이전 버전과 마찬가지로 Android 15에는 앱에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 동작 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다. 다음 동작 변경사항은 Android 15 이상을 타겟팅하는 앱에만 적용됩니다. 앱이 Android 15 이상을 타겟팅한다면 이러한 동작을 올바르게 지원하도록 앱을 수정해야 합니다(적용되는 경우).
앱의 targetSdkVersion과 관계없이 Android 15에서 실행되는 모든 앱에 영향을 미치는 동작 변경사항 목록도 검토해야 합니다.
핵심 기능
Android 15는 Android 시스템의 다양한 핵심 기능을 수정하거나 확장합니다.
포그라운드 서비스 변경사항
Android 15에서는 포그라운드 서비스가 다음과 같이 변경됩니다.
- 데이터 동기화 포그라운드 서비스 시간 초과 동작
- 새로운 미디어 처리 포그라운드 서비스 유형
- 포그라운드 서비스를 실행하는
BOOT_COMPLETEDbroadcast receiver에 대한 제한사항 - 앱이
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW권한을 보유한 동안 포그라운드 서비스 시작에 적용되는 제한사항
데이터 동기화 포그라운드 서비스 제한 시간 동작
Android 15에서는 Android 15 (API 수준 35) 이상을 타겟팅하는 앱의 dataSync에 새로운 제한 시간 동작을 도입합니다. 이 동작은 새 mediaProcessing 포그라운드 서비스 유형에도 적용됩니다.
시스템은 앱의 dataSync 서비스가 24시간 동안 총 6시간 동안 실행되도록 허용합니다. 그 후에는 실행 중인 서비스의 Service.onTimeout(int, int) 메서드 (Android 15에서 도입됨)를 호출합니다. 이때 서비스는 Service.stopSelf()를 호출할 수 있는 몇 초의 시간을 갖습니다. Service.onTimeout()가 호출되면 서비스는 더 이상 포그라운드 서비스로 간주되지 않습니다. 서비스가 Service.stopSelf()를 호출하지 않으면 시스템에서 내부 예외를 발생시킵니다. 예외는 다음 메시지와 함께 Logcat에 로깅됩니다.
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
이 동작 변경과 관련된 문제를 방지하려면 다음 중 하나 이상을 실행하세요.
- 서비스가 새
Service.onTimeout(int, int)메서드를 구현하도록 합니다. 앱이 콜백을 수신하면 몇 초 이내에stopSelf()를 호출해야 합니다. 앱을 즉시 중지하지 않으면 시스템에서 실패를 생성합니다. - 앱의
dataSync서비스가 24시간 동안 총 6시간 넘게 실행되지 않도록 합니다 (사용자가 앱과 상호작용하여 타이머를 재설정하는 경우 제외). - 직접적인 사용자 상호작용의 결과로만
dataSync포그라운드 서비스를 시작합니다. 서비스가 시작될 때 앱이 포그라운드에 있으므로 앱이 백그라운드로 전환된 후 6시간 동안 서비스가 계속 실행됩니다. dataSync포그라운드 서비스를 사용하는 대신 대체 API를 사용하세요.
앱의 dataSync 포그라운드 서비스가 지난 24시간 동안 6시간 동안 실행된 경우 사용자가 앱을 포그라운드로 가져와 (타이머 재설정) 않는 한 다른 dataSync 포그라운드 서비스를 시작할 수 없습니다. 다른 dataSync 포그라운드 서비스를 시작하려고 하면 시스템에서 '포그라운드 서비스 유형 dataSync의 시간 제한이 이미 소진됨'과 같은 오류 메시지와 함께 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException를 발생시킵니다.
테스트
앱 동작을 테스트하려면 앱이 Android 15를 타겟팅하지 않더라도 (앱이 Android 15 기기에서 실행되는 경우) 데이터 동기화 시간 제한을 사용 설정할 수 있습니다. 제한 시간을 사용 설정하려면 다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
제한에 도달할 때 앱이 어떻게 동작하는지 더 쉽게 테스트할 수 있도록 제한 시간도 조정할 수 있습니다. 새 제한 시간을 설정하려면 다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
새로운 미디어 처리 포그라운드 서비스 유형
Android 15에서는 새로운 포그라운드 서비스 유형인 mediaProcessing가 도입되었습니다. 이 서비스 유형은 미디어 파일 트랜스코딩과 같은 작업에 적합합니다. 예를 들어 미디어 앱에서 오디오 파일을 다운로드한 후 재생하기 전에 다른 형식으로 변환해야 할 수 있습니다. mediaProcessing 포그라운드 서비스를 사용하여 앱이 백그라운드에 있는 동안에도 전환이 계속되도록 할 수 있습니다.
시스템은 앱의 mediaProcessing 서비스가 24시간 동안 총 6시간 동안 실행되도록 허용합니다. 그 후에는 실행 중인 서비스의 Service.onTimeout(int, int) 메서드 (Android 15에서 도입됨)를 호출합니다. 현재 서비스는 몇 초 동안 Service.stopSelf()를 호출할 수 있습니다. 서비스가 Service.stopSelf()를 호출하지 않으면 시스템에서 내부 예외가 발생합니다. 예외는 다음 메시지와 함께 Logcat에 로깅됩니다.
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
예외가 적용되지 않도록 하려면 다음 중 하나를 수행하세요.
- 서비스가 새
Service.onTimeout(int, int)메서드를 구현하도록 합니다. 앱이 콜백을 수신하면 몇 초 내에stopSelf()를 호출해야 합니다. 앱을 즉시 중지하지 않으면 시스템에서 실패를 생성합니다. - 사용자가 앱과 상호작용하여 타이머를 재설정하지 않는 한 앱의
mediaProcessing서비스가 24시간 동안 총 6시간을 초과하여 실행되지 않아야 합니다. - 직접적인 사용자 상호작용의 결과로만
mediaProcessing포그라운드 서비스를 시작합니다. 서비스가 시작될 때 앱이 포그라운드에 있으므로 앱이 백그라운드로 전환된 후 6시간 동안 서비스가 계속 실행됩니다. mediaProcessing포그라운드 서비스를 사용하는 대신 WorkManager와 같은 대체 API를 사용하세요.
앱의 mediaProcessing 포그라운드 서비스가 지난 24시간 동안 6시간 동안 실행된 경우 사용자가 앱을 포그라운드로 가져와 (타이머 재설정) 않는 한 다른 mediaProcessing 포그라운드 서비스를 시작할 수 없습니다. 다른 mediaProcessing 포그라운드 서비스를 시작하려고 하면 시스템에서 '포그라운드 서비스 유형 mediaProcessing의 시간 제한이 이미 소진되었습니다'와 같은 오류 메시지와 함께 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException을 발생시킵니다.
mediaProcessing 서비스 유형에 관한 자세한 내용은 Android 15의 포그라운드 서비스 유형 변경사항: 미디어 처리를 참고하세요.
테스트
앱의 동작을 테스트하려면 앱이 Android 15를 타겟팅하지 않더라도 (앱이 Android 15 기기에서 실행되는 경우) 미디어 처리 시간 제한을 사용 설정할 수 있습니다. 제한 시간을 사용 설정하려면 다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
제한에 도달할 때 앱이 어떻게 동작하는지 더 쉽게 테스트할 수 있도록 제한 시간도 조정할 수 있습니다. 새 제한 시간을 설정하려면 다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
포그라운드 서비스를 실행하는 BOOT_COMPLETED broadcast receiver에 대한 제한사항
출시되는 broadcast receiver BOOT_COMPLETED개에 새로운 제한사항이 있습니다.
포그라운드 서비스가 될 수 있습니다 BOOT_COMPLETED 수신기는 다음 유형의 포그라운드 서비스를 실행할 수 없습니다.
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(이 제한은 이후microphone부터 적용되었음 Android 14)
BOOT_COMPLETED 수신기가 이러한 유형의 포그라운드를 실행하려고 하는 경우
시스템에서 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException을 발생시킵니다.
테스트
앱의 동작을 테스트하기 위해
앱이 Android 15를 타겟팅하지 않음 (앱이 Android 15
기기). 다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
기기를 다시 시작하지 않고 BOOT_COMPLETED 브로드캐스트를 전송하려면 다음 안내를 따르세요.
다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
앱이 SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 권한을 보유한 동안 포그라운드 서비스 시작에 적용되는 제한사항
이전에는 앱이 SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 권한을 보유한 경우 앱이 현재 백그라운드에 있더라도 포그라운드 서비스를 실행할 수 있었습니다 (백그라운드 시작 제한 예외 참고).
앱이 Android 15를 타겟팅하는 경우 이제 이 예외가 더 좁아집니다. 이제 앱에 SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 권한이 있어야 하며 또한 표시되는 오버레이 창이 있어야 합니다. 즉, 앱은 포그라운드 서비스를 시작하기 전에 TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY 창을 먼저 실행하고 이 창을 표시해야 합니다.
앱이 이러한 새로운 요구사항을 충족하지 않고 백그라운드에서 포그라운드 서비스를 시작하려고 하며 다른 예외가 없는 경우 시스템에서 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException이 발생합니다.
앱이 SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 권한을 선언하고 백그라운드에서 포그라운드 서비스를 실행하는 경우 이 변경사항의 영향을 받을 수 있습니다. 앱이 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException를 수신하면 앱의 작업 순서를 확인하고 앱이 백그라운드에서 포그라운드 서비스를 시작하려고 시도하기 전에 앱에 이미 활성 오버레이 창이 있는지 확인합니다. View.getWindowVisibility()를 호출하여 오버레이 창이 현재 표시되는지 확인하거나 View.onWindowVisibilityChanged()를 재정의하여 가시성이 변경될 때마다 알림을 받을 수 있습니다.
테스트
앱의 동작을 테스트하려면 앱이 Android 15를 타겟팅하지 않더라도 (앱이 Android 15 기기에서 실행되는 경우) 이러한 새로운 제한사항을 사용 설정하면 됩니다. 백그라운드에서 포그라운드 서비스를 시작하는 것에 관한 이러한 새로운 제한을 사용 설정하려면 다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
앱이 방해 금지 모드의 전역 상태를 수정할 수 있는 시점 변경
Android 15(API 수준 35) 이상을 타겟팅하는 앱은 더 이상 사용자 설정을 수정하거나 DND 모드를 사용 중지하여 기기의 전역 상태 또는 방해 금지(DND) 정책을 변경할 수 없습니다. 대신 앱은 AutomaticZenRule를 제공해야 하며, 시스템은 이를 기존의 가장 제한적인 정책 우선 적용 스킴과 함께 글로벌 정책으로 결합합니다. 이전에 전역 상태에 영향을 미쳤던 기존 API (setInterruptionFilter, setNotificationPolicy)를 호출하면 암시적 AutomaticZenRule가 생성되거나 업데이트되며, 이는 이러한 API 호출의 호출 주기에 따라 켜지거나 꺼집니다.
이 변경사항은 앱이 setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL)를 호출하고 이 호출이 이전에 소유자가 활성화한 AutomaticZenRule를 비활성화할 것으로 예상하는 경우에만 관찰 가능한 동작에 영향을 줍니다.
OpenJDK API 변경사항
Android 15에서는 최신 OpenJDK LTS 출시의 기능과 일치하도록 Android의 핵심 라이브러리를 새로고침하는 작업을 계속하고 있습니다.
다음과 같은 변경사항은 Android 15 (API 수준 35)를 타겟팅하는 앱의 앱 호환성에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
문자열 형식 API 변경: 이제 다음
String.format()및Formatter.format()API를 사용할 때 인수 색인, 플래그, 너비, 정밀도 검증이 더 엄격해집니다.String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
예를 들어 인덱스가 0인 인수가 사용되면 (형식 문자열의
%0) 다음 예외가 발생합니다.IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0이 경우 형식 문자열에서 인덱스 1 (
%1)을 사용하여 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.Arrays.asList(...).toArray()의 구성요소 유형 변경:Arrays.asList(...).toArray()를 사용할 때 결과 배열의 구성요소 유형이 이제 기본 배열의 요소 유형이 아닌Object입니다. 따라서 다음 코드에서는ClassCastException가 발생합니다.String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();이 경우 결과 배열에서
String을 구성요소 유형으로 유지하려면 대신Collection.toArray(Object[])를 사용하면 됩니다.String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);언어 코드 처리 변경사항:
LocaleAPI를 사용할 때 히브리어, 이디시어, 인도네시아어의 언어 코드가 더 이상 오래된 형식 (히브리어:iw, 이디시어:ji, 인도네시아어:in)으로 변환되지 않습니다. 이러한 언어의 언어 코드를 지정할 때는 ISO 639-1의 코드를 대신 사용하세요 (히브리어:he, 이디시어:yi, 인도네시아어:id).무작위 int 시퀀스 변경사항: https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574에서 변경된 사항에 따라 다음
Random.ints()메서드는 이제Random.nextInt()메서드와 다른 숫자 시퀀스를 반환합니다.일반적으로 이 변경사항으로 인해 앱이 중단되는 동작이 발생하지는 않지만 코드에서
Random.ints()메서드에서 생성된 시퀀스가Random.nextInt()와 일치할 것으로 예상해서는 안 됩니다.
새로운 SequencedCollection API는 앱의 빌드 구성에서 compileSdk을 업데이트하여 Android 15 (API 수준 35)를 사용한 후 앱의 호환성에 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
kotlin-stdlib의MutableList.removeFirst()및MutableList.removeLast()확장 함수와의 충돌Java의
List유형은 Kotlin의MutableList유형에 매핑됩니다.List.removeFirst()및List.removeLast()API는 Android 15(API 수준 35)에서 도입되었으므로 Kotlin 컴파일러는 함수 호출(예:list.removeFirst())을kotlin-stdlib의 확장 함수가 아닌 새로운ListAPI로 정적으로 확인합니다.compileSdk이35으로 설정되고minSdk이34이하로 설정된 상태로 앱이 다시 컴파일된 후 Android 14 이하에서 앱이 실행되면 런타임 오류가 발생합니다.java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;Android Gradle 플러그인의 기존
NewApilint 옵션은 이러한 새로운 API 사용을 포착할 수 있습니다../gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()런타임 예외와 린트 오류를 수정하려면 Kotlin에서
removeFirst()및removeLast()함수 호출을 각각removeAt(0)및removeAt(list.lastIndex)로 대체하면 됩니다. Android 스튜디오 Ladybug | 2024.1.3 이상을 사용하는 경우 이러한 오류에 대한 빠른 수정 옵션도 제공됩니다.lint 옵션이 사용 중지된 경우
@SuppressLint("NewApi")및lintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }를 삭제하는 것이 좋습니다.Java의 다른 메서드와의 충돌
기존 유형(예:
List및Deque)에 새 메서드가 추가되었습니다. 이러한 새 메서드는 다른 인터페이스 및 클래스에서 이름과 인수 유형이 동일한 메서드와 호환되지 않을 수 있습니다. 비호환성으로 인한 메서드 서명 충돌의 경우javac컴파일러는 빌드 시간 오류를 출력합니다. 예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.오류 예 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface List오류 예 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 error오류 예 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 error이러한 빌드 오류를 수정하려면 이러한 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스가 호환되는 반환 유형으로 메서드를 재정의해야 합니다. 예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
보안
Android 15에는 악성 앱으로부터 앱과 사용자를 보호하기 위해 시스템 보안을 강화하는 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
제한된 TLS 버전
Android 15에서는 TLS 버전 1.0 및 1.1의 사용을 제한합니다. 이러한 버전은 이전에 Android에서 지원 중단되었지만 이제 Android 15를 타겟팅하는 앱에서는 허용되지 않습니다.
보안 백그라운드 활동 실행
Android 15는 악성 백그라운드 앱이 다른 앱을 포그라운드로 가져오고, 권한을 상승시키고, 사용자 상호작용을 악용하는 것을 방지하는 변경사항을 추가하여 사용자를 악성 앱으로부터 보호하고 기기를 더 세밀하게 제어할 수 있도록 지원합니다. Android 10 (API 수준 29)부터 백그라운드 활동 실행이 제한되었습니다.
기타 변경사항
- 기본적으로
PendingIntent생성자를 백그라운드 활동 시작을 차단하도록 변경 이렇게 하면 앱이 악의적인 행위자가 악용할 수 있는PendingIntent를 실수로 생성하는 것을 방지할 수 있습니다. PendingIntent발신자가 허용하지 않는 한 앱을 포그라운드로 가져오지 마세요. 이 변경사항은 악성 앱이 백그라운드에서 활동을 시작하는 기능을 악용하지 못하도록 하는 데 목적이 있습니다. 기본적으로 앱은 생성자가 백그라운드 활동 시작 권한을 허용하거나 발신자에게 백그라운드 활동 시작 권한이 없는 한 작업 스택을 포그라운드로 가져올 수 없습니다.- 작업 스택의 상단 활동이 작업을 완료하는 방법을 제어합니다. 상단 활동이 작업을 완료하면 Android는 마지막으로 활성 상태였던 작업으로 돌아갑니다. 또한 최상위가 아닌 활동이 작업을 완료하면 Android는 홈 화면으로 돌아갑니다. 최상위가 아닌 활동의 완료를 차단하지 않습니다.
- 다른 앱에서 임의의 활동이 자체 작업으로 실행되지 않도록 방지 이 변경사항은 악성 앱이 다른 앱에서 온 것처럼 보이는 활동을 만들어 사용자를 피싱하는 것을 방지합니다.
- 백그라운드 활동 실행에 고려되지 않도록 표시되지 않는 창 차단 이렇게 하면 악성 앱이 백그라운드 활동 실행을 악용하여 사용자에게 원치 않는 콘텐츠나 악성 콘텐츠를 표시하는 것을 방지할 수 있습니다.
더 안전한 인텐트
Android 15에서는 인텐트에 StrictMode를 도입합니다.
Intent 사용 위반에 관한 자세한 로그를 보려면 다음 방법을 사용하세요.
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
사용자 경험 및 시스템 UI
Android 15에는 더 일관되고 직관적인 사용자 환경을 만들기 위한 몇 가지 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
창 인셋 변경
Android 15에는 창 인셋과 관련된 두 가지 변경사항이 있습니다. 가장자리에서 가장자리까지가 기본적으로 적용되며 시스템 표시줄의 기본 구성과 같은 구성 변경사항도 있습니다.
더 넓은 화면 적용
앱이 Android 15 (API 수준 35)를 타겟팅하는 경우 Android 15를 실행하는 기기에서 기본적으로 더 넓은 화면을 표시합니다.
이는 앱의 UI에 부정적인 영향을 미칠 수 있는 브레이킹 체인지입니다. 이 변경사항은 다음 UI 영역에 영향을 미칩니다.
- 동작 핸들 탐색 메뉴
- 기본적으로 투명합니다.
- 하단 오프셋이 사용 중지되어 인셋이 적용되지 않는 한 콘텐츠가 시스템 탐색 메뉴 뒤에 그려집니다.
setNavigationBarColor및R.attr#navigationBarColor는 지원 중단되었으며 동작 탐색에 영향을 미치지 않습니다.setNavigationBarContrastEnforced및R.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforced는 동작 탐색에 계속 영향을 미치지 않습니다.
- 3버튼 탐색
- 기본적으로 불투명도가 80% 로 설정되며 색상은 창 배경과 일치할 수 있습니다.
- 인셋이 적용되지 않는 한 콘텐츠가 시스템 탐색 메뉴 뒤에 그려지도록 하단 오프셋이 사용 중지되었습니다.
setNavigationBarColor및R.attr#navigationBarColor는 기본적으로 창 배경과 일치하도록 설정됩니다. 이 기본값이 적용되려면 창 배경이 색상 드로어블이어야 합니다. 이 API는 지원 중단되었지만 3버튼 탐색에 계속 영향을 미칩니다.setNavigationBarContrastEnforced및R.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforced는 기본적으로 true이며, 이는 3버튼 탐색에 80% 불투명한 배경을 추가합니다.
- 상태 표시줄
- 기본적으로 투명합니다.
- 상단 오프셋이 사용 중지되어 인셋이 적용되지 않는 한 콘텐츠가 상태 표시줄 뒤에 그려집니다.
setStatusBarColor및R.attr#statusBarColor는 지원 중단되었으며 Android 15에 영향을 미치지 않습니다.setStatusBarContrastEnforced및R.attr#statusBarContrastEnforced는 지원 중단되었지만 Android 15에 여전히 영향을 미칩니다.
- 디스플레이 컷아웃
- 플로팅되지 않은 창의
layoutInDisplayCutoutMode는LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS이어야 합니다.SHORT_EDGES,NEVER,DEFAULT는 사용자가 디스플레이 컷아웃으로 인해 검은색 막대가 표시되지 않고 가장자리까지 표시되도록ALWAYS로 해석됩니다.
- 플로팅되지 않은 창의
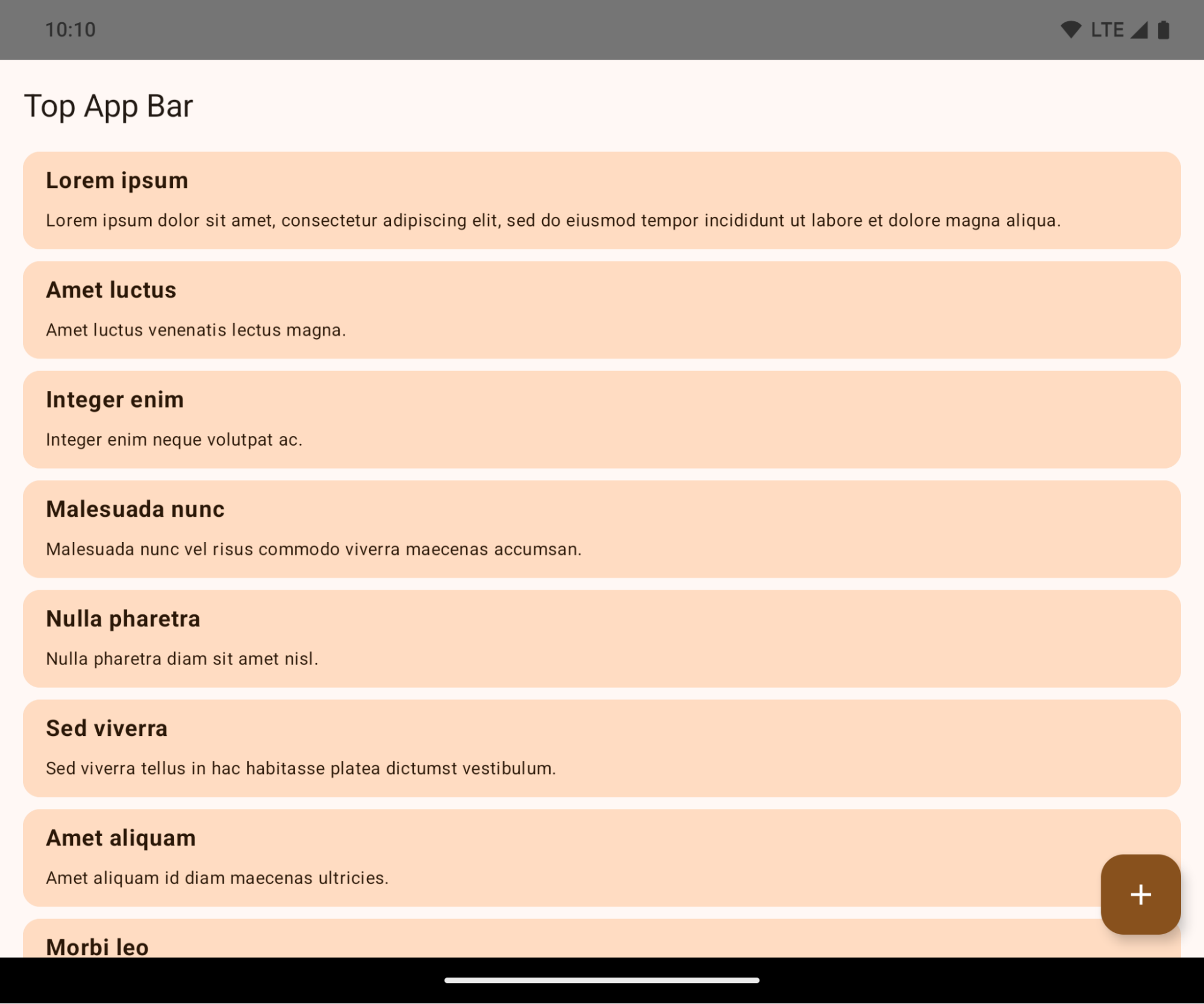
다음 예는 Android 15 (API 수준 35)를 타겟팅하기 전후와 인셋을 적용하기 전후의 앱을 보여줍니다. 이 예는 포괄적이지 않으며 Android Auto에서는 다르게 표시될 수 있습니다.
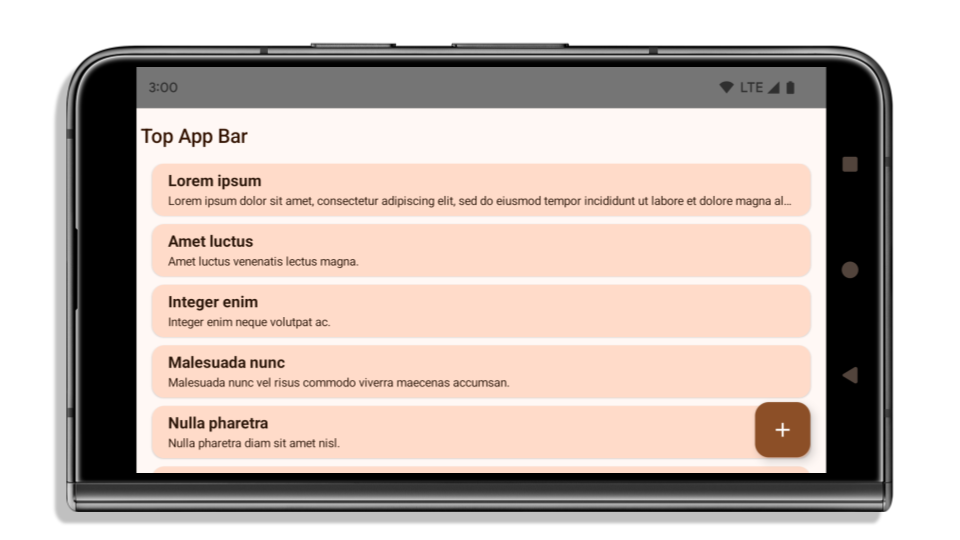
 Android 15 (API 수준 35)를 타겟팅하고 Android 15 기기에서 더 넓은 화면을 사용하는 앱 하지만 이제 Android 15 더 넓은 화면 적용으로 인해 많은 요소가 상태 표시줄, 3버튼 탐색 메뉴 또는 디스플레이 컷아웃에 의해 숨겨집니다. 숨겨진 UI에는 Material 2 상단 앱 바, 플로팅 작업 버튼, 목록 항목이 포함됩니다.
Android 15 (API 수준 35)를 타겟팅하고 Android 15 기기에서 더 넓은 화면을 사용하는 앱 하지만 이제 Android 15 더 넓은 화면 적용으로 인해 많은 요소가 상태 표시줄, 3버튼 탐색 메뉴 또는 디스플레이 컷아웃에 의해 숨겨집니다. 숨겨진 UI에는 Material 2 상단 앱 바, 플로팅 작업 버튼, 목록 항목이 포함됩니다.
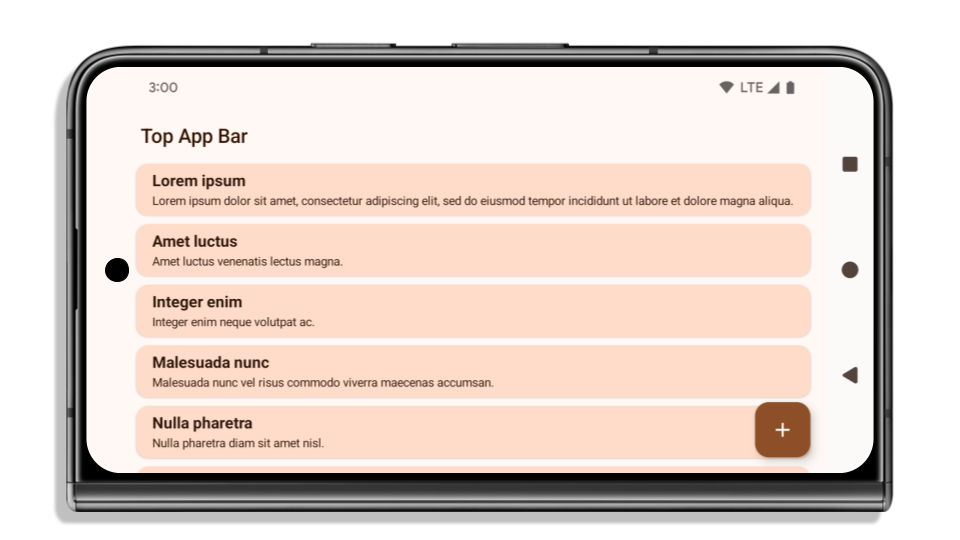
앱이 이미 더 넓은 화면을 사용하고 있는 경우 확인해야 할 사항
앱이 이미 더 넓은 화면이고 인셋을 적용하는 경우 다음 시나리오를 제외하고는 대부분 영향을 받지 않습니다. 영향을 받지 않는다고 생각하더라도 앱을 테스트하는 것이 좋습니다.
LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS대신SHORT_EDGES,NEVER또는DEFAULT을 사용하는Activity와 같은 플로팅되지 않는 창이 있습니다. 앱이 실행 시 비정상 종료되는 경우 스플래시 화면 때문일 수 있습니다. 핵심 스플래시 화면 종속 항목을 1.2.0-alpha01 이상으로 업그레이드하거나window.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always을 설정하면 됩니다.- 트래픽이 적고 UI가 가려진 화면이 있을 수 있습니다. 방문 빈도가 낮은 화면에 가려진 UI가 없는지 확인합니다. 트래픽이 적은 화면은 다음과 같습니다.
- 온보딩 또는 로그인 화면
- 설정 페이지
앱이 아직 더 넓은 화면을 지원하지 않는 경우 확인해야 할 사항
앱이 아직 더 넓은 화면을 지원하지 않는 경우 영향을 받을 가능성이 높습니다. 이미 더 넓은 화면을 사용하는 앱의 시나리오 외에도 다음 사항을 고려해야 합니다.
- 앱이 Compose에서 Material 3 구성요소(
androidx.compose.material3)(예:TopAppBar,BottomAppBar,NavigationBar)를 사용하는 경우 이러한 구성요소는 인셋을 자동으로 처리하므로 영향을 받지 않을 수 있습니다. - 앱이 Compose에서 Material 2 구성요소(
androidx.compose.material)를 사용한다면 이러한 구성요소는 인셋을 자동으로 처리하지 않습니다. 하지만 인셋에 액세스하여 수동으로 적용할 수 있습니다. androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 이상에서windowInsets매개변수를 사용하여BottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigation,NavigationRail에 인셋을 수동으로 적용합니다. 마찬가지로Scaffold에는contentWindowInsets매개변수를 사용합니다. - 앱에서 뷰와 Material 구성요소(
com.google.android.material)를 사용하는 경우BottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar,NavigationRailView,NavigationView와 같은 뷰 기반 Material 구성요소는 대부분 인셋을 처리하므로 추가 작업이 필요하지 않습니다. 하지만AppBarLayout를 사용하는 경우에는android:fitsSystemWindows="true"를 추가해야 합니다. - 맞춤 컴포저블의 경우 인셋을 패딩으로 수동으로 적용합니다. 콘텐츠가
Scaffold내에 있는 경우Scaffold패딩 값을 사용하여 인셋을 사용할 수 있습니다. 그렇지 않으면WindowInsets중 하나를 사용하여 패딩을 적용합니다. - 앱에서 뷰와
BottomSheet,SideSheet또는 맞춤 컨테이너를 사용하는 경우ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener를 사용하여 패딩을 적용합니다.RecyclerView의 경우에는 이 리스너를 사용하여 패딩을 적용하고clipToPadding="false"도 추가합니다.
앱에서 맞춤 백그라운드 보호를 제공해야 하는 경우 확인해야 할 사항
앱이 3버튼 탐색 또는 상태 표시줄에 맞춤 배경 보호를 제공해야 하는 경우 앱은 WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement()를 사용하여 시스템 표시줄 뒤에 컴포저블 또는 뷰를 배치하여 3버튼 탐색 메뉴 높이 또는 WindowInsets.Type#statusBars를 가져와야 합니다.
추가 전체 화면 리소스
인셋 적용에 관한 추가 고려사항은 전체 화면 뷰 및 전체 화면 Compose 가이드를 참고하세요.
지원 중단된 API
다음 API는 지원 중단되었지만 사용 중지되지는 않았습니다.
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(3버튼 탐색, 알파 80%)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(3버튼 탐색, 알파 80%)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
다음 API는 지원 중단되고 사용 중지됩니다.
R.attr#navigationBarColor(동작 탐색용)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(동작 탐색용)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
안정적인 구성
앱이 Android 15 (API 수준 35) 이상을 타겟팅하는 경우 Configuration에서 더 이상 시스템 표시줄을 제외하지 않습니다. 레이아웃 계산에 Configuration 클래스의 화면 크기를 사용하는 경우 필요에 따라 적절한 ViewGroup, WindowInsets 또는 WindowMetricsCalculator와 같은 더 나은 대안으로 대체해야 합니다.
Configuration는 API 1부터 사용할 수 있습니다. 일반적으로 Activity.onConfigurationChanged에서 가져옵니다. 창 밀도, 방향, 크기 등의 정보를 제공합니다. Configuration에서 반환된 창 크기에 관한 중요한 특징은 이전에는 시스템 표시줄이 제외되었다는 점입니다.
구성 크기는 일반적으로 /res/layout-h500dp와 같은 리소스 선택에 사용되며 이는 여전히 유효한 사용 사례입니다. 하지만 레이아웃 계산에 사용하는 것은 항상 권장되지 않았습니다. 이 경우 지금은 멀리 떨어져 있어야 합니다. 사용 사례에 따라 Configuration 사용을 더 적합한 것으로 대체해야 합니다.
레이아웃을 계산하는 데 사용하는 경우 CoordinatorLayout 또는 ConstraintLayout과 같은 적절한 ViewGroup를 사용하세요. 이를 사용하여 시스템 탐색 메뉴의 높이를 결정하는 경우 WindowInsets를 사용하세요. 앱 창의 현재 크기를 알고 싶다면 computeCurrentWindowMetrics를 사용하세요.
다음 목록은 이 변경사항의 영향을 받는 필드를 설명합니다.
Configuration.screenWidthDp및screenHeightDp크기에서 더 이상 시스템 표시줄이 제외되지 않습니다.Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDp은screenWidthDp및screenHeightDp변경사항의 영향을 간접적으로 받습니다.Configuration.orientation은 정사각형에 가까운 기기에서screenWidthDp및screenHeightDp변경사항의 영향을 간접적으로 받습니다.Display.getSize(Point)은Configuration의 변경사항에 간접적으로 영향을 받습니다. API 수준 30부터 지원 중단되었습니다.Display.getMetrics()는 API 수준 33부터 이미 이렇게 작동했습니다.
elegantTextHeight 속성이 기본적으로 true로 설정됨
Android 15 (API 수준 35)를 타겟팅하는 앱의 경우 elegantTextHeight TextView 속성이 기본적으로 true이 되므로 기본적으로 사용되는 소형 글꼴이 세로 측정값이 큰 스크립트로 대체되어 가독성이 훨씬 높아집니다.
좁은 글꼴은 레이아웃이 중단되는 것을 방지하기 위해 도입되었습니다. Android 13 (API 수준 33)은 텍스트 레이아웃이 fallbackLineSpacing 속성을 활용하여 세로 높이를 늘릴 수 있도록 허용하여 이러한 중단을 대부분 방지합니다.
Android 15에서는 소형 글꼴이 여전히 시스템에 남아 있으므로 앱에서 elegantTextHeight를 false로 설정하여 이전과 동일한 동작을 얻을 수 있지만 향후 출시에서는 지원되지 않을 가능성이 큽니다. 따라서 앱이 아랍어, 라오어, 미얀마어, 타밀어, 구자라트어, 칸나다어, 말라얄람어, 오디어, 텔루구어 또는 태국어 스크립트를 지원하는 경우 elegantTextHeight를 true로 설정하여 앱을 테스트합니다.
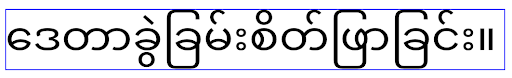
elegantTextHeight 동작
elegantTextHeight 동작복잡한 글자 모양의 TextView 너비 변경
이전 버전의 Android에서는 복잡한 도형을 사용하는 일부 필기체 글꼴이나 언어에서 이전 또는 다음 문자의 영역에 문자를 그릴 수 있습니다.
이러한 문자가 시작 또는 끝 위치에서 잘리는 경우도 있었습니다.
Android 15부터 TextView는 이러한 문자를 위한 공간을 그리기에 충분한 너비를 할당하고 앱이 왼쪽에 추가 패딩을 요청하여 클리핑을 방지할 수 있도록 합니다.
이 변경사항은 TextView가 너비를 결정하는 방식에 영향을 미치므로 앱이 Android 15 (API 수준 35) 이상을 타겟팅하는 경우 TextView는 기본적으로 더 많은 너비를 할당합니다. TextView에서 setUseBoundsForWidth API를 호출하여 이 동작을 사용 설정 또는 사용 중지할 수 있습니다.
왼쪽 패딩을 추가하면 기존 레이아웃이 정렬되지 않을 수 있으므로 Android 15 이상을 타겟팅하는 앱에서도 기본적으로 패딩이 추가되지 않습니다.
하지만 setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang를 호출하여 추가 패딩을 추가하여 잘림을 방지할 수 있습니다.
다음 예는 이러한 변경사항이 일부 글꼴 및 언어의 텍스트 레이아웃을 개선하는 방법을 보여줍니다.

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
EditText의 언어 인식 기본 행 높이
이전 버전의 Android에서는 텍스트 레이아웃이 현재 언어와 일치하는 글꼴의 행 간격을 충족하도록 텍스트 높이를 늘렸습니다. 예를 들어 콘텐츠가 일본어인 경우 일본어 글꼴의 줄 높이가 라틴어 글꼴의 줄 높이보다 약간 더 커서 텍스트의 높이가 약간 더 커졌습니다. 그러나 이러한 줄 높이의 차이에도 불구하고 다음 이미지와 같이 사용되는 언어와 관계없이 EditText 요소의 크기는 균일하게 조정되었습니다.

EditText 요소를 나타내는 상자 3개 언어마다 줄 높이가 다르지만 EditText의 높이는 동일합니다.Android 15(API 수준 35)를 타겟팅하는 앱의 경우 이제 EditText가 지정된 언어의 참조 글꼴과 일치하도록 최소 줄 높이가 예약됩니다(다음 이미지 참고).

EditText 요소를 나타내는 상자 3개 이제 EditText의 높이에 이러한 언어 글꼴의 기본 행 간격을 수용할 수 있는 공백이 포함됩니다.필요한 경우 앱은 useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum 속성을 false로 지정하여 이전 동작을 복원할 수 있으며 Kotlin 및 Java에서 setMinimumFontMetrics API를 사용하여 맞춤 최소 카테고리 측정항목을 설정할 수 있습니다.
카메라 및 미디어
Android 15에서는 Android 15 이상을 타겟팅하는 앱의 카메라 및 미디어 동작이 다음과 같이 변경됩니다.
오디오 포커스 요청 제한사항
Android 15 (API 수준 35)를 타겟팅하는 앱은 오디오 포커스를 요청하려면 최상위 앱이거나 포그라운드 서비스를 실행 중인 앱이어야 합니다. 앱이 이러한 요구사항 중 하나를 충족하지 못할 때 포커스를 요청하려고 하면 호출이 AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED를 반환합니다.
오디오 포커스 관리에서 오디오 포커스에 대해 자세히 알아보세요.
업데이트된 비 SDK 제한사항
Android 15에는 Android 개발자와의 공동작업 및 최신 내부 테스트를 기반으로 제한된 비 SDK 인터페이스의 업데이트된 목록이 포함되어 있습니다. 비 SDK 인터페이스를 제한하는 경우, 가능하면 해당 인터페이스에 대한 공개된 대안이 사용 가능한지 여부를 확인합니다.
Android 15를 타겟팅하지 않는 앱의 경우 이러한 변경사항 중 일부는 개발자에게 곧바로 영향을 주지 않을 수도 있습니다. 하지만 앱의 타겟 API 수준에 따라 앱이 일부 비 SDK 인터페이스에 액세스할 수 있지만 비 SDK 메서드나 필드를 사용하면 항상 앱이 중단될 위험이 높습니다.
앱에서 비 SDK 인터페이스를 사용하는지 확실히 알 수 없는 경우 앱을 테스트하여 확인할 수 있습니다. 앱에서 비 SDK 인터페이스를 사용하는 경우 대체 SDK로 이전을 계획해야 합니다. 일부 앱의 경우 비 SDK 인터페이스 사용에 관한 유효한 사용 사례가 있음을 알고 있습니다. 앱 기능을 구현하기 위해 비 SDK 인터페이스를 사용하는 것 외에 방법을 찾을 수 없는 경우에는 새 공개 API를 요청해야 합니다.
이 Android 버전의 변경사항을 자세히 알아보려면 Android 15의 비 SDK 인터페이스 제한사항 업데이트를 참고하세요. 비 SDK 인터페이스에 관해 전반적으로 알아보려면 비 SDK 인터페이스 제한사항을 참고하세요.

