Komponen Dialog menampilkan pesan pop-up atau meminta input pengguna di
lapisan di atas konten aplikasi utama. Hal ini menciptakan pengalaman UI yang mengganggu untuk
menarik perhatian pengguna.
Di antara kasus penggunaan untuk dialog adalah sebagai berikut:
- Mengonfirmasi tindakan pengguna, seperti saat menghapus file.
- Meminta input pengguna, seperti di aplikasi daftar tugas.
- Menampilkan daftar opsi untuk pemilihan pengguna, seperti memilih negara dalam penyiapan profil.
Topik ini menyediakan implementasi berikut:
Kompatibilitas versi
Implementasi ini mengharuskan minSDK project Anda ditetapkan ke API level 21 atau yang lebih tinggi.
Dependensi
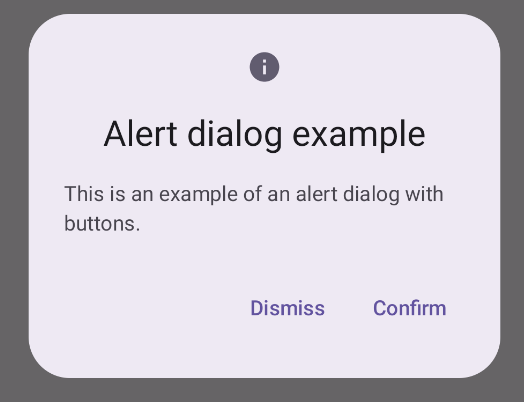
Membuat dialog Pemberitahuan
Composable AlertDialog menyediakan API yang mudah digunakan untuk membuat
dialog bertema Desain Material. Contoh berikut menerapkan dua tombol dalam
dialog pemberitahuan, satu tombol yang menutup dialog, dan tombol lain yang mengonfirmasi
permintaannya:
Implementasi ini menyiratkan composable induk yang meneruskan argumen ke composable turunan dengan cara ini:
Hasil
Poin utama
AlertDialog memiliki parameter khusus untuk menangani elemen dialog tertentu. Di antaranya adalah:
title: Teks yang muncul di sepanjang bagian atas dialog.text: Teks yang muncul di tengah dialog.icon: Grafik yang muncul di bagian atas dialog.onDismissRequest: Fungsi yang dipanggil saat pengguna menutup dialog, seperti dengan mengetuk di luarnya.dismissButton: Composable yang berfungsi sebagai tombol tutup.confirmButton: Composable yang berfungsi sebagai tombol konfirmasi.Saat pengguna mengklik salah satu tombol, dialog akan ditutup. Saat pengguna mengklik konfirmasi, tindakan ini akan memanggil fungsi yang juga menangani konfirmasi. Dalam contoh ini, fungsi tersebut adalah
onDismissRequest()danonConfirmRequest().Jika dialog Anda memerlukan kumpulan tombol yang lebih kompleks, Anda dapat mendapatkan manfaat dari penggunaan composable
Dialogdan mengisinya dengan cara yang lebih bebas.
Membuat dialog
Dialog adalah composable dasar yang tidak menyediakan gaya visual atau
slot standar untuk konten. Ini adalah penampung sederhana yang harus Anda
isi dengan penampung seperti Card. Berikut adalah beberapa parameter utama dialog:
onDismissRequest: Lambda yang dipanggil saat pengguna menutup dialog.properties: InstanceDialogPropertiesyang menyediakan beberapa cakupan tambahan untuk penyesuaian.
Membuat dialog dasar
Contoh berikut adalah implementasi dasar composable Dialog. Perhatikan bahwa kode ini menggunakan Card sebagai penampung sekunder. Tanpa Card, komponen Text
akan muncul sendiri di atas konten aplikasi utama.
Hasil
Perhatikan bahwa saat dialog terbuka, konten aplikasi utama di bawahnya akan menjadi gelap dan berwarna abu-abu:

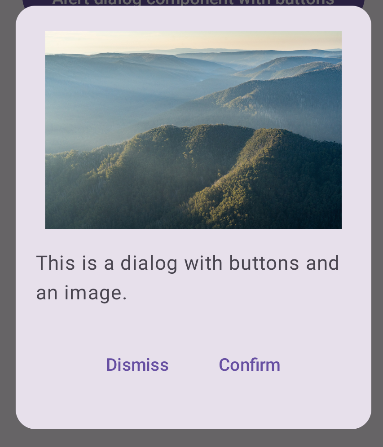
Membuat dialog lanjutan
Berikut adalah implementasi composable Dialog yang lebih canggih. Dalam
hal ini, komponen secara manual menerapkan antarmuka yang serupa dengan contoh
AlertDialog sebelumnya.
Hasil
Koleksi yang berisi panduan ini
Panduan ini adalah bagian dari koleksi Panduan Cepat pilihan yang membahas sasaran pengembangan Android yang lebih luas:

Teks tampilan

Meminta input pengguna




