Dialog উপাদানটি পপ-আপ বার্তা প্রদর্শন করে বা মূল অ্যাপের বিষয়বস্তুর উপরে একটি স্তরে ব্যবহারকারীর ইনপুট অনুরোধ করে। এটি ব্যবহারকারীর দৃষ্টি আকর্ষণ করার জন্য একটি বাধামূলক UI অভিজ্ঞতা তৈরি করে।
একটি ডায়ালগের জন্য ব্যবহারের ক্ষেত্রে নিম্নলিখিতগুলি হল:
- ব্যবহারকারীর ক্রিয়া নিশ্চিত করা, যেমন একটি ফাইল মুছে ফেলার সময়।
- ব্যবহারকারীর ইনপুট অনুরোধ করা, যেমন একটি করণীয় তালিকা অ্যাপে।
- ব্যবহারকারী নির্বাচনের জন্য বিকল্পগুলির একটি তালিকা উপস্থাপন করা, যেমন একটি প্রোফাইল সেটআপে একটি দেশ বেছে নেওয়া।
এই বিষয় নিম্নলিখিত বাস্তবায়ন প্রদান করে:
সংস্করণ সামঞ্জস্য
এই বাস্তবায়নের জন্য আপনার প্রজেক্ট minSDK এপিআই লেভেল 21 বা তার উপরে সেট করা প্রয়োজন।
নির্ভরতা
একটি সতর্কতা ডায়ালগ তৈরি করুন
AlertDialog composable একটি মেটেরিয়াল ডিজাইন থিমযুক্ত ডায়ালগ তৈরি করার জন্য একটি সুবিধাজনক API প্রদান করে। নিম্নলিখিত উদাহরণটি একটি সতর্কতা ডায়ালগে দুটি বোতাম প্রয়োগ করে, একটি যা ডায়ালগ খারিজ করে এবং অন্যটি এটির অনুরোধ নিশ্চিত করে:
এই বাস্তবায়নটি একটি অভিভাবক কম্পোজেবলকে বোঝায় যা এইভাবে শিশুর কাছে কম্পোজেবল আর্গুমেন্ট পাস করে:
ফলাফল
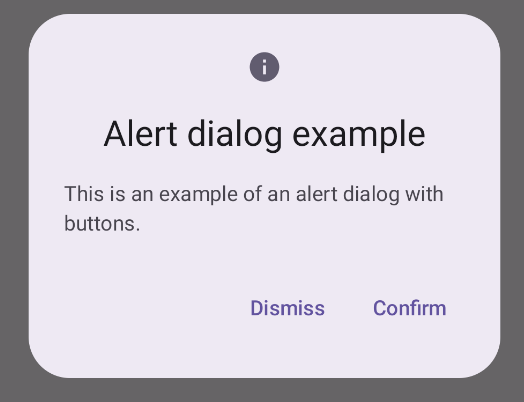
মূল পয়েন্ট
AlertDialog ডায়ালগের নির্দিষ্ট উপাদানগুলি পরিচালনা করার জন্য নির্দিষ্ট পরামিতি রয়েছে। তাদের মধ্যে নিম্নলিখিত:
-
title: ডায়ালগের শীর্ষ বরাবর প্রদর্শিত পাঠ্য। -
text: ডায়ালগের মধ্যে কেন্দ্রীভূত পাঠ্য। -
icon: ডায়ালগের শীর্ষে প্রদর্শিত গ্রাফিক। -
onDismissRequest: ব্যবহারকারী যখন ডায়ালগটি খারিজ করে, যেমন এর বাইরে ট্যাপ করে তখন ফাংশনটিকে বলা হয়। -
dismissButton: একটি সংমিশ্রণযোগ্য যা খারিজ বোতাম হিসাবে কাজ করে। confirmButton: একটি সংমিশ্রণযোগ্য যা নিশ্চিত বোতাম হিসাবে কাজ করে।ব্যবহারকারী যখন যেকোন একটি বোতামে ক্লিক করেন, ডায়ালগটি বন্ধ হয়ে যায়। যখন ব্যবহারকারী নিশ্চিত ক্লিক করে, তখন এটি একটি ফাংশনকে কল করে যা নিশ্চিতকরণ পরিচালনা করে। এই উদাহরণে, সেই ফাংশনগুলি হল
onDismissRequest()এবংonConfirmRequest()।যে ক্ষেত্রে আপনার ডায়ালগের জন্য আরও জটিল সেটের বোতাম প্রয়োজন, আপনি
Dialogকম্পোজেবল ব্যবহার করে এবং এটিকে আরও ফ্রিফর্ম পদ্ধতিতে পপুলেট করে উপকৃত হতে পারেন।
একটি ডায়ালগ তৈরি করুন
Dialog হল একটি মৌলিক রচনা যা সামগ্রীর জন্য কোনো স্টাইলিং বা পূর্বনির্ধারিত স্লট প্রদান করে না। এটি একটি সহজবোধ্য ধারক যা আপনার Card মতো একটি ধারক দিয়ে তৈরি করা উচিত। একটি ডায়ালগের কিছু মূল পরামিতি নিচে দেওয়া হল:
-
onDismissRequest: যখন ব্যবহারকারী ডায়ালগ বন্ধ করে তখন ল্যাম্বডা বলা হয়। -
properties:DialogPropertiesএকটি উদাহরণ যা কাস্টমাইজেশনের জন্য কিছু অতিরিক্ত সুযোগ প্রদান করে।
একটি মৌলিক ডায়ালগ তৈরি করুন
নিম্নলিখিত উদাহরণটি Dialog কম্পোজেবলের একটি মৌলিক বাস্তবায়ন। নোট করুন যে এটি একটি Card সেকেন্ডারি ধারক হিসাবে ব্যবহার করে। Card ছাড়া, মূল অ্যাপের বিষয়বস্তুর উপরে Text উপাদানটি একা প্রদর্শিত হবে।
ফলাফল
মনে রাখবেন যে ডায়ালগ খোলা থাকলে, এর নীচের প্রধান অ্যাপের বিষয়বস্তু অন্ধকার এবং ধূসর দেখায়:

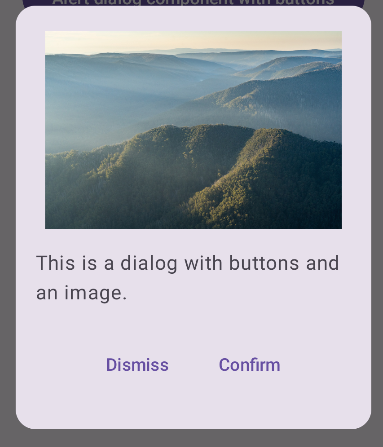
একটি উন্নত ডায়ালগ তৈরি করুন
নিম্নলিখিতটি Dialog কম্পোজেবলের আরও উন্নত প্রয়োগ করা হয়েছে। এই ক্ষেত্রে, উপাদানটি ম্যানুয়ালি পূর্ববর্তী AlertDialog উদাহরণের অনুরূপ ইন্টারফেস প্রয়োগ করে।
ফলাফল
এই নির্দেশিকা ধারণকারী সংগ্রহ
এই নির্দেশিকাটি এই কিউরেট করা কুইক গাইড সংগ্রহের অংশ যা বৃহত্তর অ্যান্ড্রয়েড উন্নয়ন লক্ষ্যগুলি কভার করে:
পাঠ্য প্রদর্শন করুন

ব্যবহারকারীর ইনপুট অনুরোধ করুন




