Android 15, önceki sürümlerde olduğu gibi uygulamanızı etkileyebilecek davranış değişiklikleri içerir. Aşağıdaki davranış değişiklikleri yalnızca Android 15 veya sonraki sürümleri hedefleyen uygulamalar için geçerlidir. Uygulamanız Android 15 veya sonraki sürümleri hedefliyorsa uygulamanızı, geçerli olduğu durumlarda bu davranışları düzgün şekilde destekleyecek şekilde değiştirmeniz gerekir.
Uygulamanızın targetSdkVersion değerinden bağımsız olarak Android 15'te çalışan tüm uygulamaları etkileyen davranış değişiklikleri listesini de inceleyin.
Temel işlevler
Android 15, Android sisteminin çeşitli temel özelliklerini değiştirir veya genişletir.
Ön plan hizmetlerinde yapılan değişiklikler
Android 15 ile ön plan hizmetlerinde aşağıdaki değişiklikleri yapıyoruz.
- Veri senkronizasyonu ön plan hizmeti zaman aşımı davranışı
- Yeni medya işleme ön plan hizmet türü
- Ön plan hizmetleri başlatan
BOOT_COMPLETEDyayın alıcılarıyla ilgili kısıtlamalar - Bir uygulama
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOWiznine sahipken ön plan hizmetlerini başlatmayla ilgili kısıtlamalar
Veri senkronizasyonu ön plan hizmeti zaman aşımı davranışı
Android 15, Android 15'i (API düzeyi 35) veya sonraki sürümleri hedefleyen uygulamalar için dataSync'te yeni bir zaman aşımı davranışı sunar. Bu davranış, yeni mediaProcessing ön plan hizmet türü için de geçerlidir.
Sistem, bir uygulamanın dataSync hizmetlerinin 24 saat içinde toplam 6 saat çalışmasına izin verir. Ardından sistem, çalışan hizmetin Service.onTimeout(int, int) yöntemini (Android 15'te kullanıma sunulmuştur) çağırır. Bu sırada hizmetin Service.stopSelf()'u araması için birkaç saniye süre tanınır. Service.onTimeout() çağrıldığında hizmet artık ön plan hizmeti olarak kabul edilmez. Hizmet Service.stopSelf()'ü çağırmazsa sistem dahili bir istisna oluşturur. İstisna, Logcat'e aşağıdaki mesajla kaydedilir:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
Bu davranış değişikliğiyle ilgili sorunları önlemek için aşağıdakilerden birini veya daha fazlasını yapabilirsiniz:
- Hizmetinizin yeni
Service.onTimeout(int, int)yöntemini uygulamasını sağlayın. Uygulamanız geri aramayı aldığında birkaç saniye içindestopSelf()'ü aradığınızdan emin olun. (Uygulamayı hemen durdurmazsanız sistem bir hata oluşturur.) - Uygulamanızın
dataSynchizmetlerinin, 24 saatlik herhangi bir dönemde toplam 6 saatten fazla çalışmadığından emin olun (kullanıcı uygulamayla etkileşime geçerek zamanlayıcıyı sıfırlamazsa). dataSyncön plan hizmetlerini yalnızca doğrudan kullanıcı etkileşimi sonucunda başlatın. Hizmetiniz başladığında uygulamanız ön planda olduğundan, uygulama arka plana geçtikten sonra hizmetiniz altı saat boyunca çalışır.dataSyncön plan hizmeti yerine alternatif bir API kullanın.
Uygulamanızın dataSync ön plan hizmeti son 24 içinde 6 saat çalıştıysa kullanıcı uygulamanızı ön plana getirmediği sürece başka bir dataSync ön plan hizmeti başlatamazsınız (bu durumda zamanlayıcı sıfırlanır). Başka bir dataSync ön plan hizmetini başlatmaya çalışırsanız sistem, "dataSync ön plan hizmet türü için zaman sınırı zaten aşıldı" gibi bir hata mesajıyla ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException oluşturur.
Test
Uygulamanızın davranışını test etmek için uygulamanız Android 15'i hedeflemese bile veri senkronizasyonu zaman aşımlarını etkinleştirebilirsiniz (uygulama Android 15 cihazda çalışıyorsa). Zaman aşımlarını etkinleştirmek için aşağıdaki adb komutunu çalıştırın:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
Ayrıca, sınıra ulaşıldığında uygulamanızın nasıl davrandığını test etmeyi kolaylaştırmak için zaman aşımı süresini ayarlayabilirsiniz. Yeni bir zaman aşımı süresi ayarlamak için aşağıdaki adb komutunu çalıştırın:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Yeni medya işleme ön plan hizmeti türü
Android 15, mediaProcessing adlı yeni bir ön plan hizmet türü kullanıma sunar. Bu hizmet türü, medya dosyalarının kodunu dönüştürme gibi işlemler için uygundur. Örneğin, bir medya uygulaması bir ses dosyası indirebilir ve dosyayı oynatmadan önce farklı bir biçime dönüştürmesi gerekebilir. Uygulama arka plandayken bile dönüşümün devam etmesini sağlamak için bir mediaProcessing ön plan hizmeti kullanabilirsiniz.
Sistem, bir uygulamanın mediaProcessing hizmetlerinin 24 saat içinde toplam 6 saat çalışmasına izin verir. Ardından, çalışan hizmetin Service.onTimeout(int, int) yöntemini (Android 15'te kullanıma sunulmuştur) çağırır. Şu anda hizmetin Service.stopSelf() hizmetini çağırmak için birkaç saniyesi var. Hizmet Service.stopSelf()'ü çağırmazsa sistem dahili bir istisna oluşturur. İstisna aşağıdaki mesajla Logcat'e kaydedilir:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
İstisnayı önlemek için aşağıdakilerden birini yapabilirsiniz:
- Hizmetinizin yeni
Service.onTimeout(int, int)yöntemini uygulamasını sağlayın. Uygulamanız geri aramayı aldığında birkaç saniye içindestopSelf()'ü aradığınızdan emin olun. (Uygulamayı hemen durdurmazsanız sistem bir hata oluşturur.) - Uygulamanızın
mediaProcessinghizmetlerinin herhangi bir 24 saatlik süre içinde toplam 6 saatten fazla çalışmadığından emin olun (kullanıcı uygulamayla etkileşim kurmadığı ve zamanlayıcıyı sıfırladığı sürece). mediaProcessingön plan hizmetlerini yalnızca doğrudan kullanıcı etkileşimi sonucunda başlatın. Hizmetiniz başladığında uygulamanız ön planda olduğundan, uygulama arka plana geçtikten sonra hizmetiniz altı saat boyunca çalışır.mediaProcessingön plan hizmeti yerine WorkManager gibi bir alternatif API kullanın.
Uygulamanızın mediaProcessing ön plan hizmetleri son 24 saat içinde 6 saat boyunca çalıştıysa kullanıcı uygulamanızı ön plana getirmediği (bu durumda zamanlayıcı sıfırlanır) sürece başka bir mediaProcessing ön plan hizmeti başlatamazsınız. Başka bir mediaProcessing ön plan hizmetini başlatmaya çalışırsanız sistem, "mediaProcessing türündeki ön plan hizmeti için zaman sınırı zaten aşıldı" gibi bir hata mesajıyla ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException oluşturur.
mediaProcessing hizmet türü hakkında daha fazla bilgi için Android 15 için ön plan hizmet türlerinde yapılan değişiklikler: Medya işleme başlıklı makaleyi inceleyin.
Test
Uygulamanızın davranışını test etmek için uygulamanız Android 15'i hedeflemese bile medya işleme zaman aşımlarını etkinleştirebilirsiniz (uygulama Android 15 cihazda çalışıyorsa). Zaman aşımlarını etkinleştirmek için aşağıdaki adb komutunu çalıştırın:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
Ayrıca, sınıra ulaşıldığında uygulamanızın nasıl davrandığını test etmeyi kolaylaştırmak için zaman aşımı süresini ayarlayabilirsiniz. Yeni bir zaman aşımı süresi ayarlamak için aşağıdaki adb komutunu çalıştırın:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Ön plan hizmeti başlatan BOOT_COMPLETED yayın alıcılarıyla ilgili kısıtlamalar
Yayınlanacak BOOT_COMPLETED yayın alıcıyla ilgili yeni kısıtlamalar var
ön plan hizmetlerini kullanabilirsiniz. BOOT_COMPLETED alıcıların
Aşağıdaki ön plan hizmeti türleri kullanılabilir:
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(bu kısıtlama,microphoneiçin geçerlidir. Android 14)
Bir BOOT_COMPLETED alıcısı bu tür ön planlardan herhangi birini başlatmaya çalışırsa
özelliklerini sunarsa sistem ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException komutunu atar.
Test
Uygulamanızın davranışını test etmek için, aşağıdaki durumlarda bile bu yeni kısıtlamaları etkinleştirebilirsiniz:
Uygulama Android 15'i hedeflemiyor (uygulama Android 15 yüklü olduğu sürece)
cihazda) olduğunu varsayalım. Aşağıdaki adb komutunu çalıştırın:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Cihazı yeniden başlatmadan BOOT_COMPLETED yayını göndermek için:
aşağıdaki adb komutunu çalıştırın:
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
Bir uygulama SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW iznine sahipken ön plan hizmetlerini başlatmayla ilgili kısıtlamalar
Önceden, SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW iznine sahip bir uygulama, o anda arka planda olsa bile ön plan hizmeti başlatabiliyordu (arka planda başlatma kısıtlamalarından muafiyetler bölümünde açıklandığı gibi).
Bir uygulama Android 15'i hedefliyorsa bu muafiyet artık daha dar olacaktır. Uygulamanın artık SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW iznine sahip olması ve ayrıca görünür bir yer paylaşımı penceresine sahip olması gerekiyor. Yani, ön plan hizmetini başlatmadan önce uygulamanın önce bir TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY penceresi başlatması ve bu pencerenin görünür olması gerekir.
Uygulamanız bu yeni koşulları karşılamadan arka plandan ön plan hizmeti başlatmaya çalışırsa (ve başka bir muafiyeti yoksa) sistem ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException hatası verir.
Uygulamanız SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW iznini beyan ediyorsa ve ön plan hizmetlerini arka plandan başlatıyorsa bu değişiklikten etkilenebilir. Uygulamanız ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException alıyorsa uygulamanızın işlem sırasını kontrol edin ve arka plandan ön plan hizmeti başlatmaya çalışmadan önce uygulamanızda etkin bir yer paylaşımı penceresi bulunduğundan emin olun. View.getWindowVisibility() çağrısını yaparak yer paylaşımı pencerenizin şu anda görünür olup olmadığını kontrol edebilir veya görünürlük her değiştiğinde bildirim almak için View.onWindowVisibilityChanged() değerini geçersiz kılabilirsiniz.
Test
Uygulamanızın davranışını test etmek için, Android 15'i hedeflemese bile bu yeni kısıtlamaları etkinleştirebilirsiniz (uygulamanız Android 15 cihazında çalışıyorsa). Arka plandan ön plan hizmetlerini başlatmayla ilgili bu yeni kısıtlamaları etkinleştirmek için aşağıdaki adb komutunu çalıştırın:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Uygulamaların Rahatsız Etmeyin modunun genel durumunu değiştirebileceği zamanlarla ilgili değişiklikler
Android 15 (API düzeyi 35) ve sonraki sürümleri hedefleyen uygulamalar artık bir cihazdaki Rahatsız Etmeyin (DND) özelliğinin genel durumunu veya politikasını değiştiremez (kullanıcı ayarlarını değiştirerek ya da DND modunu kapatarak). Bunun yerine, uygulamaların bir AutomaticZenRule sağlaması gerekir. Sistem, bu AutomaticZenRule'ı mevcut en kısıtlayıcı politikanın kazandığı şema ile birleştirerek global bir politika oluşturur. Daha önce genel durumu etkileyen mevcut API'lere yapılan çağrılar (setInterruptionFilter, setNotificationPolicy), bu API çağrılarının çağrı döngüsüne bağlı olarak etkinleştirilip devre dışı bırakılan bir örtülü AutomaticZenRule oluşturulmasına veya güncellenmesine neden olur.
Bu değişikliğin yalnızca uygulamanın setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL)'i aradığı ve bu aramanın, daha önce sahipleri tarafından etkinleştirilmiş bir AutomaticZenRule'ı devre dışı bırakmasını beklediği durumlarda gözlemlenebilir davranışı etkilediğini unutmayın.
OpenJDK API değişiklikleri
Android 15, Android'in temel kitaplıklarını en son OpenJDK LTS sürümlerindeki özelliklerle uyumlu hale getirme çalışmalarına devam ediyor.
Bu değişikliklerden bazıları, Android 15'i (API düzeyi 35) hedefleyen uygulamaların uygulama uyumluluğunu etkileyebilir:
Dize biçimlendirme API'lerinde yapılan değişiklikler: Aşağıdaki
String.format()veFormatter.format()API'leri kullanılırken bağımsız değişken dizini, işaretler, genişlik ve duyarlılık doğrulaması artık daha katı bir şekilde yapılıyor:String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
Örneğin, 0 bağımsız değişken dizini kullanıldığında (biçim dizesinde
%0) aşağıdaki istisna oluşturulur:IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0Bu durumda, biçim dizesinde 1 bağımsız değişken dizini (
%1) kullanılarak sorun düzeltilebilir.Arrays.asList(...).toArray()bileşen türünde yapılan değişiklikler:Arrays.asList(...).toArray()kullanılırken sonuçta elde edilen dizinin bileşen türü artıkObject(temel dizinin öğelerinin türü değil) olarak belirlenir. Bu nedenle, aşağıdaki kodClassCastExceptionhatası veriyor:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();Bu durumda, sonuçtaki dizide bileşen türü olarak
Stringdeğerini korumak için bunun yerineCollection.toArray(Object[])değerini kullanabilirsiniz:String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);Dil kodu işleme ile ilgili değişiklikler:
LocaleAPI'si kullanılırken İbranice, Yidiş ve Endonezce dil kodları artık eski biçimlerine (İbranice:iw, Yidiş:jive Endonezce:in) dönüştürülmüyor. Bu yerel ayarlardan birinin dil kodunu belirtirken bunun yerine ISO 639-1'deki kodları (İbranice:he, Yidiş:yive Endonezce:id) kullanın.Rastgele int dizilerinde yapılan değişiklikler: https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574 adresinde yapılan değişikliklerin ardından aşağıdaki
Random.ints()yöntemleri artıkRandom.nextInt()yöntemlerinden farklı bir sayı dizisi döndürüyor:Genel olarak bu değişiklik, uygulamanın bozulmasına neden olmamalıdır ancak kodunuz,
Random.ints()yöntemlerinden oluşturulan dizininRandom.nextInt()ile eşleşmesini beklememelidir.
Yeni SequencedCollection API'si, uygulamanızın derleme yapılandırmasında compileSdk sürümünü Android 15 (API düzeyi 35) kullanacak şekilde güncelledikten sonra uygulamanızın uyumluluğunu etkileyebilir:
MutableList.removeFirst()vekotlin-stdlib'dekiMutableList.removeLast()uzantı işlevleriyle çakışmaJava'daki
Listtürü, Kotlin'dekiMutableListtürüyle eşlenir.List.removeFirst()veList.removeLast()API'leri Android 15'te (API düzeyi 35) kullanıma sunulduğundan Kotlin derleyici, işlev çağrılarını (ör.list.removeFirst())kotlin-stdlib'deki uzantı işlevlerine değil, yeniListAPI'lerine statik olarak çözümler.Bir uygulama,
compileSdkdeğeri35,minSdkdeğeri ise34veya daha düşük olacak şekilde yeniden derlenip Android 14 ve önceki sürümlerde çalıştırılırsa çalışma zamanı hatası verilir:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;Android Gradle eklentisindeki mevcut
NewApilint seçeneği, bu yeni API kullanımlarını yakalayabilir../gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()Çalışma zamanı istisnasını ve lint hatalarını düzeltmek için
removeFirst()veremoveLast()işlev çağrıları Kotlin'de sırasıylaremoveAt(0)veremoveAt(list.lastIndex)ile değiştirilebilir. Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 veya sonraki sürümleri kullanıyorsanız bu hatalar için hızlı düzeltme seçeneği de sunulur.Lint seçeneği devre dışı bırakıldıysa
@SuppressLint("NewApi")velintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }karakterlerini kaldırabilirsiniz.Java'da diğer yöntemlerle çakışma
Mevcut türlere yeni yöntemler eklendi. Örneğin,
ListveDeque. Bu yeni yöntemler, diğer arayüzlerde ve sınıflarda aynı ada ve bağımsız değişken türlerine sahip yöntemlerle uyumlu olmayabilir. Uyumsuzluk nedeniyle yöntem imzası çakışması durumundajavacderleyicisi, derleme zamanı hatası verir. Örneğin:1. örnek hata:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface List2. örnek hata:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 error3. örnek hata:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorBu derleme hatalarını düzeltmek için bu arayüzleri uygulayan sınıf, yöntemi uyumlu bir dönüş türüyle geçersiz kılmalıdır. Örneğin:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
Güvenlik
Android 15, uygulamaları ve kullanıcıları kötü amaçlı uygulamalardan korumak için sistem güvenliğini artıran değişiklikler içerir.
Kısıtlanmış TLS sürümleri
Android 15, TLS 1.0 ve 1.1 sürümlerinin kullanımını kısıtlar. Bu sürümlerin desteği Android'de daha önce sonlandırılmıştı ancak artık Android 15'i hedefleyen uygulamalarda kullanılmasına izin verilmiyor.
Güvenli arka plan etkinliği başlatma
Android 15, kötü amaçlı arka plan uygulamalarının diğer uygulamaları ön plana çıkarmasını, ayrıcalıklarını yükseltmesini ve kullanıcı etkileşimini kötüye kullanmasını engelleyen değişiklikler ekleyerek kullanıcıları kötü amaçlı uygulamalardan korur ve cihazları üzerinde daha fazla kontrol sahibi olmalarını sağlar. Arka plan etkinliği başlatmaları, Android 10'dan (API düzeyi 29) beri kısıtlanmıştır.
Diğer değişiklikler
PendingIntentoluşturucularının arka plan etkinliği başlatmalarını varsayılan olarak engellemesini sağlayın. Bu, uygulamaların kötü niyetli kişiler tarafından kötüye kullanılabilecek birPendingIntentoluşturmasını yanlışlıkla önlemeye yardımcı olur.PendingIntentGönderen izin vermediği sürece bir uygulamayı ön plana getirmeyin. Bu değişikliğin amacı, kötü amaçlı uygulamaların arka planda etkinlik başlatma özelliğini kötüye kullanmasını önlemektir. Varsayılan olarak, oluşturucu arka plan etkinliği başlatma ayrıcalıklarına izin vermediği veya gönderen arka plan etkinliği başlatma ayrıcalıklarına sahip olmadığı sürece uygulamaların görev yığınını ön plana getirmesine izin verilmez.- Bir görev yığınındaki en üstteki etkinliğin görevini nasıl tamamlayabileceğini kontrol edin. En üstteki etkinlik bir görevi tamamlarsa Android, en son etkin olan göreve geri döner. Ayrıca, en üstteki olmayan bir etkinlik görevini tamamlarsa Android ana ekrana geri döner ve bu en üstteki olmayan etkinliğin tamamlanmasını engellemez.
- Diğer uygulamalardan rastgele etkinliklerin kendi görevinizde başlatılmasını önleyin. Bu değişiklik, kötü amaçlı uygulamaların diğer uygulamalardan geliyormuş gibi görünen etkinlikler oluşturarak kullanıcıları kimlik avı saldırılarına karşı korur.
- Görünür olmayan pencerelerin arka plan etkinliği başlatma için değerlendirilmesini engelleme. Bu, kötü amaçlı uygulamaların, kullanıcılara istenmeyen veya kötü amaçlı içerik göstermek için arka plan etkinliği başlatmalarını kötüye kullanmasını önlemeye yardımcı olur.
Daha güvenli amaçlar
Android 15, amaçlar için StrictMode özelliğini sunar.
Intent kullanım ihlalleriyle ilgili ayrıntılı günlükleri görmek için aşağıdaki yöntemi kullanın:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
Kullanıcı deneyimi ve sistem arayüzü
Android 15, daha tutarlı ve sezgisel bir kullanıcı deneyimi oluşturmayı amaçlayan bazı değişiklikler içerir.
Pencere yerleştirme değişiklikleri
Android 15'te pencere içe eklemeleriyle ilgili iki değişiklik vardır: Kenardan kenara ekranlar varsayılan olarak zorunlu kılınmıştır. Ayrıca sistem çubuklarının varsayılan yapılandırması gibi yapılandırma değişiklikleri de vardır.
Uçtan uca yaptırım
Uygulama Android 15'i (API düzeyi 35) hedefliyorsa Android 15 çalıştıran cihazlarda varsayılan olarak uçtan uca görünür.
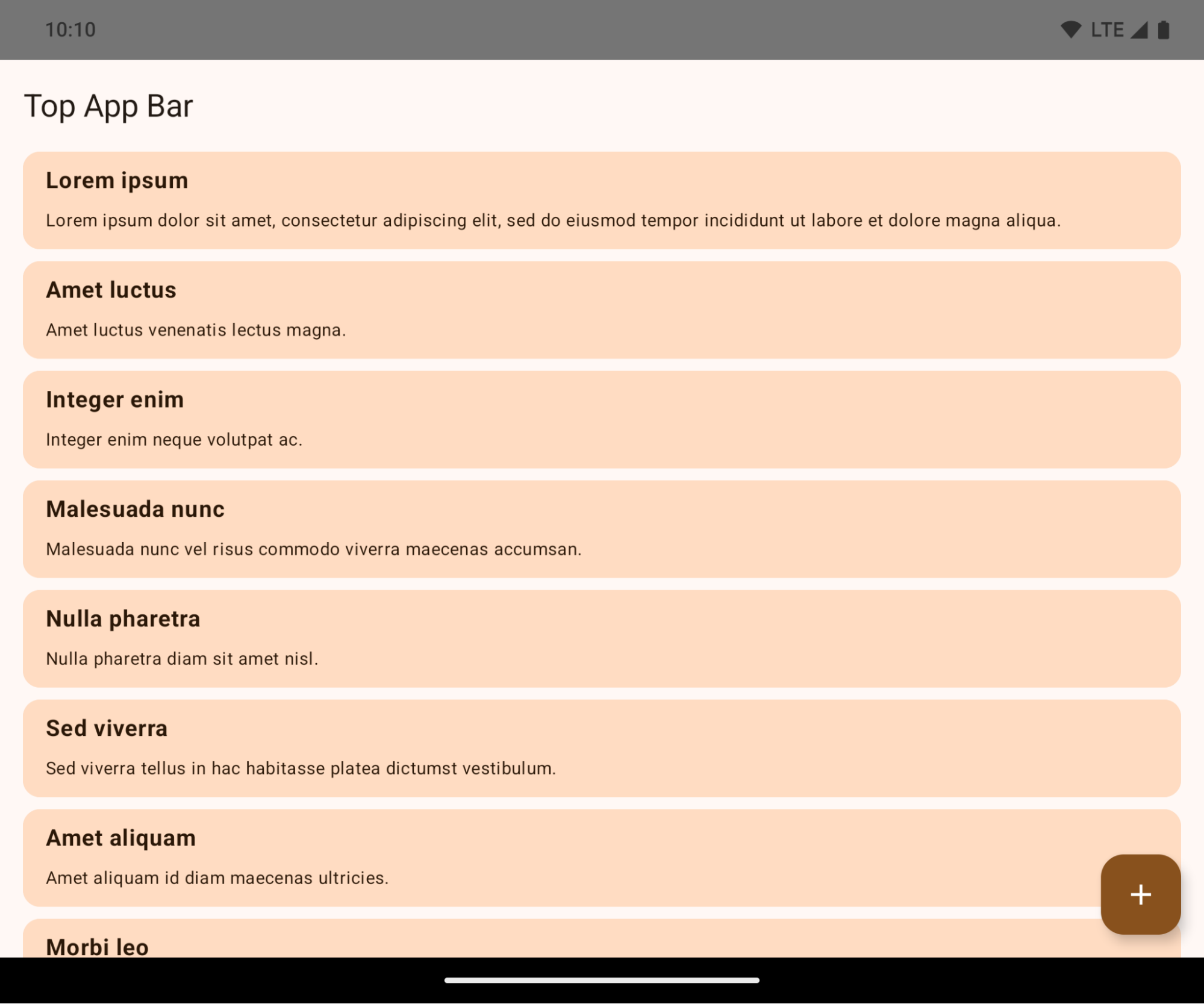
Bu, uygulamanızın kullanıcı arayüzünü olumsuz etkileyebilecek bir değişikliktir. Bu değişiklikler aşağıdaki kullanıcı arayüzü alanlarını etkiler:
- Hareketle gezinme çubuğu
- Varsayılan olarak şeffaftır.
- Alt dengeleme devre dışı bırakıldığından, ekler uygulanmadığı sürece içerik sistem gezinme çubuğunun arkasında çizilir.
setNavigationBarColorveR.attr#navigationBarColordesteği sonlandırıldı ve hareketle gezinmeyi etkilemiyor.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedveR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforced, hareketle navigasyon üzerinde etkili olmamaya devam eder.
- 3 düğmeli gezinme
- Varsayılan olarak% 80 opaklık ayarlanır ve renk, pencere arka planıyla eşleşebilir.
- İç boşluklar uygulanmadığı sürece içerik, sistem gezinme çubuğunun arkasında çizileceğinden alt dengeleme devre dışı bırakılır.
setNavigationBarColorveR.attr#navigationBarColor, varsayılan olarak pencere arka planıyla eşleşecek şekilde ayarlanır. Bu varsayılan değerin uygulanabilmesi için pencere arka planının renkli bir drawable olması gerekir. Bu API kullanımdan kaldırılmıştır ancak 3 düğmeli gezinmeyi etkilemeye devam etmektedir.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedveR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedvarsayılan olarak doğrudur. Bu, 3 düğmeli gezinmede% 80 opaklıkta bir arka plan ekler.
- Durum çubuğu
- Varsayılan olarak şeffaftır.
- Üst dengeleme devre dışı olduğundan, yerleşimler uygulanmadığı sürece içerik durum çubuğunun arkasında çizilir.
setStatusBarColorveR.attr#statusBarColorkullanımdan kaldırıldı ve Android 15'i etkilemiyor.setStatusBarContrastEnforcedveR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedkullanımdan kaldırıldı ancak Android 15'te hâlâ etkili.
- Ekran kesimi
- Sabit olmayan pencerelerin
layoutInDisplayCutoutModedeğeriLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYSolmalıdır.SHORT_EDGES,NEVERveDEFAULT,ALWAYSolarak yorumlanır. Böylece kullanıcılar, ekran kesiminden kaynaklanan siyah çubuğu görmez ve ekran uçtan uca görünür.
- Sabit olmayan pencerelerin
Aşağıdaki örnekte, Android 15'i (API düzeyi 35) hedeflemeden önce ve sonra, ayrıca ekler uygulanmadan önce ve sonraki bir uygulama gösterilmektedir. Bu örnek kapsamlı değildir ve Android Auto'da farklı görünebilir.
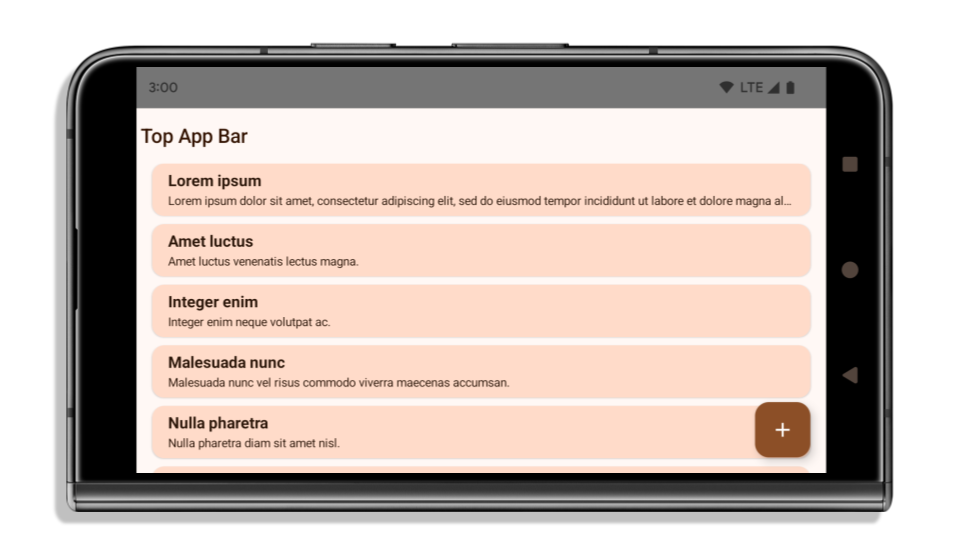

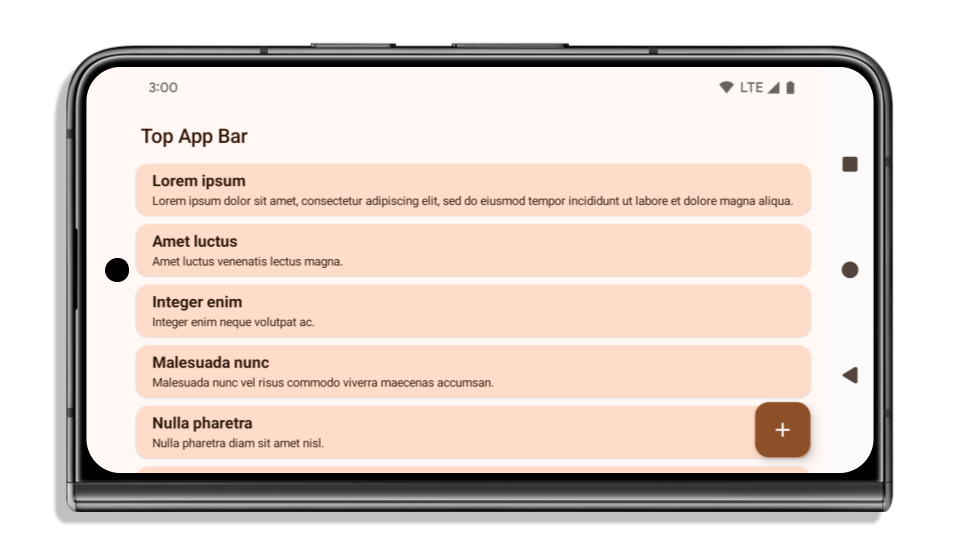
Uygulamanız zaten uçtan uca ise kontrol etmeniz gerekenler
Uygulamanız zaten uçtan uca ise ve iç kısımlar uyguluyorsa aşağıdaki senaryolar dışında bu değişiklikten büyük ölçüde etkilenmezsiniz. Ancak etkilenmediğinizi düşünüyorsanız bile uygulamanızı test etmenizi öneririz.
LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYSyerineSHORT_EDGES,NEVERveyaDEFAULTkullananActivitygibi kaymayan bir pencereniz var. Uygulamanız başlatılırken kilitleniyorsa bunun nedeni açılış ekranınız olabilir. core splashscreen bağımlılığını 1.2.0-alpha01 veya sonraki bir sürüme yükseltebilir ya dawindow.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.alwaysolarak ayarlayabilirsiniz.- Kullanıcı arayüzünün kapalı olduğu, daha az trafik alan ekranlar olabilir. Daha az ziyaret edilen bu ekranlarda kullanıcı arayüzünün kapalı olmadığını doğrulayın. Daha az trafik alan ekranlar şunlardır:
- İlk katılım veya oturum açma ekranları
- Ayarlar sayfaları
Uygulamanız henüz uçtan uca değilse kontrol etmeniz gerekenler
Uygulamanız henüz uçtan uca değilse bu durumdan etkilenmeniz olasıdır. Uygulamaların zaten uçtan uca olduğu senaryolara ek olarak aşağıdakileri de göz önünde bulundurmanız gerekir:
- Uygulamanızda
TopAppBar,BottomAppBarveNavigationBargibi Material 3 bileşenleri (androidx.compose.material3) kullanılıyorsa bu bileşenler, yerleştirmeleri otomatik olarak işlediğinden etkilenmez. - Uygulamanızda Compose'da Material 2 bileşenleri (
androidx.compose.material) kullanılıyorsa bu bileşenler, yerleştirmeleri otomatik olarak işlemez. Ancak ek yerlerine erişebilir ve bunları manuel olarak uygulayabilirsiniz. androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 ve sonraki sürümlerde,windowInsetsparametresini kullanarakBottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigationveNavigationRailiçin dolguları manuel olarak uygulayın. Aynı şekilde,ScaffoldiçincontentWindowInsetsparametresini kullanın. - Uygulamanızda görünümler ve Material Components kullanılıyorsa
(
com.google.android.material),BottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar,NavigationRailViewveyaNavigationViewgibi görünümlere dayalı Material Components'ın çoğu, iç kısımları işler ve ek çalışma gerektirmez. AncakAppBarLayoutkullanıyorsanızandroid:fitsSystemWindows="true"eklemeniz gerekir. - Özel composable'lar için dolgu olarak manuel şekilde yerleştirme uygulayın. İçeriğiniz
ScaffoldiçindeyseScaffolddolgu değerlerini kullanarak iç kısımları kullanabilirsiniz. Aksi takdirde,WindowInsetssimgelerinden birini kullanarak dolgu uygulayın. - Uygulamanızda görünümler ve
BottomSheet,SideSheetveya özel kapsayıcılar kullanılıyorsaViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListenerkullanarak dolgu uygulayın.RecyclerViewiçin bu dinleyiciyi kullanarak dolgu uygulayın veclipToPadding="false"öğesini de ekleyin.
Uygulamanızın özel arka plan koruması sunması gerekiyorsa kontrol etmeniz gerekenler
Uygulamanız 3 düğmeli gezinme veya durum çubuğu için özel arka plan koruması sunmalıdır. Uygulamanız, 3 düğmeli gezinme çubuğu yüksekliğini veya WindowInsets.Type#statusBars değerini almak için WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() kullanarak sistem çubuğunun arkasına bir composable veya görünüm yerleştirmelidir.
Ek uçtan uca kaynaklar
İç kenarlıkları uygulama konusunda ek bilgiler için Kenardan Kenara Görünümler ve Kenardan Kenara Oluşturma kılavuzlarına bakın.
Kullanımdan kaldırılan API'ler
Aşağıdaki API'lerin desteği sonlandırıldı ancak devre dışı bırakılmadı:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(3 düğmeli gezinme için, %80 alfa ile)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(3 düğmeli gezinme için, %80 alfa ile)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
Aşağıdaki API'lerin desteği sonlandırıldı ve bu API'ler devre dışı bırakıldı:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(hareketle gezinme için)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(hareketle gezinme için)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
Kararlı yapılandırma
Uygulamanız Android 15'i (API düzeyi 35) veya sonraki sürümleri hedefliyorsa Configuration artık sistem çubuklarını hariç tutmaz. Düzen hesaplaması için Configuration sınıfında ekran boyutunu kullanıyorsanız ihtiyacınıza bağlı olarak uygun bir ViewGroup, WindowInsets veya WindowMetricsCalculator gibi daha iyi alternatiflerle değiştirmeniz gerekir.
Configuration, API 1'den beri kullanılabilir. Bu bilgiler genellikle Activity.onConfigurationChanged adresinden alınır. Pencere yoğunluğu, yönü ve boyutları gibi bilgiler sağlar. Configuration işlevinden döndürülen pencere boyutlarıyla ilgili önemli bir özellik, daha önce sistem çubuklarını hariç tutmasıdır.
Yapılandırma boyutu genellikle kaynak seçimi için kullanılır (ör. /res/layout-h500dp) ve bu hâlâ geçerli bir kullanım alanıdır. Ancak düzen hesaplaması için kullanılması her zaman önerilmemiştir. Böyle bir durum söz konusuysa hemen uzaklaşmalısınız. Configuration kullanımını, kullanım alanınıza bağlı olarak daha uygun bir ifadeyle değiştirmeniz gerekir.
Düzeni hesaplamak için kullanıyorsanız ViewGroup veya ConstraintLayout gibi uygun bir ViewGroup kullanın.CoordinatorLayout Sistemin gezinme çubuğunun yüksekliğini belirlemek için kullanıyorsanız WindowInsets değerini kullanın. Uygulama pencerenizin mevcut boyutunu öğrenmek istiyorsanız computeCurrentWindowMetrics kullanın.
Aşağıdaki listede, bu değişiklikten etkilenen alanlar açıklanmaktadır:
Configuration.screenWidthDpvescreenHeightDpboyutları artık sistem çubuklarını hariç tutmuyor.Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDp,screenWidthDpvescreenHeightDp'de yapılan değişikliklerden dolaylı olarak etkilenir.Configuration.orientation, kareye yakın cihazlardascreenWidthDpvescreenHeightDpile ilgili değişikliklerden dolaylı olarak etkilenir.Display.getSize(Point),Configurationalanındaki değişikliklerden dolaylı olarak etkilenir. Bu işlev, API düzeyi 30'dan itibaren kullanımdan kaldırılmıştır.Display.getMetrics(), API düzeyi 33'ten beri bu şekilde çalışmaktadır.
elegantTextHeight özelliği varsayılan olarak true değerini alır
Android 15'i (API düzeyi 35) hedefleyen uygulamalarda elegantTextHeight TextView özelliği varsayılan olarak true olur. Bu durumda, varsayılan olarak kullanılan kompakt yazı tipi, büyük dikey metriklere sahip bazı komut dosyalarıyla değiştirilir ve çok daha okunaklı bir yazı tipi kullanılır.
Kompakt yazı tipi, düzenlerin bozulmasını önlemek için kullanıma sunulmuştur. Android 13 (API düzeyi 33), metin düzeninin fallbackLineSpacing özelliğini kullanarak dikey yüksekliği uzatmasına izin vererek bu bozulmaların çoğunu önler.
Android 15'te kompakt yazı tipi sistemde hâlâ mevcuttur. Bu nedenle, uygulamanız öncekiyle aynı davranışı elde etmek için elegantTextHeight değerini false olarak ayarlayabilir ancak bu özelliğin gelecekteki sürümlerde desteklenmeyeceği muhtemeldir. Bu nedenle, uygulamanız Arapça, Laosça, Myanmarca, Tamilce, Guceratça, Kannada, Malayalamca, Odiya, Teluguca veya Tayca yazı tiplerini destekliyorsa elegantTextHeight değerini true olarak ayarlayarak uygulamanızı test edin.
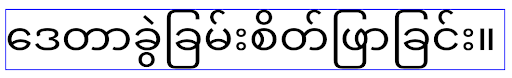
elegantTextHeight Android 14 (API düzeyi 34) ve önceki sürümleri hedefleyen uygulamalar için davranış
elegantTextHeight davranışı.TextView genişliği, karmaşık harf şekilleri için değişiyor
Android'in önceki sürümlerinde, karmaşık şekillendirmeye sahip bazı el yazısı yazı tipleri veya diller, harfleri önceki veya sonraki karakterin alanında çizebilir.
Bazı durumlarda bu tür harfler başlangıç veya bitiş konumunda kesilmiştir.
Android 15'ten itibaren TextView, bu tür harflerin çizilmesi için yeterli alan ayıran bir genişlik atar ve uygulamaların kırpmayı önlemek için sola ek dolgu istemesine olanak tanır.
Bu değişiklik, TextView öğesinin genişliği belirleme şeklini etkilediği için uygulama Android 15 (API düzeyi 35) veya sonraki sürümleri hedefliyorsa TextView varsayılan olarak daha fazla genişlik ayırır. Bu davranışı TextView üzerinde setUseBoundsForWidth API'yi çağırarak etkinleştirebilir veya devre dışı bırakabilirsiniz.
Sol dolgu eklemek mevcut düzenlerde hizalama sorunlarına neden olabileceğinden, Android 15 veya sonraki sürümleri hedefleyen uygulamalarda bile dolgu varsayılan olarak eklenmez.
Ancak setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang işlevini çağırarak kırpmayı önlemek için ek dolgu ekleyebilirsiniz.
Aşağıdaki örneklerde, bu değişikliklerin bazı yazı tipleri ve diller için metin düzenini nasıl iyileştirebileceği gösterilmektedir.

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
EditText için yerel ayara duyarlı varsayılan satır yüksekliği
Android'in önceki sürümlerinde metin düzeni, metnin yüksekliğini mevcut yerel ayarla eşleşen yazı tipinin satır yüksekliğine uyacak şekilde uzatıyordu. Örneğin, içerik Japonca ise Japonca yazı tipinin satır yüksekliği Latin alfabesindeki yazı tipinin satır yüksekliğinden biraz daha yüksek olduğundan metnin yüksekliği de biraz daha yüksek olur. Ancak satır yüksekliklerindeki bu farklılıklara rağmen EditText öğesi, aşağıdaki resimde gösterildiği gibi kullanılan yerel ayardan bağımsız olarak tek tip bir boyuta sahipti:

EditText öğelerini temsil eden üç kutu. Bu diller birbirinden farklı satır yüksekliklerine sahip olsa da EditText'ün yüksekliği aynıdır.Android 15'i (API düzeyi 35) hedefleyen uygulamalarda, EditText için minimum satır yüksekliği artık aşağıdaki resimde gösterildiği gibi belirtilen yerel dilin referans yazı tipiyle eşleşecek şekilde ayrılmıştır:

EditText öğelerini temsil eden üç kutu. EditText öğesinin yüksekliği artık bu dillerin yazı tiplerinin varsayılan satır yüksekliğini barındıracak şekilde boşluk içeriyor.Gerekirse uygulamanız, useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum özelliğini false olarak belirterek önceki davranışı geri yükleyebilir ve Kotlin ile Java'da setMinimumFontMetrics API'sini kullanarak özel minimum dikey metrikler ayarlayabilir.
Kamera ve medya içerikleri
Android 15, Android 15 veya sonraki sürümleri hedefleyen uygulamalarda kamera ve medya davranışıyla ilgili aşağıdaki değişiklikleri yapar.
Ses odağı isteğinde bulunmayla ilgili kısıtlamalar
Android 15'i (API düzeyi 35) hedefleyen uygulamaların ses odağını istemesi için en üstteki uygulama olması veya ön planda bir hizmetin çalışıyor olması gerekir. Bir uygulama bu koşullardan birini karşılamıyorken odaklanma isteğinde bulunursa çağrı AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED döndürülür.
Ses odak noktası hakkında daha fazla bilgiyi Ses odak noktasını yönetme başlıklı makalede bulabilirsiniz.
SDK olmayan arayüzlerle ilgili kısıtlamalar güncellendi
Android 15, Android geliştiricilerle işbirliği ve en son dahili testlere dayalı olarak kısıtlanmış SDK dışı arayüzlerin güncellenmiş listelerini içerir. Mümkün olduğunda, SDK olmayan arayüzleri kısıtlamadan önce herkese açık alternatiflerin kullanılabilir olmasını sağlarız.
Uygulamanız Android 15'i hedeflemiyorsa bu değişikliklerin bazıları sizi hemen etkilemeyebilir. Ancak uygulamanızın hedef API düzeyine bağlı olarak bazı SDK dışı arayüzlere erişmesi mümkün olsa da herhangi bir SDK dışı yöntem veya alan kullanmak uygulamanızın bozulma riskini her zaman yüksek oranda artırır.
Uygulamanızın SDK dışı arayüzler kullanıp kullanmadığından emin değilseniz öğrenmek için uygulamanızı test edebilirsiniz. Uygulamanız SDK dışı arayüzleri kullanıyorsa SDK alternatiflerine geçişi planlamaya başlamalısınız. Bununla birlikte, bazı uygulamaların SDK dışı arayüzleri kullanmak için geçerli kullanım alanları olduğunu anlıyoruz. Uygulamanızdaki bir özellik için SDK olmayan bir arayüz kullanmaya alternatif bulamıyorsanız yeni bir genel API isteğinde bulunmanız gerekir.
Android'in bu sürümündeki değişiklikler hakkında daha fazla bilgi edinmek için Android 15'teki SDK dışı arayüz kısıtlamalarında yapılan güncellemeler başlıklı makaleyi inceleyin. Genel olarak SDK olmayan arayüzler hakkında daha fazla bilgi edinmek için SDK olmayan arayüzlerde kısıtlamalar başlıklı makaleyi inceleyin.
