Come le release precedenti, Android 15 include modifiche al comportamento che potrebbero influire sulla tua app. Le seguenti modifiche al comportamento si applicano esclusivamente alle app che hanno come target Android 15 o versioni successive. Se la tua app ha come target Android 15 o versioni successive, devi modificarla per supportare correttamente questi comportamenti, ove applicabile.
Assicurati di esaminare anche l'elenco delle modifiche al comportamento che interessano tutte le app
in esecuzione su Android 15, indipendentemente dal targetSdkVersion della tua app.
Funzionalità di base
Android 15 modifica o espande varie funzionalità di base del sistema Android.
Modifiche ai servizi in primo piano
Con Android 15 stiamo apportando le seguenti modifiche ai servizi in primo piano.
- Comportamento del timeout del servizio in primo piano di sincronizzazione dei dati
- Nuovo tipo di servizio in primo piano per l'elaborazione di contenuti multimediali
- Limitazioni relative ai broadcast receiver
BOOT_COMPLETEDche avviano servizi in primo piano - Restrizioni relative all'avvio dei servizi in primo piano quando un'app detiene l'autorizzazione
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
Comportamento del timeout del servizio in primo piano di sincronizzazione dei dati
Android 15 introduce un nuovo comportamento di timeout in dataSync per le app che hanno come target Android 15 (livello API 35) o versioni successive. Questo comportamento si applica anche al nuovo
mediaProcessing tipo di servizio in primo piano.
Il sistema consente l'esecuzione dei servizi dataSync di un'app per un totale di 6 ore
in un periodo di 24 ore, dopodiché il sistema chiama il metodo
Service.onTimeout(int, int) del servizio in esecuzione (introdotto in Android
15). Al momento, il servizio ha alcuni secondi di tempo per chiamare
Service.stopSelf(). Quando viene chiamato Service.onTimeout(), il servizio non è più considerato un servizio in primo piano. Se il servizio non chiama Service.stopSelf(), il sistema genera un'eccezione interna. L'eccezione viene registrata in Logcat con il seguente messaggio:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
Per evitare problemi con questa modifica del comportamento, puoi eseguire una o più delle seguenti operazioni:
- Chiedi al tuo servizio di implementare il nuovo metodo
Service.onTimeout(int, int). Quando l'app riceve il Callback, assicurati di chiamarestopSelf()entro alcuni secondi. Se non interrompi immediatamente l'app, il sistema genera un errore. - Assicurati che i servizi
dataSyncdella tua app non vengano eseguiti per più di un totale di 6 ore in un periodo di 24 ore (a meno che l'utente non interagisca con l'app, reimpostando il timer). - Avvia
dataSyncservizi in primo piano solo a seguito dell'interazione diretta degli utenti. Poiché la tua app è in primo piano all'avvio del servizio, il tuo servizio ha a disposizione tutte le sei ore dopo il passaggio dell'app in background. - Anziché utilizzare un servizio in primo piano
dataSync, utilizza un'API alternativa.
Se i servizi in primo piano dataSync della tua app sono stati in esecuzione per 6 ore nelle ultime 24, non puoi avviare un altro servizio in primo piano dataSync a meno che l'utente non abbia portato la tua app in primo piano (il che reimposta il timer). Se provi a avviare un altro servizio in primo piano dataSync, il sistema genera un messaggio di errore ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException come "Tempo limite già esaurito per il servizio in primo piano di tipo dataSync".
Test
Per testare il comportamento dell'app, puoi attivare i timeout della sincronizzazione dei dati anche se la tua app non ha come target Android 15 (a condizione che l'app sia in esecuzione su un dispositivo Android 15). Per abilitare i timeout, esegui questo comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
Puoi anche modificare il periodo di timeout per testare più facilmente il comportamento della tua app quando viene raggiunto il limite. Per impostare un nuovo periodo di timeout, esegui il
seguente comando adb:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Nuovo tipo di servizio in primo piano per l'elaborazione multimediale
Android 15 introduces a new foreground service type, mediaProcessing. This
service type is appropriate for operations like transcoding media files. For
example, a media app might download an audio file and need to convert it to a
different format before playing it. You can use a mediaProcessing foreground
service to make sure the conversion continues even while the app is in the
background.
The system permits an app's mediaProcessing services to run for a total of 6
hours in a 24-hour period, after which the system calls the running service's
Service.onTimeout(int, int) method (introduced in Android
15). At this time, the service has a few seconds to call
Service.stopSelf(). If the service does not
call Service.stopSelf(), the system throws an internal exception. The
exception is logged in Logcat with the following message:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
To avoid having the exception, you can do one of the following:
- Have your service implement the new
Service.onTimeout(int, int)method. When your app receives the callback, make sure to callstopSelf()within a few seconds. (If you don't stop the app right away, the system generates a failure.) - Make sure your app's
mediaProcessingservices don't run for more than a total of 6 hours in any 24-hour period (unless the user interacts with the app, resetting the timer). - Only start
mediaProcessingforeground services as a result of direct user interaction; since your app is in the foreground when the service starts, your service has the full six hours after the app goes to the background. - Instead of using a
mediaProcessingforeground service, use an alternative API, like WorkManager.
If your app's mediaProcessing foreground services have run for 6 hours in the
last 24, you cannot start another mediaProcessing foreground service unless
the user has brought your app to the foreground (which resets the timer). If you
try to start another mediaProcessing foreground service, the system throws
ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
with an error message like "Time limit already exhausted for foreground service
type mediaProcessing".
For more information about the mediaProcessing service type, see Changes to
foreground service types for Android 15: Media processing.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable media processing timeouts even if
your app is not targeting Android 15 (as long as the app is running on an
Android 15 device). To enable timeouts, run the following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
You can also adjust the timeout period, to make it easier to test how your
app behaves when the limit is reached. To set a new timeout period, run the
following adb command:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Limitazioni relative ai BOOT_COMPLETED broadcast receiver che avviano servizi in primo piano
Esistono nuove limitazioni per i BOOT_COMPLETED ricevitori di trasmissione che avviano servizi in primo piano. BOOT_COMPLETED di destinatari non sono autorizzati ad avviare il
i seguenti tipi di servizi in primo piano:
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(questa limitazione è in vigore permicrophonedal giorno Android 14)
Se un receiver BOOT_COMPLETED tenta di avviare uno di questi tipi di servizi in primo piano, il sistema genera un'eccezione ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
Test
Per verificare il comportamento della tua app, puoi attivare queste nuove limitazioni anche se le tue
L'app non ha come target Android 15 (purché l'app sia installata su un Android 15)
dispositivo). Esegui il seguente comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Per inviare un annuncio BOOT_COMPLETED senza riavviare il dispositivo:
esegui questo comando adb:
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
Restrizioni relative all'avvio dei servizi in primo piano quando un'app dispone dell'autorizzazione SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
In precedenza, se un'app disponeva dell'autorizzazione SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW, poteva avviare un servizio in primo piano anche se l'app era attualmente in background (come discusso nella sezione Esclusioni dalle limitazioni di avvio in background).
Se un'app ha come target Android 15, l'esenzione è ora più limitata. Ora l'app deve avere l'autorizzazione SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW e anche una finestra overlay visibile. In altre parole, l'app deve prima avviare una finestra TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY e la finestra deve essere visibile prima di avviare un servizio in primo piano.
Se la tua app tenta di avviare un servizio in primo piano in background senza
soddisfare questi nuovi requisiti (e non ha altre esenzioni), il
sistema restituisce ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
Se la tua app dichiara l'autorizzazione SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
e avvia servizi in primo piano in background, potrebbe essere interessata da questa
modifica. Se la tua app riceve un ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException, controlla l'ordine di operazioni dell'app e assicurati che abbia già una finestra in overlay attiva prima di tentare di avviare un servizio in primo piano da un servizio in background. Puoi controllare se la finestra dell'overlay è attualmente visibile
chiamando View.getWindowVisibility() oppure
puoi eseguire l'override di View.onWindowVisibilityChanged()
per ricevere una notifica ogni volta che la visibilità cambia.
Test
Per testare il comportamento della tua app, puoi attivare queste nuove limitazioni anche se la tua app non ha come target Android 15 (a condizione che l'app sia in esecuzione su un dispositivo Android 15). Per attivare queste nuove limitazioni per l'avvio dei servizi in primo piano
dall'background, esegui il seguente comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Modifiche all'orario in cui le app possono modificare lo stato globale della modalità Non disturbare
Le app che hanno come target Android 15 (livello API 35) e versioni successive non possono più modificare lo stato o i criteri globali della modalità Non disturbare (ND) su un dispositivo (modificando le impostazioni utente o disattivando la modalità ND). Le app devono invece fornire un AutomaticZenRule, che il sistema combina in una norma globale con lo schema vigente che prevede l'applicazione della norma più restrittiva. Le chiamate alle API esistenti che precedentemente influivano sullo stato globale (setInterruptionFilter,
setNotificationPolicy) comportano la creazione o l'aggiornamento di un valore AutomaticZenRule implicito, che viene attivato e disattivato in base al ciclo di chiamata di queste chiamate API.
Tieni presente che questa modifica influisce sul comportamento osservabile solo se l'app chiama setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) e si aspetta che la chiamata disattivi un AutomaticZenRule precedentemente attivato dai relativi proprietari.
Modifiche all'API OpenJDK
Android 15 continua il lavoro di aggiornamento delle librerie di base di Android per allinearle alle funzionalità delle ultime versioni LTS di OpenJDK.
Alcune di queste modifiche possono influire sulla compatibilità delle app che hanno come target Android 15 (livello API 35):
Modifiche alle API di formattazione delle stringhe: la convalida di indice, flag, larghezza e precisione degli argomenti è ora più rigorosa quando si utilizzano le seguenti API
String.format()eFormatter.format():String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
Ad esempio, la seguente eccezione viene generata quando viene utilizzato un indice di argomento pari a 0 (
%0nella stringa di formato):IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0In questo caso, il problema può essere risolto utilizzando un indice di argomento pari a 1 (
%1nella stringa di formato).Modifiche al tipo di componente di
Arrays.asList(...).toArray(): quando utilizziArrays.asList(...).toArray(), il tipo di componente dell'array risultante è oraObject, non il tipo degli elementi dell'array sottostante. Pertanto, il seguente codice genera unClassCastException:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();In questo caso, per conservare
Stringcome tipo di componente nell'array risultante, puoi utilizzareCollection.toArray(Object[]):String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);Modifiche alla gestione dei codici lingua: quando utilizzi l'API
Locale, i codici lingua per ebraico, yiddish e indonesiano non vengono più convertiti nei loro moduli obsoleti (ebraico:iw, yiddish:jie indonesiano:in). Quando specifichi il codice lingua per una di queste impostazioni internazionali, utilizza i codici ISO 639-1 (ebraico:he, yiddish:yie indonesiano:id).Modifiche alle sequenze di numeri interi casuali: in seguito alle modifiche apportate in https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574, i seguenti metodi
Random.ints()ora restituiscono una sequenza di numeri diversa rispetto ai metodiRandom.nextInt():In generale, questa modifica non dovrebbe comportare un comportamento che interrompe il funzionamento dell'app, ma il tuo codice non deve prevedere che la sequenza generata dai metodi
Random.ints()corrisponda aRandom.nextInt().
La nuova API SequencedCollection può influire sulla compatibilità della tua app
dopo che avrai aggiornato compileSdk nella configurazione di build della tua app per utilizzare
Android 15 (livello API 35):
Collisione con le funzioni di estensione
MutableList.removeFirst()eMutableList.removeLast()inkotlin-stdlibIl tipo
Listin Java viene mappato al tipoMutableListin Kotlin. Poiché le APIList.removeFirst()eList.removeLast()sono state introdotte in Android 15 (livello API 35), il compilatore Kotlin risolve le chiamate di funzioni, ad esempiolist.removeFirst(), in modo statico alle nuove APIListanziché alle funzioni di estensione inkotlin-stdlib.Se un'app viene ricompilata con
compileSdkimpostato su35eminSdkimpostato su34o versioni precedenti e poi viene eseguita su Android 14 e versioni precedenti, viene generato un errore di runtime:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;L'opzione lint
NewApiesistente nel plug-in Android per Gradle può rilevare questi nuovi utilizzi dell'API../gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()Per correggere l'eccezione di runtime e gli errori di lint, le chiamate di funzione
removeFirst()eremoveLast()possono essere sostituite rispettivamente conremoveAt(0)eremoveAt(list.lastIndex)in Kotlin. Se utilizzi Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 o versioni successive, è disponibile anche un'opzione di correzione rapida per questi errori.Valuta la possibilità di rimuovere
@SuppressLint("NewApi")elintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }se l'opzione di controllo è stata disattivata.Collisione con altri metodi in Java
Sono stati aggiunti nuovi metodi ai tipi esistenti, ad esempio
ListeDeque. Questi nuovi metodi potrebbero non essere compatibili con i metodi con lo stesso nome e gli stessi tipi di argomenti in altre interfacce e classi. In caso di collisione della firma del metodo con incompatibilità, il compilatorejavacrestituisce un errore in fase di compilazione. Per esempio:Errore di esempio 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface ListEsempio di errore 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorErrore di esempio 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorPer correggere questi errori di compilazione, la classe che implementa queste interfacce deve eseguire l'override del metodo con un tipo restituito compatibile. Ad esempio:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
Sicurezza
Android 15 include modifiche che promuovono la sicurezza del sistema per proteggere le app e gli utenti da app dannose.
Versioni TLS con limitazioni
Android 15 restricts the usage of TLS versions 1.0 and 1.1. These versions had previously been deprecated in Android, but are now disallowed for apps targeting Android 15.
Avvio di attività in background protette
Android 15 protegge gli utenti da app dannose e offre loro un maggiore controllo sui propri dispositivi aggiungendo modifiche che impediscono alle app dannose in background di portare altre app in primo piano, elevare i propri privilegi e abusare dell'interazione con l'utente. Gli avvii di attività in background sono limitati a partire da Android 10 (livello API 29).
Altre modifiche
- Modifica i creator di
PendingIntentin modo che blocchino l'avvio delle attività in background per impostazione predefinita. In questo modo, si impedisce alle app di creare accidentalmente unPendingIntentche potrebbe essere sfruttato da malintenzionati. - Non portare un'app in primo piano a meno che il mittente
PendingIntentnon lo consenta. Questa modifica ha lo scopo di impedire alle app dannose di abusare della possibilità di avviare attività in background. Per impostazione predefinita, le app non sono autorizzate a portare in primo piano lo stack di attività, a meno che il creatore non consenta i privilegi di avvio dell'attività in background o il mittente non disponga di questi privilegi. - Controlla come l'attività principale di una pila di attività può terminare l'attività. Se l'attività in primo piano termina un'attività, Android torna all'ultima attività attiva. Inoltre, se un'attività non in primo piano termina la sua attività, Android tornerà alla schermata Home e non bloccherà il completamento di questa attività non in primo piano.
- Impedisci l'avvio di attività arbitrarie da altre app nella tua attività. Questa modifica impedisce alle app dannose di effettuare phishing sugli utenti creando attività che sembrano provenire da altre app.
- Bloccare l'avvio di attività in background per le finestre non visibili. In questo modo, si impedisce alle app dannose di utilizzare in modo improprio l'avvio di attività in background per mostrare agli utenti contenuti indesiderati o dannosi.
Intenzioni più sicure
Android 15 introduces StrictMode for
intents.
In order to see detailed logs about Intent usage violations, use following
method:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
Esperienza utente e UI di sistema
Android 15 include alcune modifiche volte a creare un'esperienza utente più coerente e intuitiva.
Modifiche all'inserto della finestra
There are two changes related to window insets in Android 15: edge-to-edge is enforced by default, and there are also configuration changes, such as the default configuration of system bars.
Applicazione edge-to-edge
Le app sono edge-to-edge per impostazione predefinita sui dispositivi con Android 15 se l'app ha come target Android 15 (livello API 35).
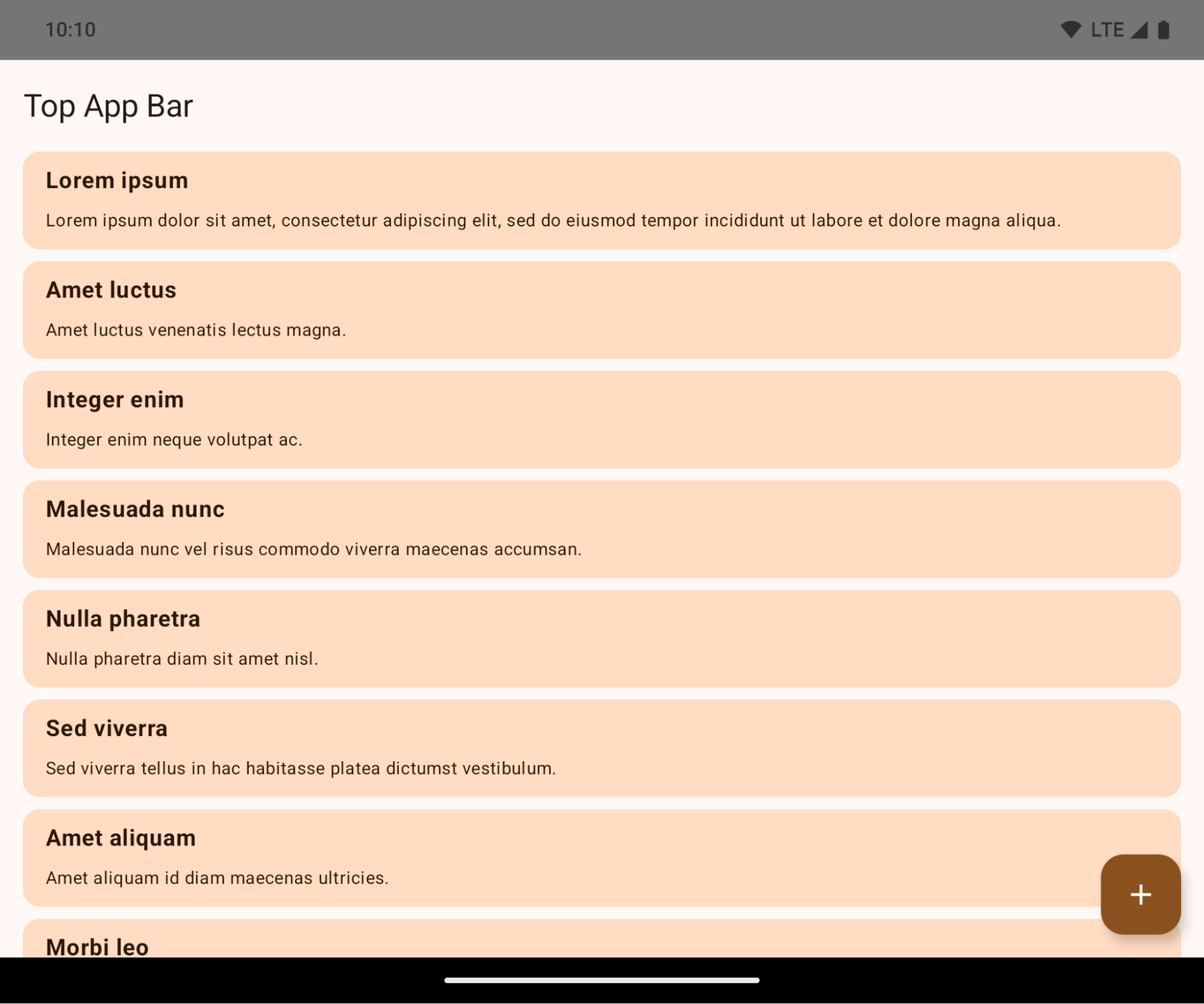
Si tratta di una modifica che causa interruzioni e che potrebbe influire negativamente sull'interfaccia utente della tua app. Le modifiche interessano le seguenti aree dell'interfaccia utente:
- Barra di navigazione con maniglia per i gesti
- Trasparente per impostazione predefinita.
- L'offset inferiore è disattivato, quindi i contenuti vengono visualizzati dietro la barra di navigazione del sistema, a meno che non vengano applicati gli inset.
setNavigationBarColoreR.attr#navigationBarColorsono obsoleti e non influiscono sulla navigazione tramite gesti.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedeR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedcontinuano a non influire sulla navigazione tramite gesti.
- Navigazione con tre pulsanti
- Opacità impostata all'80% per impostazione predefinita, con il colore che potrebbe corrispondere allo sfondo della finestra.
- Offset inferiore disattivato, quindi i contenuti vengono visualizzati dietro la barra di navigazione del sistema a meno che non vengano applicati gli inset.
setNavigationBarColoreR.attr#navigationBarColorsono impostati per corrispondere allo sfondo della finestra per impostazione predefinita. Lo sfondo della finestra deve essere una risorsa drawable a colori per l'applicazione di questo valore predefinito. Questa API è ritirata, ma continua a influire sulla navigazione con tre pulsanti.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedeR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedè impostato su true per impostazione predefinita, il che aggiunge uno sfondo opaco all'80% alla navigazione con tre pulsanti.
- Barra di stato
- Trasparente per impostazione predefinita.
- L'offset superiore è disattivato, quindi i contenuti vengono visualizzati dietro la barra di stato, a meno che non vengano applicati gli inset.
setStatusBarColoreR.attr#statusBarColorsono obsoleti e non hanno alcun effetto su Android 15.setStatusBarContrastEnforcedeR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedsono deprecati, ma hanno ancora un effetto su Android 15.
- Ritaglio del display
layoutInDisplayCutoutModedelle finestre non mobili deve essereLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS.SHORT_EDGES,NEVEReDEFAULTvengono interpretati comeALWAYSin modo che gli utenti non vedano una barra nera causata dal ritaglio del display e che appaia da bordo a bordo.
L'esempio seguente mostra un'app prima e dopo aver scelto come target Android 15 (livello API 35) e prima e dopo l'applicazione degli inset. Questo esempio non è esaustivo e potrebbe essere visualizzato in modo diverso su Android Auto.
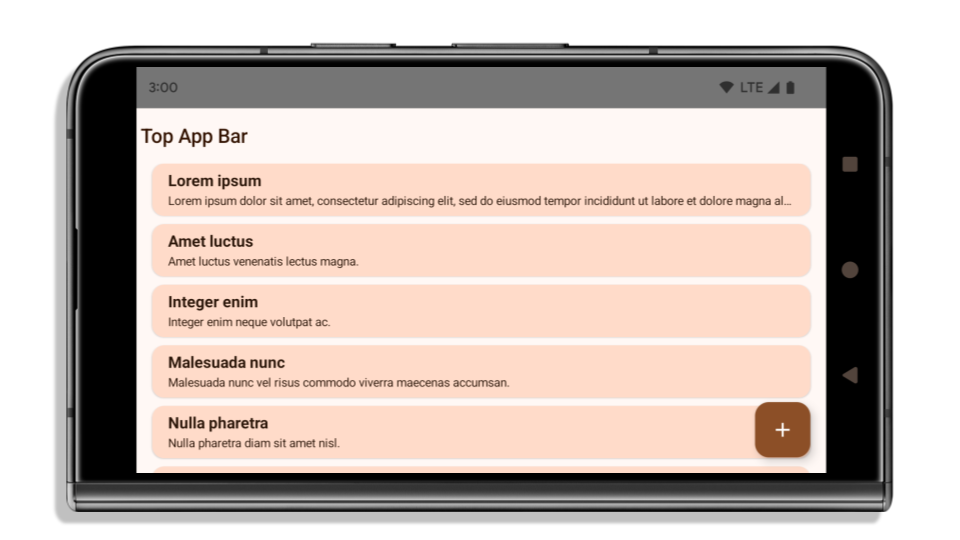

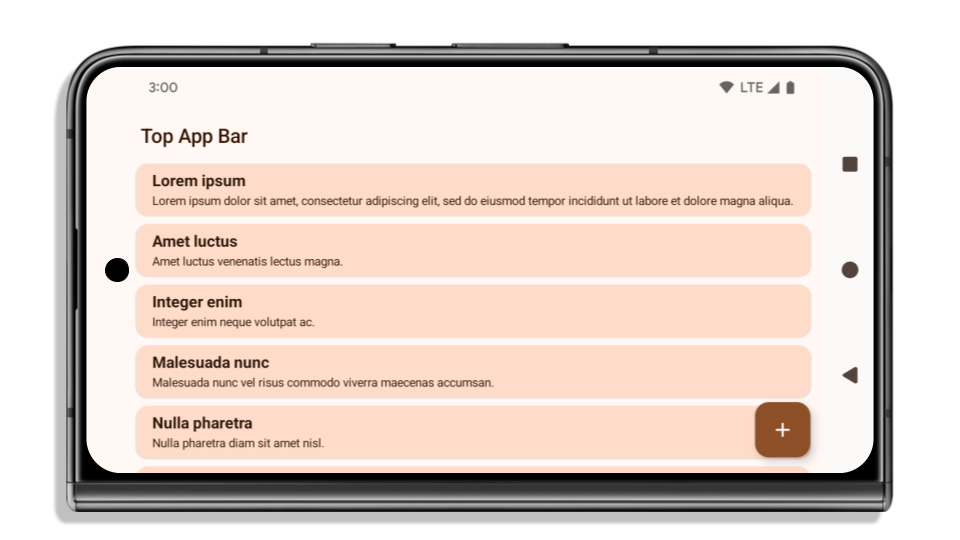
Cosa controllare se la tua app è già edge-to-edge
Se la tua app è già edge-to-edge e applica gli inset, non subirai alcun impatto, tranne nei seguenti scenari. Tuttavia, anche se ritieni di non essere interessato, ti consigliamo di testare la tua app.
- Hai una finestra non mobile, ad esempio un
Activityche utilizzaSHORT_EDGES,NEVERoDEFAULTanzichéLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS. Se la tua app si arresta in modo anomalo all'avvio, il problema potrebbe essere dovuto alla schermata iniziale. Puoi eseguire l'upgrade della dipendenza core splashscreen alla versione 1.2.0-alpha01 o successive oppure impostarewindow.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always. - Potrebbero esserci schermate con traffico inferiore e UI occlusa. Verifica che queste
schermate meno visitate non abbiano un'interfaccia utente occlusa. Le schermate con meno traffico includono:
- Schermate di onboarding o accesso
- Pagine Impostazioni
Cosa controllare se la tua app non è già edge-to-edge
Se la tua app non è già edge-to-edge, è molto probabile che tu sia interessato. Oltre agli scenari per le app già edge-to-edge, devi considerare quanto segue:
- Se la tua app utilizza i componenti Material 3 (
androidx.compose.material3) in Compose, comeTopAppBar,BottomAppBareNavigationBar, è probabile che questi componenti non siano interessati perché gestiscono automaticamente gli inset. - Se la tua app utilizza i componenti Material 2 (
androidx.compose.material) in Compose, questi componenti non gestiscono automaticamente gli inset. Tuttavia, puoi accedere agli inserti e applicarli manualmente. In androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 e versioni successive, utilizza il parametrowindowInsetsper applicare i margini interni manualmente perBottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigationeNavigationRail. Analogamente, utilizza il parametrocontentWindowInsetsperScaffold. - Se la tua app utilizza viste e componenti Material
(
com.google.android.material), la maggior parte dei componenti Material basati sulle viste, comeBottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar,NavigationRailViewoNavigationView, gestisce gli inserti e non richiede ulteriori interventi. Tuttavia, se utilizziAppBarLayout, devi aggiungereandroid:fitsSystemWindows="true". - Per i composable personalizzati, applica gli inset manualmente come padding. Se i tuoi
contenuti si trovano all'interno di un
Scaffold, puoi utilizzare gli inserti con iScaffoldvalori di spaziatura interna. In caso contrario, applica il riempimento utilizzando uno deiWindowInsets. - Se la tua app utilizza visualizzazioni e
BottomSheet,SideSheeto contenitori personalizzati, applica il padding utilizzandoViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener. PerRecyclerView, applica la spaziatura interna utilizzando questo listener e aggiungi ancheclipToPadding="false".
Cosa controllare se la tua app deve offrire la protezione in background personalizzata
Se la tua app deve offrire una protezione personalizzata dello sfondo alla navigazione con tre pulsanti o
alla barra di stato, deve posizionare un elemento componibile o una visualizzazione dietro la barra di sistema
utilizzando WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() per ottenere l'altezza della barra di navigazione
con tre pulsanti o WindowInsets.Type#statusBars.
Risorse aggiuntive da bordo a bordo
Per ulteriori considerazioni sull'applicazione degli inset, consulta le guide Visualizzazioni da bordo a bordo e Composizione da bordo a bordo.
API deprecate
Le seguenti API sono obsolete, ma non disabilitate:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(per la navigazione con tre pulsanti, con trasparenza all'80%)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(per la navigazione con tre pulsanti, con trasparenza all'80%)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
Le seguenti API sono obsolete e disabilitate:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(per la navigazione tramite gesti)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(per la navigazione tramite gesti)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
Configurazione stabile
If your app targets Android 15 (API level 35) or higher, Configuration no
longer excludes the system bars. If you use the screen size in the
Configuration class for layout calculation, you should replace it with better
alternatives like an appropriate ViewGroup, WindowInsets, or
WindowMetricsCalculator depending on your need.
Configuration has been available since API 1. It is typically obtained from
Activity.onConfigurationChanged. It provides information like window density,
orientation, and sizes. One important characteristic about the window sizes
returned from Configuration is that it previously excluded the system bars.
The configuration size is typically used for resource selection, such as
/res/layout-h500dp, and this is still a valid use case. However, using it for
layout calculation has always been discouraged. If you do so, you should move
away from it now. You should replace the use of Configuration with something
more suitable depending on your use case.
If you use it to calculate the layout, use an appropriate ViewGroup, such as
CoordinatorLayout or ConstraintLayout. If you use it to determine the height
of the system navbar, use WindowInsets. If you want to know the current size
of your app window, use computeCurrentWindowMetrics.
The following list describes the fields affected by this change:
Configuration.screenWidthDpandscreenHeightDpsizes no longer exclude the system bars.Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpis indirectly affected by changes toscreenWidthDpandscreenHeightDp.Configuration.orientationis indirectly affected by changes toscreenWidthDpandscreenHeightDpon close-to-square devices.Display.getSize(Point)is indirectly affected by the changes inConfiguration. This was deprecated beginning in API level 30.Display.getMetrics()has already worked like this since API level 33.
L'attributo elegantTextHeight è impostato su true per impostazione predefinita
Per le app destinate ad Android 15 (livello API 35), l'attributo
elegantTextHeight TextView diventa true per impostazione predefinita, sostituendo il carattere compatto utilizzato per impostazione predefinita con alcuni script con metriche verticali grandi con uno molto più leggibile.
Il carattere compatto è stato introdotto per evitare interruzioni dei layout. Android 13 (livello API 33) impedisce molte di queste interruzioni consentendo al layout del testo di estendere l'altezza verticale utilizzando l'attributo fallbackLineSpacing.
In Android 15, il carattere compatto rimane nel sistema, quindi la tua app può impostare elegantTextHeight su false per ottenere lo stesso comportamento di prima, ma è improbabile che sia supportato nelle release future. Pertanto, se la tua app supporta i seguenti script: arabo, lao, birmano, tamil, gujarati, kannada, malayalam, oriya, telugu o thailandese, testa la tua app impostando elegantTextHeight su true.
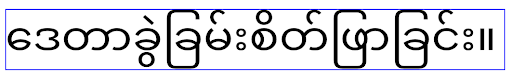 Comportamento di
Comportamento di elegantTextHeight per le app che hanno come target Android 14 (livello API 34) e versioni precedenti.
elegantTextHeight per le app destinate ad Android 15.Modifiche alla larghezza di TextView per forme di lettere complesse
In previous versions of Android, some cursive fonts or languages that have
complex shaping might draw the letters in the previous or next character's area.
In some cases, such letters were clipped at the beginning or ending position.
Starting in Android 15, a TextView allocates width for drawing enough space
for such letters and allows apps to request extra paddings to the left to
prevent clipping.
Because this change affects how a TextView decides the width, TextView
allocates more width by default if the app targets Android 15 (API level 35) or
higher. You can enable or disable this behavior by calling the
setUseBoundsForWidth API on TextView.
Because adding left padding might cause a misalignment for existing layouts, the
padding is not added by default even for apps that target Android 15 or higher.
However, you can add extra padding to preventing clipping by calling
setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang.
The following examples show how these changes can improve text layout for some fonts and languages.

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
Altezza della riga predefinita in base alle impostazioni internazionali per EditText
In previous versions of Android, the text layout stretched the height of the
text to meet the line height of the font that matched the current locale. For
example, if the content was in Japanese, because the line height of the Japanese
font is slightly larger than the one of a Latin font, the height of the text
became slightly larger. However, despite these differences in line heights, the
EditText element was sized uniformly, regardless
of the locale being used, as illustrated in the following image:

EditText elements that
can contain text from English (en), Japanese (ja), and Burmese (my). The
height of the EditText is the same, even though these languages
have different line heights from each other.For apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35), a minimum line height is now
reserved for EditText to match the reference font for the specified Locale, as
shown in the following image:

EditText elements that
can contain text from English (en), Japanese (ja), and Burmese (my). The
height of the EditText now includes space to accommodate the
default line height for these languages' fonts.If needed, your app can restore the previous behavior by specifying the
useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum attribute
to false, and your app can set custom minimum vertical metrics using the
setMinimumFontMetrics API in Kotlin and Java.
Fotocamera e contenuti multimediali
Android 15 apporta le seguenti modifiche al comportamento della fotocamera e dei contenuti multimediali per le app che hanno come target Android 15 o versioni successive.
Limitazioni relative alla richiesta di messa a fuoco dell'audio
Apps that target Android 15 (API level 35) must be the top app or running a
foreground service in order to request audio focus. If an app
attempts to request focus when it does not meet one of these requirements, the
call returns AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED.
You can learn more about audio focus at Manage audio focus.
Limitazioni relative alle interfacce non SDK aggiornate
Android 15 include elenchi aggiornati di interfacce non SDK con limitazioni basati sulla collaborazione con gli sviluppatori Android e sui test interni più recenti. Ove possibile, ci assicuriamo che siano disponibili alternative pubbliche prima di limitare le interfacce non SDK.
Se la tua app non ha come target Android 15, alcune di queste modifiche potrebbero non interessarti immediatamente. Tuttavia, anche se è possibile che la tua app acceda ad alcune interfacce non SDK a seconda del livello API target dell'app, l'utilizzo di qualsiasi metodo o campo non SDK comporta sempre un rischio elevato di interruzione dell'app.
Se non sai con certezza se la tua app utilizza interfacce non SDK, puoi testarla per scoprirlo. Se la tua app si basa su interfacce non SDK, devi iniziare a pianificare una migrazione ad alternative SDK. Tuttavia, siamo consapevoli che alcune app hanno casi d'uso validi per l'utilizzo di interfacce non SDK. Se non riesci a trovare un'alternativa all'utilizzo di un'interfaccia non SDK per una funzionalità della tua app, devi richiedere una nuova API pubblica.
Per scoprire di più sulle modifiche in questa release di Android, consulta Aggiornamenti alle limitazioni relative alle interfacce non SDK in Android 15. Per saperne di più sulle interfacce non SDK in generale, consulta Limitazioni relative alle interfacce non SDK.

