Android 15 為開發人員推出了強大的新功能和 API。以下各節會簡要說明這些功能,協助您開始使用相關 API。
如需新增、修改及移除 API 的詳細清單,請參閱 API 差異比較表。如要進一步瞭解新增的 API,請參閱 Android API 參考資料 - 針對 Android 15,請尋找 API 級別 35 中新增的 API。如要瞭解平台變更可能對應用程式造成的影響,請務必查看指定 Android 15 的應用程式和所有應用程式的 Android 15 行為變更。
相機和媒體
Android 15 包含多種功能,可提升相機和媒體體驗,並提供工具和硬體,協助創作者在 Android 上實現創意。
如要進一步瞭解 Android 媒體和相機的最新功能和開發人員解決方案,請觀看 Google I/O 的「建構現代 Android 媒體和相機體驗」演講。
低光源增強
Android 15 推出了 低光源增強功能,這是可用於 Camera 2 和 夜間模式相機擴充功能的自動曝光模式。低光源增強功能會在低光源環境中調整預覽串流的曝光量。這與夜間模式相機擴充功能建立靜態圖片的方式不同,因為夜間模式會結合一系列相片,建立單一經過強化的圖片。夜間模式雖然非常適合用於拍攝靜態相片,但無法建立連續的畫面串流,而低光增強功能則可以。因此,低光增強功能可啟用相機功能,例如:
- 提供強化圖片預覽功能,方便使用者在低光源環境下拍攝相片
- 在光線不足的環境下掃描 QR code
啟用低光源增強功能後,系統會在光線較暗時自動開啟,並在光線較強時關閉。
應用程式可以在低光源環境下錄製預覽串流,以便儲存經過調亮的影片。
詳情請參閱「低光增強」。
應用程式內攝影機控制項
Android 15 新增了擴充功能,可進一步控管相機硬體及其在支援裝置上的演算法:
HDR 動態範圍控制
Android 15 會選擇適合底層裝置功能和面板位元深度的 HDR 空間。對於含有大量 SDR 內容的網頁 (例如顯示單一 HDR 縮圖的訊息應用程式),這種行為可能會對 SDR 內容的觀看亮度造成負面影響。在 Android 15 中,您可以使用 setDesiredHdrHeadroom 控制 HDR 空間,以便在 SDR 和 HDR 內容之間取得平衡。
音量控制

Android 15 開始支援 CTA-2075 音量標準,協助您 可避免音訊音量不一致的情況,同時確保使用者不必一直 調整音量。系統會利用輸出裝置 (耳機和喇叭) 的已知特性,以及 AAC 音訊內容提供的音量中繼資料,智慧調整音訊音量和動態範圍壓縮等級。
如要啟用這項功能,請務必確保檔案含有音量中繼資料
您的 AAC 內容,並在應用程式中啟用平台功能。為此,您
透過以下方式將 LoudnessCodecController 物件執行個體化:
呼叫其 create 工廠方法,並與音訊
來自相關聯 AudioTrack 的工作階段 ID;本
系統就會開始自動套用音訊更新您可以傳遞 OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener,藉此修改或篩選音量參數,再套用至 MediaCodec。
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer 也會更新,使用
透過 LoudnessCodecController API 完美整合應用程式。
虛擬 MIDI 2.0 裝置
Android 13 新增了支援功能,可透過 USB 連線至MIDI 2.0 裝置,並透過通用 MIDI 封包 (UMP) 進行通訊。Android 15 將 UMP 支援擴展至虛擬 MIDI 應用程式,讓合成應用程式可透過虛擬 MIDI 2.0 裝置控制合成器應用程式,就像使用 USB MIDI 2.0 裝置一樣。
更有效率的 AV1 軟體解碼

dav1d 是 VideoLAN 推出的熱門 AV1 軟體解碼器,適用於不支援硬體 AV1 解碼功能的 Android 裝置。dav1d 的效能比舊版 AV1 軟體解碼器高出 3 倍,可讓更多使用者 (包括部分低階和中階裝置) 播放 HD AV1 影片。
您的應用程式必須透過名稱 "c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder" 呼叫 dav1d,才能選擇使用 dav1d。在後續更新中,dav1d 將成為預設的 AV1 軟體解碼器。這項支援功能已標準化,並向後移植至接收 Google Play 系統更新的 Android 11 裝置。
開發人員工作效率和工具
我們致力於提升您的工作效率,因此大部分工作都圍繞著 Android Studio、Jetpack Compose 和 Android Jetpack 程式庫等工具進行,但我們也不斷尋找平台上的各種方法,協助您更輕鬆地實現願景。
OpenJDK 17 更新
Android 15 持續更新 Android 核心程式庫,以便與最新版 OpenJDK LTS 中的功能保持一致。
這次更新包含以下重點功能和改善項目:
- 改善 NIO 緩衝區的使用體驗
- 串流
- 其他
math和strictmath方法 util套件更新,包括依序的collection、map和setByteBuffer在Deflater中的支援- 安全性更新,例如
X500PrivateCredential和安全性金鑰更新
這些 API 會透過 Google Play 系統更新,在搭載 Android 12 (API 級別 31) 以上版本的 10 億部裝置上進行更新,因此您可以指定最新的程式設計功能。
PDF 改善
Android 15 對 PdfRenderer 進行了大幅改善。
相互整合應用程式可導入轉譯等進階功能
受密碼保護的檔案、註解、表單編輯、
搜尋及選取副本。支援線性化 PDF 最佳化功能,可加快本機 PDF 檢視速度並減少資源使用量。Jetpack PDF 程式庫會使用這些 API,簡化在應用程式中新增 PDF 檢視功能的程序。
PdfRenderer 已移至可透過 Google Play 系統更新進行更新的模組,不受平台版本影響。我們會透過建立與 Android 15 以下版本相容的 API 途徑 (稱為 PdfRendererPreV),將這些變更回溯至 Android 11 (API 級別 30)。
自動切換語言的改良功能
Android 14 在音訊中新增了裝置端多語言辨識功能,可自動切換語言,但這可能會導致字詞遺漏,尤其是在兩次發音之間的暫停時間較短時。Android 15 新增了額外控制項,協助應用程式根據用途調整此切換功能。EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS 會將自動切換限制在音訊工作階段的開頭,而 EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES 會在指定次數的切換後停用語言切換功能。如果您預期在工作階段中會使用單一語言,且該語言應自動偵測,這些選項就特別實用。
改良 OpenType 變數字型 API
Android 15 改善了 OpenType 變數字型的可用性。您可以建立
來自變數字型的 FontFamily 例項,但未指定粗軸
與 buildVariableFamily API 互動文字轉譯器會覆寫這個值
配合顯示文字。wght 軸。
使用 API 可大幅簡化建立 Typeface 的程式碼:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
先前,如要建立相同的 Typeface,您需要使用更多程式碼:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
以下範例說明使用舊版和新版 API 建立的 Typeface 如何算繪:
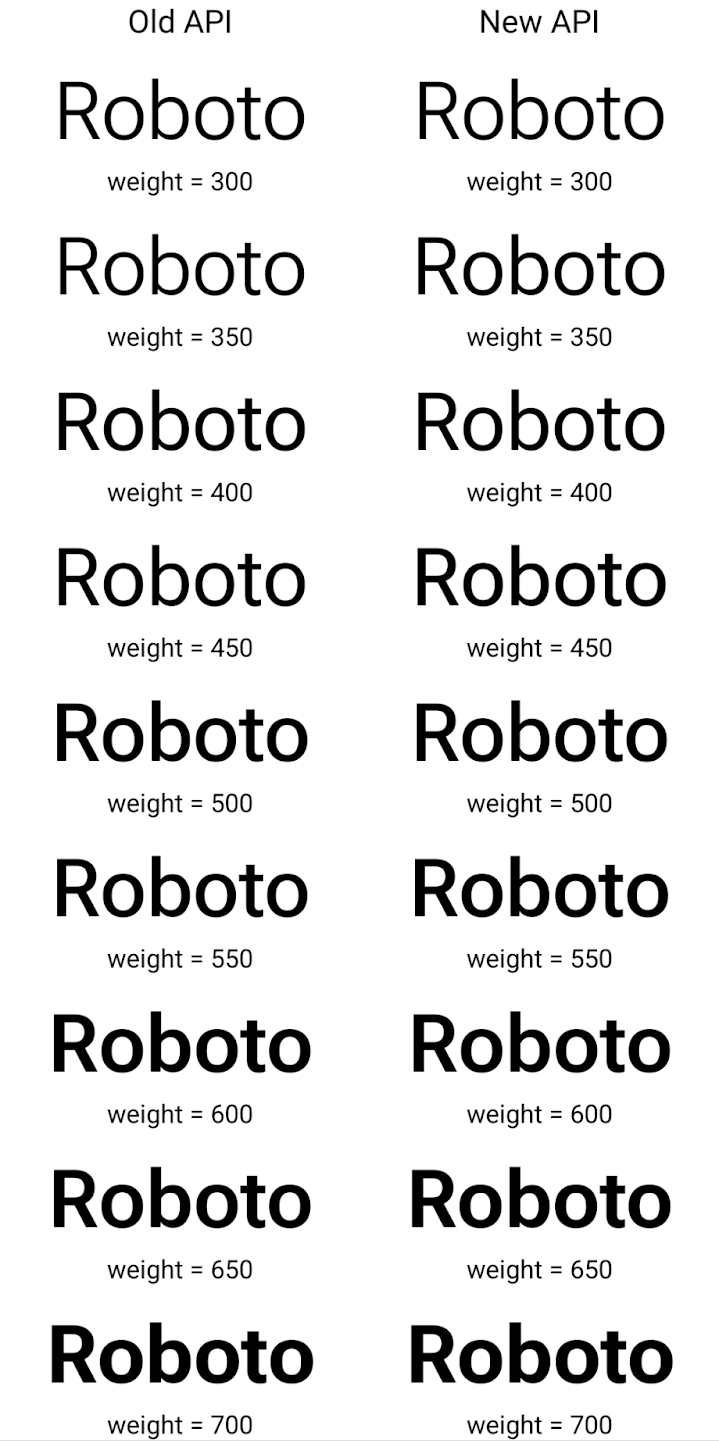
在這個範例中,使用舊版 API 建立的 Typeface 無法為 350、450、550 和 650 Font 例項建立準確的字型粗細,因此轉譯器會改用最接近的粗細。如此
那麼轉譯值會是 300 而不是 350,而是顯示 400,而非 450;且
依此類推相反地,使用新 API 建立的 Typeface 會以動態方式建立
指定權重的 Font 例項,因此會以 350 為單位呈現準確的權重
450、550 和 650。
精細的換行符號控制選項
從 Android 15 開始,TextView 和基礎的斷行元件可保留文字的指定部分,以便在同一行中顯示,藉此改善可讀性。您可以在字串資源或 createNoBreakSpan 中使用 <nobreak> 標記,充分利用這項換行自訂功能。同樣地,您也可以使用 <nohyphen> 標記或 createNoHyphenationSpan,避免系統斷字。
舉例來說,下列字串資源未包含換行符號,因此在顯示「Pixel 8 Pro」時,文字會在不適當的位置中斷:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
相反地,這個字串資源包含 <nobreak> 標記,可將「Pixel 8 Pro」這個詞組包起來,並防止換行:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
下圖顯示這些字串的算繪方式差異:

<nobreak> 標記包裝「Pixel 8 Pro」詞組的一行文字版面配置。
<nobreak> 標記包裝。封存應用程式
Android 和 Google Play 去年宣布支援應用程式封存功能,使用者可以在 Google Play 上使用 Android App Bundle 發布的應用程式,從裝置上部分移除不常使用的應用程式,藉此釋出空間。Android 15 提供應用程式封存和解封存的作業系統層級支援功能,讓所有應用程式商店更輕鬆地實作這項功能。
具有 REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES 權限的應用程式可以呼叫
PackageInstaller requestArchive 方法,要求封存
已安裝的應用程式套件,會移除 APK 和任何快取檔案,但會保留
使用者資料。系統會透過
LauncherApps API;使用者會看到 UI 樣式,藉此突顯這些
個應用程式已封存。使用者輕觸封存的應用程式時,負責的安裝程式
會收到取消封存的要求,而且還原程序可以
由 ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED 廣播監控。
使用開發人員選項在裝置上啟用 16 KB 模式
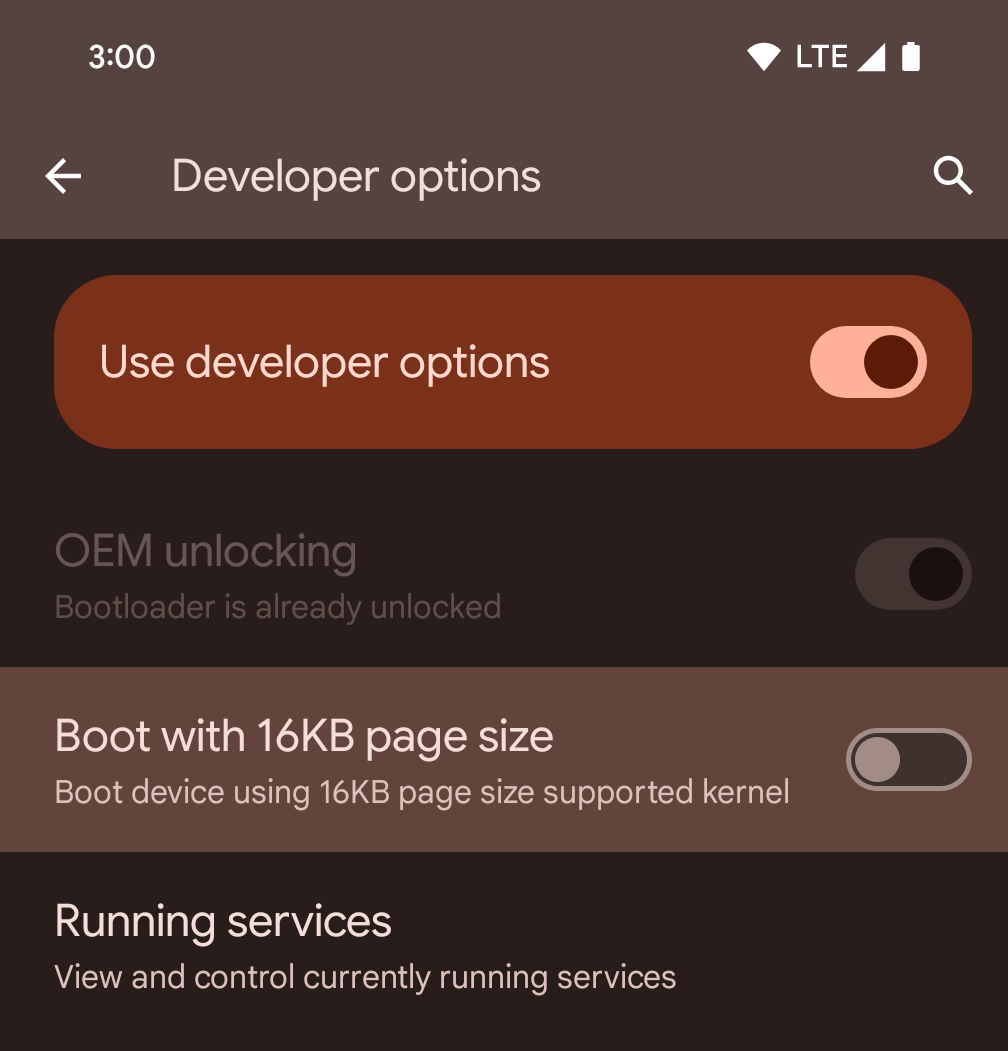
切換「以 16KB 頁面大小啟動」開發人員選項,即可在 16 KB 模式下啟動裝置。
在 Android 15 的 QPR 版本中,您可以使用特定裝置上的開發人員選項,以 16 KB 模式啟動裝置,並執行裝置端測試。使用開發人員選項前,請依序前往「設定」>「系統」>「軟體更新」,並套用所有可用的更新。
下列裝置提供這項開發人員選項:
Pixel 8 和 8 Pro (搭載 Android 15 QPR1 以上版本)
Pixel 8a (搭載 Android 15 QPR1 以上版本)
Pixel 9、Pixel 9 Pro 和 Pixel 9 Pro XL (搭載 Android 15 QPR2 以上版本)
Pixel 9a (搭載 Android 16 以上版本)
圖形
Android 15 帶來最新的圖像改善項目,包括 ANGLE 和 Canvas 圖像系統的增強功能。
更新 Android 的 GPU 存取權

與早期核心作業系統會在單一 CPU 上執行,並使用以固定函式管道為基礎的 API 存取 GPU 不同,Android 硬體已大幅進化。自 Android 7.0 (API 級別 24) 起,NDK 就提供 Vulkan® 圖形 API,其中包含低階抽象化功能,可更貼近現代 GPU 硬體、更有效地支援多個 CPU 核心,並減少 CPU 驅動程式額外負擔,進而提升應用程式效能。所有新型遊戲引擎都支援 Vulkan。
Vulkan 是 Android 對 GPU 的偏好介面。因此,Android 15 包含 ANGLE 做為可選的圖層,可在 Vulkan 上執行 OpenGL® ES。改用 ANGLE 可將 Android OpenGL 實作標準化,進而改善相容性,在某些情況下還能提升效能。您可以在 Android 15 上依序前往「設定」->「系統」->「開發人員選項」->「實驗功能:啟用 ANGLE」,啟用開發人員選項,藉此使用 ANGLE 測試 OpenGL ES 應用程式的穩定性和效能。
Android ANGLE 的 Vulkan 時程表
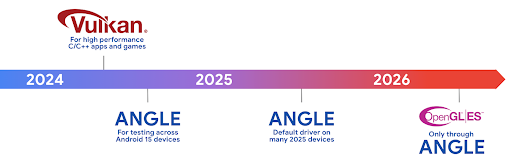
為了簡化 GPU 堆疊,我們日後會在更多新裝置上提供 ANGLE 做為 GL 系統驅動程式,並預期 OpenGL/ES 日後只會透過 ANGLE 提供。不過,我們計劃繼續在所有裝置上支援 OpenGL ES。
建議採取的後續步驟
使用開發人員選項選取 OpenGL ES 的 ANGLE 驅動程式,並測試應用程式。對於新專案,我們強烈建議使用 Vulkan 開發 C/C++。
Canvas 改善項目
Android 15 持續將 Android 的 Canvas 圖形系統改良為現代化版本,並提供額外功能:
Matrix44提供 4x4 矩陣,用於轉換座標,您應在 3D 中操控畫布時使用此矩陣。clipShader會將目前的短片與指定的著色器相交,而clipOutShader會將短片設為目前的短片與著色器的差異,並將每個著色器視為 Alpha 遮罩。這可有效繪製複雜的形狀。
效能和電池
Android 持續致力於協助您提升應用程式的效能和品質。Android 15 導入的 API 可協助您更有效率地執行應用程式中的工作、提升應用程式效能,以及收集應用程式的洞察資訊。
如要瞭解省電最佳做法、如何偵錯網路和耗電量,以及我們如何在 Android 15 和近期 Android 版本中提升背景作業的省電效率,請參閱 Google I/O 的「提升 Android 背景作業的省電效率」演講。
ApplicationStartInfo API
在先前的 Android 版本中,應用程式啟動過程一直是個謎。在應用程式中判斷應用程式是否從冷、暖或熱狀態啟動,是一項挑戰。您也難以瞭解應用程式在各個啟動階段 (分支程序、呼叫 onCreate、繪製第一個影格等) 花費的時間。在 Application 類別例項化時,您無法得知應用程式是從廣播、內容供應器、工作、備份、啟動完成、鬧鐘或 Activity 啟動。
Android 15 的 ApplicationStartInfo API 提供上述所有功能,甚至更多。您甚至可以選擇在流程中加入自己的時間戳記,方便集中收集時間資料。除了收集指標,您也可以使用 ApplicationStartInfo 直接改善應用程式啟動效能。舉例來說,如果應用程式因廣播而啟動,您可以避免在 Application 類別中執行與 UI 相關的程式庫例項,以免造成不必要的負擔。
應用程式大小詳細資訊
自 Android 8.0 (API 級別 26) 起,Android 已納入 StorageStats.getAppBytes API,可將應用程式的安裝大小以單一位元組數字做為總和,包括 APK 大小、從 APK 擷取的檔案大小,以及裝置上產生的檔案 (例如預先編譯 (AOT) 的編譯程式碼)。就應用程式使用儲存空間的方式而言,這個數字並沒有太多洞察資訊。
Android 15 新增了 StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]) API,可讓您深入瞭解應用程式如何使用所有空間,包括 APK 檔案分割、AOT 和加速相關程式碼、DEX 中繼資料、程式庫和引導設定檔。
應用程式管理的剖析
Android 15 包含 ProfilingManager 類別,可讓您從應用程式內收集剖析資訊,例如記憶體快照資料、記憶體快照資料、堆疊取樣等。它會為您的應用程式提供回呼,並提供標記來識別輸出檔案,該檔案會傳送至應用程式的檔案目錄。API 會實施頻率限制,盡可能降低對效能的影響。
如要簡化應用程式中的剖析要求建構程序,建議您使用對應的 Profiling AndroidX API (適用於 Core 1.15.0-rc01 以上版本)。
SQLite 資料庫改善項目
Android 15 推出 SQLite API,可公開基礎 SQLite 引擎的進階功能,針對應用程式可能出現的特定效能問題進行調整。這些 API 已隨 SQLite 更新至 3.44.3 版一併提供。
開發人員應參考提升 SQLite 效能的最佳做法 充分運用 SQLite 資料庫,尤其是處理大型資料集時 或執行容易受到延遲時間影響的查詢時
- 唯讀延遲交易:在發出唯讀交易 (不包含寫入陳述式) 時,請使用
beginTransactionReadOnly()和beginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)發出唯讀DEFERRED交易。這類交易可以同時執行,如果資料庫處於 WAL 模式,則可以與IMMEDIATE或EXCLUSIVE交易同時執行。 - 資料列計數與 ID:新增了 API 以擷取已變更的計數
資料列或上次插入的資料列 ID,且無須發出額外查詢。
getLastChangedRowCount()會傳回資料列數量 最新的 SQL 陳述式已插入、更新或刪除 目前交易,而getTotalChangedRowCount()會傳回目前連線的計數。getLastInsertRowId()會傳回要在目前連線中插入的最後一列的rowid。 - 原始陳述式:發布原始 SQlite 陳述式,略過便利性 以及可能會產生的任何額外處理負擔。
Android 動態效能架構更新
Android 15 持續投入 Android 動態效能架構 (ADPF),這組 API 可讓遊戲和需要耗用大量效能執行的應用程式,直接與 Android 裝置的電力和熱溫系統互動。在支援的裝置上,Android 15 新增 ADPF 功能:
- 提供提示工作階段的省電模式,用來指出相關聯的執行緒應以省電為優先,而非效能,非常適合長時間執行的背景工作負載。
- GPU 和 CPU 工作時間長度都能在提示工作階段中回報,讓系統同時調整 CPU 和 GPU 頻率,以最佳方式滿足工作負載需求。
- 熱力上升空間閾值:根據上升空間預測結果,解讀可能的熱力限制狀態。
如要進一步瞭解如何在應用程式和遊戲中使用 ADPF,請參閱說明文件。
隱私權
Android 15 包含多種功能,可協助應用程式開發人員保護使用者隱私權。
螢幕錄影偵測
Android 15 新增支援應用程式,偵測出 。每當應用程式在螢幕錄影中從可見轉為不可見,系統就會叫用回呼。如果系統正在記錄註冊程序的 UID 所擁有的活動,就會將應用程式視為可見。這樣一來,如果應用程式執行敏感作業,您就可以通知使用者正在進行錄影。
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
擴充 IntentFilter 功能
Android 15 版本內建支援透過 UriRelativeFilterGroup 更精確地解析 Intent,其中包含一組 UriRelativeFilter 物件,可形成一組必須滿足的 Intent 比對規則,包括網址查詢參數、網址片段,以及封鎖或排除規則。
您可以在 AndroidManifest XML 檔案中使用 <uri-relative-filter-group> 標記定義這些規則,並視需要納入 android:allow 標記。這些標記可包含使用現有資料標記屬性的 <data> 標記,以及 android:query 和 android:fragment 屬性。
以下是 AndroidManifest 語法範例:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
私人空間
使用者可透過私人空間在裝置上建立獨立空間,在多一層驗證機制下,隱藏敏感應用程式,防止他人窺探。私人空間會使用個別的使用者設定檔。使用者可以選擇使用裝置鎖定或專屬的鎖定因素來解鎖私人空間。
私人空間中的應用程式會顯示在啟動器的獨立容器中,並在私人空間鎖定時,隱藏在近期使用畫面、通知、設定和其他應用程式中。使用者產生和下載的內容 (例如媒體或檔案) 和帳戶會在私人空間和主空間之間分開。在私人空間解鎖後,您可以使用系統 Sharesheet 和相片挑選工具,讓應用程式存取不同空間的內容。
使用者無法將現有應用程式和相關資料移至私人空間。相反地,使用者可在私人空間中選取安裝選項,然後使用所需的應用程式商店安裝應用程式。私人空間中的應用程式會以個別副本的形式安裝,與主要空間中的任何應用程式不同 (同一個應用程式的新副本)。
使用者鎖定私人空間時,系統會停止設定檔。設定檔停止時,私人空間中的應用程式就會停止運作,無法執行前景或背景活動,包括顯示通知。
建議您使用私人空間測試應用程式,確保應用程式能正常運作,尤其是如果您的應用程式屬於下列任一類別:
- 應用程式包含工作資料夾的邏輯,假設應用程式的任何已安裝副本 (不在主要資料夾中) 都位於工作資料夾中。
- 醫療應用程式
- 啟動器應用程式
- 應用程式商店應用程式
查詢「所選相片存取權」的最新使用者選取項目
現在應用程式只能醒目顯示最近選取的相片和影片
授予媒體的部分存取權。這項功能可改善經常要求存取相片和影片存取權的應用程式使用者體驗。如要在應用程式中使用這項功能,請啟用
查詢 MediaStore 時有 QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY 引數
透過 ContentResolver 關閉通知。
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Android 版 Privacy Sandbox
Android 15 包含最新的 Android Ad Services 擴充功能,其中整合了 Android 版 Privacy Sandbox 的最新版本。這項新增功能是我們開發新技術的一部分,旨在強化使用者隱私,並在行動應用程式中提供有效的個人化廣告體驗。我們的 Privacy Sandbox 頁面提供 Android 版 Privacy Sandbox 開發人員預覽版和 Beta 版計畫的更多資訊,協助您開始使用。
Health Connect
Android 15 整合了 Health Connect by Android 的最新擴充功能,這是一個安全且集中式的平台,可用於管理及分享應用程式收集的健康與健身資料。這次更新新增了健身、營養、皮膚溫度、訓練計畫等其他資料類型的支援。
皮膚溫度追蹤功能可讓使用者透過穿戴式裝置或其他追蹤裝置,儲存及分享更準確的溫度資料。
訓練計畫是結構化的運動計畫,可協助使用者達成健身目標。訓練計畫支援各種完成和表現目標:
如要進一步瞭解 Android 中的 Health Connect 最新更新,請觀看 Google I/O 大會的 透過 Android 健康資料建構可調整的體驗演講。
應用程式分享螢幕畫面
Android 15 支援應用程式畫面分享功能,因此使用者可以只分享或錄製應用程式視窗,而非整個裝置畫面。這項功能最初是在 Android 14 QPR2 中啟用,其中包含 MediaProjection 回呼,可讓應用程式自訂應用程式螢幕分享體驗。請注意,如果應用程式指定 Android 14 (API 級別 34) 以上版本,則每個 MediaProjection 擷取工作階段都需要使用者同意。
使用者體驗和系統 UI
Android 15 可讓應用程式開發人員和使用者進一步控管及彈性設定裝置,以符合自身需求。
如要進一步瞭解如何運用 Android 15 的最新改善項目,提升應用程式的使用者體驗,請觀看 Google I/O 的「改善 Android 應用程式的使用者體驗」演講。
使用 Generated Previews API 取得更豐富的小工具預覽畫面
在 Android 15 之前,您只能指定 靜態圖片或版面配置資源。這些預覽畫面通常與實際小工具放置在主畫面時的外觀大不相同。此外,您無法使用 Jetpack Glance 建立靜態資源,因此 Glance 開發人員必須截取小工具的螢幕截圖,或建立 XML 版面配置,才能預覽小工具。
Android 15 開始支援產生的預覽畫面。這表示應用程式小工具供應者可以產生 RemoteViews,用於取用器預覽畫面,而非靜態資源。
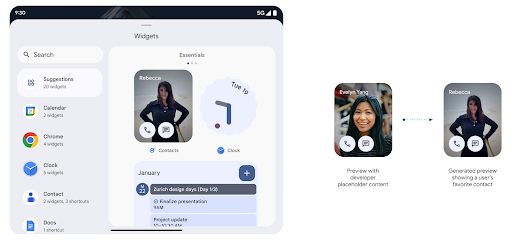
推送 API
應用程式可以透過推送 API 提供產生的預覽畫面。應用程式可以在生命週期的任何時間點提供預覽畫面,且不會收到來自主機的明確要求,要求提供預覽畫面。預覽會保存在 AppWidgetService 中。
主機則可隨選要求叢集以下範例會載入 XML 小工具
版面配置資源並將其設為預覽:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
預期的流程如下:
- 小工具提供者隨時都會呼叫
setWidgetPreview。提供的 預覽內容會連同其他供應商資訊保留在AppWidgetService中。 setWidgetPreview會透過AppWidgetHost.onProvidersChanged回呼通知主機已更新的預覽畫面。做為回應 主機重新載入所有供應商資訊。- 在顯示小工具預覽畫面時,主機會檢查
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories,以及 類別可供使用,呼叫AppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreview到 會傳回這個供應商的儲存預覽畫面。
何時呼叫 setWidgetPreview
由於沒有回呼可提供預覽畫面,應用程式可以在執行期間隨時選擇傳送預覽畫面。預覽畫面的更新頻率取決於小工具的用途。
以下清單說明預先發布版用途的兩大類別:
- 供應商在小工具預覽畫面中顯示實際資料,例如個人化資料 或最新資訊這些供應商可在使用者登入或在應用程式中完成初始設定後,設定預覽畫面。之後,他們可以設定定期執行的作業,以所選頻率更新預覽畫面。例如相片、日曆、天氣或新聞
- 在預覽畫面中顯示靜態資訊,或在快速操作小工具中不顯示任何資料的供應商。這些供應商可以在應用程式首次啟動時設定預覽畫面。例如快速開車 動作小工具或 Chrome 捷徑小工具
部分供應商可能會在中心模式挑選器中顯示靜態預覽畫面,但實際上 主畫面上挑選器的資訊。這些供應商應依照這兩種用途設定預覽畫面。
子母畫面
Android 15 引進了子母畫面 (PiP) 的變更,確保進入 PiP 模式時的轉換更加流暢。這對在主要 UI 上疊加 UI 元素的應用程式而言十分有用,因為這些元素會進入 PiP。
開發人員使用 onPictureInPictureModeChanged 回呼來定義邏輯
可切換重疊 UI 元素的顯示設定。這個回呼為
子母畫面進入或離開動畫播放完畢時觸發。開始時間倒數計時
Android 15 的 PictureInPictureUiState 類別包含其他狀態。
透過此 UI 狀態,指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 的應用程式將觀察
透過以下方式叫用 Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged 回呼:
isTransitioningToPip()。另有
在子母畫面模式下,許多與應用程式無關的 UI 元素,
包含建議、即將推出
影片、評分和標題當應用程式進入子母畫面模式時,請使用
使用 onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged 回呼隱藏這些 UI 元素。當
應用程式從子母畫面視窗進入全螢幕模式,並使用
用來取消隱藏這些元素的 onPictureInPictureModeChanged 回呼,如
下列範例:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
針對 PiP 視窗,快速切換不相關的 UI 元素可確保 PiP 進入動畫更流暢,且不會閃爍。
更完善的「零打擾」規則
AutomaticZenRule 可讓應用程式自訂注意力
管理 (請勿打擾) 規則,並決定何時啟用或停用
具體做法是指示 Kubernetes 建立並維護
一或多個代表這些 Pod 的物件Android 15 大幅強化上述規則,目標是改善
使用者體驗包含以下強化項目:
- 將類型新增至
AutomaticZenRule,讓系統套用特殊類型 來處理部分規則 - 將圖示新增至
AutomaticZenRule,讓模式更容易辨識。 - 將
triggerDescription字串新增至AutomaticZenRule,用來描述 規則對使用者的有效條件 - 已新增
ZenDeviceEffects敬上 到AutomaticZenRule,允許規則觸發灰階等事件 顯示螢幕、夜間模式,或是調暗桌布
為通知管道設定 VibrationEffect
Android 15 支援使用 NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect 為特定管道設定豐富的震動效果,讓使用者不必查看裝置,就能區分不同類型的通知。
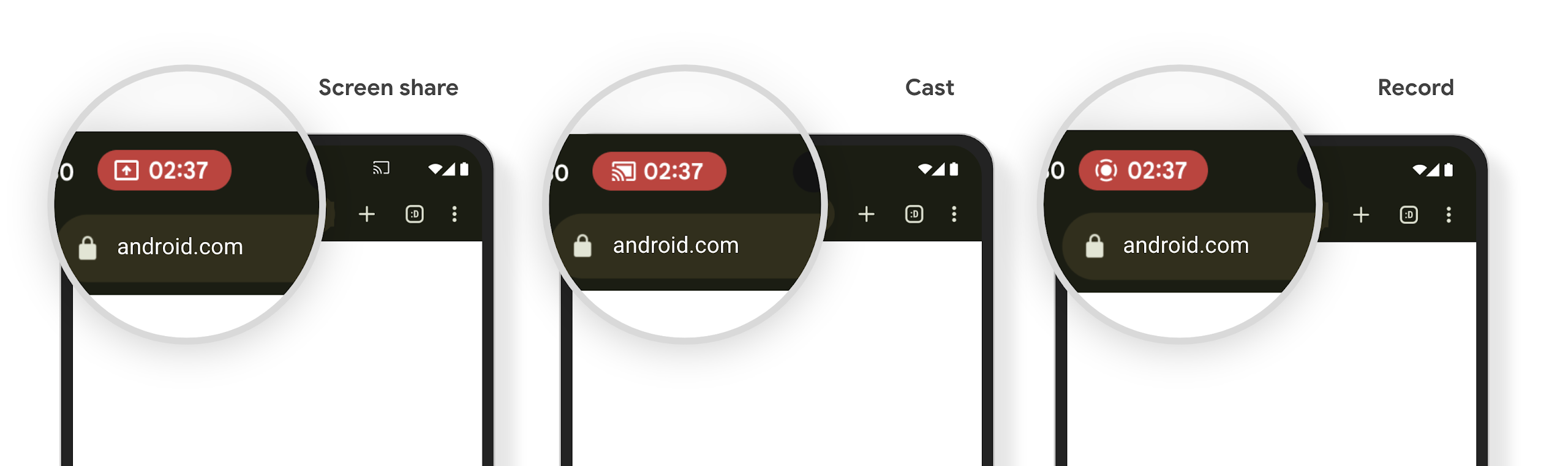
媒體投影狀態列晶片和自動停止
媒體投影功能可能會揭露使用者的私人資訊。新的醒目狀態列方塊可讓使用者瞭解任何正在進行的螢幕投影作業。使用者可以輕觸方塊停止投放、分享或錄製螢幕畫面。此外,為了提供更直覺的使用者體驗,現在裝置螢幕鎖定時,任何進行中的螢幕投影作業都會自動停止。
大螢幕和板型規格
Android 15 可讓應用程式充分運用 Android 的板型規格,包括大螢幕、可翻轉和折疊式裝置。
改善大螢幕多工處理功能
Android 15 可讓使用者在大螢幕裝置上更妥善地進行多工處理。適用對象 舉例來說,使用者可以儲存喜愛的分割畫面應用程式組合,以便快速 ,並將工作列固定在畫面上,即可快速切換應用程式。也就是說 確保應用程式會自動調適,比以往更重要。
Google I/O 大會建構可自動調整的 Android 環境 應用程式以及使用 Material 3 建構使用者介面 自動調整程式庫 這能幫助您,而我們的說明文件也更勝以往,能進一步協助您運用大型語言設計 螢幕。
支援封面螢幕
應用程式可以宣告 Android 15 使用的屬性,讓 Application 或 Activity 顯示在支援翻轉裝置的小型封面螢幕上。這些螢幕太小,無法視為 Android 應用程式可執行的相容目標,但您的應用程式可以選擇支援這些螢幕,讓應用程式可在更多地方使用。
連線能力
Android 15 更新了平台,讓您的應用程式能使用通訊和無線技術的最新進展。
衛星支援
Android 15 持續擴大平台支援範圍,包括衛星連線,以及 包含一些 UI 元素,確保 衛星連線環境。
應用程式可以使用 ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() 執行下列操作:
會偵測裝置是否與衛星連線
可能無法使用完整網路服務的原因此外,Android 15
支援簡訊和多媒體訊息應用程式,以及預先載入的 RCS 應用程式
可以收發訊息的衛星連線。
更流暢的 NFC 體驗
Android 15 正在努力讓輕觸付款體驗更流暢可靠,同時繼續支援 Android 強大的 NFC 應用程式生態系統。在支援的裝置上,應用程式可以要求 NfcAdapter 進入觀察模式,在該模式下,裝置會聆聽但不會回應 NFC 讀卡器,並傳送應用程式的 NFC 服務 PollingFrame
物件進行處理。PollingFrame 物件可用於在首次與 NFC 讀取器通訊前進行驗證,在許多情況下可支援單按鈕交易。
此外,應用程式可以在支援的裝置上註冊篩選器,以便在檢查迴圈活動發生時收到通知,進而與多個支援 NFC 的應用程式順利運作。
錢包角色
Android 15 推出了錢包角色,可與使用者偏好的錢包應用程式進行更緊密的整合。這個角色會取代 NFC 預設感應式付款設定。使用者可以依序前往「設定」>「應用程式」>「預設應用程式」,管理錢包角色持有人。
當您為付款類別註冊的 AID 轉送 NFC 輕觸動作時,就會使用錢包角色。除非另一個已註冊相同 AID 的應用程式在前景執行,否則點選動作一律會傳送至錢包角色持有者。
這個角色也用於決定 Wallet 快速存取設定方塊在啟用時應顯示的位置。將角色設為「None」時,系統就不會提供快速存取圖塊,且付款類別的 NFC 輕觸動作只會傳送至前景應用程式。
安全性
Android 15 可協助您提升應用程式安全性、保護應用程式資料,並讓使用者進一步瞭解及掌控自己的資料。如要進一步瞭解我們如何強化使用者防護機制,以及保護應用程式免於新威脅侵擾,請觀看 Google I/O 的這場演講。
整合 Credential Manager 與自動填入功能
從 Android 15 開始,開發人員可以將特定檢視畫面 (例如使用者名稱或密碼欄位) 與憑證管理工具要求連結,在登入程序中更輕鬆地提供客製化使用者體驗。當使用者將焦點放在其中一個檢視畫面時,系統會將相應要求傳送至憑證管理工具。系統會從各個供應器匯總產生的憑證,並顯示在自動填入備用 UI 中,例如內嵌建議或下拉式建議。Jetpack androidx.credentials 程式庫是開發人員偏好的端點,不久後將可在 Android 15 以上版本中進一步強化這項功能。
整合單鍵註冊和登入功能與生物特徵辨識提示功能
Credential Manager 會將生物特徵辨識提示訊息整合至憑證建立和登入程序,因此提供者不必管理生物特徵辨識提示訊息。因此,憑證提供者只需要專注於 建立和取得流量的結果,並透過生物特徵辨識流程結果增強。 這個簡化程序可建立更有效率且精簡的憑證建立和擷取程序。
端對端加密的金鑰管理
我們在 Android 15 中推出 E2eeContactKeysManager,這項功能可提供 OS 層級 API 來儲存加密編譯公用金鑰,方便在 Android 應用程式中進行端對端加密 (E2EE)。
E2eeContactKeysManager 旨在整合平台聯絡人應用程式,為使用者提供集中式方式,管理及驗證聯絡人的公開金鑰。
內容 URI 的權限檢查
Android 15 推出一組 API,可針對內容 URI 執行權限檢查:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull:會對內容 URI 執行完整權限檢查。Activity資訊清單屬性requireContentUriPermissionFromCaller:這會在活動啟動時,對提供的內容 URI 強制執行指定權限。Activity呼叫端的ComponentCaller類別:代表啟動活動的應用程式。
無障礙設定
Android 15 新增了多項功能,可提升使用者無障礙體驗。
更優質的點字體驗
在 Android 15 中,我們讓 TalkBack 支援透過 USB 和安全藍牙使用 HID 標準的點字顯示器。
這個標準與滑鼠和鍵盤使用的標準類似,可協助 Android 隨著時間支援更多種類的點字顯示器。
國際化
Android 15 新增了多項功能,可提升使用者在不同語言環境下的裝置使用體驗。
中日韓變數字型
從 Android 15 開始,適用於中文、日文和韓文 (CJK) 的字型檔案 NotoSansCJK,現在已變成可變字型。變數字型為中日韓語言開啟了創意排版的可能性。設計人員可以探索更多樣式,並製作出以往難以或無法達成的視覺效果強烈版面配置。

字元間對齊
從 Android 15 開始,系統可根據字母間距,使用字母間距
使用 JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER。有多字的理由
Android 8.0 (API 級別 26) 首次推出的功能,以及跨字元
對於使用
空白字元做為區隔,例如中文、日文等。

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE 設定日文內容的版面配置。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE 設定英文內容的版面配置。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD 設定日文內容的版面配置。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD 的英文文字版面配置。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER 的日文文字版面配置。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER 為英文內容的版面配置。自動換行設定
Android 已開始在下列國家/地區支援日文和韓文的詞組換行符號:
Android 13 (API 級別 33)。不過,雖然使用詞組的分行符號改善了
簡短的文字易讀性,對長行文字的效果不佳。
在 Android 15 中,應用程式只能針對短行套用以詞組為準的換行符號
方法是使用 LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
如果有需要 SQL 指令的分析工作負載
則 BigQuery 可能是最佳選擇這個選項可為文字選取最合適的字詞樣式選項。
以短行文字來說,使用以詞組為基準的換行符號,運作方式也相同
如 LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE,如
如下圖片:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
套用詞組換行,讓文字更清晰易讀。
這與套用
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE。對於較長的文字,LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO 會使用 no
斷行文字樣式,功能與
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE,如
如下圖片:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
套用不換行的文字樣式,讓文字更清晰易讀。
這與套用
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE。額外的日文變體假名字型
在 Android 15 中,這是日文平假名 (也稱為 Hentaigana) 的字型檔案 系統預設會整合在一起由於平假名字元的形狀獨特,因此可為圖像或設計增添獨特風格,同時也能確保古代日本文件的正確傳遞和理解。

VideoLAN cone Copyright (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. 任何人都可以使用或修改這個標誌或修改版本,以便提及 VideoLAN 專案或 VideoLAN 團隊開發的任何產品,但這並不表示專案認可該標誌或修改版本。
Vulkan 和 Vulkan 標誌是 Khronos Group Inc.的註冊商標。
OpenGL 是註冊商標,OpenGL ES 標誌則是 Hewlett Packard Enterprise 的商標,已獲 Khronos 使用許可。
