Önceki sürümlerde olduğu gibi Android 16 da uygulamanızı etkileyebilecek davranış değişiklikleri içerir. Aşağıdaki davranış değişiklikleri yalnızca Android 16 veya sonraki sürümleri hedefleyen uygulamalar için geçerlidir. Uygulamanız Android 16 veya sonraki sürümleri hedefliyorsa uygulanabilir durumlarda bu davranışları destekleyecek şekilde uygulamanızı değiştirmeniz gerekir.
Uygulamanızın targetSdkVersion değerinden bağımsız olarak, Android 16'da çalışan tüm uygulamaları etkileyen davranış değişiklikleri listesini de incelemeyi unutmayın.
Kullanıcı deneyimi ve sistem arayüzü
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), daha tutarlı ve sezgisel bir kullanıcı deneyimi oluşturmak için aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Uçtan uca kapsam dışında kalma özelliği kaldırılıyor
Android 15'i (API düzeyi 35) hedefleyen uygulamalarda Android 15'te uçtan uca görünüm zorunlu kılındı. Ancak uygulamanız R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement değerini true olarak ayarlayarak bu zorunluluğu devre dışı bırakabilir. Android 16'yı (API düzeyi 36) hedefleyen uygulamalarda R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement desteği sonlandırıldı ve devre dışı bırakıldı. Uygulamanız uçtan uca ekran özelliğini devre dışı bırakamaz.
- Uygulamanız Android 16'yı (API düzeyi 36) hedefliyorsa ve Android 15 cihazda çalışıyorsa
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementçalışmaya devam eder. - Uygulamanız Android 16'yı (API düzeyi 36) hedefliyorsa ve Android 16 cihazda çalışıyorsa
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementdevre dışı bırakılır.
Android 16'da test için uygulamanızın uçtan uca desteklediğinden emin olun ve R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement kullanımını kaldırın. Böylece uygulamanız Android 15 cihazlarda da uçtan uca desteklenir. Uçtan uca desteği için Compose (Oluşturma) ve Views (Görünümler) kılavuzuna bakın.
Tahmin edilen geri gitme özelliği için taşıma veya devre dışı bırakma işlemi gerekir
Android 16'yı (API düzeyi 36) veya sonraki sürümleri hedefleyen ve Android 16 ya da sonraki sürümlerin yüklü olduğu cihazlarda çalışan uygulamalarda tahmin edilen geri gitme sistem animasyonları (ana sayfaya geri gitme, görevler arası geçiş ve etkinlikler arası geçiş) varsayılan olarak etkindir.
Ayrıca, onBackPressed aranmaz ve KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK artık gönderilmez.
Uygulamanız geri etkinliğini yakalıyorsa ve henüz tahmini geri özelliğine geçmediyseniz uygulamanızı desteklenen geri gezinme API'lerini kullanacak şekilde güncelleyin veya uygulamanızın AndroidManifest.xml dosyasının <application> ya da <activity> etiketinde android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback özelliğini false olarak ayarlayarak geçici olarak devre dışı bırakın.
Elegant Font API'leri kullanımdan kaldırıldı ve devre dışı bırakıldı
Android 15'i (API düzeyi 35) hedefleyen uygulamalarda elegantTextHeight
TextView özelliği varsayılan olarak true şeklinde ayarlanır. Bu sayede, kompakt yazı tipi çok daha okunabilir bir yazı tipiyle değiştirilir. elegantTextHeight özelliğini false olarak ayarlayarak bu durumu geçersiz kılabilirsiniz.
Android 16, elegantTextHeight özelliğinin desteğini sonlandırır. Uygulamanız Android 16'yı hedeflediğinde bu özellik yoksayılır. Bu API'ler tarafından kontrol edilen "UI
fonts" desteği sonlandırılıyor. Bu nedenle, Arapça, Lao, Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Telugu veya Tayca dillerinde tutarlı ve gelecekte de geçerli olacak metin oluşturma için tüm düzenleri uyarlamanız gerekir.
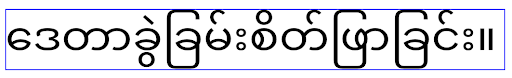 Android 14'ü (API düzeyi 34) ve önceki sürümleri hedefleyen uygulamalarda veya
Android 14'ü (API düzeyi 34) ve önceki sürümleri hedefleyen uygulamalarda veya elegantTextHeight özelliğini false olarak ayarlayarak varsayılan davranışı geçersiz kılan Android 15'i (API düzeyi 35) hedefleyen uygulamalarda elegantTextHeight davranışı. Android 16'yı (API düzeyi 36) hedefleyen uygulamalar veya
Android 16'yı (API düzeyi 36) hedefleyen uygulamalar veya elegantTextHeight özelliğini false olarak ayarlayarak varsayılanı geçersiz kılmayan Android 15'i (API düzeyi 35) hedefleyen uygulamalar için elegantTextHeight davranışı.Temel işlevler
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), Android sisteminin çeşitli temel özelliklerini değiştiren veya genişleten aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Sabit ücretli iş planlaması optimizasyonu
Android 16'yı hedeflemeden önce, scheduleAtFixedRate geçerli bir işlem yaşam döngüsü dışında olduğu için bir görev yürütmeyi kaçırdığında, uygulama geçerli bir yaşam döngüsüne döndüğünde tüm kaçırılan yürütmeler hemen yürütülür.
Android 16'yı hedeflerken, uygulama geçerli bir yaşam döngüsüne döndüğünde en fazla bir scheduleAtFixedRate yürütme işleminin eksikliği hemen yürütülür. Bu davranış değişikliğinin uygulama performansını iyileştirmesi bekleniyor. Uygulamanızın etkilenip etkilenmediğini kontrol etmek için uygulamanızda bu davranışı test edin.
Uygulama uyumluluk çerçevesini kullanarak ve STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS uyumluluk işaretini etkinleştirerek de test yapabilirsiniz.
Cihaz form faktörleri
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), büyük ekranlı cihazlarda gösterilen uygulamalar için aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Uyarlanabilir düzenler
With Android apps now running on a variety of devices (such as phones, tablets, foldables, desktops, cars, and TVs) and windowing modes on large screens (such as split screen and desktop windowing), developers should build Android apps that adapt to any screen and window size, regardless of device orientation. Paradigms like restricting orientation and resizability are too restrictive in today's multidevice world.
Ignore orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions no longer apply on displays with smallest width >= 600dp. Apps fill the entire display window, regardless of aspect ratio or a user's preferred orientation, and pillarboxing isn't used.
This change introduces a new standard platform behavior. Android is moving toward a model where apps are expected to adapt to various orientations, display sizes, and aspect ratios. Restrictions like fixed orientation or limited resizability hinder app adaptability. Make your app adaptive to deliver the best possible user experience.
You can also test this behavior by using the
app compatibility framework and enabling the
UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT compat flag.
Common breaking changes
Ignoring orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions might impact your app's UI on some devices, especially elements that were designed for small layouts locked in portrait orientation: for example, issues like stretched layouts and off-screen animations and components. Any assumptions about aspect ratio or orientation can cause visual issues with your app. Learn more about how to avoid them and improve your app's adaptive behaviour.
Allowing device rotation results in more activity re-creation, which can result in losing user state if not properly preserved. Learn how to correctly save UI state in Save UI states.
Implementation details
The following manifest attributes and runtime APIs are ignored across large screen devices in full-screen and multi-window modes:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
The following values for screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation(), and
getRequestedOrientation() are ignored:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
Regarding display resizability, android:resizeableActivity="false",
android:minAspectRatio, and android:maxAspectRatio have no effect.
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), app orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio constraints are ignored on large screens by default, but every app that isn't fully ready can temporarily override this behavior by opting out (which results in the previous behavior of being placed in compatibility mode).
Exceptions
The Android 16 orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions don't apply in the following situations:
- Games (based on the
android:appCategoryflag) - Users explicitly opting in to the app's default behavior in aspect ratio settings of the device
- Screens that are smaller than
sw600dp
Opt out temporarily
To opt out a specific activity, declare the
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY manifest property:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
If too many parts of your app aren't ready for Android 16, you can opt out completely by applying the same property at the application level:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
Sağlık ve fitness
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), sağlık ve fitness verileriyle ilgili aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Sağlık ve fitness izinleri
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36) veya sonraki sürümleri hedefleyen uygulamalar için,
BODY_SENSORS izinler, android.permissions.health altında daha ayrıntılı izinler kullanır. Bu izinler Health Connect tarafından da kullanılır.
Android 16'dan itibaren, daha önce BODY_SENSORS veya BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND iznini gerektiren tüm API'ler bunun yerine ilgili android.permissions.health iznini gerektirir. Bu durum aşağıdaki veri türlerini, API'leri ve ön plan hizmeti türlerini etkiler:
- Wear OS'teki Sağlık Hizmetleri'nden
HEART_RATE_BPM - Android Sensor Manager'dan
Sensor.TYPE_HEART_RATE - Wear OS'te
ProtoLayout'denheartRateAccuracyveheartRateBpm FOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTH,BODY_SENSORSyerine ilgiliandroid.permission.healthizninin gerektiği yerlerde
Uygulamanız bu API'leri kullanıyorsa ilgili ayrıntılı izinleri istemelidir:
- Nabız, SpO2 veya deri sıcaklığının kullanım sırasında izlenmesi için:
BODY_SENSORSyerineandroid.permissions.healthaltındaki ayrıntılı izni (ör.READ_HEART_RATE) isteyin. - Arka planda sensör erişimi için
BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUNDyerine requestREAD_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDkullanın.
Bu izinler, sağlık, fitness ve sağlıklı yaşam verileri için Android veri deposu olan Health Connect'ten veri okuma erişimini koruyan izinlerle aynıdır.
Mobil uygulamalar
READ_HEART_RATE ve diğer ayrıntılı izinleri kullanmaya geçen mobil uygulamalar, uygulamanın gizlilik politikasını göstermek için etkinlik bildirmelidir. Bu, Health Connect ile aynı koşuldur.
Bağlantı
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), çevre birimi cihazlarla bağlantıyı iyileştirmek için Bluetooth yığınında aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Bağlantı kaybı ve şifreleme değişikliklerini işlemek için yeni amaçlar
Daha iyi bağ kaybı yönetimi kapsamında Android 16, uygulamalara bağ kaybı ve şifreleme değişiklikleri hakkında daha fazla bilgi sağlamak için 2 yeni intent de sunar.
Android 16'yı hedefleyen uygulamalar artık:
- Uzaktan bağ kaybı algılandığında
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent'i alır. Bu sayede daha bilgilendirici kullanıcı geri bildirimleri sağlayabilir ve uygun işlemleri yapabilirler. - Bağlantının şifreleme durumu değiştiğinde bir
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent'i alın. Şifreleme durumu değişikliği, şifreleme algoritması değişikliği ve şifreleme anahtarı boyutu değişikliği buna dahildir. Uygulamalar, daha sonraACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent'i aldıktan sonra bağlantı başarıyla şifrelenirse bağın geri yüklendiğini dikkate almalıdır.
Farklı OEM uygulamalarında uyum sağlama
Android 16 bu yeni intent'leri kullanıma sunsa da bunların uygulanması ve yayınlanması farklı cihaz üreticilerine (OEM'ler) göre değişiklik gösterebilir. Uygulamanızın tüm cihazlarda tutarlı ve güvenilir bir deneyim sunmasını sağlamak için geliştiricilerin, bağlantı kaybı işlemelerini bu olası varyasyonlara sorunsuz bir şekilde uyum sağlayacak şekilde tasarlamaları gerekir.
Aşağıdaki uygulama davranışlarını öneririz:
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent'i yayınlanırsa:ACL (Asenkron Bağlantısız) bağlantısının bağlantısı sistem tarafından kesilir ancak cihazın bağ bilgileri saklanır (burada açıklandığı gibi).
Uygulamanız, bağlantı kaybı algılama için birincil sinyal olarak bu intent'i kullanmalı ve cihazı unutma veya yeniden eşleme işlemini başlatmadan önce kullanıcıyı uzak cihazın kapsama alanında olduğunu onaylamasına yönlendirmelidir.
Bir cihaz
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGalındıktan sonra bağlantısını keserse uygulamanız, cihaz artık sistemle bağlı olmayabileceğinden yeniden bağlantı kurarken dikkatli olmalıdır.ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent'i yayınlanmıyorsa:ACL bağlantısı bağlı kalır ve Android 15'teki davranışla aynı şekilde cihazın bağ bilgileri sistem tarafından kaldırılır.
Bu senaryoda, uygulamanız, bağ kaybı etkinliklerini algılayıp yönetmek için önceki Android sürümlerindeki mevcut bağ kaybı işleme mekanizmalarını kullanmaya devam etmelidir.
Bluetooth eşlemesini kaldırmanın yeni yolu
Android 16'yı hedefleyen tüm uygulamalar artık CompanionDeviceManager'teki herkese açık bir API'yi kullanarak Bluetooth cihazlarının eşlemesini kaldırabilir. Bir tamamlayıcı cihaz CDM ilişkisi olarak yönetiliyorsa uygulama, ilişkili cihazdaki yeni removeBond(int) API'yi kullanarak Bluetooth bağını kaldırmayı tetikleyebilir. Uygulama, Bluetooth cihaz yayın etkinliğini dinleyerek ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED bağ durumu değişikliklerini izleyebilir.
Güvenlik
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36) aşağıdaki güvenlik değişikliklerini içerir.
MediaStore sürüm kilitleme
Android 16 veya sonraki sürümleri hedefleyen uygulamalarda MediaStore#getVersion() artık her uygulamaya özgü olacak. Bu sayede, kötüye kullanımı ve parmak izi teknikleri için kullanımını önlemek amacıyla sürüm dizesinden tanımlayıcı özellikler kaldırılır. Uygulamalar bu sürümün biçimiyle ilgili herhangi bir varsayıma kapılmamalıdır. Uygulamalar, bu API'yi kullanırken sürüm değişikliklerini zaten ele almalıdır. Geliştirici, bu API'nin amaçlanan kapsamının dışında ek bilgiler elde etmeye çalışmadığı sürece çoğu durumda mevcut davranışlarını değiştirmeleri gerekmez.
Daha güvenli intent'ler
Safer Intents özelliği, Android'in amaç çözümleme mekanizmasının güvenliğini artırmak için tasarlanmış çok aşamalı bir güvenlik girişimidir. Amaç, niyet işleme sırasında kontroller ekleyerek ve belirli ölçütleri karşılamayan niyetleri filtreleyerek uygulamaları kötü amaçlı işlemlerden korumaktır.
Android 15'te gönderen uygulamaya odaklanan bu özellik, Android 16 ile birlikte kontrolü alan uygulamaya kaydırarak geliştiricilerin uygulama manifestlerini kullanarak katı amaç çözümlemeyi etkinleştirmesine olanak tanır.
İki önemli değişiklik uygulanıyor:
Belirgin Intent'ler Hedef Bileşenin Intent Filtresiyle Eşleşmelidir: Bir intent bir bileşeni açıkça hedefliyorsa bu bileşenin intent filtresiyle eşleşmelidir.
İşlem içermeyen Intent'ler herhangi bir Intent Filtresiyle eşleşemez: İşlemi belirtilmemiş Intent'ler herhangi bir Intent filtresiyle eşleşmemelidir.
Bu değişiklikler yalnızca birden fazla uygulamanın söz konusu olduğu durumlarda geçerlidir ve tek bir uygulamadaki amaç işleme özelliğini etkilemez.
Etki
Etkinleştirme özelliği, geliştiricilerin bu özelliğin geçerli olması için uygulama manifestlerinde açıkça etkinleştirmesi gerektiği anlamına gelir. Bu nedenle, özelliğin etkisi yalnızca geliştiricileri aşağıdaki koşulları karşılayan uygulamalarla sınırlı olacaktır:
- Daha Güvenli Amaçlar özelliği ve avantajları hakkında bilgi sahibi olmalıdır.
- Uygulamalarına daha katı amaç işleme uygulamalarını dahil etmeyi aktif olarak seçmelidir.
Bu etkinleştirme yaklaşımı, mevcut daha az güvenli amaç çözümleme davranışına bağlı olabilecek mevcut uygulamaların bozulma riskini en aza indirir.
Android 16'daki ilk etkisi sınırlı olsa da Safer Intents girişimi, gelecekteki Android sürümlerinde daha geniş bir etki yaratacak bir yol haritasına sahiptir. Nihayetinde katı amaç çözümlemeyi varsayılan davranış haline getirmek planlanmaktadır.
Daha Güvenli Amaçlar özelliği, kötü amaçlı uygulamaların amaç çözümleme mekanizmasındaki güvenlik açıklarından yararlanmasını zorlaştırarak Android ekosisteminin güvenliğini önemli ölçüde artırabilir.
Ancak mevcut uygulamalarla ilgili olası uyumluluk sorunlarını gidermek için devre dışı bırakma ve zorunlu yaptırım geçişi dikkatli bir şekilde yönetilmelidir.
Uygulama
Geliştiricilerin, uygulama manifestlerinde intentMatchingFlags özelliğini kullanarak daha katı amaç eşleşmesini açıkça etkinleştirmesi gerekir.
Özelliğin uygulamanın tamamı için etkinleştirildiği ancak alıcıda devre dışı bırakıldığı/devre dışı bırakma seçeneğinin kullanıldığı bir örneği aşağıda bulabilirsiniz:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
Desteklenen işaretler hakkında daha fazla bilgi:
| İşaret Adı | Açıklama |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Gelen intent'ler için daha katı eşleşme uygular. |
| yok | Gelen amaçlar için tüm özel eşleşme kurallarını devre dışı bırakır. Birden fazla işaret belirtilirken çakışan değerler, "none" işaretine öncelik verilerek çözülür. |
| allowNullAction | Eşleşme kurallarını gevşeterek işlem içermeyen niyetlerin eşleşmesine izin verir. Belirli bir davranış elde etmek için "enforceIntentFilter" ile birlikte kullanılacak bu işaret |
Test ve Hata Ayıklama
Yaptırım etkin olduğunda, niyet çağıran niyeti düzgün şekilde doldurmuşsa uygulamalar doğru şekilde çalışır.
Ancak engellenen amaçlar, "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" ve "Access blocked:" gibi uyarı günlüğü mesajlarını "PackageManager." etiketiyle tetikler."PackageManager."
Bu, uygulamayı etkileyebilecek olası bir soruna işaret eder ve dikkat gerektirir.
Logcat filtresi:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
GPU sistem çağrısı filtreleme
Mali GPU yüzeyini sağlamlaştırmak için kullanımdan kaldırılan veya yalnızca GPU geliştirmesi için tasarlanan Mali GPU IOCTL'leri üretim derlemelerinde engellenmiştir. Ayrıca, GPU profil oluşturma için kullanılan IOCTL'ler kabuk işlemi veya hata ayıklanabilir uygulamalarla sınırlandırılmıştır. Platform düzeyindeki politika hakkında daha fazla bilgi için SAC güncellemesine bakın.
Bu değişiklik, Mali GPU'yu kullanan Pixel cihazlarda (Pixel 6-9) gerçekleşir. Arm, r54p2 sürümündeki Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst dosyasında IOCTL'lerinin resmi sınıflandırmasını sağlamıştır. Bu liste, gelecekteki sürücü sürümlerinde güncellenmeye devam edecektir.
Bu değişiklik, desteklenen grafik API'lerini (Vulkan ve OpenGL dahil) etkilemez ve geliştiricileri veya mevcut uygulamaları etkilemesi beklenmez. Streamline Performance Analyzer ve Android GPU Inspector gibi GPU profil oluşturma araçları etkilenmez.
Test
Aşağıdakine benzer bir SELinux reddi görüyorsanız uygulamanız bu değişiklikten etkilenmiş olabilir:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
Uygulamanızın engellenen IOCTL'leri kullanması gerekiyorsa lütfen hata bildiriminde bulunun ve bildirimi android-partner-security@google.com adresine atayın.
SSS
Bu politika değişikliği tüm OEM'ler için geçerli mi? Bu değişiklik isteğe bağlı olacak ancak bu sağlamlaştırma yöntemini kullanmak isteyen tüm OEM'ler tarafından kullanılabilecek. Değişikliği uygulama talimatlarını uygulama belgelerinde bulabilirsiniz.
Bu özelliği uygulamak için OEM kod tabanında değişiklik yapmak zorunlu mu yoksa bu özellik varsayılan olarak yeni bir AOSP sürümüyle mi geliyor? Platform düzeyindeki değişiklik, varsayılan olarak yeni bir AOSP sürümüyle birlikte gelir. Sağlayıcılar, bu değişikliği uygulamak isterlerse kod tabanlarında etkinleştirebilirler.
IOCTL listesinin güncel tutulmasından SoC'ler mi sorumludur? Örneğin, cihazım ARM Mali GPU kullanıyorsa değişiklikler için ARM ile iletişime geçmem gerekir mi? Her SoC, sürücü yayınlandıktan sonra IOCTL listelerini cihaz başına güncellemelidir. Örneğin, ARM, sürücü güncellemesi yaptığında kendisine ait yayınlanmış IOCTL listesini günceller. Ancak OEM'ler, güncellemeleri SEPolicy'lerine dahil ettiklerinden ve gerektiğinde seçilen özel IOCTL'leri listelere eklediklerinden emin olmalıdır.
Bu değişiklik, piyasada bulunan tüm Pixel cihazlara otomatik olarak mı uygulanır yoksa kullanıcının bir ayarı etkinleştirmesi mi gerekir? Bu değişiklik, Mali GPU'yu kullanan tüm Pixel cihazlar için geçerlidir (Pixel 6-9). Bu değişikliğin uygulanması için kullanıcı işlemi gerekmez.
Bu politikanın kullanılması çekirdek sürücüsünün performansını etkiler mi? Bu politika, GFXBench kullanılarak Mali GPU'da test edilmiş ve GPU performansında ölçülebilir bir değişiklik gözlemlenmemiştir.
IOCTL listesinin mevcut kullanıcı alanı ve çekirdek sürücüsü sürümleriyle uyumlu olması gerekir mi? Evet, izin verilen IOCTL'lerin listesi hem kullanıcı alanı hem de çekirdek sürücüleri tarafından desteklenen IOCTL'lerle senkronize edilmelidir. Kullanıcı alanındaki veya çekirdek sürücüsündeki IOCTL'ler güncellenirse SEPolicy IOCTL listesinin de eşleşecek şekilde güncellenmesi gerekir.
ARM, IOCTL'leri "kısıtlanmış" / "enstrümantasyon" olarak sınıflandırdı ancak bazılarını üretim kullanım alanlarında kullanmak ve/veya diğerlerini reddetmek istiyoruz. Kullanıcı alanı Mali kitaplıklarının yapılandırmasına bağlı olarak, kullandıkları IOCTL'leri nasıl sınıflandıracaklarına karar vermek OEM/SoC'lerin sorumluluğundadır. Bu konuda karar vermenize yardımcı olması için ARM'nin listesini kullanabilirsiniz ancak her OEM/SoC'nin kullanım alanı farklı olabilir.
Gizlilik
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36) aşağıdaki gizlilik değişikliklerini içerir.
Yerel Ağ İzni
LAN'daki cihazlara, INTERNET iznine sahip tüm uygulamalar erişebilir.
Bu, uygulamaların yerel cihazlara bağlanmasını kolaylaştırır ancak kullanıcının parmak izini oluşturma ve konum için proxy olma gibi gizlilik etkileri de vardır.
Yerel Ağ Korumaları projesi, yerel ağa erişimi yeni bir çalışma zamanı izniyle sınırlayarak kullanıcının gizliliğini korumayı amaçlar.
Yayın planı
Bu değişiklik, sırasıyla 25Q2 ve 26Q2 olmak üzere iki sürüm arasında uygulanacaktır. Geliştiricilerin 25Q2 için bu yönergelere uyması ve geri bildirim paylaşması zorunludur. Çünkü bu korumalar daha sonraki bir Android sürümünde zorunlu kılınacaktır. Ayrıca, aşağıdaki yönergeleri kullanarak örtülü yerel ağ erişimine bağlı senaryoları güncellemeleri ve kullanıcıların yeni izni reddetmesine ve iptal etmesine hazırlanmaları gerekir.
Etki
LNP, şu anki aşamada etkinleştirilmesi gereken bir özelliktir. Bu nedenle, yalnızca etkinleştirilen uygulamalar etkilenir. Katılma aşamasının amacı, uygulama geliştiricilerin uygulamalarının hangi bölümlerinin örtülü yerel ağ erişimine bağlı olduğunu anlamalarını sağlamaktır. Böylece, bir sonraki sürümde bu bölümler için izin koruması hazırlayabilirler.
Uygulamalar, kullanıcının yerel ağına aşağıdaki yöntemlerle erişirse etkilenir:
- Yerel ağ adreslerinde (ör. mDNS veya SSDP hizmeti keşif protokolü) ham soketlerin doğrudan veya kitaplık aracılığıyla kullanımı
- Yerel ağa erişen çerçeve düzeyindeki sınıfların (ör. NsdManager) kullanılması
Yerel ağ adresine giden ve gelen trafik için yerel ağ erişimi izni gerekir. Aşağıdaki tabloda sık rastlanan bazı durumlar listelenmiştir:
| Uygulama Düşük Düzeyli Ağ İşlemi | Yerel Ağ İzni Gerekli |
|---|---|
| Giden TCP bağlantısı oluşturma | evet |
| Gelen TCP bağlantılarını kabul etme | evet |
| UDP tek noktaya yayın, çok noktaya yayın veya yayın gönderme | evet |
| Gelen UDP tek yayını, çoklu yayını ve yayını alma | evet |
Bu kısıtlamalar, ağ yığınına derinlemesine uygulanır ve bu nedenle tüm ağ API'leri için geçerlidir. Yerel veya yönetilen kodda oluşturulan soketler, Cronet ve OkHttp gibi ağ kitaplıkları ve bunların üzerinde uygulanan tüm API'ler buna dahildir. Yerel ağdaki hizmetleri (ör. .local soneki olanlar) çözmeye çalışmak için yerel ağ izni gerekir.
Yukarıdaki kurallarla ilgili istisnalar:
- Bir cihazın DNS sunucusu yerel ağdaysa bu cihaza veya bu cihazdan gelen trafik (53 numaralı bağlantı noktasında) için yerel ağ erişim izni gerekmez.
- Uygulama içi seçici olarak Çıkış Değiştirici'yi kullanan uygulamaların yerel ağ izinlerine ihtiyacı olmayacak (2025'in 4. çeyreğinde daha fazla bilgi paylaşılacak).
Geliştirici Kılavuzu (Etkinleştirme)
Yerel ağ kısıtlamalarını etkinleştirmek için aşağıdakileri yapın:
- Cihazda 25Q2 Beta 3 veya sonraki bir sürümü yükleyin.
- Test edilecek uygulamayı yükleyin.
adb'de Appcompat işaretini açın/kapatın:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Cihazı yeniden başlatın
Artık uygulamanızın yerel ağa erişimi kısıtlanmıştır ve yerel ağa erişme girişimleri soket hatalarına yol açar. Uygulama sürecinizin dışında yerel ağ işlemleri gerçekleştiren API'ler (ör. NsdManager) kullanıyorsanız bu API'ler, kayıt aşamasında etkilenmez.
Erişimi geri yüklemek için uygulamanıza NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES izni vermeniz gerekir.
- Uygulamanın, manifest dosyasında
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESiznini beyan ettiğinden emin olun. - Ayarlar > Uygulamalar > [Uygulama Adı] > İzinler > Yakındaki cihazlar > İzin ver'e gidin.
Uygulamanızın yerel ağa erişimi geri yüklenir ve tüm senaryolarınız, uygulamayı kaydetmeden önceki gibi çalışır.
Yerel ağ koruması zorunlu kılındıktan sonra uygulama ağ trafiği şu şekilde etkilenecek:
| İzin | Giden LAN İsteği | Giden/Gelen İnternet İsteği | Gelen LAN İsteği |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verildi | Works | Works | Works |
| İzin Verilmedi | Başarısızlar | Works | Başarısızlar |
Uygulama uyumluluğu işaretini devre dışı bırakmak için aşağıdaki komutu kullanın.
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Hatalar
Bu kısıtlamalardan kaynaklanan hatalar, yerel bir ağ adresine gönderme veya gönderme varyantı çağrıldığında arayan sokete döndürülür.
Örnek hatalar:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Yerel Ağ Tanımı
Bu projedeki yerel ağ, kablosuz veya Ethernet gibi yayın yapabilen bir ağ arayüzünü kullanan bir IP ağıdır ancak hücresel (WWAN) veya VPN bağlantıları hariçtir.
Aşağıdakiler yerel ağ olarak kabul edilir:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Bağlantı Yerel
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Bağlantı yerel
- Doğrudan bağlı rotalar
- Thread gibi saplama ağlar
- Birden fazla alt ağ (henüz belli değil)
Ayrıca, hem çok noktalı yayın adresleri (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) hem de IPv4 yayın adresi (255.255.255.255) yerel ağ adresleri olarak sınıflandırılır.
Uygulamaya ait fotoğraflar
Android 16 veya sonraki sürümleri çalıştıran cihazlarda SDK 36 veya sonraki sürümleri hedefleyen bir uygulama tarafından fotoğraf ve video izinleri istendiğinde, seçili medyaya erişimi sınırlamayı seçen kullanıcılar, uygulamaya ait tüm fotoğrafları fotoğraf seçicide önceden seçili olarak görür. Kullanıcılar önceden seçilmiş öğelerden herhangi birinin seçimini kaldırabilir. Bu durumda uygulamanın söz konusu fotoğraf ve videolara erişimi iptal edilir.
