Android 15 wprowadza świetne funkcje i interfejsy API dla deweloperów. W kolejnych sekcjach znajdziesz podsumowanie tych funkcji, które pomoże Ci rozpocząć korzystanie z powiązanych interfejsów API.
Szczegółową listę dodanych, zmodyfikowanych i usuniętych interfejsów API znajdziesz w raporcie o różnicach w interfejsach API. Szczegółowe informacje o dodanych interfejsach API znajdziesz w dokumentacji interfejsu Android API. W przypadku Androida 15 poszukaj interfejsów API dodanych na poziomie 35. Aby dowiedzieć się więcej o obszarach, w których zmiany na platformie mogą mieć wpływ na Twoje aplikacje, zapoznaj się ze zmianami w Androidzie 15 w przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 15 i w przypadku wszystkich aplikacji.
Aparat i multimedia
Android 15 zawiera wiele funkcji, które poprawiają działanie aparatu i multimediów oraz zapewniają dostęp do narzędzi i sprzętu, które pomagają twórcom realizować swoje pomysły na Androidzie.
Więcej informacji o najnowszych funkcjach i rozwiązaniach dla deweloperów dotyczących multimediów i aparatu na Androida znajdziesz w prezentacji Tworzenie nowoczesnych aplikacji multimedialnych i do obsługi aparatu na Androida z konferencji Google I/O.
Doświetlanie w słabym oświetleniu
Android 15 wprowadza wzmocnienie w słabym oświetleniu, czyli tryb automatycznej ekspozycji dostępny zarówno w aplikacji Aparat 2, jak i w rozszerzeniu aparatu w trybie nocnym. Tryb słabego oświetlenia dostosowuje ekspozycję strumienia podglądu w warunkach słabego oświetlenia. Jest to inne podejście niż w przypadku rozszerzenia aparatu w trybie nocnym, które łączy serię zdjęć w jedno ulepszone zdjęcie. Chociaż tryb nocny doskonale sprawdza się w przypadku zdjęć, nie umożliwia ciągłego przesyłania ujęć, czego nie można powiedzieć o trybie Boost w oświetleniu słabym. Dzięki temu tryb Low Light Boost umożliwia korzystanie z takich funkcji aparatu, jak:
- Udostępnianie ulepszonej podglądu obrazu, aby użytkownicy mogli lepiej kadrować zdjęcia w warunkach słabego oświetlenia
- Skanowanie kodów QR w warunkach słabego oświetlenia
Jeśli włączysz tryb słabego oświetlenia, włączy się on automatycznie, gdy poziom światła będzie niski, i wyłączy, gdy będzie jaśniej.
Aplikacje mogą nagrywać strumień podglądu w warunkach słabego oświetlenia, aby zapisać film z podwyższoną jasnością.
Więcej informacji znajdziesz w artykule Zwiększanie jasności w słabym oświetleniu.
Ustawienia kamery w aplikacji
Android 15 dodaje rozszerzenie, które zapewnia większą kontrolę nad sprzętem aparatu i jego algorytmami na obsługiwanych urządzeniach:
- Zaawansowane ustawienia siły błysku umożliwiające precyzyjne sterowanie natężeniem błysku w trybach
SINGLEiTORCHpodczas fotografowania.
Kontrola zakresu dynamicznego HDR
Android 15 wybiera zakres HDR odpowiedni dla możliwości urządzenia i głębi bitowej panelu. W przypadku stron zawierających dużo treści SDR, takich jak aplikacja do obsługi wiadomości wyświetlająca pojedynczą miniaturę HDR, takie działanie może negatywnie wpływać na postrzeganą jasność treści SDR. Android 15 umożliwia kontrolowanie marginesu HDR za pomocą setDesiredHdrHeadroom, aby zachować równowagę między treściami SDR a HDR.
Sterowanie głośnością

Android 15 obsługuje standard głośności CTA-2075, który pomaga uniknąć niespójności głośności dźwięku i zapewnia, że użytkownicy nie muszą ciągle dostosowywać głośności podczas przełączania się między treściami. System wykorzystuje znane cechy urządzeń wyjściowych (słuchawek i głośników) oraz metadane dotyczące głośności dostępne w treściach audio AAC, aby inteligentnie dostosowywać głośność dźwięku i poziom kompresji zakresu dynamicznego.
Aby włączyć tę funkcję, musisz się upewnić, że metadane dotyczące głośności są dostępne w:
swoich treści AAC i włącz tę funkcję w aplikacji. Do tego:
utwórz instancję obiektu LoudnessCodecController według
Wywołuje metodę fabryczną create z dźwiękiem.
identyfikator sesji z powiązanego konta AudioTrack; w tym
automatycznie rozpocznie stosowanie aktualizacji audio. Możesz przekazać parametr OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener, aby zmodyfikować lub odfiltrować parametry głośności, zanim zostaną one zastosowane w MediaCodec.
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
Zostanie też zaktualizowany odtwarzacz AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer,
Interfejsy API LoudnessCodecController umożliwiające płynną integrację aplikacji.
Wirtualne urządzenia MIDI 2.0
W Androidzie 13 dodano obsługę łączenia się z urządzeniami MIDI 2.0 przez USB, które komunikują się za pomocą pakietów Universal MIDI (UMP). Android 15 rozszerza obsługę UMP na wirtualne aplikacje MIDI, umożliwiając aplikacjom do komponowania sterowanie syntezatorami jako wirtualnym urządzeniem MIDI 2.0, tak jak w przypadku urządzenia USB MIDI 2.0.
Wydajniejsze dekodowanie oprogramowania AV1

dav1d, popularny dekoder oprogramowania AV1 firmy VideoLAN, jest dostępny na urządzeniach z Androidem, które nie obsługują dekodowania AV1 na poziomie sprzętowym. dav1d jest nawet 3 razy wydajniejszy niż starszy dekoder oprogramowania AV1, co umożliwia odtwarzanie treści AV1 w jakości HD przez więcej użytkowników, w tym na niektórych urządzeniach niskiego i średniego poziomu.
Aplikacja musi wyrazić zgodę na korzystanie z dav1d, wywołując go po imieniu "c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". W kolejnej aktualizacji dav1d stanie się domyślnym dekoderem AV1. Ta obsługa jest ujednolicona i wstecznie przenoszona na urządzenia z Androidem 11, które otrzymują aktualizacje systemowe Google Play.
Wydajność i narzędzia dla programistów
Większość naszych działań mających na celu zwiększenie Twojej produktywności koncentruje się na narzędziach takich jak Android Studio, Jetpack Compose i biblioteki Android Jetpack. Zawsze jednak szukamy sposobów, aby ułatwić Ci realizację Twojej wizji na platformie.
Aktualizacje OpenJDK 17
Android 15 kontynuuje odświeżanie podstawowych bibliotek Androida, aby dostosować je do funkcji w najnowszych wersjach OpenJDK LTS.
Zawiera on te najważniejsze funkcje i ulepszenia:
- Ulepszenia dotyczące buforów NIO
- Transmisje
- Dodatkowe metody
mathistrictmath utilaktualizacje pakietu, w tym sekwencyjnecollection,mapisetByteBufferwDeflater- Aktualizacje zabezpieczeń, takie jak
X500PrivateCredentiali aktualizacje klucza zabezpieczeń
Te interfejsy API są aktualizowane na ponad miliardzie urządzeń z Androidem 12 (poziom interfejsu API 31) lub nowszym w ramach aktualizacji systemu Google Play, dzięki czemu możesz kierować reklamy na najnowsze funkcje programistyczne.
Ulepszenia plików PDF
Android 15 zawiera znaczne ulepszenia interfejsów API PdfRenderer. Aplikacje mogą zawierać zaawansowane funkcje, takie jak renderowanie plików chronionych hasłem, adnotacje, edytowanie formularzy, wyszukiwanie i wybieranie z kopiowaniem. Obsługiwane są optymalizacje linearyzowanych plików PDF, które przyspieszają wyświetlanie lokalnych plików PDF i zmniejszają wykorzystanie zasobów.
Biblioteka PDF Jetpacka używa tych interfejsów API, aby ułatwić dodawanie do aplikacji możliwości wyświetlania plików PDF.
Sekcja PdfRenderer została przeniesiona do modułu, który może być aktualizowany za pomocą Google
Aktualizacje systemu Google Play niezależne od wersji platformy, a my
aby wrócić do Androida 11 (poziom interfejsu API 30) przez utworzenie
platformy API dostępnej w wersjach starszych niż Android 15
PdfRendererPreV
Ulepszenia automatycznego przełączania języka
Android 14 dodał na urządzeniu rozpoznawanie wielu języków w dźwięku z automatycznym przełączaniem się między językami, ale może to powodować pomijanie słów, zwłaszcza gdy języki przełączają się z mniejszą przerwą między dwoma wypowiedziami. Android 15 wprowadza dodatkowe opcje, które pomagają aplikacjom dostosować przełączanie do ich przypadku użycia.
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLISogranicza automatyczne przełączanie do początku sesji audio, podczas gdy EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHESdezaktywuje przełączanie języka po określonej liczbie przełączeń. Te opcje są szczególnie przydatne, jeśli spodziewasz się, że w trakcie sesji będzie używany tylko jeden język, który powinien być automatycznie wykrywany.
Ulepszony interfejs OpenType Variable Font API
W Androidzie 15 łatwiejsza obsługa czcionki zmiennej OpenType. Za pomocą interfejsu API buildVariableFamily możesz utworzyć instancję FontFamily z czcionki zmiennej bez określania osi wag. W celu dopasowania wyświetlanego tekstu render tekstu zastępuje wartość osi wght.
Korzystanie z interfejsu API znacznie upraszcza kod potrzebny do utworzenia Typeface:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
Wcześniej, aby utworzyć ten sam Typeface, potrzeba więcej więcej kodu:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
Oto przykład renderowania Typeface utworzonego za pomocą starego i nowego interfejsu API:
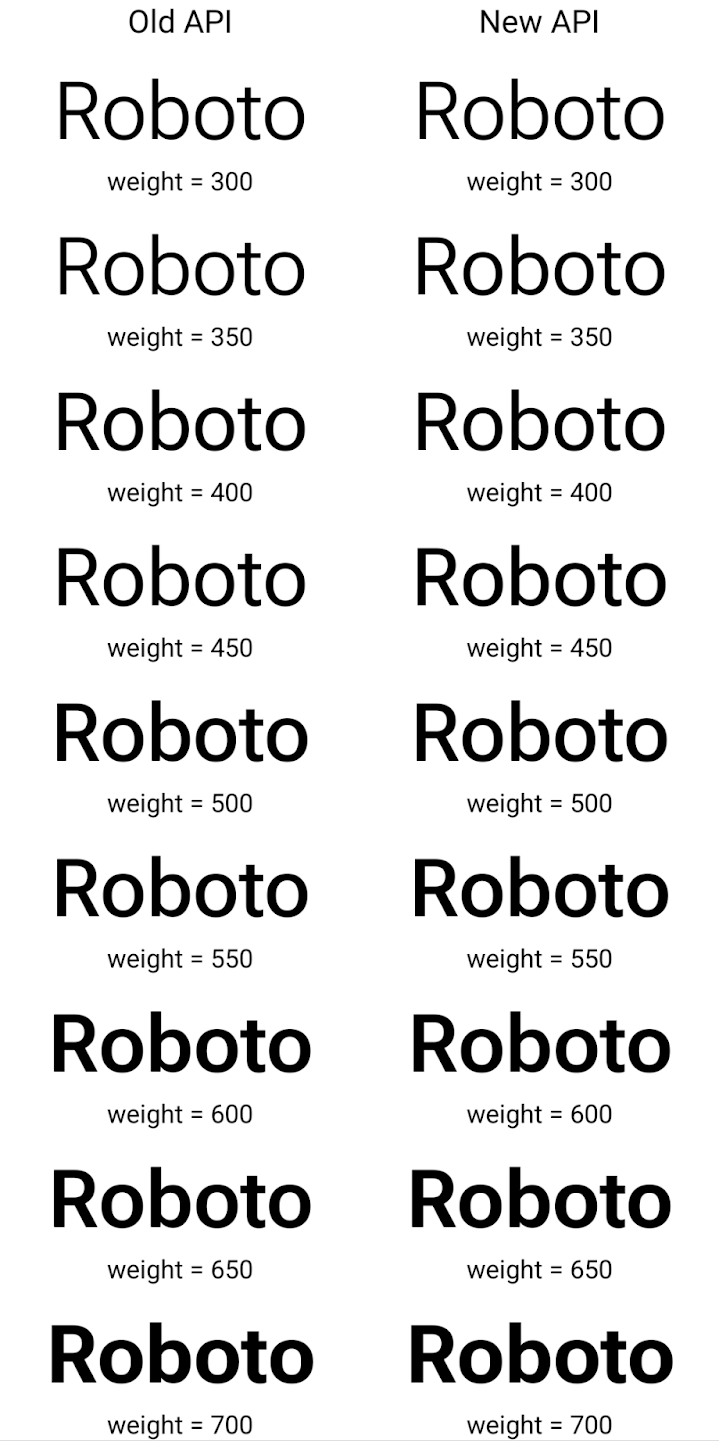
W tym przykładzie Typeface utworzony za pomocą starego interfejsu API nie ma możliwości tworzenia dokładnych wartości wagi czcionki dla instancji 350, 450, 550 i 650Font, więc renderowanie wraca do wartości najbliższej. W tym przypadku zamiast 350 wyświetlana jest wartość 300, zamiast 450 – 400 itd. Natomiast interfejs Typeface utworzony przy użyciu nowych interfejsów API dynamicznie tworzy
wystąpienie Font dla danej wagi, więc dokładne wagi są renderowane dla 350,
450, 550 i 650.
Szczegółowe ustawienia podziału wiersza
Począwszy od Androida 15 TextView i powiązany z nimi podział wiersza mogą zachować daną część tekstu w tym samym wierszu, aby zwiększyć czytelność. Możesz skorzystać z tej opcji dostosowywania znaku końca wiersza, używając tagu <nobreak> w zasobach napisów lub w pliku createNoBreakSpan. Podobnie możesz zachować słowa przed dzieleniem na sylaby, używając tagu <nohyphen> lub createNoHyphenationSpan.
Na przykład ten zasób z ciągiem znaków nie zawiera podziału wiersza i renderuje się z tekstem „Pixel 8 Pro” w nieodpowiednim miejscu:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
Ten zasób ciągu znaków zawiera natomiast tag <nobreak>, który otacza wyrażenie „Pixel 8 Pro” i zapobiega podziałom wiersza:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
Różnica w sposobie renderowania tych ciągów znaków jest widoczna na tych obrazach:

<nobreak>.
<nobreak>.Archiwizacja aplikacji
W zeszłym roku Android i Google Play ogłosiły obsługę archiwizacji aplikacji, aby umożliwić użytkownikom zwolnienie miejsca na urządzeniu przez częściowe usunięcie rzadko używanych aplikacji opublikowanych w Google Play za pomocą pakietu aplikacji na Androida. Android 15 obejmuje archiwizację aplikacji na poziomie systemu operacyjnego i cofania archiwizacji, co ułatwia wdrożenie tej funkcji we wszystkich sklepach z aplikacjami.
Aplikacje z uprawnieniami REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES mogą wywoływać
Metoda PackageInstaller requestArchive prośby o zarchiwizowanie
zainstalowany pakiet aplikacji, który usuwa plik APK i wszelkie pliki z pamięci podręcznej, ale pozostaje bez zmian.
danych użytkownika. Zarchiwizowane aplikacje są zwracane jako aplikacje, które można wyświetlić w
interfejsy API LauncherApps; użytkownicy zobaczą w interfejsie podkreślenie,
aplikacje są zarchiwizowane. Jeśli użytkownik kliknie zarchiwizowaną aplikację, odpowiedzialny instalator
otrzyma prośbę o przywrócenie go z archiwum. Proces przywracania
jest monitorowana przez transmisję ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED.
Włączanie trybu 16 KB na urządzeniu za pomocą opcji programisty
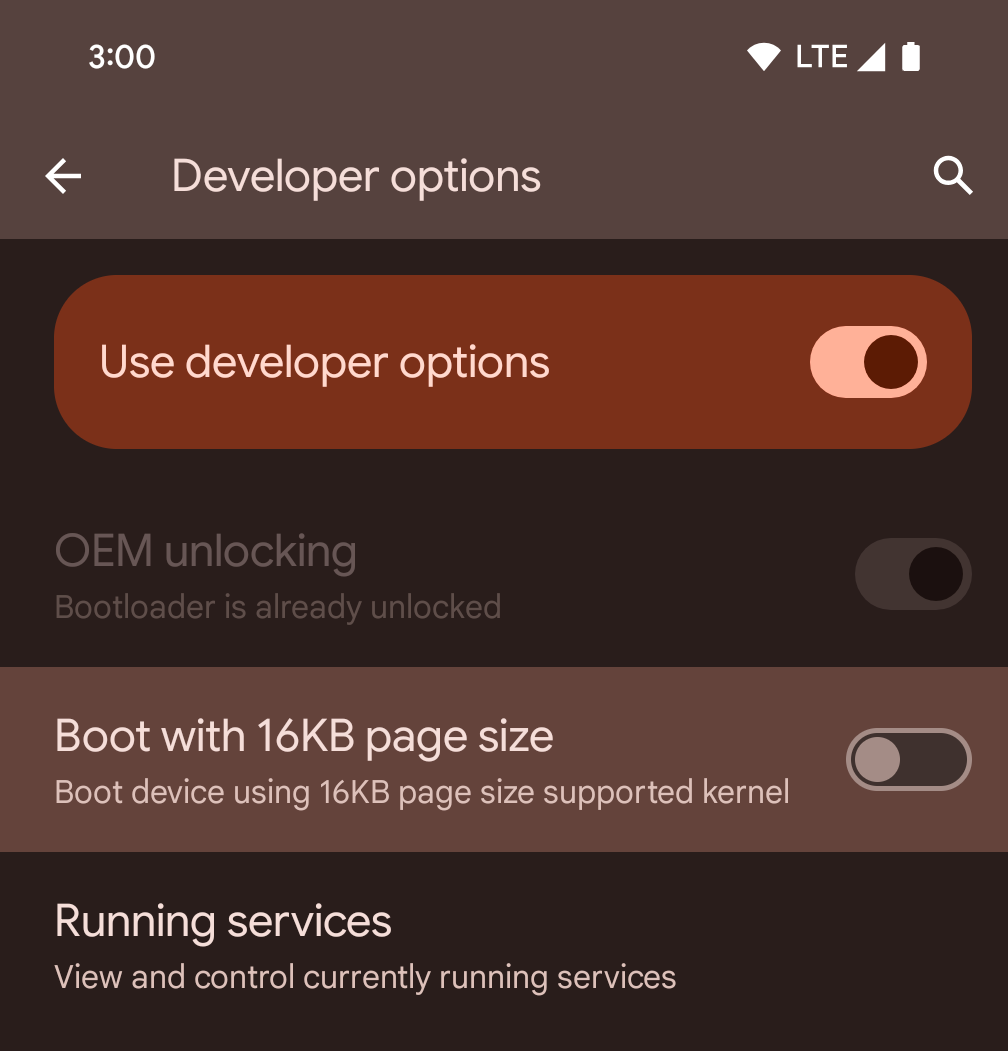
Włącz opcję programisty Uruchom ze stroną 16 KB, aby uruchomić urządzenie w trybie 16 KB.
W wersjach QPR Androida 15 możesz skorzystać z opcji dla programistów dostępnej na niektórych urządzeniach, aby uruchomić urządzenie w trybie 16 KB i przeprowadzić testowanie na urządzeniu. Zanim skorzystasz z opcji programisty, otwórz Ustawienia > System > Aktualizacje oprogramowania i zastosuj dostępne aktualizacje.
Ta opcja dla deweloperów jest dostępna na tych urządzeniach:
Pixel 8 i 8 Pro (z Androidem 15 QPR1 lub nowszym)
Pixel 8a (z Androidem 15 QPR1 lub nowszym)
Pixel 9, 9 Pro i 9 Pro XL (z Androidem 15 QPR2 Beta 2 lub nowszym)
Grafika
Android 15 wprowadza najnowsze ulepszenia grafiki, w tym ANGLE i dodatki do systemu graficznego Canvas.
Modernizacja dostępu do GPU na Androidzie

Sprzęt Androida zmienił się od czasów, gdy główne jądro systemu operacyjnego działało na jednym procesorze CPU, a do kart graficznych uzyskiwano dostęp za pomocą interfejsów API opartych na stałych ścieżkach funkcji. Interfejs Vulkan® API do obsługi grafiki jest dostępny w NDK od wersji Androida 7.0 (poziom interfejsu API 24) i zawiera abstrakcję na niższym poziomie, która lepiej odzwierciedla nowoczesne GPU, lepiej skaluje się do obsługi wielu rdzeni procesora i zapewnia mniejsze obciążenie procesora przez sterownik, co przekłada się na większą wydajność aplikacji. Vulkan jest obsługiwany przez wszystkie nowoczesne silniki gier.
Vulkan jest preferowanym interfejsem Androida do obsługi GPU. Dlatego Android 15 zawiera ANGLE jako opcjonalną warstwę do uruchamiania OpenGL® ES na platformie Vulkan. Przejście na ANGLE pozwoli ustandaryzować implementację OpenGL na Androidzie, co zwiększy zgodność i w niektórych przypadkach wydajność. Stabilność i wydajność aplikacji OpenGL ES możesz sprawdzić za pomocą ANGLE, włączając opcję dla programistów w Ustawienia -> System -> Opcje programisty -> Eksperymentalnie: włącz ANGLE w Androidzie 15.
Plan rozwoju ANGLE na Androida na platformie Vulkan
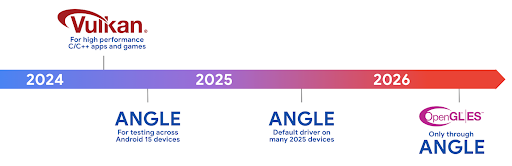
W ramach uproszczenia naszego pakietu GPU będziemy w przyszłości dostarczać ANGLE jako systemowy sterownik GL na kolejnych nowych urządzeniach. W przyszłości OpenGL/ES będzie dostępny tylko za pomocą ANGLE. Planujemy jednak nadal obsługiwać OpenGL ES na wszystkich urządzeniach.
Zalecane kolejne kroki
W opcjach deweloperskich wybierz sterownik ANGLE dla OpenGL ES i przetestuj aplikację. W przypadku nowych projektów zdecydowanie zalecamy używanie Vulkana w przypadku języków C/C++.
Ulepszenia Canvas
Android 15 to kontynuacja modernizacji systemu graficznego Canvas w Androidzie z dodatkowymi funkcjami:
Matrix44udostępnia macierz 4 x 4 do przekształcania współrzędnych, która powinna być używana, gdy chcesz manipulować płótnem w 3D.clipShaderprzecina bieżący klip ze wskazanym shaderem, aclipOutShaderustawia klip na różnicę między bieżącym klipem a shaderem, przy czym shader jest traktowany jako maska alfa. Umożliwia to wydajne rysowanie złożonych kształtów.
Wydajność i bateria
Android nadal koncentruje się na pomaganiu w poprawianiu wydajności i jakości aplikacji. Android 15 wprowadza interfejsy API, które pomagają wydajniej wykonywać zadania w aplikacji, optymalizować jej działanie i zbierać o niej informacje.
Aby poznać sprawdzone metody oszczędzania baterii, debugowania wykorzystania sieci i energii oraz dowiedzieć się więcej o tym, jak zwiększamy wydajność baterii w przypadku pracy w tle na Androidzie 15 i nowszych wersjach Androida, obejrzyj prezentację Zwiększanie wydajności baterii w przypadku pracy w tle na Androidzie z konferencji Google I/O.
ApplicationStartInfo API
W poprzednich wersjach Androida uruchamianie aplikacji było trochę tajemnicze. Trudno było określić, czy aplikacja została uruchomiona „na zimno”, „na ciepło” czy z pamięci. Trudno też było ustalić, ile czasu aplikacja spędziła w różnych fazach uruchamiania: dzielenia procesu, wywoływania funkcji onCreate, rysowania pierwszego kadru itp. Gdy instancja klasy Application została utworzona, nie było sposobu na ustalenie, czy aplikacja została uruchomiona przez transmisję, dostawcę treści, zadanie, kopię zapasową, uruchomienie, alarm czy Activity.
Interfejs API ApplicationStartInfo w Androidzie 15 zapewnia wszystkie te funkcje i wiele więcej. Możesz nawet dodać do przepływu własne sygnały czasu, aby zbierać dane o czasie w jednym miejscu. Oprócz zbierania danych możesz używać ApplicationStartInfo do bezpośredniej optymalizacji uruchamiania aplikacji. Możesz na przykład wyeliminować kosztowne instancjonowanie bibliotek związanych z interfejsem użytkownika w klasie Application, gdy aplikacja uruchamia się z powodu transmisji.
Szczegółowe informacje o rozmiarze aplikacji
Od Androida 8.0 (poziom interfejsu API 26) Android zawiera interfejs API StorageStats.getAppBytes, który podsumowuje rozmiar zainstalowanej aplikacji jako pojedynczą liczbę bajtów będącą sumą rozmiaru pliku APK, rozmiaru plików wyodrębnionych z pliku APK oraz plików wygenerowanych na urządzeniu, takich jak kod skompilowany z wyprzedzeniem (AOT). Ta liczba nie dostarcza zbyt wielu informacji o tym, jak aplikacja wykorzystuje miejsce na dane.
Android 15 dodaje interfejs API StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]), który pozwala uzyskać informacje o tym, jak aplikacja wykorzystuje całą dostępną przestrzeń, w tym podziały pliku APK, kod AOT i kod związany z przyspieszeniem, metadane dex, biblioteki i profilowanie kierunkowe.
Profilowanie zarządzane przez aplikację
Android 15 zawiera klasę ProfilingManager, która umożliwia zbieranie informacji o profilowaniu z aplikacji, takich jak zrzuty stosu, profile stosu, próbkowanie stosu itp. Wywołuje ona Twoją aplikację z dołączonym tagiem, aby zidentyfikować plik wyjściowy, który jest dostarczany do katalogu plików aplikacji. Interfejs API stosuje ograniczanie szybkości, aby zminimalizować wpływ na wydajność.
Aby uprościć tworzenie żądań profilowania w aplikacji, zalecamy użycie odpowiedniego interfejsu AndroidX API Profiling, dostępnego w wersji Core 1.15.0-rc01 lub nowszej.
Ulepszenia bazy danych SQLite
Android 15 wprowadza interfejsy API SQLite, które udostępniają zaawansowane funkcje podstawowego mechanizmu SQLite, ukierunkowane na konkretne problemy z wydajnością, które mogą wystąpić w aplikacjach. Te interfejsy API są uwzględnione w aktualizacji SQLite do wersji 3.44.3.
Aby w pełni wykorzystać możliwości bazy danych SQLite, zwłaszcza w przypadku dużych baz danych lub wykonywania zapytań wrażliwych na opóźnienia, deweloperzy powinni zapoznać się z najlepszymi praktykami dotyczącymi wydajności SQLite.
- Transakcje odroczone tylko do odczytu: w przypadku zawierania transakcji, które są
tylko do odczytu (bez instrukcji zapisu), należy użyć funkcji
beginTransactionReadOnly()ibeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener). do wystawiania transakcjiDEFERREDtylko do odczytu. Takie transakcje mogą być realizowane jednocześnie, a jeśli baza danych jest w trybie WAL, można prowadzić równolegle zIMMEDIATElubEXCLUSIVEtransakcjami. - Liczba i identyfikatory wierszy: dodano interfejsy API, które umożliwiają pobieranie liczby zmienionych wierszy lub identyfikatora ostatniego wstawionego wiersza bez wysyłania dodatkowego zapytania.
getLastChangedRowCount()zwraca liczbę wierszy, które zostały wstawione, zaktualizowane lub usunięte przez najnowszą instrukcję SQL w ciągu bieżącej transakcji, agetTotalChangedRowCount()zwraca liczbę dla bieżącego połączenia.getLastInsertRowId()zwracarowidostatniego wiersza, który ma zostać wstawiony w bieżącym połączeniu. - Instrukcje w postaci łańcucha znaków: instrukcje w postaci łańcucha znaków, które są wysyłane do bazy danych SQLite, omijając wrappery i dodatkowe obciążenia przetwarzania, które mogą one generować.
Aktualizacje Android Dynamic Performance Framework
Android 15 to kontynuacja naszych działań związanych z ramami pracy Android Dynamic Performance Framework (ADPF), czyli zestawu interfejsów API, które umożliwiają grze lub aplikacji o wysokich wymaganiach dotyczących wydajności bezpośrednią interakcję z systemami zasilania i termicznymi urządzeń z Androidem. Na obsługiwanych urządzeniach Android 15 dodaje funkcje ADPF:
- Tryb oszczędzania energii w przypadku sesji podpowiedzi, aby wskazać, że powiązane wątki powinny preferować oszczędzanie energii zamiast wydajności, co jest przydatne w przypadku długotrwałych zadań wykonywanych w tle.
- Czas pracy GPU i procesora może być zgłaszany w sesjach podpowiedzi, co pozwala systemowi dostosowywać częstotliwości procesora i karty graficznej, aby jak najlepiej spełniać wymagania dotyczące obciążenia.
- Próg temperatury, aby interpretować możliwy stan ograniczania temperatury na podstawie prognozy dotyczącej temperatury.
Więcej informacji o używaniu plików ADPF w aplikacjach i grach znajdziesz w dokumentacji.
Prywatność
Android 15 zawiera różne funkcje, które pomagają programistom chronić prywatność użytkowników.
Wykrywanie nagrywania ekranu
Android 15 obsługuje aplikacje, aby wykrywać w trakcie nagrywania. Funkcja wywołania zwrotnego jest wywoływana, gdy aplikacja przechodzi z widocznego stanu do niewidocznego w nagraniu ekranu. Aplikacja jest są uznawane za widoczne, jeśli działania należące do identyfikatora UID procesu rejestracji są nie są zapisywane. Dzięki temu, jeśli aplikacja wykonuje działanie związane z poufnymi danymi, możesz poinformować użytkownika, że jest nagrywany.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
Rozszerzone możliwości IntentFilter
Android 15 obsługuje dokładniejsze Intent dzięki UriRelativeFilterGroup, który zawiera zestaw obiektów UriRelativeFilter tworzących zestaw zasad dopasowania Intent, które muszą być spełnione, w tym parametry zapytania URL, fragmenty adresów URL oraz reguły blokowania lub wykluczania.
Te reguły można zdefiniować w pliku XML AndroidManifest za pomocą tagu <uri-relative-filter-group>, który może opcjonalnie zawierać tag android:allow. Mogą one zawierać tagi <data>, które używają istniejących atrybutów tagów danych, a także atrybutów android:query i android:fragment.
Oto przykład składni AndroidManifest:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
Przestrzeń prywatna
Przestrzeń prywatna umożliwia użytkownikom utworzenie osobnego obszaru na urządzeniu, w którym mogą ukryć aplikacje poufne przed ciekawskimi spojrzeniami, korzystając z dodatkowego poziomu uwierzytelniania. Przestrzeń prywatna korzysta z osobnego profilu użytkownika. Użytkownik może wybrać blokadę urządzenia lub osobny czynnik blokady dla przestrzeni prywatnej.
Aplikacje w obszarze prywatnym są widoczne w oddzielnym kontenerze w wyszukiwarce i są ukryte w widoku Ostatnie, w powiadomieniach, ustawieniach i innych aplikacjach, gdy obszar prywatny jest zablokowany. Treści utworzone i pobrane przez użytkownika (np. multimedia lub pliki) oraz konta są rozdzielone między przestrzeń prywatną a przestrzeń główną. Arkusz udostępniania i selektor zdjęć można używać do przyznawania aplikacjom dostępu do treści w różnych przestrzeniach, gdy przestrzeń prywatna jest odblokowana.
Użytkownicy nie mogą przenosić istniejących aplikacji i ich danych do przestrzeni prywatnej. Zamiast tego użytkownicy wybierają opcję instalacji w przestrzeni prywatnej, aby zainstalować aplikację w dowolnym sklepie z aplikacjami. Aplikacje w przestrzeni prywatnej są instalowane jako osobne kopie aplikacji w przestrzeni głównej (nowe kopie tej samej aplikacji).
Gdy użytkownik zablokuje przestrzeń prywatną, profil zostanie zatrzymany. Gdy profil jest zatrzymany, aplikacje w obszarze prywatnej nie są już aktywne i nie mogą wykonywać działań na pierwszym planie ani w tle, w tym wyświetlać powiadomień.
Zalecamy przetestowanie aplikacji w obszarze prywatnym, aby mieć pewność, że działa ona zgodnie z oczekiwaniami, zwłaszcza jeśli należy do jednej z tych kategorii:
- Aplikacje z logiką dla profili służbowych, która zakłada, że wszystkie zainstalowane kopie aplikacji, które nie znajdują się na profilu głównym, znajdują się na profilu służbowym.
- Aplikacje medyczne
- Aplikacje menu
- Aplikacje ze sklepu z aplikacjami
Sprawdzanie najnowszych wyborów użytkownika w przypadku dostępu do wybranych zdjęć
Aplikacje mogą teraz wyróżniać tylko ostatnio wybrane zdjęcia i filmy, gdy użytkownik przyzna uprawnienia do multimediów w ramach dostępu częściowego. Ta funkcja może poprawić wyniki
aplikacji, które często proszą o dostęp do zdjęć,
filmy. Aby korzystać z tej funkcji w aplikacji, włącz argument QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY podczas wysyłania zapytania MediaStore za pomocą interfejsu ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Piaskownica prywatności na Androida
Android 15 zawiera najnowsze rozszerzenia Usług reklamowych Androida, które obejmują najnowszą wersję Piaskownicy prywatności na Androidzie. Ta funkcja jest częścią naszych działań mających na celu opracowanie technologii, które poprawią prywatność użytkowników oraz umożliwią skuteczne, spersonalizowane reklamy w aplikacjach mobilnych. Na stronie Piaskownicy prywatności znajdziesz więcej informacji o Piaskownicy prywatności w wersji dla deweloperów i w programach beta na Androida, które pomogą Ci zacząć.
Health Connect
Android 15 łączy najnowsze rozszerzenia Health Connect by Android – bezpieczne i scentralizowane platforma, która pozwala zarządzać zbieranymi przez aplikacje danymi o zdrowiu i aktywności fizycznej oraz je udostępniać. Ta aktualizacja obsługa dodatkowych typów danych dotyczących fitnessu, odżywianie, temperatura skóry, plany treningów itp.
Śledzenie temperatury skóry umożliwia użytkownikom przechowywanie i udostępnianie dokładniejszych danych o temperaturze z urządzenia do noszenia lub innego urządzenia śledzącego.
Plany treningowe to usystematyzowane plany treningowe, które pomagają użytkownikom osiągnąć cele fitnessowe. Plany treningowe obejmują różne cele dotyczące ukończenia i wyników:
- Cele dotyczące ukończenia treningu związane z spalaniem kalorii, dystansem, czasem trwania, powtórzeniem i liczbą kroków.
- Docelowa skuteczność w okolicach jak najwięcej powtórzeń (AMRAP), kadencja, tętno, moc, ostrzegalne tempo wysiłku oraz prędkości.
Więcej informacji o najnowszych aktualizacjach Health Connect na Androidzie znajdziesz w prezencie Tworzenie dostosowanych usług z Androidem Health z Google I/O.
Udostępnianie ekranu aplikacji
Android 15 obsługuje udostępnianie ekranu aplikacji, dzięki czemu użytkownicy mogą udostępniać lub nagrywać tylko okno aplikacji, a nie cały ekran urządzenia. Ta funkcja, która została po raz pierwszy włączona w Androidzie 14 QPR2, obejmuje wywołania MediaProjection, które umożliwiają aplikacji dostosowywanie udostępniania ekranu. Pamiętaj, że w przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 14 (poziom API 34) lub nowszego wymagana jest zgoda użytkownika na każdą sesję rejestrowania MediaProjection.
Wrażenia użytkowników i interfejs systemu
Android 15 zapewnia deweloperom aplikacji i użytkownikom większą kontrolę i elastyczność w konfigurowaniu urządzenia pod kątem swoich potrzeb.
Więcej informacji o tym, jak wykorzystać najnowsze ulepszenia w Androidzie 15, aby zwiększyć wygodę korzystania z aplikacji, znajdziesz w prezentacji Ulepszanie wrażeń użytkowników aplikacji na Androida z Google I/O.
Bogatsze podglądy widżetów dzięki interfejsowi Generated Previews API
Przed Androidem 15 jedynym sposobem wyświetlania podglądów selektora widżetów było określenie statycznych zasobów obrazów lub układu. Te podglądy często znacznie różnią się od wyglądu widżetu na ekranie głównym. Ponadto za pomocą Jetpack Glance nie można tworzyć zasobów statycznych, więc deweloper Glance musiał zrobić zrzut ekranu z widżetem lub utworzyć układ XML, aby wyświetlić jego podgląd.
Android 15 obsługuje wygenerowane podglądy. Oznacza to, że dostawcy widżetów aplikacji mogą generować RemoteViews, aby używać go jako podglądu selektora zamiast zasobu statycznego.
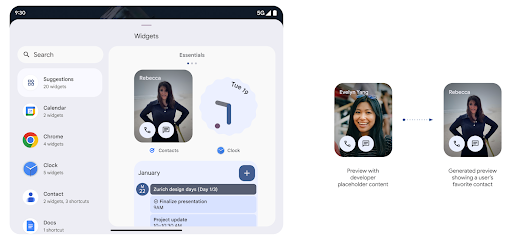
Interfejs API usługi Push
Aplikacje mogą udostępniać wygenerowane podglądy za pomocą interfejsu API push. Aplikacje mogą udostępniać podglądy w dowolnym momencie ich cyklu życia i nie muszą otrzymać wyraźnej prośby od gospodarza. Podglądy są przechowywane w AppWidgetService, a gospodarze mogą je żądać na żądanie. W tym przykładzie wczytujemy zasób układu widżetu XML i ustawiamy go jako podgląd:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
Oczekiwany przebieg:
- W dowolnym momencie dostawca widżetu może wywołać funkcję
setWidgetPreview. Udostępnione podglądy są przechowywane wAppWidgetServicewraz z innymi informacjami o dostawcy. setWidgetPreviewinformuje hostów o zaktualizowanym podglądzie za pomocą wywołania zwrotnegoAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChanged. W odpowiedzi host widżetu ponownie wczytuje wszystkie informacje dostawcy.- Podczas wyświetlania podglądu widżetu host sprawdza, czy
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategoriesjest dostępna, a jeśli tak, wywołuje funkcjęAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreview, aby zwrócić zapisany podgląd dla tego dostawcy.
Kiedy zadzwonić do: setWidgetPreview
Ponieważ nie ma wywołania zwrotnego, które umożliwia wyświetlanie podglądów, aplikacje mogą wysyłać podglądy w dowolnym momencie, gdy są uruchomione. Częstotliwość aktualizacji podglądu zależy od przypadku użycia widżetu.
Na liście poniżej znajdziesz 2 główne kategorie przypadków użycia podglądu:
- Dostawcy, którzy wyświetlają prawdziwe dane w podglądzie widżetów, np. informacje spersonalizowane lub najnowsze informacje. Ci dostawcy mogą ustawić podgląd po zalogowaniu się użytkownika lub po wykonaniu wstępnej konfiguracji w aplikacji. Następnie mogą skonfigurować zadanie okresowe, aby aktualizować podgląd w wybranym interwale. Przykładami tego typu widżetów są widżety ze zdjęciami, kalendarza, pogody lub wiadomościami.
- Dostawcy, którzy wyświetlają w podglądach informacje statyczne lub widżety szybkich działań, które nie wyświetlają żadnych danych. Ci dostawcy mogą ustawić podgląd tylko raz przy pierwszym uruchomieniu aplikacji. Przykładami tego typu widżetów są widżet Szybkie działania na Dysku lub widżet skrótów w Chrome.
Niektórzy dostawcy mogą wyświetlać podgląd statyczny w selektorze trybu centrali, ale w selektorze na ekranie głównym mogą wyświetlać prawdziwe informacje. Podczas ustawiania podglądów dostawcy ci powinni postępować zgodnie ze wskazówkami dotyczącymi obu tych przypadków użycia.
Obraz w obrazie
Android 15 wprowadza zmiany w trybie obrazu w obrazie (PIP), które zapewniają jeszcze płynniejsze przejście do tego trybu. Jest to korzystne w przypadku aplikacji, które mają elementy UI nałożone na główny interfejs użytkownika i przechodzą do trybu PiP.
Deweloperzy używają wywołania zwrotnego onPictureInPictureModeChanged do definiowania logiki
który przełącza widoczność nakładanych elementów interfejsu. Ten wywołanie zwrotne jest wywoływane po zakończeniu animacji otwierania lub zamykania okna PiP. Początek za
Androida 15, klasa PictureInPictureUiState zawiera kolejny stan.
W takim stanie interfejsu aplikacje kierowane na Androida 15 (poziom interfejsu API 35) odnotowują
Wywołanie zwrotne Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged z
isTransitioningToPip() od razu po rozpoczęciu animacji funkcji obraz w obrazie. Istnieją
wiele elementów interfejsu, które nie są istotne dla aplikacji w trybie Obraz w obrazie,
przykładowe widoki lub układ strony z informacjami, takimi jak sugestie,
filmów, ocen i tytułów. Gdy aplikacja przejdzie do trybu Picture-in-Picture, użyj wywołania zwrotnego onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged, aby ukryć te elementy interfejsu. Gdy
przejdzie do trybu pełnoekranowego z okna funkcji obraz w obrazie, użyj
Wywołanie zwrotne onPictureInPictureModeChanged do odkrycia tych elementów, jak w tym przykładzie
w tych przykładach:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
Ten szybki przełącznik widoczności nieistotnych elementów interfejsu (dla okna PIP) pomaga aby uzyskać płynniejszą i wolną od migotania animacja PIP.
Ulepszone reguły trybu Nie przeszkadzać
AutomaticZenRule umożliwia aplikacjom dostosowywanie uwagi
Reguły zarządzania (Nie przeszkadzać) i określanie, kiedy mają być aktywowane lub dezaktywowane
. Android 15 znacznie ulepsza te reguły, aby poprawić komfort użytkowników. Wprowadzono te ulepszenia:
- Dodaję typy do
AutomaticZenRule, aby umożliwić systemowi zastosowanie specjalnych traktowanie pewnych zasad. - Dodaję ikonę do interfejsu
AutomaticZenRule, aby pomóc w ulepszaniu trybów i rozpoznawalna. - Dodawanie do
AutomaticZenRuleciągutriggerDescription, który opisuje warunki, po spełnieniu których reguła powinna zostać aktywowana dla użytkownika. - Dodane
ZenDeviceEffectsdoAutomaticZenRule, co umożliwia regułom wywoływanie takich funkcji jak skali szarości wyświetlacza, tryb nocny lub przyciemnienie tapety.
Ustawianie VibrationEffect dla kanałów powiadomień
Android 15 obsługuje ustawienia silnych wibracji dla przychodzących powiadomień przez
za pomocą NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect, więc
użytkownicy mogą odróżniać
różne typy powiadomień bez
patrząc na urządzenie.
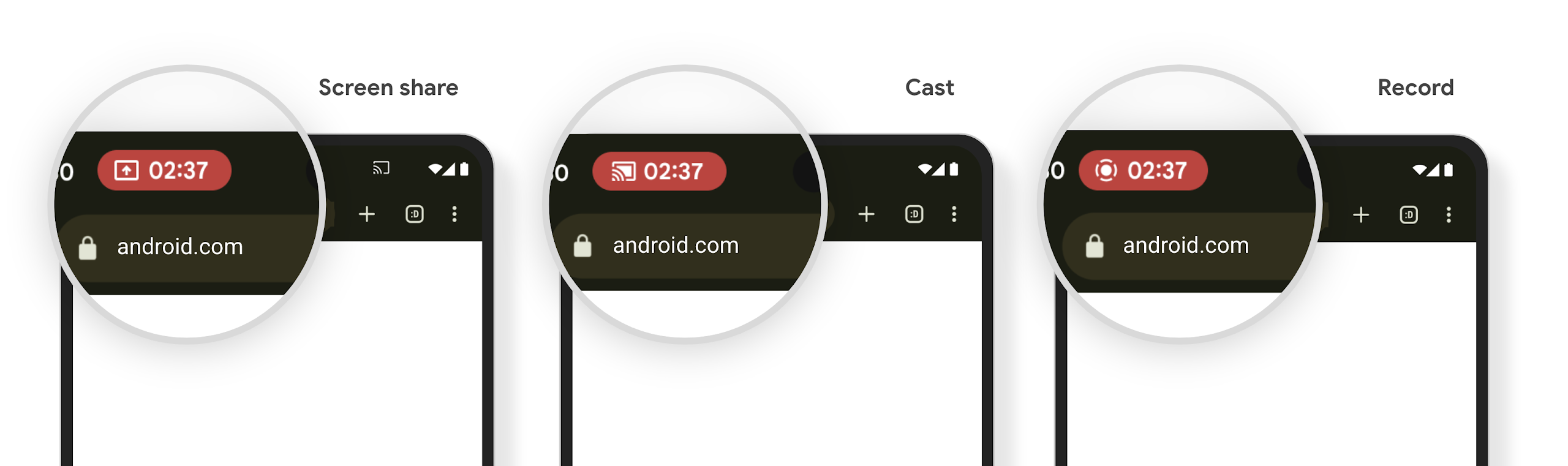
Element na pasku stanu wyświetlania multimediów i automatyczne zatrzymywanie
Projekcja multimediów może ujawnić prywatne informacje o użytkowniku. Nowy, dobrze widoczny element na pasku stanu informuje użytkowników o działającej projekcji ekranu. Użytkownicy mogą kliknąć chip, aby zatrzymać udostępnianie, przesyłanie lub nagrywanie ekranu. Aby zapewnić użytkownikom bardziej intuicyjną obsługę, wyświetlanie na ekranie w trakcie jest teraz automatycznie wstrzymywane, gdy ekran urządzenia jest zablokowany.
Duże ekrany i formaty
Android 15 zapewnia aplikacjom obsługę, która pozwala w pełni wykorzystać możliwości różnych form urządzeń z Androidem, w tym dużych ekranów, urządzeń składanych i z klapką.
Ulepszona wielozadaniowość na dużym ekranie
Android 15 daje użytkownikom więcej możliwości wykonywania wielu zadań jednocześnie na urządzeniach z dużym ekranem. Dla: Na przykład użytkownicy mogą zapisać ulubione kombinacje aplikacji podzielone na podzielony ekran, dostęp do paska aplikacji na ekranie i przypinanie go, aby szybko przełączać się między aplikacjami. Oznacza to, że że zapewnienie adaptacji aplikacji jest teraz ważniejsze niż kiedykolwiek.
W ramach Google I/O odbywają się sesje poświęcone tworzeniu adaptacyjnego Androida Apps i Building UI with the Material 3 biblioteka adaptacyjna może pomóc, a nasza dokumentacja jest pomocna w zaprojektowaniu .
Obsługa ekranu zewnętrznego
Aplikacja może deklarować właściwość, której Android 15 używa do wyświetlania elementów Application lub Activity na małych ekranach okładki obsługiwanych urządzeń z ekranem składanym. Te ekrany są zbyt małe, aby uznać je za kompatybilne cele dla aplikacji na Androida, ale możesz włączyć obsługę tych ekranów, aby udostępnić aplikację w większej liczbie miejsc.
Łączność
Android 15 aktualizuje platformę, aby zapewnić Twojej aplikacji dostęp do najnowszych osiągnięć w zakresie technologii komunikacyjnych i bezprzewodowych.
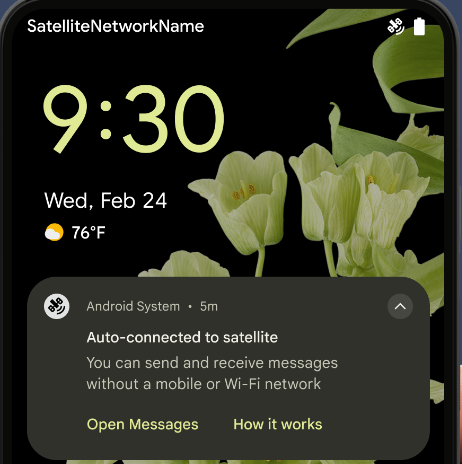
Obsługa satelitarna
Android 15 rozszerza obsługę platformy w zakresie łączności satelitarnej, zawiera kilka elementów UI, by zapewnić spójność połączenia satelitarnego.
Aplikacje mogą używać ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() do wykrywania, kiedy urządzenie jest połączone z satelitą, dzięki czemu użytkownicy lepiej rozumieją, dlaczego pełne usługi sieciowe mogą być niedostępne. Android 15 obsługuje też aplikacje SMS i MMS oraz wstępnie zainstalowane aplikacje RCS, które umożliwiają korzystanie z łączności satelitarnej do wysyłania i odbierania wiadomości.
Płynniejsze działanie NFC
Android 15 czyni korzystanie z płatności zbliżeniowych wygodniejszym i bardziej niezawodnym, a jednocześnie nadal obsługuje solidny ekosystem aplikacji NFC. Na obsługiwanych urządzeniach aplikacje mogą prosić NfcAdapter o wejście w tryb obserwacji, w którym urządzenie nasłuchuje, ale nie reaguje na czytniki NFC, wysyłając PollingFrame
obiekty usługi NFC aplikacji do przetwarzania. Obiekty PollingFrame mogą być używane do uwierzytelniania przed pierwszym nawiązaniem komunikacji z czytnikiem NFC, co w wielu przypadkach umożliwia transakcję jednym kliknięciem.
Aplikacje mogą też zarejestrować filtr na obsługiwanych urządzeniach, aby otrzymywać powiadomienia o aktywności pętli zapytań, co umożliwia płynne działanie z wieloma aplikacjami obsługującymi NFC.
Rola w Portfelu
Android 15 wprowadza rolę Portfela, która umożliwia ściślejszą integrację z ulubioną aplikacją portfela użytkownika. Ta rola zastępuje domyślne ustawienie płatności zbliżeniowych NFC. Użytkownicy mogą zarządzać właścicielem roli Portfel, klikając Ustawienia > Aplikacje > Domyślne aplikacje.
Rola Portfela jest używana podczas kierowania dotykiem NFC do identyfikatorów AID zarejestrowanych w kategorii płatności. Kliknięcia zawsze trafiają do posiadacza roli w Portfelu, chyba że na pierwszym planie działa inna aplikacja zarejestrowana z tym samym identyfikatorem AID.
Ta rola służy też do określenia, gdzie ma się wyświetlać kafelek Szybki dostęp w Portfelu po jego aktywowaniu. Gdy rola jest ustawiona na „Brak”, kafelek Szybki dostęp jest niedostępny, a dotknięcia NFC w ramach kategorii płatności są dostarczane tylko do aplikacji na pierwszym planie.
Bezpieczeństwo
Android 15 pomaga zwiększyć bezpieczeństwo aplikacji, chronić jej dane oraz zapewnia użytkownikom większą przejrzystość i kontrolę nad ich danymi. Więcej informacji o tym, co robimy, aby ulepszać zabezpieczenia użytkowników i chronić Twoją aplikację przed nowymi zagrożeniami, znajdziesz w prezentacji Safeguarding user security on Android (Zapewnianie bezpieczeństwa użytkowników na Androidzie) z konferencji Google I/O.
Integracja Credential Manager z autouzupełnianiem
Począwszy od Androida 15 deweloperzy mogą połączyć określone widoki, takie jak pola nazwy użytkownika lub hasła, z żądaniami menedżera danych uwierzytelniających, co ułatwia dostosowanie interfejsu do potrzeb użytkownika podczas procesu logowania. Gdy użytkownik skupi się na jednym z tych widoków, do Menedżera danych logowania zostanie wysłane odpowiednie żądanie. Uzyskane dane są agregowane w ramach dostawców i wyświetlane w interfejsach autouzupełniania, takich jak sugestie w polu tekstowym lub sugestie w menu. Biblioteka Jetpack androidx.credentials to preferowany punkt końcowy dla deweloperów. Wkrótce będzie ona dostępna w celu dalszego ulepszania tej funkcji w Androidzie 15 i nowszych.
Integracja rejestracji i logowania jednym dotknięciem z prośbami o uwierzytelnianie biometryczne
Menedżer danych uwierzytelniających integruje prompty biometryczne z procesami tworzenia danych uwierzytelniających i logowania, dzięki czemu dostawcy nie muszą zarządzać promptami biometrycznymi. Dlatego dostawcy danych uwierzytelniających mogą się skupić jedynie na wyników tworzenia i odbierania przepływów, wzbogaconych o wynik przepływu biometrycznego. Ten uproszczony proces umożliwia bardziej wydajne i prostsze tworzenie oraz pobieranie danych logowania.
Zarządzanie kluczami w przypadku pełnego szyfrowania
W Androidzie 15 wprowadzamy interfejs E2eeContactKeysManager, który ułatwia szyfrowanie end-to-end (E2EE) w aplikacjach na Androida dzięki interfejsowi API na poziomie systemu operacyjnego do przechowywania kluczy publicznych kryptograficznych.
E2eeContactKeysManager jest przeznaczony do integracji z aplikacją Kontakty na platformie, aby zapewnić użytkownikom scentralizowany sposób zarządzania i weryfikowania kluczy publicznych kontaktów.
Sprawdzanie uprawnień dotyczących identyfikatorów URI treści
Android 15 wprowadza zestaw interfejsów API, które przeprowadzają sprawdzanie uprawnień w przypadku adresów URI treści:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: sprawdzanie wszystkich uprawnień w przypadku identyfikatorów URI treści.- Atrybut pliku manifestu
ActivityrequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: podczas uruchamiania aktywności wymusza określone uprawnienia dla podanych identyfikatorów URI treści. ComponentCallerclass dla wywołującychActivity: ta klasa reprezentuje aplikację, która uruchomiła aktywność.
Ułatwienia dostępu
Android 15 zawiera funkcje, które zwiększają dostępność dla użytkowników.
Better Braille
W Androidzie 15 umożliwiliśmy TalkBackowi obsługę monitorów brajlowskich, które korzystają ze standardu HID przez USB i bezpieczny Bluetooth.
Ten standard, podobnie jak standardy używane przez myszy i klawiatury, pomoże Androidowi z czasem obsługiwać szerszą gamę monitorów brajlowskich.
Internacjonalizacja
Android 15 zawiera funkcje i możliwości, które uzupełniają wygodę korzystania z urządzenia w różnych językach.
Czcionka zmienna CJK
Od wersji 15 Androida plik czcionki dla języków chińskiego, japońskiego i koreańskiego (CJK) NotoSansCJK jest teraz czcionką zmienną. Czcionki zmienne otwierają nowe możliwości kreatywnej typografii w językach CJK. Projektanci mogą odkrywać szerszy zakres stylów i tworzyć atrakcyjne wizualnie układy, które wcześniej były trudne lub niemożliwe do osiągnięcia.

Justowanie między znakami
Od Androida 15 tekst można wyrównać do lewej, korzystając z odstępów między literami za pomocą znaku JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. Poprzednie uzasadnienie między słowami:
po raz pierwszy wprowadzona w Androidzie 8.0 (poziom interfejsu API 26)
daje podobne możliwości w językach korzystających z funkcji
znak odstępu na potrzeby segmentacji, np. w języku chińskim, japońskim itp.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.Konfiguracja automatycznego podziału wiersza
Android zaczął obsługiwać podziały wierszy oparte na wyrażenia w języku japońskim i koreańskim od
Android 13 (poziom API 33). Mimo że podziały wierszy oparte na wyrażeniach poprawiają
czytelność krótkich wierszy tekstu, dlatego nie sprawdzają się w przypadku długich wierszy.
Na Androidzie 15 aplikacje mogą stosować podziały wierszy oparte na wyrażeniach tylko w przypadku krótkich wierszy
tekstu, za pomocą funkcji LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
. Ta opcja powoduje wybranie najlepszej opcji stylu tekstu dla tekstu.
W przypadku krótkich wierszy tekstu stosuje się znaki końca wiersza oparte na frazie, które działają tak samo jak LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE, jak pokazano na poniższym obrazie:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
stosuje podziały wierszy oparte na wyrażeniach, aby poprawić czytelność tekstu.
Ta metoda działa tak samo jak stosowana
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE.W przypadku dłuższych wierszy tekstu LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO używa operatora nie
stylu słów podziału wiersza, który działa tak samo jak
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE, jak widać w tabeli
ten obraz:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
nie stosuje się stylu łamania wiersza, aby poprawić czytelność tekstu.
Ta metoda działa tak samo jak stosowana
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE.Dodatkowa czcionka japońska Hentaigana
W Androidzie 15 domyślnie jest dołączony plik czcionki starej japońskiej Hiragana (zwanej Hentaigana). Dzięki wyjątkowym kształtom postaci hentaigana charakterystyczne dla dzieła sztuki lub wzornictwa, a także pomagają zachować wierność przekazywanie i rozumienie starożytnych japońskich dokumentów.

VideoLAN cone Copyright (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. To logo lub jego zmodyfikowana wersja może być używane lub modyfikowane przez dowolną osobę w odniesieniu do projektu VideoLAN lub dowolnego produktu opracowanego przez zespół VideoLAN, ale nie oznacza poparcia przez projekt.
Vulkan i logo Vulkan są zastrzeżonymi znakami towarowymi Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL jest zastrzeżonym znakiem towarowym, a logo OpenGL ES jest znakiem towarowym firmy Hewlett Packard Enterprise używanym za zgodą Khronos.

