注意: 2021 年 8 月より、すべての新規アプリは App Bundle として公開する必要があります。アプリを Google Play に公開する場合は、Android App Bundle を作成してアップロードします。こうすることで、各ユーザーのデバイス設定に合わせて最適化された APK が Google Play によって自動的に生成、配信されるため、ユーザーはアプリの実行に必要なコードとリソースをダウンロードするだけで済みます。複数の APK を公開することは、AAB 形式をサポートしていないストアに公開する場合に便利です。その場合は、各 APK のビルド、署名、管理を自分で行う必要があります。
可能であれば常に、すべての対象デバイスをサポートする単一の APK をビルドすることをおすすめしますが、さまざまなアプリケーション バイナリ インターフェース(ABI)をサポートするファイルが原因で、APK のサイズが非常に大きくなることがあります。APK のサイズを小さくする方法の 1 つとして、特定の ABI 用のファイルを含む複数の APK を作成する方法があります。
Gradle では、各 ABI に固有のコードとリソースのみを含む APK を個別に作成できます。このページでは、複数の APK を生成するようにビルドを構成する方法について説明します。ABI に基づかないさまざまなバージョンのアプリを作成する必要がある場合は、代わりにビルド バリアントを使用します。
複数の APK 用のビルドを構成する
複数の APK 用のビルドを構成するには、モジュール レベルの build.gradle ファイルに splits ブロックを追加します。splits ブロック内で、Gradle が ABI ごとの APK を生成する方法を規定する abi ブロックを指定します。
ABI 用の複数の APK の構成
ABI ごとに異なる APK を作成するには、splits ブロックの内側に abi ブロックを追加します。abi ブロックで、希望する ABI のリストを指定します。
各 ABI に複数の APK を構成するには、以下の Gradle DSL オプションを使用します。
-
Groovy の場合は
enable、Kotlin スクリプトの場合はisEnable - この要素を
trueに設定した場合、定義した ABI に基づいて Gradle で複数の APK が生成されます。デフォルト値はfalseです。 -
exclude -
Gradle での APK 生成の対象外の ABI をカンマ区切りのリストで指定します。ほとんどの ABI 用の APK を生成するものの、アプリでサポートしない一部の ABI を除外する必要がある場合は、
excludeを使用します。 -
reset() -
ABI のデフォルトのリストをクリアします。
include要素と組み合わせて、追加したい ABI を指定する場合にのみ使用します。次のスニペットは、
reset()を呼び出してリストをクリアしてからincludeを使用することで、x86とx86_64にのみ ABI のリストを設定しています。reset() // Clears the default list from all ABIs to no ABIs. include "x86", "x86_64" // Specifies the two ABIs we want to generate APKs for.
-
include -
Gradle での APK 生成の対象の ABI をカンマ区切りのリストで指定します。
reset()と組み合わせて ABI の正確なリストを指定する場合にのみ使用します。 -
Groovy の場合は
universalApk、Kotlin スクリプトの場合はisUniversalApk -
trueを指定すると、ABI ごとの APK に加えてユニバーサル APK が Gradle で生成されます。ユニバーサル APK には、1 つの APK にすべての ABI のコードとリソースが含まれます。デフォルト値はfalseです。
次の例では、各 ABI(x86 と x86_64)用の APK を個別に生成しています。そのために、reset() を使用して ABI の空のリストを作成してから、APK をそれぞれ取得する ABI のリストを include で指定しています。
Groovy
android { ... splits { // Configures multiple APKs based on ABI. abi { // Enables building multiple APKs per ABI. enable true // By default all ABIs are included, so use reset() and include to specify that you only // want APKs for x86 and x86_64. // Resets the list of ABIs for Gradle to create APKs for to none. reset() // Specifies a list of ABIs for Gradle to create APKs for. include "x86", "x86_64" // Specifies that you don't want to also generate a universal APK that includes all ABIs. universalApk false } } }
Kotlin
android { ... splits { // Configures multiple APKs based on ABI. abi { // Enables building multiple APKs per ABI. isEnable = true // By default all ABIs are included, so use reset() and include to specify that you only // want APKs for x86 and x86_64. // Resets the list of ABIs for Gradle to create APKs for to none. reset() // Specifies a list of ABIs for Gradle to create APKs for. include("x86", "x86_64") // Specifies that you don't want to also generate a universal APK that includes all ABIs. isUniversalApk = false } } }
サポート対象 ABI のリストについては、サポート対象 ABI をご覧ください。
ネイティブ / C++ コードを含まないプロジェクト
ネイティブ/C++ コードを含まないプロジェクトの場合、[Build Variants] パネルには、図 1 に示すように、[Module] と [Active Build Variant] という 2 つの列が表示されます。
![[ビルド バリアント] パネル](https://developer.android.com/static/studio/images/build/build-variants.png?authuser=8&hl=ja)
図 1. ネイティブ/C++ コードを含まないプロジェクトの場合、[Build Variants] パネルには 2 つの列が表示されます。
モジュールの [Active Build Variant] 値により、デプロイされ、エディタで表示されるビルド バリアントが決定されます。バリアントを切り替えるには、モジュールの [Active Build Variant] セルをクリックし、リスト フィールドから目的のバリアントを選択します。
ネイティブ / C++ コードを含むプロジェクト
ネイティブ/C++ コードを使用するプロジェクトの場合、図 2 に示すように、[Build Variants] パネルには、[Module]、[Active Build Variant]、[Active ABI] の 3 つの列が表示されます。
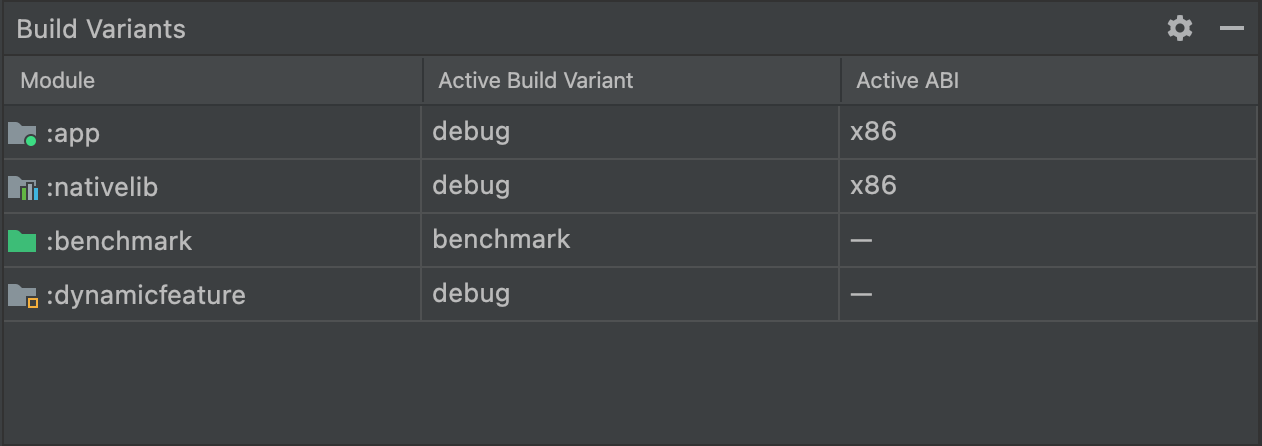 図 2. ネイティブ/C++ コードを含むプロジェクトの場合、[Build Variants] パネルに [Active ABI] 列が追加されます。
図 2. ネイティブ/C++ コードを含むプロジェクトの場合、[Build Variants] パネルに [Active ABI] 列が追加されます。
デプロイされ、エディタに表示されるビルド バリアントは、モジュールの [Active Build Variant] 値によって決定されます。ネイティブ モジュールの場合は、[Active ABI] 値によってエディタが使用する ABI が決定されますが、デプロイされるものには影響しません。
ビルドタイプまたは ABI を変更するには:
- [Active Build Variant] 列または [Active ABI] 列のセルをクリックします。
- リストから目的のバリアントまたは ABI を選択します。新しい同期が自動的に実行されます。
アプリまたはライブラリ モジュールのいずれかの列を変更すると、すべての依存行に変更が適用されます。
バージョン管理の構成
Gradle で複数の APK を生成する場合、デフォルトでは、モジュール レベルの build.gradle ファイルまたは build.gradle.kts ファイルで指定されているバージョン情報がすべての APK に対して適用されます。Google Play ストアでは、同一アプリの複数の APK が同じバージョン情報を持つことは認められていないため、Play ストアにアップロードする前に、各 APK の
versionCode が一意の値になっていることを確認する必要があります。
モジュール レベルの build.gradle ファイルを構成して、各 APK の versionCode をオーバーライドできます。複数の APK を設定する各 ABI に一意の数値を割り当てるマッピングを作成することで、defaultConfig ブロックまたは productFlavors ブロック内で定義されたバージョン コードと ABI に割り当てられた数値を組み合わせた値で出力バージョン コードをオーバーライドできます。
次の例では、x86 ABI の APK には versionCode 2004 が割り当てられ、x86_64 ABI の APK には versionCode 3004 が割り当てられます。
1000 のような増分の大きいバージョン コードを割り当てると、後でアプリの更新が必要になったときに一意のバージョン コードを割り当てることができます。たとえば、その後のアップデートで defaultConfig.versionCode が 5 に進められると、Gradle によって x86 APK には versionCode 2005、x86_64 APK には 3005 が割り当てられます。
ヒント: ビルドにユニバーサル APK が含まれている場合、他のどの APK よりも小さい versionCode を割り当てます。Google Play ストアは、対象デバイスと互換性があり、versionCode が最も大きいアプリのバージョンをインストールするため、小さい versionCode をユニバーサル APK に割り当てることで、Google Play ストアでユニバーサル APK にフォールバックする前に、いずれかの APK がインストールされるようになります。次のサンプルコードは、ユニバーサル APK のデフォルトの versionCode をオーバーライドしないことにより、これに対処しています。
Groovy
android { ... defaultConfig { ... versionCode 4 } splits { ... } } // Map for the version code that gives each ABI a value. ext.abiCodes = ['armeabi-v7a':1, x86:2, x86_64:3] import com.android.build.OutputFile // For each APK output variant, override versionCode with a combination of // ext.abiCodes * 1000 + variant.versionCode. In this example, variant.versionCode // is equal to defaultConfig.versionCode. If you configure product flavors that // define their own versionCode, variant.versionCode uses that value instead. android.applicationVariants.all { variant -> // Assigns a different version code for each output APK // other than the universal APK. variant.outputs.each { output -> // Stores the value of ext.abiCodes that is associated with the ABI for this variant. def baseAbiVersionCode = // Determines the ABI for this variant and returns the mapped value. project.ext.abiCodes.get(output.getFilter(OutputFile.ABI)) // Because abiCodes.get() returns null for ABIs that are not mapped by ext.abiCodes, // the following code doesn't override the version code for universal APKs. // However, because you want universal APKs to have the lowest version code, // this outcome is desirable. if (baseAbiVersionCode != null) { // Assigns the new version code to versionCodeOverride, which changes the // version code for only the output APK, not for the variant itself. Skipping // this step causes Gradle to use the value of variant.versionCode for the APK. output.versionCodeOverride = baseAbiVersionCode * 1000 + variant.versionCode } } }
Kotlin
android { ... defaultConfig { ... versionCode = 4 } splits { ... } } // Map for the version code that gives each ABI a value. val abiCodes = mapOf("armeabi-v7a" to 1, "x86" to 2, "x86_64" to 3) import com.android.build.api.variant.FilterConfiguration.FilterType.* // For each APK output variant, override versionCode with a combination of // abiCodes * 1000 + variant.versionCode. In this example, variant.versionCode // is equal to defaultConfig.versionCode. If you configure product flavors that // define their own versionCode, variant.versionCode uses that value instead. androidComponents { onVariants { variant -> // Assigns a different version code for each output APK // other than the universal APK. variant.outputs.forEach { output -> val name = output.filters.find { it.filterType == ABI }?.identifier // Stores the value of abiCodes that is associated with the ABI for this variant. val baseAbiCode = abiCodes[name] // Because abiCodes.get() returns null for ABIs that are not mapped by ext.abiCodes, // the following code doesn't override the version code for universal APKs. // However, because you want universal APKs to have the lowest version code, // this outcome is desirable. if (baseAbiCode != null) { // Assigns the new version code to output.versionCode, which changes the version code // for only the output APK, not for the variant itself. output.versionCode.set(baseAbiCode * 1000 + (output.versionCode.get() ?: 0)) } } } }
別のバージョン コード スキームの例については、バージョン コードの割り当てをご覧ください。
複数の APK をビルドする
複数の APK をビルドするようにモジュール レベルの build.gradle または build.gradle.kts ファイルを構成したら、[Build] > [Build APK] をクリックして、[Project] ペインで現在選択されているモジュールの APK をすべてビルドします。Gradle は、プロジェクトの build/outputs/apk/ ディレクトリに各 ABI 用の APK を作成します。
Gradle は、複数の APK を構成した ABI ごとに APK をビルドします。
たとえば、次の build.gradle スニペットでは、x86 と x86_64 の ABI に対して複数の APK のビルドが可能です。
Groovy
... splits { abi { enable true reset() include "x86", "x86_64" } }
Kotlin
... splits { abi { isEnable = true reset() include("x86", "x86_64") } }
この例の構成の出力には、以下の 4 つの APK が含まれます。
app-X86-release.apk:x86ABI 専用のコードとリソースが含まれます。app-X86_64-release.apk:x86_64ABI 専用のコードとリソースが含まれます。
ABI に基づいて複数の APK をビルドする場合、build.gradle ファイル(Groovy の場合)の splits.abi ブロックで universalApk true を指定するか、build.gradle.kts ファイル(Kotlin スクリプトの場合)の splits.abi ブロックで isUniversalApk = true を指定すると、Gradle により、すべての ABI 用のコードとリソースを含む APK のみが生成されます。
APK ファイル名の形式
複数の APK をビルドする場合、Gradle は次のスキームの APK ファイル名を生成します。
modulename-ABI-buildvariant.apk
スキームのコンポーネントは次のとおりです。
-
modulename - ビルド対象のモジュール名を指定します。
-
ABI -
ABI 用の複数の APK が有効になっている場合、APK の ABI を指定します(
x86など)。 -
buildvariant -
ビルド対象のビルド バリアントを指定します(
debugなど)。
