1. Before you begin
In this codelab, you learn about a fundamental part of Android: the activity lifecycle.
During its lifetime, an activity transitions through, and sometimes back to, various states. This transitioning of states is known as the activity lifecycle.
In Android, an activity is the entry point for interacting with the user.
In the past, one activity would display one screen in an app. With current best practices, one activity might display multiple screens by swapping them in and out as needed.
The activity lifecycle extends from the creation of the activity to its destruction, when the system reclaims that activity's resources. As a user navigates in and out of an activity, each activity transitions between different states in the activity lifecycle.
As an Android developer, you need to understand the activity lifecycle. If your activities do not correctly respond to lifecycle state changes, your app can generate strange bugs, confusing behavior for your users, or use too many Android system resources. Understanding the Android lifecycle and responding correctly to lifecycle state changes is an important part of Android development.
Prerequisites
- Knowledge of what an activity is and how to create one in your app
- Knowledge of what an activity's
onCreate()method does and the kind of operations that are performed in that method
What you'll learn
- How to print logging information to the Logcat
- The basics of the
Activitylifecycle and the callbacks that are invoked when the activity moves between states - How to override lifecycle callback methods to perform operations at different times in the activity lifecycle
What you'll build
- Modify a starter app, called Dessert Clicker, to add logging information that's displayed in the Logcat.
- Override lifecycle callback methods and log changes to the activity state.
- Run the app and note the logging information that appears as the activity starts, stops, and resumes.
- Implement
rememberSaveableto retain app data that may be lost if the device configuration changes.
2. App Overview
In this codelab, you work with a starter app called Dessert Clicker. In Dessert Clicker, each time the user taps a dessert on the screen, the app "purchases" the dessert for the user. The app updates values in the layout for the:
- Number of desserts that are "purchased"
- Total revenue for the "purchased" desserts

This app contains several bugs related to the Android lifecycle. For example, in certain circumstances, the app resets the dessert values to 0. Understanding the Android lifecycle will help you understand why these problems happen and how to fix them.
Download the starter code
In Android Studio, open the basic-android-kotlin-compose-training-dessert-clicker folder.
3. Explore the lifecycle methods and add basic logging
Every activity has what is known as a lifecycle. This term is an allusion to plant and animal lifecycles, like the lifecycle of a butterfly—the different states of the butterfly show its growth from egg to caterpillar to pupa to butterfly to death.
Similarly, the activity lifecycle consists of the different states that an activity can go through, from when the activity first initializes to its destruction, at which time the operating system (OS) reclaims its memory. Typically, the entry point of a program is the main() method. Android activities, however, begin with the onCreate() method; this method would be the equivalent of the egg stage in the above example. You have used activities already, many times throughout this course, and you might recognize the onCreate() method. As the user starts your app, navigates between activities, navigates inside and outside of your app, the activity changes state.
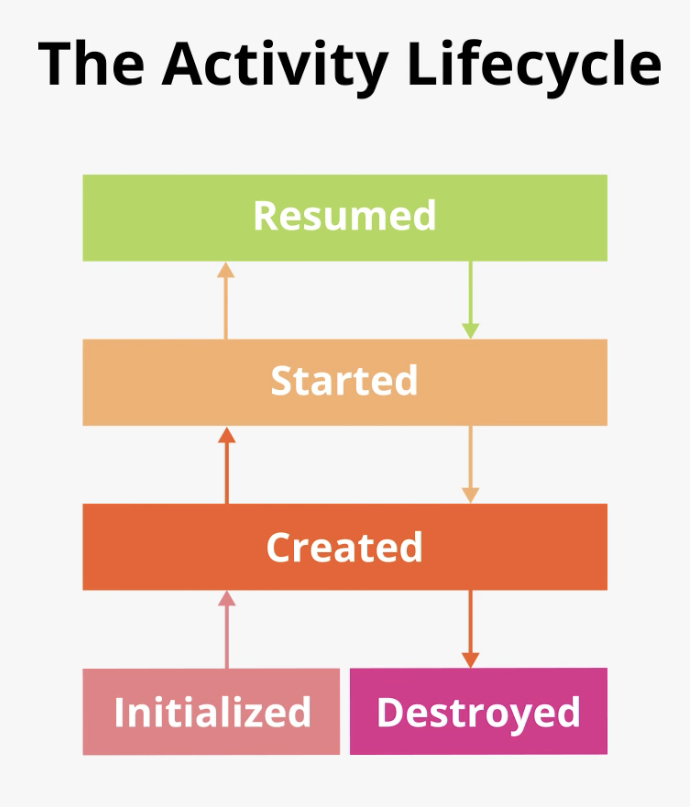
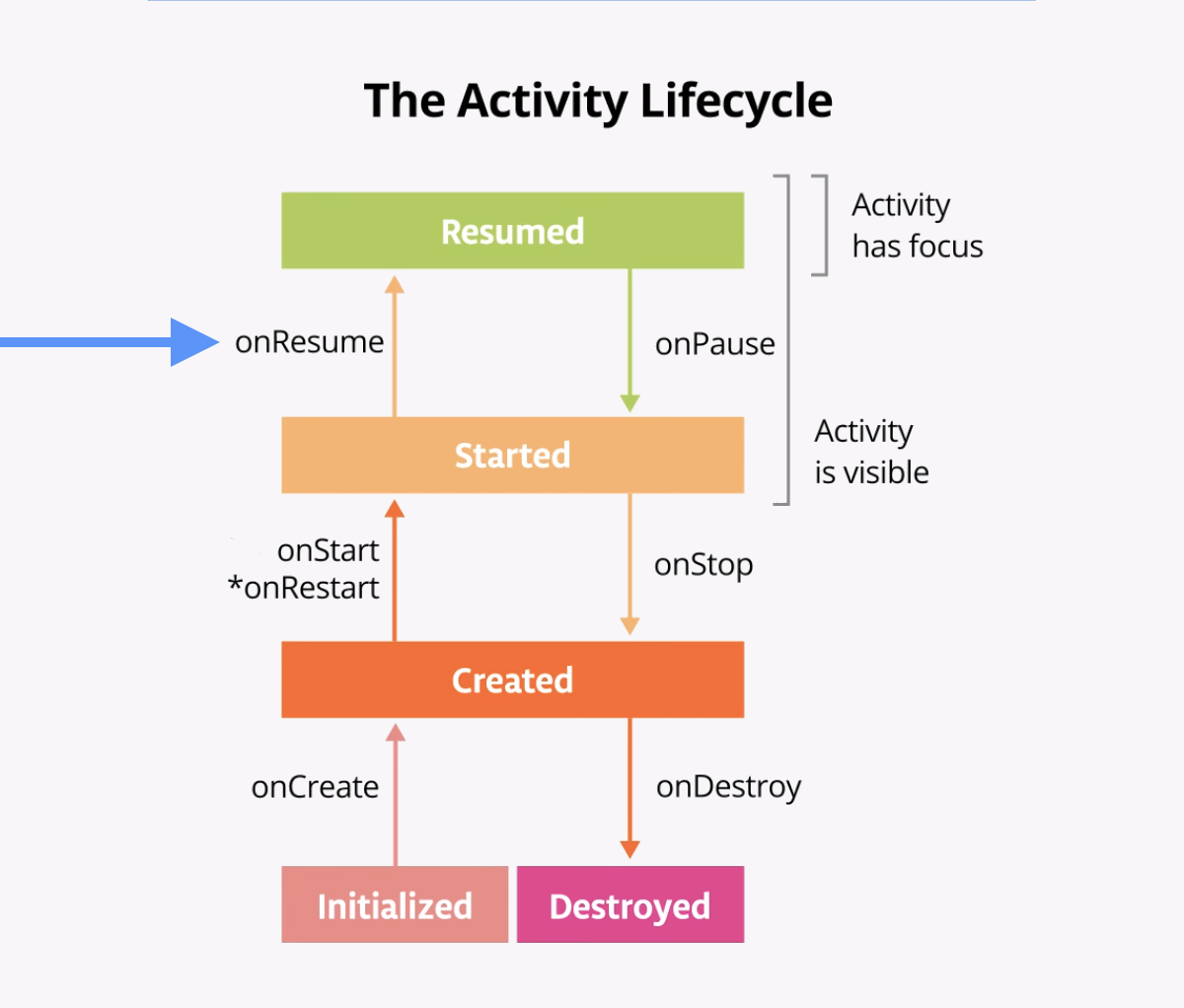
The following diagram shows all the activity lifecycle states. As their names indicate, these states represent the status of the activity. Notice that, unlike the butterfly lifecycle, an activity can go back and forth between states throughout the lifecycle, instead of only moving in a single direction.
Often, you want to change some behavior, or run some code, when the activity lifecycle state changes. Therefore, the Activity class itself, and any subclasses of Activity such as ComponentActivity, implement a set of lifecycle callback methods. Android invokes these callbacks when the activity moves from one state to another, and you can override those methods in your own activities to perform tasks in response to those lifecycle state changes. The following diagram shows the lifecycle states along with the available overridable callbacks.
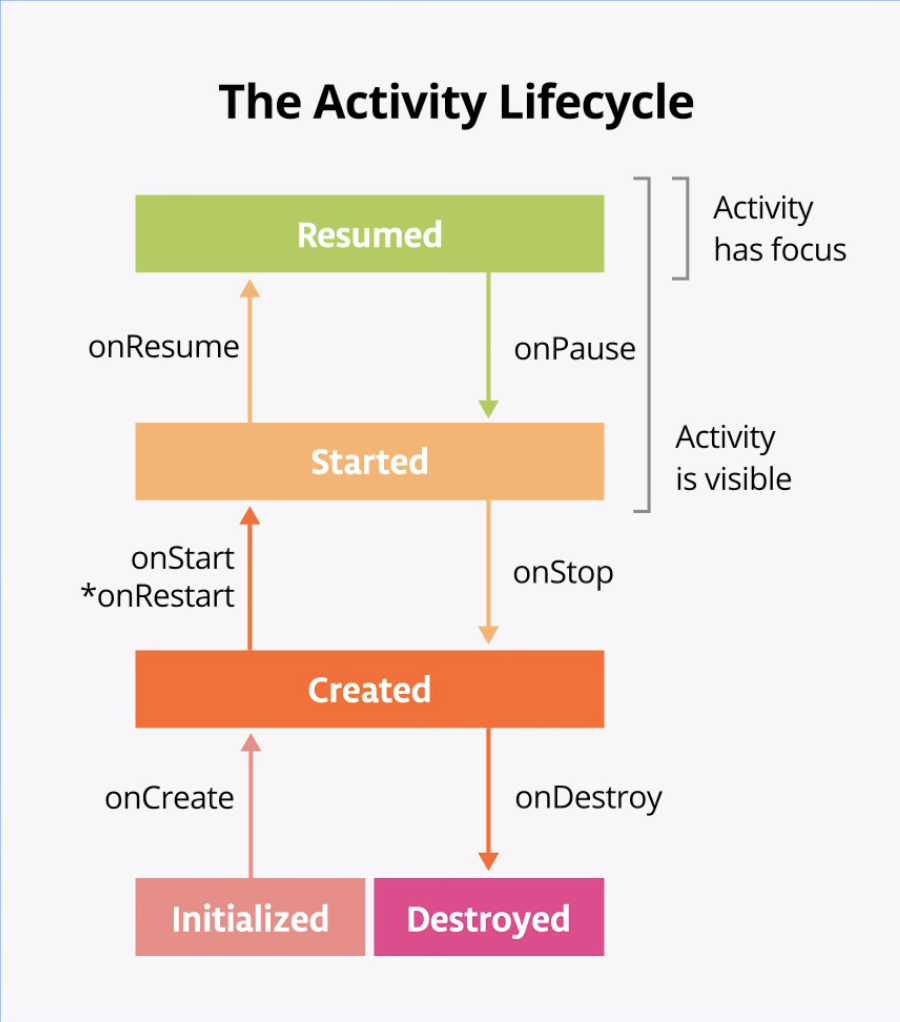
It's important to know when Android invokes the overridable callbacks and what to do in each callback method, but both of these diagrams are complex and can be confusing. In this codelab, instead of just reading what each state and callback means, you're going to do some detective work and build your understanding of the Android activity lifecycle.
Step 1: Examine the onCreate() method and add logging
To figure out what's going on with the Android lifecycle, it's helpful to know when the various lifecycle methods are called. This information helps you identify where things are going wrong in the Dessert Clicker app.
A simple way to determine this information is to use the Android logging functionality. Logging enables you to write short messages to a console while the app runs and use it to see when different callbacks are triggered.
- Run the Dessert Clicker app and tap several times on the picture of the dessert. Note how the value for Desserts sold and the total dollar amount changes.
- Open
MainActivity.ktand examine theonCreate()method for this activity:
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
// ...
}
In the activity lifecycle diagram, you may recognize the onCreate() method, because you've used this callback before. It's the one method that every activity must implement. The onCreate() method is where you should do any one-time initializations for your activity. For example, in onCreate(), you call setContent(), which specifies the activity's UI layout.
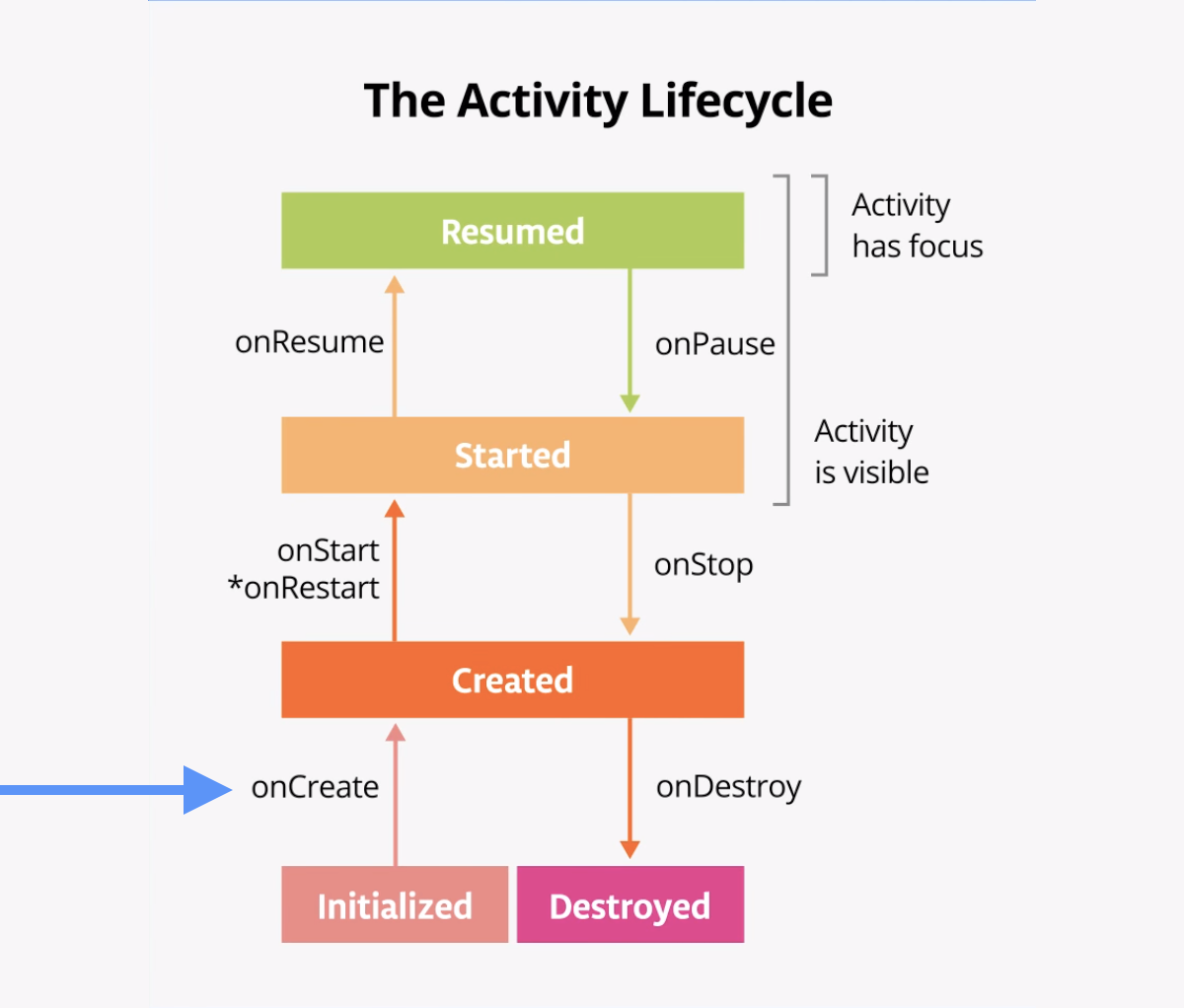
The onCreate() lifecycle method is called once, just after the activity initializes—when the OS creates the new Activity object in memory. After onCreate() executes, the activity is considered created.
- Add the following constant at the top level of the
MainActivity.kt, above the class declarationclass MainActivity.
A good convention is to declare a TAG constant in your file as its value will not change.
To mark it as a compile-time constant, use const when declaring the variable. A compile-time constant is a value that is known during compilation.
private const val TAG = "MainActivity"
- In the
onCreate()method, just after the call tosuper.onCreate(), add the following line:
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate Called")
- Import the
Logclass, if necessary (pressAlt+Enter, orOption+Enteron a Mac, and select Import.) If you enabled auto imports, this should happen automatically.
import android.util.Log
The Log class writes messages to the Logcat. The Logcat is the console for logging messages. Messages from Android about your app appear here, including the messages you explicitly send to the log with the Log.d() method or other Log class methods.
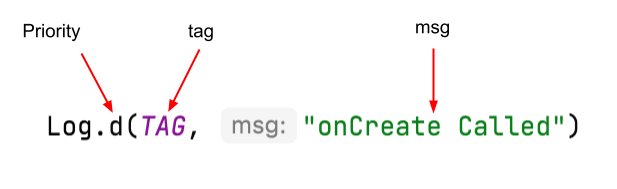
There are three important aspects of the Log instruction:
- The priority of the log message, that is, how important the message is. In this case, the
Log.v()logs verbose messages.Log.d()method writes a debug message. Other methods in theLogclass includeLog.i()for informational messages,Log.w()for warnings, andLog.e()for error messages. - The log
tag(the first parameter), in this case"MainActivity". The tag is a string that lets you more easily find your log messages in the Logcat. The tag is typically the name of the class. - The actual log message, called
msg(the second parameter), is a short string, which in this case is"onCreate Called".
- Compile and run the Dessert Clicker app. You don't see any behavior differences in the app when you tap the dessert. In Android Studio, at the bottom of the screen, click the Logcat tab.
- In the Logcat window, type
tag:MainActivityinto the search field.
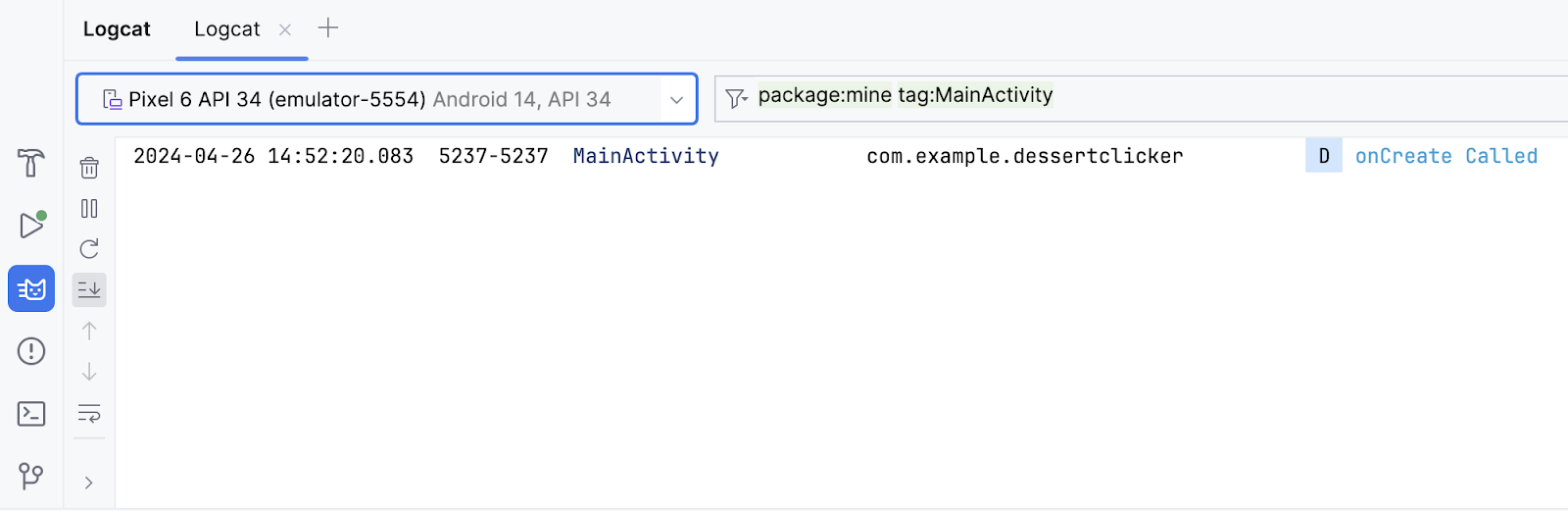
The Logcat can contain many messages, most of which aren't useful to you. You can filter the Logcat entries in many ways, but searching is the easiest. Because you used MainActivity as the log tag in your code, you can use that tag to filter the log. Your log message includes the date and time, your log tag, the name of the package (com.example.dessertclicker), and the actual message. Because this message appears in the log, you know that onCreate()was executed.
Step 2: Implement the onStart() method
The onStart() lifecycle method is called just after onCreate(). After onStart() runs, your activity is visible on the screen. Unlike onCreate(), which is called only once to initialize your activity, onStart()can be called by the system many times in the lifecycle of your activity.
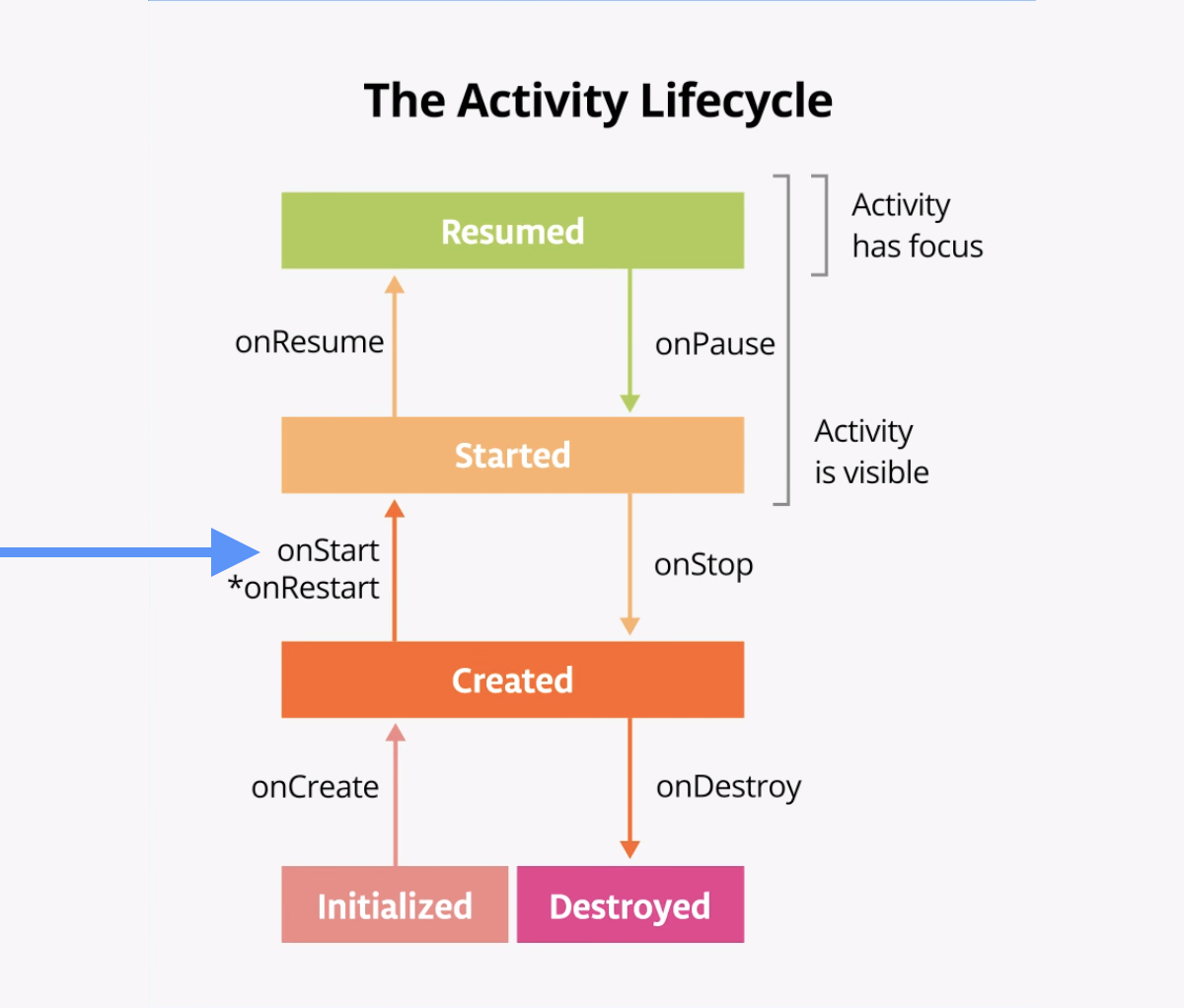
Note that onStart()is paired with a corresponding onStop()lifecycle method. If the user starts your app and then returns to the device's home screen, the activity is stopped and is no longer visible on screen.
- In Android Studio, with
MainActivity.ktopen and the cursor within theMainActivityclass, select Code > Override Methods... or pressControl+O. A dialog appears with a long list of all the methods you can override in this class.
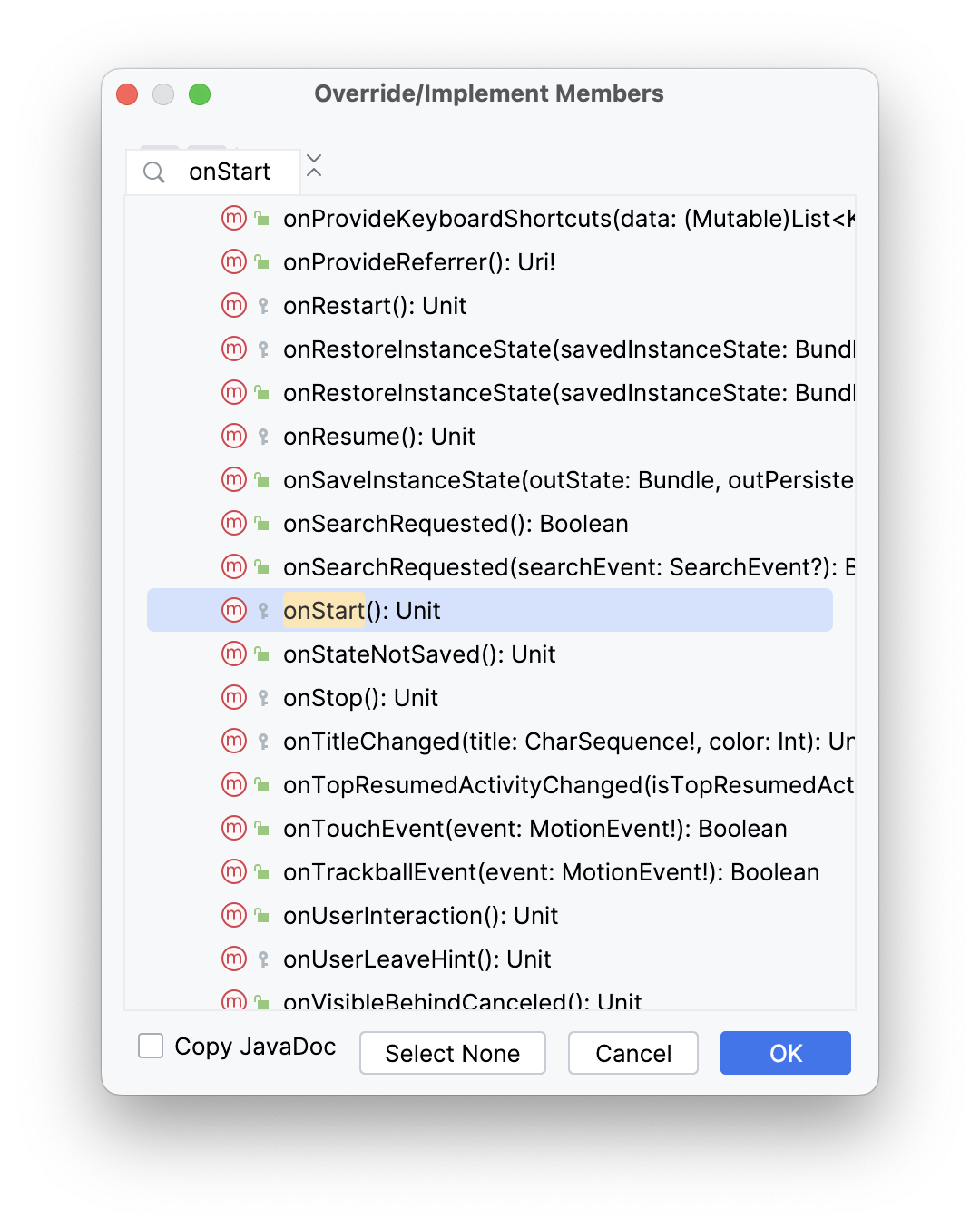
- Start entering
onStartto search for the correct method. To scroll to the next matching item, use the down arrow. ChooseonStart()from the list and click OK to insert the boilerplate override code. The code looks like the following example:
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
}
- Inside the
onStart()method, add a log message:
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
Log.d(TAG, "onStart Called")
}
- Compile and run the Dessert Clicker app and open the Logcat pane.
- Type
tag:MainActivityinto the search field to filter the log. Notice that both theonCreate()andonStart()methods were called one after the other, and that your activity is visible on screen. - Press the Home button on the device and then use the Recents screen to return to the activity. Notice that the activity resumes where it left off, with all the same values, and that
onStart()is logged a second time to Logcat. Notice also that theonCreate()method is not called again.
2024-04-26 14:54:48.721 5386-5386 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onCreate Called 2024-04-26 14:54:48.756 5386-5386 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onStart Called 2024-04-26 14:55:41.674 5386-5386 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onStart Called
Step 3: Add more log statements
In this step, you implement logging for all the other lifecycle methods.
- Override the remainder of the lifecycle methods in your
MainActivityand add log statements for each one, as shown in the following code:
override fun onResume() {
super.onResume()
Log.d(TAG, "onResume Called")
}
override fun onRestart() {
super.onRestart()
Log.d(TAG, "onRestart Called")
}
override fun onPause() {
super.onPause()
Log.d(TAG, "onPause Called")
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
Log.d(TAG, "onStop Called")
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy Called")
}
- Compile and run Dessert Clicker again and examine Logcat.
Notice that this time, in addition to onCreate() and onStart(), there's a log message for the onResume() lifecycle callback.
2024-04-26 14:56:48.684 5484-5484 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onCreate Called 2024-04-26 14:56:48.709 5484-5484 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onStart Called 2024-04-26 14:56:48.713 5484-5484 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onResume Called
When an activity starts from the beginning, you see all three of these lifecycle callbacks called in order:
onCreate()when the system creates the app.onStart()makes the app visible on the screen, but the user is not yet able to interact with it.onResume()brings the app to the foreground, and the user is now able to interact with it.
Despite the name, the onResume() method is called at startup, even if there is nothing to resume.
4. Explore lifecycle use cases
Now that you have set up the Dessert Clicker app for logging, you're ready to start using the app and exploring how lifecycle callbacks are triggered.
Use case 1: Opening and closing the activity
You start with the most basic use case, which is to start your app for the first time and then close the app.
- Compile and run the Dessert Clicker app, if it is not already running. As you've seen, the
onCreate(),onStart(), andonResume()callbacks are called when the activity starts for the first time.
2024-04-26 14:56:48.684 5484-5484 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onCreate Called 2024-04-26 14:56:48.709 5484-5484 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onStart Called 2024-04-26 14:56:48.713 5484-5484 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onResume Called
- Tap the cupcake a few times.
- Tap the Back button on the device.
Notice in Logcat that onPause() and onStop() are called in that order.
2024-04-26 14:58:19.984 5484-5484 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onPause Called 2024-04-26 14:58:20.491 5484-5484 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onStop Called 2024-04-26 14:58:20.517 5484-5484 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onDestroy Called
In this case, using the Back button causes the activity (and the app) to be removed from the screen and moved to the back of the activity stack.
The Android OS might close your activity if your code manually calls the activity's finish() method or if the user force-quits the app. For example, the user can force-quit or close the app in the Recents screen. The OS might also shut down your activity on its own if your app has not been onscreen for a long time. Android does so to preserve battery life and to reclaim the resources the app was using so they are available to other apps. These are just a few examples of why the Android system destroys your activity. There are additional cases when the Android system destroys your activity without providing a warning.
Use case 2: Navigating away from and back to the activity
Now that you've started the app and closed it, you've seen most of the lifecycle states for when the activity gets created for the first time. You've also seen most of the lifecycle states that the activity goes through when it gets closed. But as users interact with their Android devices, they switch between apps, return home, start new apps, and handle interruptions by other activities such as phone calls.
Your activity does not close down entirely every time the user navigates away from that activity:
- When your activity is no longer visible on screen, the status is known as putting the activity into the background. The opposite of this is when the activity is in the foreground, or onscreen.
- When the user returns to your app, that same activity is restarted and becomes visible again. This part of the lifecycle is called the app's visible lifecycle.
When your app is in the background, it generally should not be actively running to preserve system resources and battery life. You use the Activity lifecycle and its callbacks to know when your app is moving to the background so that you can pause any ongoing operations. You then restart the operations when your app comes into the foreground.
In this step, you look at the activity lifecycle when the app goes into the background and returns again to the foreground.
- With the Dessert Clicker app running, click the cupcake a few times.
- Press the Home button on your device and observe the Logcat in Android Studio. Returning to the home screen puts your app into the background, rather than shutting down the app altogether. Notice that the
onPause()andonStop()methods are called.
2024-04-26 15:00:04.905 5590-5590 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onPause Called 2024-04-26 15:00:05.430 5590-5590 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onStop Called
When onPause() is called, the app no longer has focus. After onStop(), the app is no longer visible on screen. Although the activity is stopped, the Activity object is still in memory in the background. The Android OS has not destroyed the activity. The user might return to the app, so Android keeps your activity resources around.
- Use the Recents screen to return to the app. On the emulator, the Recents screen can be accessed by the square system button shown in the image below.
Notice in Logcat that the activity restarts with onRestart() and onStart() and then resumes with onResume().
2024-04-26 15:00:39.371 5590-5590 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onRestart Called 2024-04-26 15:00:39.372 5590-5590 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onStart Called 2024-04-26 15:00:39.374 5590-5590 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onResume Called
When the activity returns to the foreground, the onCreate() method is not called again. The activity object was not destroyed, so it doesn't need to be created again. Instead of onCreate(), the onRestart() method is called. Notice that this time when the activity returns to the foreground, the Desserts sold number is retained.
- Start at least one app other than Dessert Clicker so that the device has a few apps in its Recents screen.
- Bring up the Recents screen and open another recent activity. Then go back to recent apps and bring Dessert Clicker back to the foreground.
Notice that you see the same callbacks in Logcat here as when you pressed the Home button. onPause() and onStop() are called when the app goes into the background, and then onRestart(), onStart(), and onResume() are called when it comes back.
These methods are called when the app stops and moves into the background or when the app restarts and returns to the foreground. If you need to do some work in your app during these cases, then override the relevant lifecycle callback method.
Use case 3: Partially hide the activity
You've learned that when an app is started and onStart() is called, the app becomes visible on the screen. When onResume() is called, the app gains the user focus–that is, the user can interact with the app. The part of the lifecycle in which the app is fully onscreen and has user focus is called the foreground lifetime.
When the app goes into the background, the focus is lost after onPause(), and the app is no longer visible after onStop().
The difference between focus and visibility is important. An activity can be partially visible on the screen but not have the user focus. In this step, you look at one case in which an activity is partially visible but doesn't have user focus.
- With the Dessert Clicker app running, click the Share button in the top right of the screen.
The sharing activity appears in the lower half of the screen, but the activity is still visible in the top half.
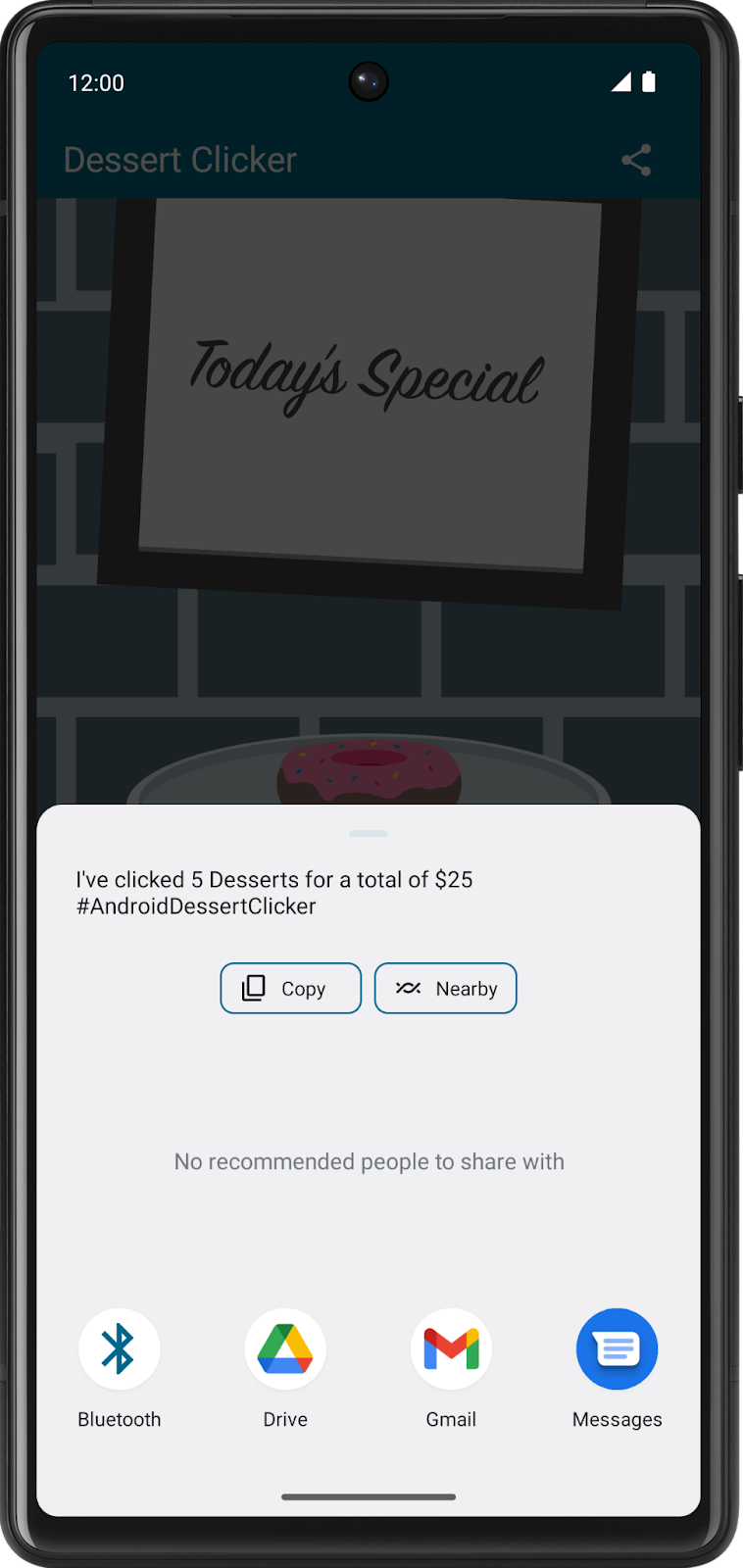
- Examine Logcat and note that only
onPause()was called.
2024-04-26 15:01:49.535 5590-5590 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onPause Called
In this use case, onStop() is not called because the activity is still partially visible. But the activity does not have user focus, and the user can't interact with it—the "share" activity that's in the foreground has the user focus.
Why is this difference important? The interruption with only onPause() usually lasts a short time before returning to your activity or navigating to another activity or app. You generally want to keep updating the UI so the rest of your app doesn't appear to freeze.
Whatever code runs in onPause() blocks other things from displaying, so keep the code in onPause() lightweight. For example, if a phone call comes in, the code in onPause() may delay the incoming-call notification.
- Click outside the share dialog to return to the app, and notice that
onResume()is called.
Both onResume() and onPause() have to do with focus. The onResume() method is called when the activity gains focus, and onPause() is called when the activity loses focus.
5. Explore configuration changes
There's another case in managing the activity lifecycle that is important to understand: how configuration changes affect the lifecycle of your activities.
A configuration change occurs when the state of the device changes so radically that the easiest way for the system to resolve the change is to completely shut down and rebuild the activity. For example, if the user changes the device language, the whole layout might need to change to accommodate different text directions and string lengths. If the user plugs the device into a dock or adds a physical keyboard, the app layout may need to take advantage of a different display size or layout. And if the device orientation changes—if the device is rotated from portrait to landscape or back the other way—the layout might need to change to fit the new orientation. Let's look at how the app behaves in this scenario.
The last lifecycle callback to demonstrate is onDestroy(), which is called after onStop(). It is called just before the activity is destroyed. This can happen when the app's code calls finish(), or the system needs to destroy and recreate the activity because of a configuration change.
Configuration change causes onDestroy() to be called
Screen rotation is one type of a configuration change that causes the activity to shutdown and restart. To simulate this configuration change and examine its effects, complete the following steps:
- Compile and run your app.
- Ensure the screen rotation lock in the emulator is disabled.
- Rotate the device or emulator to landscape mode. You can rotate the emulator left or right with the rotation buttons.
- Examine Logcat and understand that as the activity shuts down, it calls
onPause(),onStop(), andonDestroy(), in that order.
2024-04-26 15:03:32.183 5716-5716 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onPause Called 2024-04-26 15:03:32.185 5716-5716 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onStop Called 2024-04-26 15:03:32.205 5716-5716 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onDestroy Called
Data loss on device rotation
- Compile and run your app and open Logcat.
- Click the cupcake a few times and note that the desserts sold and total revenue are not zero.
- Ensure the screen rotation lock in the emulator is disabled.
- Rotate the device or emulator to landscape mode. You can rotate the emulator left or right with the rotation buttons.
- Examine the output in Logcat. Filter the output on
MainActivity.
2024-04-26 15:04:29.356 5809-5809 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onCreate Called 2024-04-26 15:04:29.378 5809-5809 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onStart Called 2024-04-26 15:04:29.382 5809-5809 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onResume Called 2024-04-26 15:06:52.168 5809-5809 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onPause Called 2024-04-26 15:06:52.183 5809-5809 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onStop Called 2024-04-26 15:06:52.219 5809-5809 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onDestroy Called 2024-04-26 15:06:52.302 5809-5809 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onCreate Called 2024-04-26 15:06:52.308 5809-5809 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onStart Called 2024-04-26 15:06:52.312 5809-5809 MainActivity com.example.dessertclicker D onResume Called
Notice that when the device or emulator rotates the screen, the system calls all the lifecycle callbacks to shut down the activity. Then, as the activity is re-created, the system calls all the lifecycle callbacks to start the activity.
When the device is rotated, and the activity is shut down and re-created, the activity re-starts with default values—the dessert image, number of desserts sold, and total revenue reset back to zero.
To learn why these values are being reset and how to correct them, you need to learn about the lifecycle of a composable and how it knows to observe and retain its state.
Lifecycle of a composable
The UI of your app is initially built from running composable functions in a process called Composition.
When the state of your app changes, a recomposition is scheduled. Recomposition is when Compose re-executes the composable functions whose state might have changed and creates an updated UI. The Composition is updated to reflect these changes.
The only way to create or update a Composition is by its initial composition and subsequent recompositions.
Composable functions have their own lifecycle that is independent of the Activity lifecycle. Its lifecycle is composed of the events: enters the Composition, recomposing 0 or more times, and then leaving the Composition.
In order for Compose to track and trigger a recomposition, it needs to know when state has changed. To indicate to Compose that it should track an object's state, the object needs to be of type State or MutableState. The State type is immutable and can only be read. A MutableState type is mutable and allows reads and writes.
You have already seen and used MutableState in the Lemonade app and the Tip Time app in prior codelabs.
To create the mutable variable revenue, you declare it using mutableStateOf. 0 is its initial default value.
var revenue = mutableStateOf(0)
While this is enough to have Compose trigger a recomposition when the revenue value changes, it is not enough to retain its updated value. Each time the composable is reexecuted, it will reinitialize the revenue value to its initial default value of 0.
To instruct Compose to retain and reuse its value during recompositions, you need to declare it with the remember API.
var revenue by remember { mutableStateOf(0) }
If the value of revenue changes, Compose schedules all composable functions that read this value for recomposition.
While Compose remembers the revenue state during recompositions, it does not retain this state during a configuration change. For Compose to retain the state during a configuration change, you must use rememberSaveable.
For additional practice and information, please refer to Intro to state in Compose codelab.
Use rememberSaveable to save values across configuration changes
You use the rememberSaveable function to save values that you need if Android OS destroys and recreates the activity.
To save values during recompositions, you need to use remember. Use rememberSaveable to save values during recompositions AND configuration changes.
Saving the value using rememberSaveable ensures that it is available when the activity is restored, if it is needed.
- In
MainActivity, update the group of five variables that currently useremembertorememberSaveable.
var revenue by remember { mutableStateOf(0) }
...
var currentDessertImageId by remember {
mutableStateOf(desserts[currentDessertIndex].imageId)
}
var revenue by rememberSaveable { mutableStateOf(0) }
...
var currentDessertImageId by rememberSaveable {
mutableStateOf(desserts[currentDessertIndex].imageId)
}
- Compile and run your app.
- Click the cupcake a few times and note that the desserts sold and total revenue are not zero.
- Rotate the device or emulator to landscape mode.
- Observe that after the activity is destroyed and recreated, the dessert image, desserts sold, and total revenue are restored to their previous values.
6. Solution code
7. Summary
Activity lifecycle
- The activity lifecycle is a set of states through which an activity transitions. The activity lifecycle begins when the Android OS first creates the activity and ends when the OS destroys the activity.
- As the user navigates between activities, and inside and outside of your app, each activity moves between states in the activity lifecycle.
- Each state in the activity lifecycle has a corresponding callback method you can override in your
Activityclass. The core set of lifecycle methods are:onCreate(),onRestart(),onStart(),onResume(),onPause(),onStop(),onDestroy(). - To add behavior that occurs when your activity transitions into a lifecycle state, override the state's callback method.
- To add skeleton override methods to your classes in Android Studio, select Code > Override Methods... or press
Control+O.
Logging with Log
- The Android logging API, and specifically the
Logclass, enables you to write short messages that are displayed in the Logcat within Android Studio. - Use
Log.d()to write a debug message. This method takes two arguments: the log tag, typically the name of the class, and the log message, a short string. - Use the Logcat window in Android Studio to view the system logs, including the messages you write.
Configuration changes
- A configuration change occurs when the state of the device changes so radically that the easiest way for the system to resolve the change is to destroy and rebuild the activity.
- The most common example of a configuration change is when the user rotates the device from portrait to landscape mode, or from landscape to portrait mode. A configuration change can also occur when the device language changes or a user plugs in a hardware keyboard.
- When a configuration change occurs, Android invokes all the activity lifecycle's shutdown callbacks. Android then restarts the activity from scratch, running all the lifecycle startup callbacks.
- When Android shuts down an app because of a configuration change, it restarts the activity with
onCreate(). - To save a value that needs to survive a configuration change, declare its variables with
rememberSaveable.
