リストを使用すると、Wear OS デバイス上でユーザーが選択肢の中から簡単にアイテムを選択できるようになります。
ウェアラブル UI ライブラリには、ウェアラブル デバイス向けに最適化されたリストを作成するための RecyclerView の実装である WearableRecyclerView クラスが用意されています。ウェアラブル アプリでこのインターフェースを使用するには、新しい WearableRecyclerView コンテナを作成します。
単純なアイテム(アプリ ランチャーなど)の長いリストや連絡先リストには WearableRecyclerView を使用します。各アイテムには、短い文字列と、関連付けられているアイコンを表示できます。また、各アイテムに文字列とアイコンのどちらかしか表示できないこともあります。
注: 複雑なレイアウトは避けてください。特にウェアラブルは画面サイズが限られているため、ユーザーが一瞥しただけでどのようなアイテムなのかを理解できるようにする必要があります。
既存の RecyclerView クラスを拡張することにより、WearableRecyclerView API ではデフォルトで、縦スクロールできるアイテムリストが直線状に表示されます。WearableRecyclerView API を使用すると、ウェアラブル アプリで曲線レイアウトと円形スクロール操作を有効にすることもできます。
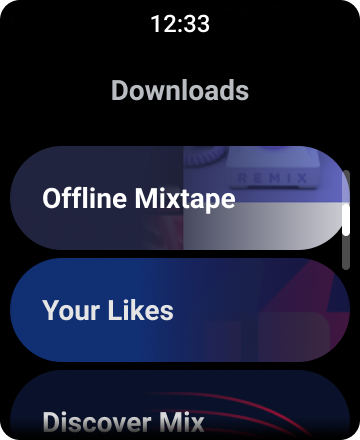
図 1. Wear OS のデフォルトのリスト表示
このガイドでは、WearableRecyclerView クラスを使用して Wear OS アプリにリストを作成する方法、スクロール可能なアイテムの曲線レイアウトを有効にする方法、スクロール時の子の表示をカスタマイズする方法について説明します。
XML を使用して WearableRecyclerView をアクティビティに追加する
次のレイアウトでは、アクティビティに WearableRecyclerView を追加します。
<androidx.wear.widget.WearableRecyclerView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/recycler_launcher_view" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:scrollbars="vertical" />
次に、アクティビティに適用する WearableRecyclerView の例を示します。
Kotlin
class MainActivity : Activity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) } ... }
Java
public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } ... }
曲線レイアウトを作成する
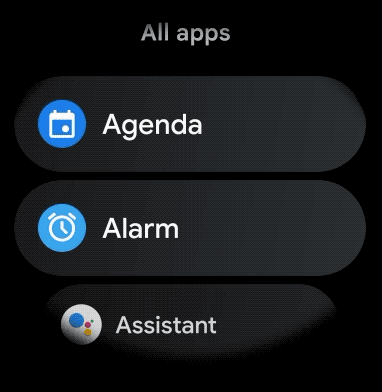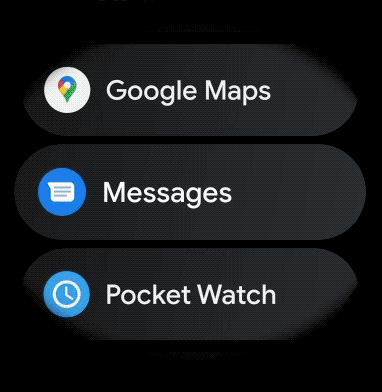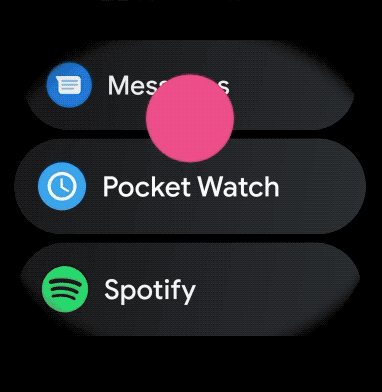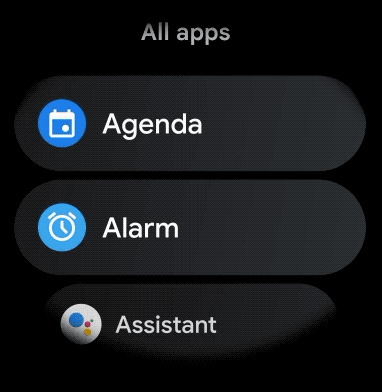
ウェアラブル アプリにスクロール可能なアイテムの曲線レイアウトを作成する手順は次のとおりです。
-
対象の XML レイアウト内で、メインコンテナとして
WearableRecyclerViewを使用します。 -
setEdgeItemsCenteringEnabled(boolean)メソッドをtrueに設定します。これにより、画面上のリストの最初と最後のアイテムが、垂直方向に中央揃えで配置されます。 -
WearableRecyclerView.setLayoutManager()メソッドを使用して、画面上のアイテムのレイアウトを設定します。
Kotlin
wearableRecyclerView.apply { // To align the edge children (first and last) with the center of the screen. isEdgeItemsCenteringEnabled = true ... layoutManager = WearableLinearLayoutManager(this@MainActivity) }
Java
// To align the edge children (first and last) with the center of the screen. wearableRecyclerView.setEdgeItemsCenteringEnabled(true); ... wearableRecyclerView.setLayoutManager( new WearableLinearLayoutManager(this));
スクロール時の子の表示に関して具体的なカスタマイズ要件がある場合(たとえば、アイテムがスクロールされて中央から離れるときにアイコンとテキストのサイズを変更する場合)は、
WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback クラスを拡張して
onLayoutFinished メソッドをオーバーライドします。
次のコード スニペットは、WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback クラスを拡張することで、中央から離れるにつれサイズが変更されるようにアイテムのスクロールをカスタマイズする例を示しています。
Kotlin
/** How much icons should scale, at most. */ private const val MAX_ICON_PROGRESS = 0.65f class CustomScrollingLayoutCallback : WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback() { private var progressToCenter: Float = 0f override fun onLayoutFinished(child: View, parent: RecyclerView) { child.apply { // Figure out % progress from top to bottom. val centerOffset = height.toFloat() / 2.0f / parent.height.toFloat() val yRelativeToCenterOffset = y / parent.height + centerOffset // Normalize for center. progressToCenter = Math.abs(0.5f - yRelativeToCenterOffset) // Adjust to the maximum scale. progressToCenter = Math.min(progressToCenter, MAX_ICON_PROGRESS) scaleX = 1 - progressToCenter scaleY = 1 - progressToCenter } } }
Java
public class CustomScrollingLayoutCallback extends WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback { /** How much icons should scale, at most. */ private static final float MAX_ICON_PROGRESS = 0.65f; private float progressToCenter; @Override public void onLayoutFinished(View child, RecyclerView parent) { // Figure out % progress from top to bottom. float centerOffset = ((float) child.getHeight() / 2.0f) / (float) parent.getHeight(); float yRelativeToCenterOffset = (child.getY() / parent.getHeight()) + centerOffset; // Normalize for center. progressToCenter = Math.abs(0.5f - yRelativeToCenterOffset); // Adjust to the maximum scale. progressToCenter = Math.min(progressToCenter, MAX_ICON_PROGRESS); child.setScaleX(1 - progressToCenter); child.setScaleY(1 - progressToCenter); } }
Kotlin
wearableRecyclerView.layoutManager = WearableLinearLayoutManager(this, CustomScrollingLayoutCallback())
Java
CustomScrollingLayoutCallback customScrollingLayoutCallback = new CustomScrollingLayoutCallback(); wearableRecyclerView.setLayoutManager( new WearableLinearLayoutManager(this, customScrollingLayoutCallback));

