Nền tảng Android 15 có các thay đổi về hành vi có thể ảnh hưởng đến ứng dụng của bạn. Những thay đổi về hành vi sau đây áp dụng cho tất cả ứng dụng khi chạy trên Android 15, bất kể targetSdkVersion. Bạn nên kiểm thử ứng dụng rồi sửa đổi để hỗ trợ những thay đổi này cho phù hợp (nếu cần).
Ngoài ra, hãy nhớ tham khảo danh sách các thay đổi về hành vi chỉ ảnh hưởng đến những ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 15.
Chức năng cốt lõi
Android 15 sửa đổi hoặc mở rộng nhiều chức năng cốt lõi của hệ thống Android.
Thay đổi đối với trạng thái dừng gói
Ý định của trạng thái gói FLAG_STOPPED (mà người dùng có thể tham gia vào các bản dựng AOSP bằng cách nhấn và giữ biểu tượng ứng dụng rồi chọn "Buộc dừng") luôn là giữ cho ứng dụng ở trạng thái này cho đến khi người dùng xoá ứng dụng khỏi trạng thái này một cách rõ ràng bằng cách trực tiếp chạy ứng dụng hoặc gián tiếp tương tác với ứng dụng (thông qua trang chia sẻ hoặc tiện ích, chọn ứng dụng làm hình nền động, v.v.). Trong Android 15, chúng tôi đã cập nhật hành vi của hệ thống để phù hợp với hành vi dự kiến này. Ứng dụng chỉ được xoá khỏi trạng thái đã dừng thông qua hành động trực tiếp hoặc gián tiếp của người dùng.
Để hỗ trợ hành vi dự kiến, ngoài các hạn chế hiện có, hệ thống cũng huỷ tất cả ý định đang chờ xử lý khi ứng dụng chuyển sang trạng thái dừng trên thiết bị chạy Android 15. Khi hành động của người dùng xoá ứng dụng khỏi trạng thái đã dừng, thông báo truyền tin ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED sẽ được gửi đến ứng dụng, tạo cơ hội để đăng ký lại mọi ý định đang chờ xử lý.
Bạn có thể gọi phương thức ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped() mới để xác nhận xem ứng dụng đã được chuyển sang trạng thái dừng hay chưa.
Hỗ trợ kích thước trang 16 KB
Trước đây, Android chỉ hỗ trợ kích thước trang bộ nhớ 4 KB, giúp tối ưu hoá hiệu suất bộ nhớ hệ thống cho tổng dung lượng bộ nhớ trung bình mà các thiết bị Android thường có. Kể từ Android 15, AOSP hỗ trợ các thiết bị được định cấu hình để sử dụng kích thước trang 16 KB (thiết bị 16 KB). Nếu ứng dụng của bạn sử dụng bất kỳ thư viện NDK nào, trực tiếp hoặc gián tiếp thông qua một SDK, thì bạn sẽ cần phải tạo lại ứng dụng để ứng dụng hoạt động trên các thiết bị 16 KB này.
Khi các nhà sản xuất thiết bị tiếp tục sản xuất thiết bị có bộ nhớ vật lý (RAM) lớn hơn, nhiều thiết bị trong số này sẽ áp dụng kích thước trang 16 KB (và cuối cùng là lớn hơn) để tối ưu hoá hiệu suất của thiết bị. Việc thêm khả năng hỗ trợ cho các thiết bị có kích thước trang 16 KB giúp ứng dụng của bạn chạy trên những thiết bị này và giúp ứng dụng của bạn hưởng lợi từ những điểm cải thiện hiệu suất liên quan. Nếu không được biên dịch lại, các ứng dụng sẽ không hoạt động trên các thiết bị 16 KB trong các bản phát hành Android sau này.
Để giúp bạn thêm tính năng hỗ trợ cho ứng dụng, chúng tôi đã cung cấp hướng dẫn về cách kiểm tra xem ứng dụng của bạn có bị ảnh hưởng hay không, cách tạo lại ứng dụng (nếu có) và cách kiểm thử ứng dụng trong môi trường 16 KB bằng trình mô phỏng (bao gồm cả hình ảnh hệ thống Android 15 cho Trình mô phỏng Android).
Lợi ích và mức tăng hiệu suất
Các thiết bị được định cấu hình với kích thước trang 16 KB sử dụng nhiều bộ nhớ hơn một chút trung bình, nhưng cũng có nhiều điểm cải tiến về hiệu suất cho cả hệ thống và ứng dụng:
- Giảm thời gian khởi chạy ứng dụng khi hệ thống chịu áp lực về bộ nhớ: Trung bình thấp hơn 3,16%, với mức cải thiện đáng kể hơn (lên đến 30%) đối với một số ứng dụng mà chúng tôi đã thử nghiệm
- Giảm mức tiêu thụ điện năng trong quá trình khởi chạy ứng dụng: trung bình giảm 4,56%
- Khởi động máy ảnh nhanh hơn: trung bình khởi động nóng nhanh hơn 4,48% và khởi động nguội nhanh hơn 6,60%
- Cải thiện thời gian khởi động hệ thống: trung bình cải thiện 8% (khoảng 950 mili giây)
Những cải tiến này dựa trên thử nghiệm ban đầu của chúng tôi và kết quả trên các thiết bị thực tế có thể sẽ khác. Chúng tôi sẽ phân tích thêm về những lợi ích có thể xảy ra đối với ứng dụng trong quá trình kiểm thử.
Kiểm tra xem ứng dụng của bạn có bị ảnh hưởng hay không
Nếu ứng dụng của bạn sử dụng mã gốc, thì bạn nên tạo lại ứng dụng để hỗ trợ các thiết bị 16 KB. Nếu không chắc chắn liệu ứng dụng của mình có dùng mã gốc hay không, bạn có thể dùng Công cụ phân tích APK để xác định xem có mã gốc nào hay không, sau đó kiểm tra mức căn chỉnh của các phân đoạn ELF cho mọi thư viện dùng chung mà bạn tìm thấy. Android Studio cũng cung cấp các tính năng giúp bạn tự động phát hiện các vấn đề về căn chỉnh.
Nếu ứng dụng của bạn chỉ dùng mã viết bằng ngôn ngữ lập trình Java hoặc Kotlin, bao gồm tất cả các thư viện hoặc SDK, thì ứng dụng của bạn đã hỗ trợ thiết bị 16 KB. Tuy nhiên, bạn nên kiểm thử ứng dụng trong môi trường 16 KB để xác minh rằng không có hồi quy không mong muốn nào trong hành vi của ứng dụng.
Những thay đổi bắt buộc đối với một số ứng dụng để hỗ trợ không gian riêng tư
Không gian riêng tư là một tính năng mới trong Android 15, cho phép người dùng tạo một không gian riêng biệt trên thiết bị của họ để bảo vệ các ứng dụng nhạy cảm khỏi những ánh mắt tò mò, thông qua một lớp xác thực bổ sung. Vì các ứng dụng trong không gian riêng tư bị hạn chế chế độ hiển thị, nên một số loại ứng dụng cần thực hiện thêm các bước để có thể xem và tương tác với các ứng dụng trong không gian riêng tư của người dùng.
Tất cả ứng dụng
Vì các ứng dụng trong không gian riêng tư được lưu giữ trong một hồ sơ người dùng riêng biệt, tương tự như hồ sơ công việc, nên các ứng dụng không được giả định rằng mọi bản sao đã cài đặt của ứng dụng không có trong hồ sơ chính đều nằm trong hồ sơ công việc. Nếu ứng dụng của bạn có logic liên quan đến các ứng dụng hồ sơ công việc đưa ra giả định này, bạn cần điều chỉnh logic này.
Ứng dụng y tế
Khi người dùng khoá không gian riêng tư, tất cả ứng dụng trong không gian riêng tư sẽ bị dừng và các ứng dụng đó không thể thực hiện hoạt động trên nền trước hoặc nền sau, bao gồm cả việc hiển thị thông báo. Hành vi này có thể ảnh hưởng nghiêm trọng đến việc sử dụng và chức năng của các ứng dụng y tế được cài đặt trong không gian riêng tư.
Trải nghiệm thiết lập không gian riêng tư cảnh báo người dùng rằng không gian riêng tư không phù hợp với những ứng dụng cần thực hiện các hoạt động quan trọng trên nền trước hoặc nền, chẳng hạn như hiển thị thông báo từ các ứng dụng y tế. Tuy nhiên, các ứng dụng không thể xác định xem chúng có đang được sử dụng trong không gian riêng tư hay không, vì vậy, các ứng dụng không thể hiển thị cảnh báo cho người dùng trong trường hợp này.
Vì những lý do này, nếu bạn phát triển một ứng dụng y tế, hãy xem xét mức độ ảnh hưởng của tính năng này đến ứng dụng của bạn và thực hiện các hành động thích hợp (chẳng hạn như thông báo cho người dùng không cài đặt ứng dụng của bạn trong không gian riêng tư) để tránh làm gián đoạn các chức năng quan trọng của ứng dụng.
Ứng dụng trình chạy
Nếu phát triển ứng dụng trình chạy, bạn phải làm như sau thì các ứng dụng trong không gian riêng mới hiển thị:
- Ứng dụng của bạn phải được chỉ định làm ứng dụng trình chạy mặc định cho thiết bị, nghĩa là sở hữu vai trò
ROLE_HOME. - Ứng dụng phải khai báo quyền thông thường
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILEStrong tệp kê khai của ứng dụng.
Các ứng dụng trình chạy khai báo quyền ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES phải xử lý các trường hợp sử dụng không gian riêng tư sau:
- Ứng dụng của bạn phải có vùng chứa trình chạy riêng cho các ứng dụng được cài đặt trong không gian riêng tư. Sử dụng phương thức
getLauncherUserInfo()để xác định loại hồ sơ người dùng đang được xử lý. - Người dùng phải có thể ẩn và hiện vùng chứa không gian riêng tư.
- Người dùng phải có thể khoá và mở khoá vùng chứa không gian riêng tư. Sử dụng phương thức
requestQuietModeEnabled()để khoá (bằng cách truyềntrue) hoặc mở khoá (bằng cách truyềnfalse) không gian riêng tư. Khi khoá, không có ứng dụng nào trong vùng chứa không gian riêng tư sẽ hiển thị hoặc được phát hiện thông qua các cơ chế như tìm kiếm. Ứng dụng của bạn phải đăng ký một trình thu cho các thông báo truyền tin
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLEvàACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLE, đồng thời cập nhật giao diện người dùng trong ứng dụng khi trạng thái khoá hoặc mở khoá của vùng chứa không gian riêng thay đổi. Cả hai thông báo truyền tin này đều bao gồmEXTRA_USERmà ứng dụng của bạn có thể dùng để tham chiếu đến người dùng hồ sơ riêng tư.Bạn cũng có thể sử dụng phương thức
isQuietModeEnabled()để kiểm tra xem hồ sơ không gian riêng tư có bị khoá hay không.
Ứng dụng trên cửa hàng ứng dụng
Không gian riêng tư có một nút "Cài đặt ứng dụng" sẽ khởi chạy một ý định ngầm ẩn để cài đặt ứng dụng vào không gian riêng tư của người dùng. Để ứng dụng của bạn nhận được ý định ngầm ẩn này, hãy khai báo <intent-filter> trong tệp kê khai của ứng dụng bằng <category> của CATEGORY_APP_MARKET.
Đã xoá phông chữ biểu tượng cảm xúc dựa trên PNG
Tệp phông chữ biểu tượng cảm xúc cũ, dựa trên PNG (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf) đã bị xoá, chỉ còn lại tệp dựa trên vectơ. Kể từ Android 13 (API cấp 33), tệp phông chữ biểu tượng cảm xúc mà trình kết xuất biểu tượng cảm xúc của hệ thống sử dụng đã thay đổi từ tệp dựa trên PNG thành tệp dựa trên vectơ. Hệ thống giữ lại tệp phông chữ cũ trong Android 13 và 14 vì lý do tương thích, để các ứng dụng có trình kết xuất phông chữ riêng có thể tiếp tục sử dụng tệp phông chữ cũ cho đến khi có thể nâng cấp.
Để kiểm tra xem ứng dụng của bạn có bị ảnh hưởng hay không, hãy tìm các tệp tham chiếu đến tệp NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf trong mã của ứng dụng.
Bạn có thể chọn điều chỉnh ứng dụng theo một số cách:
- Sử dụng API nền tảng để hiển thị văn bản. Bạn có thể kết xuất văn bản thành một
Canvasđược hỗ trợ bitmap và sử dụng văn bản đó để lấy hình ảnh thô nếu cần. - Thêm tính năng hỗ trợ phông chữ COLRv1 vào ứng dụng. Thư viện nguồn mở FreeType hỗ trợ COLRv1 ở phiên bản 2.13.0 trở lên.
- Trong trường hợp cuối cùng, bạn có thể gói tệp phông chữ biểu tượng cảm xúc cũ (
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) vào APK, mặc dù trong trường hợp đó, ứng dụng của bạn sẽ thiếu các bản cập nhật biểu tượng cảm xúc mới nhất. Để biết thêm thông tin, hãy xem trang dự án GitHub của biểu tượng cảm xúc Noto.
Tăng phiên bản SDK mục tiêu tối thiểu từ 23 lên 24
Android 15 được xây dựng dựa trên
những thay đổi đã được thực hiện trong Android 14 và mở rộng
tăng cường bảo mật. Trong Android 15, ứng dụng có
Không thể cài đặt targetSdkVersion thấp hơn 24.
Việc yêu cầu các ứng dụng đáp ứng các cấp độ API hiện đại giúp đảm bảo tính bảo mật và
quyền riêng tư.
Phần mềm độc hại thường nhắm đến các cấp độ API thấp hơn để né tránh tính bảo mật và quyền riêng tư
được giới thiệu trong các phiên bản Android cao hơn. Ví dụ: một số ứng dụng độc hại sử dụng targetSdkVersion 22 để tránh phải tuân theo mô hình quản lý quyền khi bắt đầu chạy ra mắt năm 2015 trên Android 6.0 Marshmallow (API cấp 23). Thay đổi này của Android 15 khiến phần mềm độc hại khó tránh được bảo mật hơn
và quyền riêng tư. Đang cố cài đặt một ứng dụng nhắm đến API thấp hơn
cấp độ dẫn đến lỗi cài đặt, với một thông báo như sau
xuất hiện trong Logcat:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
Trên các thiết bị nâng cấp lên Android 15, mọi ứng dụng có targetSdkVersion thấp hơn
vẫn còn cài đặt hơn 24.
Nếu cần kiểm thử một ứng dụng nhắm đến cấp độ API cũ hơn, hãy dùng lệnh ADB sau đây:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
Bảo mật và quyền riêng tư
Android 15 ra mắt các biện pháp mạnh mẽ để chống gian lận bằng mật mã một lần (OTP) và bảo vệ nội dung nhạy cảm của người dùng, tập trung vào việc tăng cường bảo vệ Dịch vụ trình nghe thông báo và tính năng chia sẻ màn hình. Các tính năng nâng cao chính bao gồm việc loại bỏ mã OTP khỏi thông báo mà các ứng dụng không đáng tin cậy có thể truy cập, ẩn thông báo trong khi chia sẻ màn hình và bảo mật các hoạt động trong ứng dụng khi mã OTP được đăng. Những thay đổi này nhằm bảo vệ nội dung nhạy cảm của người dùng khỏi các bên không được uỷ quyền.
Nhà phát triển cần lưu ý những điều sau để đảm bảo ứng dụng của họ tương thích với các thay đổi trong Android 15:
Xoá OTP
Android sẽ ngăn các ứng dụng không đáng tin cậy triển khai NotificationListenerService đọc nội dung chưa bị loại bỏ khỏi thông báo khi phát hiện thấy mã xác thực một lần (OTP). Các ứng dụng đáng tin cậy như hiệp hội trình quản lý thiết bị đồng hành được miễn các quy định hạn chế này.
Bảo vệ tính năng chia sẻ màn hình
- Nội dung thông báo sẽ bị ẩn trong các phiên chia sẻ màn hình để bảo vệ quyền riêng tư của người dùng. Nếu ứng dụng triển khai
setPublicVersion(), Android sẽ hiển thị phiên bản công khai của thông báo đóng vai trò là thông báo thay thế trong các ngữ cảnh không an toàn. Nếu không, nội dung thông báo sẽ bị loại bỏ mà không có thêm ngữ cảnh nào. - Nội dung nhạy cảm như nhập mật khẩu sẽ bị ẩn khỏi người xem từ xa để ngăn việc tiết lộ thông tin nhạy cảm của người dùng.
- Hoạt động của các ứng dụng đăng thông báo trong khi chia sẻ màn hình và phát hiện thấy mã xác thực một lần sẽ bị ẩn. Nội dung ứng dụng bị ẩn khỏi trình xem từ xa khi khởi chạy.
- Ngoài tính năng tự động xác định các trường nhạy cảm của Android, nhà phát triển có thể đánh dấu thủ công các phần của ứng dụng là nhạy cảm bằng cách sử dụng
setContentSensitivity. Phần này sẽ bị ẩn khỏi người xem từ xa trong khi chia sẻ màn hình. - Nhà phát triển có thể chọn bật/tắt tuỳ chọn Tắt tính năng bảo vệ khi chia sẻ màn hình trong phần Tuỳ chọn dành cho nhà phát triển để được miễn trừ khỏi các biện pháp bảo vệ khi chia sẻ màn hình cho mục đích minh hoạ hoặc thử nghiệm. Trình ghi màn hình hệ thống mặc định sẽ được miễn trừ khỏi những thay đổi này vì bản ghi vẫn nằm trên thiết bị.
Camera và nội dung nghe nhìn
Android 15 thực hiện những thay đổi sau đối với hành vi của camera và nội dung nghe nhìn cho tất cả các ứng dụng.
Việc phát trực tiếp và phát âm thanh từ bộ nhớ ngoài sẽ làm mất hiệu lực các bản âm thanh trực tiếp hoặc bản âm thanh từ bộ nhớ ngoài đã mở trước đó khi đạt đến giới hạn tài nguyên
Trước Android 15, nếu một ứng dụng yêu cầu phát trực tiếp hoặc phát âm thanh khi một ứng dụng khác đang phát âm thanh và đã đạt đến giới hạn tài nguyên, thì ứng dụng đó sẽ không mở được AudioTrack mới.
Kể từ Android 15, khi một ứng dụng yêu cầu phát trực tiếp hoặc phát tải xuống và đạt đến giới hạn tài nguyên, hệ thống sẽ vô hiệu hoá mọi đối tượng AudioTrack đang mở để ngăn việc thực hiện yêu cầu bản nhạc mới.
(Các kênh âm thanh trực tiếp và tải xuống thường được mở để phát các định dạng âm thanh nén. Các trường hợp sử dụng phổ biến để phát âm thanh trực tiếp bao gồm truyền trực tuyến âm thanh đã mã hoá qua HDMI đến TV. Các bản nhạc tải xuống thường được dùng để phát âm thanh nén trên thiết bị di động có tính năng tăng tốc DSP phần cứng.)
Trải nghiệm người dùng và giao diện người dùng hệ thống
Android 15 có một số thay đổi nhằm mang đến trải nghiệm người dùng nhất quán và trực quan hơn.
Ảnh động xem trước thao tác quay lại được bật cho những ứng dụng đã chọn sử dụng
Kể từ Android 15, tuỳ chọn dành cho nhà phát triển về ảnh động xem trước thao tác quay lại đã bị xoá. Giờ đây, ảnh động hệ thống như quay lại trang chủ, giữa các tác vụ và giữa các hoạt động sẽ xuất hiện cho các ứng dụng đã chọn sử dụng tính năng xem trước thao tác quay lại hoàn toàn hoặc ở cấp độ hoạt động. Nếu ứng dụng của bạn bị ảnh hưởng, hãy làm như sau:
- Đảm bảo rằng ứng dụng của bạn đã được di chuyển đúng cách để sử dụng cử chỉ vuốt ngược để dự đoán.
- Đảm bảo rằng các hiệu ứng chuyển đổi mảnh của bạn hoạt động với tính năng điều hướng xem trước thao tác quay lại.
- Di chuyển khỏi hiệu ứng chuyển động và hiệu ứng chuyển đổi khung, thay vào đó, hãy sử dụng hiệu ứng chuyển đổi ảnh động và androidx.
- Di chuyển khỏi ngăn xếp lui mà
FragmentManagerkhông biết. Thay vào đó, hãy sử dụng ngăn xếp lui doFragmentManagerhoặc thành phần Điều hướng quản lý.
Tiện ích bị vô hiệu hoá khi người dùng buộc dừng một ứng dụng
Nếu người dùng buộc dừng một ứng dụng trên thiết bị chạy Android 15, thì hệ thống sẽ tạm thời tắt tất cả tiện ích của ứng dụng đó. Các tiện ích có màu xám và người dùng không thể tương tác với các tiện ích đó. Lý do là kể từ Android 15, hệ thống sẽ huỷ tất cả ý định đang chờ xử lý của ứng dụng khi ứng dụng bị buộc dừng.
Hệ thống sẽ bật lại các tiện ích đó vào lần tiếp theo người dùng khởi chạy ứng dụng.
Để biết thêm thông tin, hãy xem phần Thay đổi đối với trạng thái gói đã dừng.
Chế độ cảnh báo bằng chip trên thanh trạng thái truyền nội dung nghe nhìn sẽ thông báo cho người dùng về việc chia sẻ màn hình, truyền và ghi hình
Các lỗ hổng liên quan đến tính năng chiếu màn hình làm lộ dữ liệu riêng tư của người dùng, chẳng hạn như thông tin tài chính, vì người dùng không nhận ra màn hình thiết bị của họ đang được chia sẻ.
Đối với các ứng dụng chạy trên thiết bị có Android 15 QPR1 trở lên, một khối thanh trạng thái lớn và nổi bật sẽ cảnh báo người dùng về mọi hoạt động chiếu màn hình đang diễn ra. Người dùng có thể nhấn vào khối này để ngừng chia sẻ, truyền hoặc ghi lại màn hình của họ. Ngoài ra, tính năng chiếu màn hình sẽ tự động dừng khi màn hình thiết bị bị khoá.
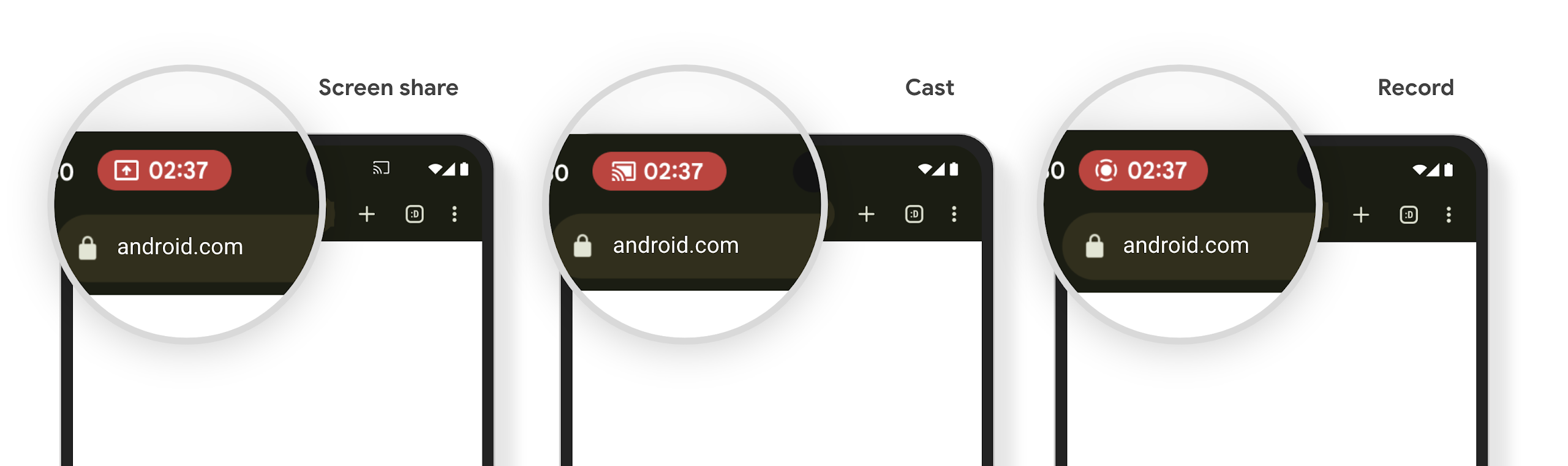
Kiểm tra xem ứng dụng của bạn có bị ảnh hưởng hay không
Theo mặc định, ứng dụng của bạn sẽ bao gồm khối thanh trạng thái và tự động tạm ngưng tính năng chiếu màn hình khi màn hình khoá kích hoạt.
Để tìm hiểu thêm về cách kiểm thử ứng dụng cho các trường hợp sử dụng này, hãy xem phần Khối thanh trạng thái và tính năng tự động dừng.
Hạn chế quyền truy cập mạng khi ở nền sau
Trong Android 15, các ứng dụng bắt đầu yêu cầu mạng bên ngoài vòng đời quy trình hợp lệ sẽ nhận được một ngoại lệ. Thông thường, UnknownHostException hoặc IOException liên quan đến ổ cắm khác. Các yêu cầu mạng xảy ra bên ngoài vòng đời hợp lệ thường là do các ứng dụng vô tình tiếp tục yêu cầu mạng ngay cả sau khi ứng dụng không còn hoạt động.
Để giảm thiểu trường hợp ngoại lệ này, hãy đảm bảo các yêu cầu mạng của bạn nhận biết được vòng đời và bị huỷ khi rời khỏi vòng đời quy trình hợp lệ bằng cách sử dụng các thành phần nhận biết được vòng đời. Nếu bạn cần yêu cầu mạng xảy ra ngay cả khi người dùng rời khỏi ứng dụng, hãy cân nhắc lên lịch yêu cầu mạng bằng WorkManager hoặc tiếp tục một tác vụ hiển thị với người dùng bằng Dịch vụ trên nền trước.
Ngừng sử dụng
Với mỗi bản phát hành, một số API Android cụ thể có thể trở nên lỗi thời hoặc cần được tái cấu trúc để mang lại trải nghiệm tốt hơn cho nhà phát triển hoặc hỗ trợ các tính năng mới của nền tảng. Trong những trường hợp này, chúng tôi chính thức ngừng cung cấp các API lỗi thời và hướng dẫn nhà phát triển sử dụng các API thay thế.
Ngừng cung cấp có nghĩa là chúng tôi đã ngừng hỗ trợ chính thức cho các API này, nhưng các API này sẽ vẫn được cung cấp cho nhà phát triển. Để tìm hiểu thêm về những điểm ngừng sử dụng đáng chú ý trong bản phát hành Android này, hãy xem trang ngừng sử dụng.

