metrics with one that is much more readable.
The compact font was introduced to prevent breaking layouts; Android 13 (API
level 33) prevents many of these breakages by allowing the text layout to
stretch the vertical height utilizing the fallbackLineSpacing
attribute.
In Android 15, the compact font still remains in the system, so your app can set
elegantTextHeight to false to get the same behavior as before, but it is
unlikely to be supported in upcoming releases. So, if your app supports the
following scripts: Arabic, Lao, Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam,
Odia, Telugu or Thai, test your app by setting elegantTextHeight to true.
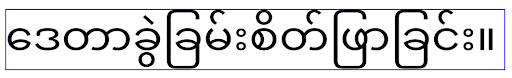
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android 14 (API level 34) and lower.
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android 15.تغيير عرض TextView لأشكال الحروف المعقّدة
In previous versions of Android, some cursive fonts or languages that have
complex shaping might draw the letters in the previous or next character's area.
In some cases, such letters were clipped at the beginning or ending position.
Starting in Android 15, a TextView allocates width for drawing enough space
for such letters and allows apps to request extra paddings to the left to
prevent clipping.
Because this change affects how a TextView decides the width, TextView
allocates more width by default if the app targets Android 15 (API level 35) or
higher. You can enable or disable this behavior by calling the
setUseBoundsForWidth API on TextView.
Because adding left padding might cause a misalignment for existing layouts, the
padding is not added by default even for apps that target Android 15 or higher.
However, you can add extra padding to preventing clipping by calling
setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang.
The following examples show how these changes can improve text layout for some fonts and languages.

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
ارتفاع السطر التلقائي المتوافق مع اللغة المحلية في EditText
في الإصدارات السابقة من Android، كان تنسيق النص يمدّد ارتفاع
النص ليتناسب مع ارتفاع سطر الخط الذي يتطابق مع اللغة الحالية. على سبيل المثال، إذا كان المحتوى باللغة اليابانية، يصبح ارتفاع النص أكبر قليلاً لأنّ ارتفاع السطر للخط الياباني
أكبر قليلاً من ارتفاع السطر للخط اللاتيني. ومع ذلك، على الرغم من هذه الاختلافات في ارتفاعات السطور، تم ضبط حجم العنصر
EditText بشكلٍ موحّد، بغض النظر عن
اللغة المستخدَمة، كما هو موضّح في الصورة التالية:

EditText عنصرًا يمكن أن يحتوي
على نص باللغة الإنجليزية (en) واليابانية (ja) والبورمية (my). يكون
ارتفاع الرمز EditText متطابقًا، على الرغم من أنّ هذه اللغات
لها ارتفاعات سطور مختلفة عن بعضها.بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 15 من Android (المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، تم الآن تخصيص الحد الأدنى لارتفاع السطر
لـ EditText لمطابقة الخط المرجعي للّغة المحدّدة، كما هو موضح
في الصورة التالية:

EditText عنصرًا يمكن أن يحتوي
على نص باللغة الإنجليزية (en) واليابانية (ja) والبورمية (my). يتضمّن الآن
ارتفاع الرمز EditText مساحة لاستيعاب
ارتفاع السطر التلقائي لخطوط هذه اللغات.يمكن لتطبيقك استعادة السلوك السابق إذا لزم الأمر من خلال تحديد سمة
useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum
على false، ويمكن لتطبيقك ضبط الحد الأدنى المخصّص للمقاييس العمودية باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
setMinimumFontMetrics في Kotlin وJava.
الكاميرا والوسائط
يُجري Android 15 التغييرات التالية على سلوك الكاميرا والوسائط في التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 15 من Android أو الإصدارات الأحدث.
القيود المفروضة على طلب التركيز على الصوت
يجب أن تكون التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) هي التطبيق الأهم أو أن تعمل
بخدمة في المقدّمة من أجل طلب تركيز الصوت. إذا حاول أحد التطبيقات طلب التركيز عندما لا يستوفي أحد هذه المتطلبات، يعرض الإجراء AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED.
يمكنك الاطّلاع على مزيد من المعلومات حول ميزة "تركيز الصوت" في مقالة إدارة ميزة "تركيز الصوت".
تعديل القيود المفروضة على حِزم تطوير البرامج (SDK) غير التابعة لجهات خارجية
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 15 قوائم معدَّلة لواجهات برمجة التطبيقات غير التابعة لحزمة SDK والمقيّدة، وذلك استنادًا إلى التعاون مع مطوّري تطبيقات Android وأحدث الاختبارات الداخلية. نحرص دائمًا على توفير بدائل متاحة للجميع قبل فرض قيود على الواجهات غير المتوفّرة في حزمة SDK.
إذا كان تطبيقك لا يستهدف الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android، قد لا تؤثّر بعض هذه التغييرات فيك على الفور. ومع ذلك، على الرغم من إمكانية وصول تطبيقك إلى بعض الواجهات غير التابعة لحزمة SDK استنادًا إلى مستوى واجهة برمجة التطبيقات المستهدَف في تطبيقك، فإنّ استخدام أي طريقة أو حقل غير تابع لحزمة SDK ينطوي دائمًا على خطر كبير بتعطُّل تطبيقك.
إذا لم تكن متأكدًا مما إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم واجهات غير متوفرة في حزمة SDK، يمكنك اختبار تطبيقك لمعرفة ذلك. إذا كان تطبيقك يعتمد على واجهات غير تابعة لحزمة SDK، عليك البدء في التخطيط لنقل البيانات إلى بدائل حزمة SDK. ومع ذلك، نتفهّم أنّ بعض التطبيقات لديها حالات استخدام صالحة لواجهات غير متوفرة في SDK. إذا لم تتمكّن من العثور على بديل لاستخدام واجهة غير تابعة لحزمة SDK لإحدى الميزات في تطبيقك، عليك طلب واجهة برمجة تطبيقات عامة جديدة.
لمزيد من المعلومات عن التغييرات في هذا الإصدار من Android، اطّلِع على التعديلات على قيود واجهات غير حزمة SDK في Android 15. للاطّلاع على مزيد من المعلومات حول الواجهات غير المتوفّرة في حزمة SDK بشكل عام، اطّلِع على مقالة القيود المفروضة على الواجهات غير المتوفّرة في حزمة SDK.

