Gemini Developer API की मदद से, Google के Gemini मॉडल ऐक्सेस किए जा सकते हैं. इससे आपको अपने Android ऐप्लिकेशन में, जनरेटिव एआई की बेहतरीन सुविधाएँ बनाने में मदद मिलती है. जैसे, बातचीत वाली चैट, इमेज जनरेट करना (Nano Banana की मदद से), और टेक्स्ट, इमेज, ऑडियो, और वीडियो इनपुट के आधार पर टेक्स्ट जनरेट करना.
Gemini Pro और Flash मॉडल को ऐक्सेस करने के लिए, Firebase AI Logic के साथ Gemini Developer API का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. इसकी मदद से, बिना क्रेडिट कार्ड के भी शुरुआत की जा सकती है. साथ ही, इसमें बिना किसी शुल्क के इस्तेमाल की जा सकने वाली कई सुविधाएं उपलब्ध हैं. जब आपको पता चल जाए कि इंटिग्रेशन काम कर रहा है, तब पैसे चुकाकर ली जाने वाली सदस्यता पर स्विच करके, इसे बड़े पैमाने पर इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है.

शुरू करना
अपने ऐप्लिकेशन से सीधे तौर पर Gemini API का इस्तेमाल करने से पहले, आपको कुछ काम करने होंगे. जैसे, प्रॉम्प्ट देने के बारे में जानना. साथ ही, एसडीके का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए Firebase और अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को सेट अप करना.
प्रॉम्प्ट के साथ एक्सपेरिमेंट करना
प्रॉम्प्ट आज़माने से, आपको अपने Android ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए सबसे सही फ़्रेज़, कॉन्टेंट, और फ़ॉर्मैट ढूंढने में मदद मिल सकती है. Google AI Studio एक इंटिग्रेटेड डेवलपमेंट एनवायरमेंट (आईडीई) है. इसका इस्तेमाल, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के इस्तेमाल के उदाहरणों के लिए प्रॉम्प्ट के प्रोटोटाइप बनाने और उन्हें डिज़ाइन करने के लिए किया जा सकता है.
इस्तेमाल के उदाहरण के लिए असरदार प्रॉम्प्ट बनाने में, कई तरह के एक्सपेरिमेंट शामिल होते हैं. यह इस प्रोसेस का एक अहम हिस्सा है. Firebase के दस्तावेज़ में जाकर, प्रॉम्प्ट के बारे में ज़्यादा जानें.
जब आपको लगे कि आपका प्रॉम्प्ट पूरी तरह तैयार है, तो <> बटन पर क्लिक करके कोड स्निपेट पाएं. इन्हें अपने कोड में जोड़ा जा सकता है.
Firebase प्रोजेक्ट सेट अप करना और अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को Firebase से कनेक्ट करना
जब आपका ऐप्लिकेशन एपीआई को कॉल करने के लिए तैयार हो जाए, तब Firebase AI Logic का इस्तेमाल शुरू करने के लिए गाइड में दिए गए "पहला चरण" में दिए गए निर्देशों का पालन करें. इससे आपको अपने ऐप्लिकेशन में Firebase और SDK टूल सेट अप करने में मदद मिलेगी.
Gradle डिपेंडेंसी जोड़ना
अपने ऐप्लिकेशन मॉड्यूल में यह Gradle डिपेंडेंसी जोड़ें:
Kotlin
dependencies { // ... other androidx dependencies // Import the BoM for the Firebase platform implementation(platform("com.google.firebase:firebase-bom:34.9.0")) // Add the dependency for the Firebase AI Logic library When using the BoM, // you don't specify versions in Firebase library dependencies implementation("com.google.firebase:firebase-ai") }
Java
dependencies { // Import the BoM for the Firebase platform implementation(platform("com.google.firebase:34.9.0")) // Add the dependency for the Firebase AI Logic library When using the BoM, // you don't specify versions in Firebase library dependencies implementation("com.google.firebase:firebase-ai") // Required for one-shot operations (to use `ListenableFuture` from Guava // Android) implementation("com.google.guava:guava:31.0.1-android") // Required for streaming operations (to use `Publisher` from Reactive // Streams) implementation("org.reactivestreams:reactive-streams:1.0.4") }
जनरेटिव मॉडल को शुरू करना
GenerativeModel को इंस्टैंशिएट करके और मॉडल का नाम तय करके शुरू करें:
Kotlin
// Start by instantiating a GenerativeModel and specifying the model name: val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()) .generativeModel("gemini-2.5-flash")
Java
GenerativeModel firebaseAI = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI()) .generativeModel("gemini-2.5-flash"); GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(firebaseAI);
Gemini Developer API के साथ इस्तेमाल किए जा सकने वाले उपलब्ध मॉडल के बारे में ज़्यादा जानें. मॉडल पैरामीटर कॉन्फ़िगर करने के बारे में ज़्यादा जानें.
अपने ऐप्लिकेशन से Gemini Developer API का इस्तेमाल करना
SDK टूल का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, Firebase और ऐप्लिकेशन सेट अप करने के बाद, अब आपके पास अपने ऐप्लिकेशन से Gemini Developer API के साथ इंटरैक्ट करने का विकल्प है.
टेक्स्ट जनरेट करना
टेक्स्ट के तौर पर जवाब जनरेट करने के लिए, अपने प्रॉम्प्ट के साथ generateContent() को कॉल करें.
Kotlin
scope.launch { val response = model.generateContent("Write a story about a magic backpack.") }
Java
Content prompt = new Content.Builder() .addText("Write a story about a magic backpack.") .build(); ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(prompt); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { String resultText = result.getText(); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor);
इमेज और अन्य मीडिया से टेक्स्ट जनरेट करना
टेक्स्ट के साथ-साथ इमेज या अन्य मीडिया वाले प्रॉम्प्ट से भी टेक्स्ट जनरेट किया जा सकता है. generateContent() को कॉल करते समय, मीडिया को इनलाइन डेटा के तौर पर पास किया जा सकता है.
उदाहरण के लिए, बिटमैप का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, image कॉन्टेंट टाइप का इस्तेमाल करें:
Kotlin
scope.launch { val response = model.generateContent( content { image(bitmap) text("what is the object in the picture?") } ) }
Java
Content content = new Content.Builder() .addImage(bitmap) .addText("what is the object in the picture?") .build(); ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(content); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { String resultText = result.getText(); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor);
ऑडियो फ़ाइल पास करने के लिए, inlineData कॉन्टेंट टाइप का इस्तेमाल करें:
Kotlin
scope.launch { val contentResolver = applicationContext.contentResolver contentResolver.openInputStream(audioUri).use { stream -> stream?.let { val bytes = it.readBytes() val prompt = content { inlineData(bytes, "audio/mpeg") // Specify the appropriate audio MIME type text("Transcribe this audio recording.") } val response = model.generateContent(prompt) } } }
Java
ContentResolver resolver = applicationContext.getContentResolver(); try (InputStream stream = resolver.openInputStream(audioUri)) { File audioFile = new File(new URI(audioUri.toString())); int audioSize = (int) audioFile.length(); byte[] audioBytes = new byte[audioSize]; if (stream != null) { stream.read(audioBytes, 0, audioBytes.length); stream.close(); // Provide a prompt that includes audio specified earlier and text Content prompt = new Content.Builder() .addInlineData(audioBytes, "audio/mpeg") // Specify the appropriate audio MIME type .addText("Transcribe what's said in this audio recording.") .build(); // To generate text output, call `generateContent` with the prompt ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(prompt); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { String text = result.getText(); Log.d(TAG, (text == null) ? "" : text); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to generate a response", t); } }, executor); } else { Log.e(TAG, "Error getting input stream for file."); // Handle the error appropriately } } catch (IOException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to read the audio file", e); } catch (URISyntaxException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Invalid audio file", e); }
वीडियो फ़ाइल देने के लिए, inlineData कॉन्टेंट टाइप का इस्तेमाल जारी रखें:
Kotlin
scope.launch { val contentResolver = applicationContext.contentResolver contentResolver.openInputStream(videoUri).use { stream -> stream?.let { val bytes = it.readBytes() val prompt = content { inlineData(bytes, "video/mp4") // Specify the appropriate video MIME type text("Describe the content of this video") } val response = model.generateContent(prompt) } } }
Java
ContentResolver resolver = applicationContext.getContentResolver(); try (InputStream stream = resolver.openInputStream(videoUri)) { File videoFile = new File(new URI(videoUri.toString())); int videoSize = (int) videoFile.length(); byte[] videoBytes = new byte[videoSize]; if (stream != null) { stream.read(videoBytes, 0, videoBytes.length); stream.close(); // Provide a prompt that includes video specified earlier and text Content prompt = new Content.Builder() .addInlineData(videoBytes, "video/mp4") .addText("Describe the content of this video") .build(); // To generate text output, call generateContent with the prompt ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(prompt); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { String resultText = result.getText(); System.out.println(resultText); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (URISyntaxException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
इसी तरह, PDF (application/pdf) और सादा टेक्स्ट (text/plain) वाले दस्तावेज़ भी पास किए जा सकते हैं. इसके लिए, उनके MIME टाइप को पैरामीटर के तौर पर पास करें.
एक से ज़्यादा बार की गई बातचीत
इसमें एक से ज़्यादा बार बातचीत करने की सुविधा भी मिलती है. startChat() फ़ंक्शन का इस्तेमाल करके, चैट शुरू करें. मॉडल को मैसेज
इतिहास दिया जा सकता है. हालांकि, यह ज़रूरी नहीं है. इसके बाद, चैट मैसेज भेजने के लिए sendMessage() फ़ंक्शन को कॉल करें.
Kotlin
val chat = model.startChat( history = listOf( content(role = "user") { text("Hello, I have 2 dogs in my house.") }, content(role = "model") { text("Great to meet you. What would you like to know?") } ) ) scope.launch { val response = chat.sendMessage("How many paws are in my house?") }
Java
Content.Builder userContentBuilder = new Content.Builder(); userContentBuilder.setRole("user"); userContentBuilder.addText("Hello, I have 2 dogs in my house."); Content userContent = userContentBuilder.build(); Content.Builder modelContentBuilder = new Content.Builder(); modelContentBuilder.setRole("model"); modelContentBuilder.addText("Great to meet you. What would you like to know?"); Content modelContent = modelContentBuilder.build(); List<Content> history = Arrays.asList(userContent, modelContent); // Initialize the chat ChatFutures chat = model.startChat(history); // Create a new user message Content.Builder messageBuilder = new Content.Builder(); messageBuilder.setRole("user"); messageBuilder.addText("How many paws are in my house?"); Content message = messageBuilder.build(); // Send the message ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = chat.sendMessage(message); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { String resultText = result.getText(); System.out.println(resultText); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor);
Android डिवाइस पर Nano Banana की मदद से इमेज जनरेट करना
Gemini 2.5 Flash Image मॉडल (इसे Nano Banana भी कहा जाता है) में, दुनिया की जानकारी और तर्क का इस्तेमाल करके इमेज जनरेट करने और उनमें बदलाव करने की क्षमता होती है. यह कॉन्टेक्स्ट के हिसाब से इमेज जनरेट करता है. साथ ही, टेक्स्ट और इमेज के आउटपुट को बेहतरीन तरीके से ब्लेंड या इंटरलीव करता है. यह लंबे टेक्स्ट सीक्वेंस के साथ सटीक विज़ुअल भी जनरेट कर सकता है. साथ ही, यह बातचीत के दौरान इमेज में बदलाव करने की सुविधा देता है. हालांकि, इस दौरान इमेज का कॉन्टेक्स्ट नहीं बदलता.
Gemini के बजाय, Imagen मॉडल का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. खास तौर पर, अच्छी क्वालिटी की इमेज जनरेट करने के लिए. इसके लिए, फ़ोटोरियलिज़्म, कलात्मक बारीकी या खास स्टाइल की ज़रूरत होती है. हालांकि, Android ऐप्लिकेशन के क्लाइंट-साइड के ज़्यादातर इस्तेमाल के उदाहरणों के लिए, Gemini काफ़ी होगा.
इस गाइड में, Android के लिए Firebase AI Logic SDK टूल का इस्तेमाल करके, Gemini 2.5 Flash Image मॉडल (Nano Banana) को इस्तेमाल करने का तरीका बताया गया है. Gemini की मदद से इमेज जनरेट करने के बारे में ज़्यादा जानने के लिए, Firebase पर Gemini की मदद से इमेज जनरेट करना लेख पढ़ें. अगर आपको Imagen मॉडल का इस्तेमाल करना है, तो दस्तावेज़ देखें.
जनरेटिव मॉडल को शुरू करना
GenerativeModel को इंस्टैंशिएट करें और मॉडल का नाम gemini-2.5-flash-image-preview डालें. पुष्टि करें कि आपने responseModalities को कॉन्फ़िगर किया हो, ताकि उसमें TEXT और IMAGE, दोनों शामिल हों.
Kotlin
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel( modelName = "gemini-2.5-flash-image-preview", // Configure the model to respond with text and images (required) generationConfig = generationConfig { responseModalities = listOf( ResponseModality.TEXT, ResponseModality.IMAGE ) } )
Java
GenerativeModel ai = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel( "gemini-2.5-flash-image-preview", // Configure the model to respond with text and images (required) new GenerationConfig.Builder() .setResponseModalities(Arrays.asList(ResponseModality.TEXT, ResponseModality.IMAGE)) .build() ); GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(ai);
इमेज जनरेट करना (सिर्फ़ टेक्स्ट वाला इनपुट)
Gemini मॉडल को सिर्फ़ टेक्स्ट वाला प्रॉम्प्ट देकर, इमेज जनरेट करने के लिए कहा जा सकता है:
Kotlin
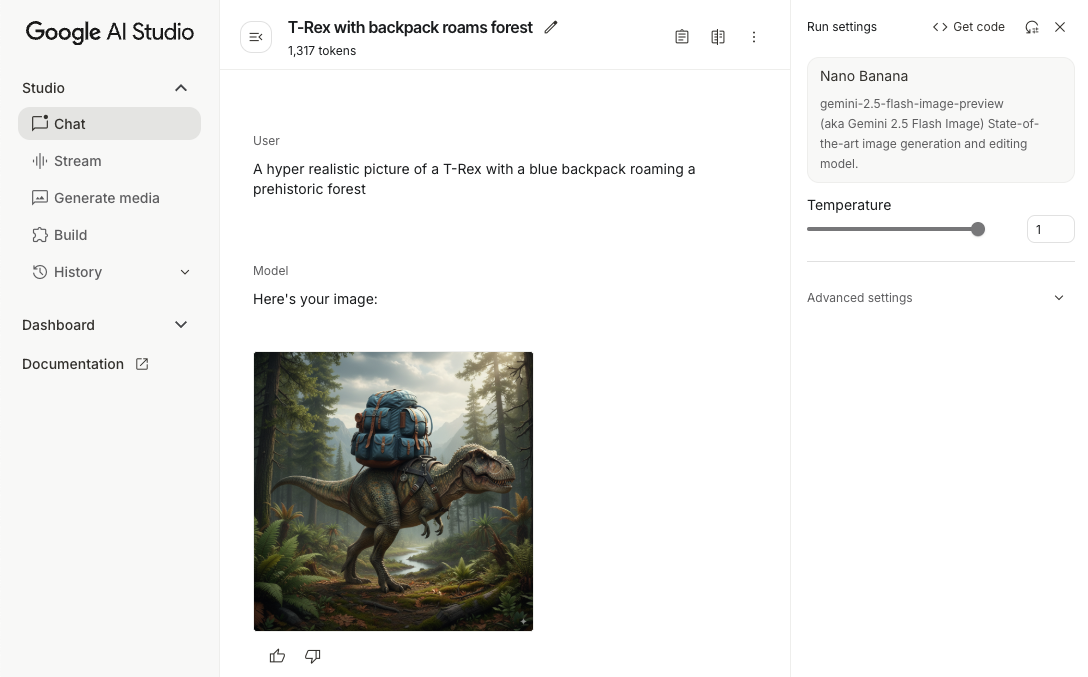
scope.launch { // Provide a text prompt instructing the model to generate an image val prompt = "A hyper realistic picture of a t-rex with a blue bag pack roaming a pre-historic forest." // To generate image output, call `generateContent` with the text input val generatedImageAsBitmap: Bitmap? = model.generateContent(prompt) .candidates.first().content.parts.filterIsInstance<ImagePart>() .firstOrNull()?.image }
Java
// Provide a text prompt instructing the model to generate an image Content prompt = new Content.Builder() .addText("Generate an image of the Eiffel Tower with fireworks in the background.") .build(); // To generate an image, call `generateContent` with the text input ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(prompt); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { // iterate over all the parts in the first candidate in the result object for (Part part : result.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts()) { if (part instanceof ImagePart) { ImagePart imagePart = (ImagePart) part; // The returned image as a bitmap Bitmap generatedImageAsBitmap = imagePart.getImage(); break; } } } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor);
इमेज में बदलाव करना (टेक्स्ट और इमेज इनपुट)
Gemini मॉडल से, मौजूदा इमेज में बदलाव करने के लिए कहा जा सकता है. इसके लिए, अपने प्रॉम्प्ट में टेक्स्ट और एक या उससे ज़्यादा इमेज शामिल करें:
Kotlin
scope.launch { // Provide a text prompt instructing the model to edit the image val prompt = content { image(bitmap) text("Edit this image to make it look like a cartoon") } // To edit the image, call `generateContent` with the prompt (image and text input) val generatedImageAsBitmap: Bitmap? = model.generateContent(prompt) .candidates.first().content.parts.filterIsInstance<ImagePart>().firstOrNull()?.image // Handle the generated text and image }
Java
// Provide an image for the model to edit Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(resources, R.drawable.scones); // Provide a text prompt instructing the model to edit the image Content promptcontent = new Content.Builder() .addImage(bitmap) .addText("Edit this image to make it look like a cartoon") .build(); // To edit the image, call `generateContent` with the prompt (image and text input) ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(promptcontent); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { // iterate over all the parts in the first candidate in the result object for (Part part : result.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts()) { if (part instanceof ImagePart) { ImagePart imagePart = (ImagePart) part; Bitmap generatedImageAsBitmap = imagePart.getImage(); break; } } } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor);
कई बार की बातचीत के ज़रिए, इमेज में बदलाव करना
इमेज एडिटिंग के लिए बातचीत वाली सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, कई बार की जाने वाली चैट का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. इससे, ओरिजनल इमेज को फिर से भेजे बिना, बदलावों को बेहतर बनाने के लिए फ़ॉलो-अप अनुरोध किए जा सकते हैं.
सबसे पहले, startChat() के साथ चैट शुरू करें. इसके लिए, मैसेज का इतिहास भी दिया जा सकता है. इसके बाद, sendMessage() का इस्तेमाल करके मैसेज भेजें:
Kotlin
scope.launch { // Create the initial prompt instructing the model to edit the image val prompt = content { image(bitmap) text("Edit this image to make it look like a cartoon") } // Initialize the chat val chat = model.startChat() // To generate an initial response, send a user message with the image and text prompt var response = chat.sendMessage(prompt) // Inspect the returned image var generatedImageAsBitmap: Bitmap? = response .candidates.first().content.parts.filterIsInstance<ImagePart>().firstOrNull()?.image // Follow up requests do not need to specify the image again response = chat.sendMessage("But make it old-school line drawing style") generatedImageAsBitmap = response .candidates.first().content.parts.filterIsInstance<ImagePart>().firstOrNull()?.image }
Java
// Provide an image for the model to edit Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(resources, R.drawable.scones); // Initialize the chat ChatFutures chat = model.startChat(); // Create the initial prompt instructing the model to edit the image Content prompt = new Content.Builder() .setRole("user") .addImage(bitmap) .addText("Edit this image to make it look like a cartoon") .build(); // To generate an initial response, send a user message with the image and text prompt ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = chat.sendMessage(prompt); // Extract the image from the initial response ListenableFuture<Bitmap> initialRequest = Futures.transform(response, result -> { for (Part part : result.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts()) { if (part instanceof ImagePart) { ImagePart imagePart = (ImagePart) part; return imagePart.getImage(); } } return null; }, executor); // Follow up requests do not need to specify the image again ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> modelResponseFuture = Futures.transformAsync( initialRequest, generatedImage -> { Content followUpPrompt = new Content.Builder() .addText("But make it old-school line drawing style") .build(); return chat.sendMessage(followUpPrompt); }, executor); // Add a final callback to check the reworked image Futures.addCallback(modelResponseFuture, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { for (Part part : result.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts()) { if (part instanceof ImagePart) { ImagePart imagePart = (ImagePart) part; Bitmap generatedImageAsBitmap = imagePart.getImage(); break; } } } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor);
ध्यान रखने वाली बातें और सीमाएं
इन बातों और सीमाओं का ध्यान रखें:
- आउटपुट फ़ॉर्मैट: इमेज, PNG फ़ॉर्मैट में जनरेट होती हैं. इनका डाइमेंशन ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा 1024 पिक्सल होता है.
- इनपुट टाइप: यह मॉडल, इमेज जनरेट करने के लिए ऑडियो या वीडियो इनपुट का इस्तेमाल नहीं करता है.
- भाषा से जुड़ी सहायता: बेहतर परफ़ॉर्मेंस के लिए, इन भाषाओं का इस्तेमाल करें:
अंग्रेज़ी (
en), मेक्सिकन स्पैनिश (es-mx), जापानी (ja-jp), चाइनीज़ (zh-cn), और हिन्दी (hi-in). - जनरेट करने से जुड़ी समस्याएं:
- ऐसा हो सकता है कि इमेज जनरेट करने की सुविधा हमेशा काम न करे. इस वजह से, कभी-कभी सिर्फ़ टेक्स्ट वाला आउटपुट मिलता है. इमेज के तौर पर आउटपुट पाने के लिए, साफ़ तौर पर निर्देश दें. उदाहरण के लिए, "एक इमेज जनरेट करो", "साथ-साथ इमेज उपलब्ध कराओ", "इमेज अपडेट करो".
- ऐसा हो सकता है कि मॉडल, जवाब जनरेट करने के बीच में ही रुक जाए. फिर से कोशिश करें या कोई दूसरा प्रॉम्प्ट आज़माएं.
- मॉडल, टेक्स्ट को इमेज के तौर पर जनरेट कर सकता है. टेक्स्ट के तौर पर जवाब देने के लिए, साफ़ तौर पर निर्देश दें. उदाहरण के लिए, "इमेज के साथ-साथ टेक्स्ट भी जनरेट करो".
ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, Firebase का दस्तावेज़ देखें.
अगले चरण
ऐप्लिकेशन सेट अप करने के बाद, इन बातों का ध्यान रखें:
- GitHub पर, Android Quickstart Firebase सैंपल ऐप्लिकेशन और Android AI सैंपल कैटलॉग देखें.
- अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को प्रोडक्शन के लिए तैयार करें. इसमें Firebase App Check सेट अप करना भी शामिल है, ताकि Gemini API को बिना अनुमति वाले क्लाइंट के गलत इस्तेमाल से बचाया जा सके.
- Firebase के दस्तावेज़ में, Firebase के एआई लॉजिक के बारे में ज़्यादा जानें.
