Die Komponente Dialog zeigt Pop-up-Nachrichten an oder fordert Nutzereingaben in einer Ebene über dem Hauptinhalt der App an. Sie unterbricht die Nutzeroberfläche, um die Aufmerksamkeit der Nutzer zu erregen.
Zu den Anwendungsfällen für einen Dialog gehören:
- Bestätigung von Nutzeraktionen, z. B. beim Löschen einer Datei.
- Nutzereingaben anfordern, z. B. in einer To-do-Liste-App
- Eine Liste von Optionen für die Nutzerauswahl präsentieren, z. B. die Auswahl eines Landes bei der Profileinrichtung.
In diesem Thema werden die folgenden Implementierungen beschrieben:
Versionskompatibilität
Für diese Implementierung muss das minSDK Ihres Projekts auf API-Level 21 oder höher festgelegt sein.
Abhängigkeiten
Dialogfeld „Benachrichtigung erstellen“
Das AlertDialog-Komposit bietet eine praktische API zum Erstellen eines Dialogfelds im Material Design-Design. Im folgenden Beispiel werden zwei Schaltflächen in einem Benachrichtigungsdialogfeld implementiert, eine zum Schließen des Dialogfelds und eine zum Bestätigen der Anfrage:
Diese Implementierung setzt ein übergeordnetes Composeable voraus, das Argumente auf diese Weise an das untergeordnete Composeable übergibt:
Ergebnisse
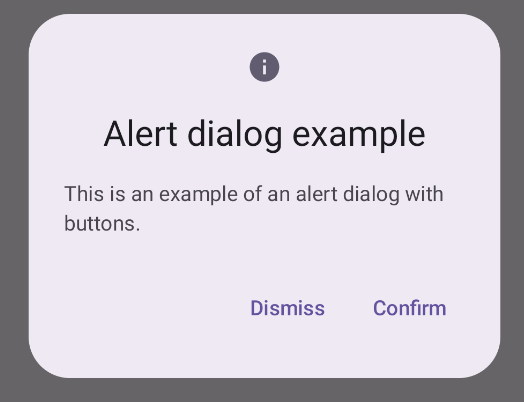
Wichtige Fakten
AlertDialog hat bestimmte Parameter für die Verarbeitung bestimmter Elemente des Dialogs. Dazu gehören:
title: Der Text, der oben im Dialogfeld angezeigt wird.text: Der Text, der mittig im Dialogfeld angezeigt wird.icon: Die Grafik oben im Dialogfeld.onDismissRequest: Die Funktion, die aufgerufen wird, wenn der Nutzer das Dialogfeld schließt, z. B. indem er außerhalb davon tippt.dismissButton: Ein Composeable, das als Schaltfläche zum Schließen dient.confirmButton: Ein Composeable, das als Bestätigungsschaltfläche dient.Wenn der Nutzer auf eine der Schaltflächen klickt, wird das Dialogfeld geschlossen. Wenn der Nutzer auf „Bestätigen“ klickt, wird eine Funktion aufgerufen, die auch die Bestätigung verarbeitet. In diesem Beispiel sind das
onDismissRequest()undonConfirmRequest().Wenn Ihr Dialogfeld eine komplexere Reihe von Schaltflächen erfordert, können Sie die
Dialog-Komponente verwenden und sie freier gestalten.
Dialogfeld erstellen
Dialog ist ein einfaches Composeable, das kein Styling und keine vordefinierten Slots für Inhalte bietet. Es ist ein einfacher Container, den Sie mit einem Container wie Card füllen sollten. Im Folgenden sind einige der wichtigsten Parameter eines Dialogs aufgeführt:
onDismissRequest: Der Lambda-Ausdruck, der aufgerufen wird, wenn der Nutzer das Dialogfeld schließt.properties: Eine Instanz vonDialogProperties, die zusätzliche Möglichkeiten zur Anpassung bietet.
Einfachen Dialog erstellen
Das folgende Beispiel ist eine grundlegende Implementierung des Dialog-Kompositionstyps. Beachten Sie, dass ein Card als sekundärer Container verwendet wird. Ohne die Card würde die Text-Komponente allein über dem Hauptinhalt der App angezeigt werden.
Ergebnis
Wenn das Dialogfeld geöffnet ist, werden die Hauptinhalte der App darunter abgedunkelt und ausgegraut:

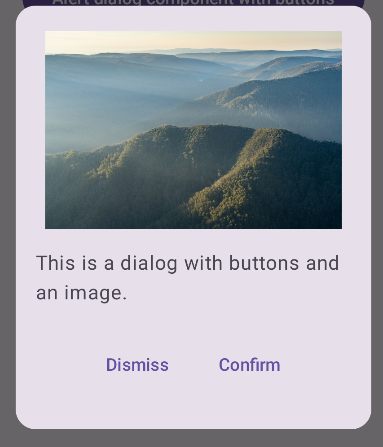
Erweitertes Dialogfeld erstellen
Im Folgenden finden Sie eine erweiterte Implementierung des Dialog-Kompositionstyps. In diesem Fall implementiert die Komponente manuell eine ähnliche Benutzeroberfläche wie im vorherigen AlertDialog-Beispiel.
Ergebnis
Sammlungen, die diesen Leitfaden enthalten
Dieser Leitfaden ist Teil der folgenden ausgewählten Sammlungen von Kurzanleitungen, die allgemeinere Ziele der Android-Entwicklung abdecken:

Anzeigetext

Nutzereingabe anfordern



