1. 准备工作
在之前的 Codelab 中,您了解了 activity 的生命周期以及与配置更改相关的生命周期问题。发生配置更改时,您可以通过不同的方式保存应用数据,例如使用 rememberSaveable 或保存实例状态。不过,这些方式可能会造成问题。大多数情况下,您可以使用 rememberSaveable,但这可能意味着将逻辑保留在可组合函数中或附近。随着应用体量不断变大,您应将数据和逻辑从可组合函数中移出。在此 Codelab 中,您将了解如何利用 Android Jetpack 库、ViewModel 和 Android 应用架构准则,以高度可靠的方式设计应用并在配置更改期间保留应用数据。
Android Jetpack 库是一系列库的集合,可以让您更轻松地开发出优质的 Android 应用。这些库能帮助您遵循最佳实践、省去编写样板代码的工作并简化复杂任务,以便集中精力编写重要的代码(例如应用逻辑)。
应用架构是指一组应用设计规则。就像房屋的蓝图一样,架构为应用提供了结构。良好的应用架构能让代码在未来几年内始终保持可靠性、灵活性、可伸缩性、可测试性和可维护性。应用架构指南提供了有关应用架构的建议和推荐的最佳实践。
在此 Codelab 中,您将学习如何使用 ViewModel,它是 Android Jetpack 库中的架构组件之一,可用于存储应用数据。当框架在配置更改或其他事件期间销毁并重新创建 activity 时,存储的数据不会丢失。不过,如果 activity 因进程终止而被销毁,数据将会丢失。ViewModel 只能通过快速重新创建 activity 缓存数据。
前提条件
- 了解 Kotlin,包括函数、lambda 和无状态可组合函数
- 具备在 Jetpack Compose 中构建布局的基础知识
- 具备有关 Material Design 的基础知识
学习内容
- Android 应用架构简介
- 如何在应用中使用
ViewModel类 - 如何使用
ViewModel在设备配置更改时保留界面数据
构建内容
- 一个让用户猜乱序词(打乱字母顺序的词)的 Unscramble 游戏应用
所需条件
- 最新版本的 Android Studio
- 互联网连接,用于下载起始代码
2. 应用概览
游戏概览
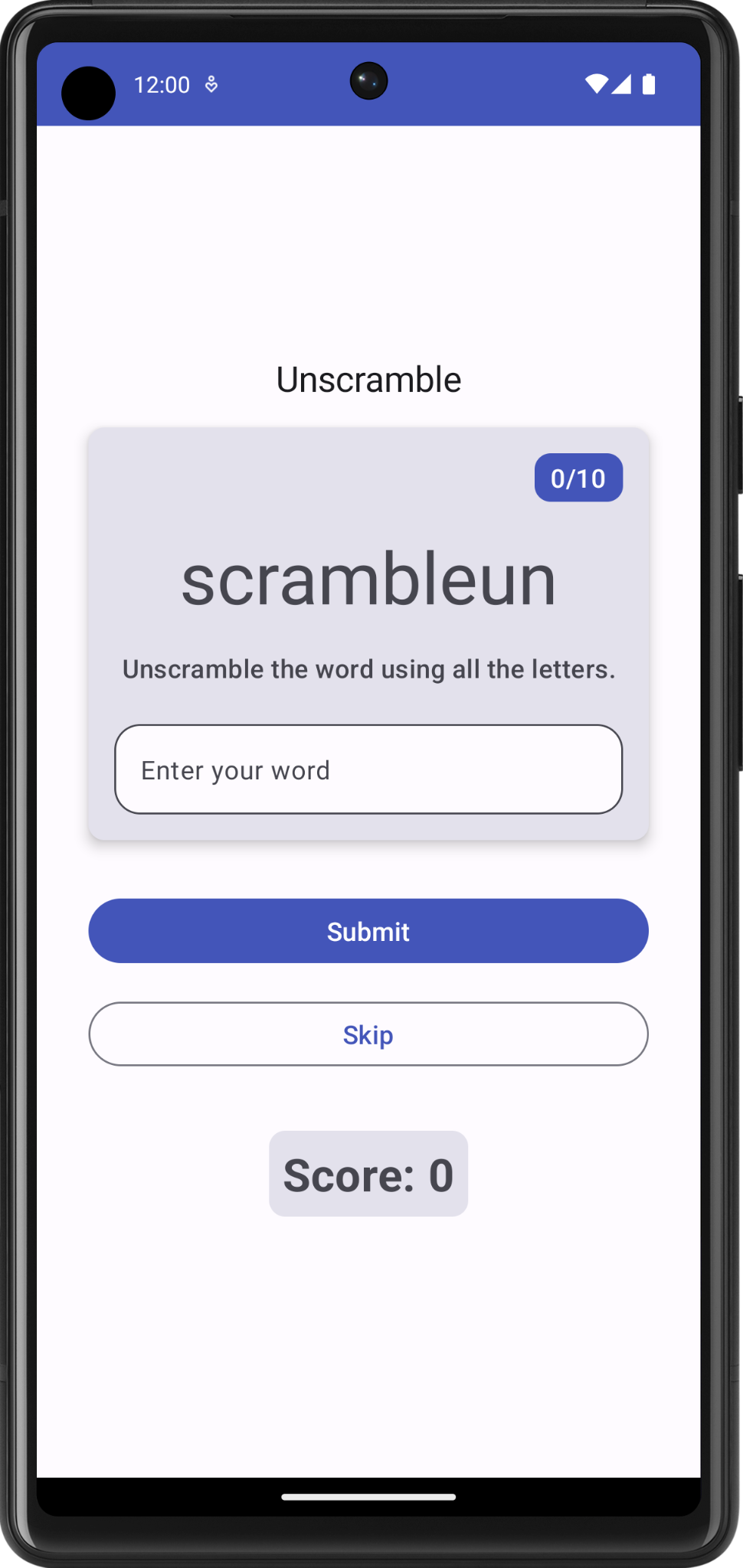
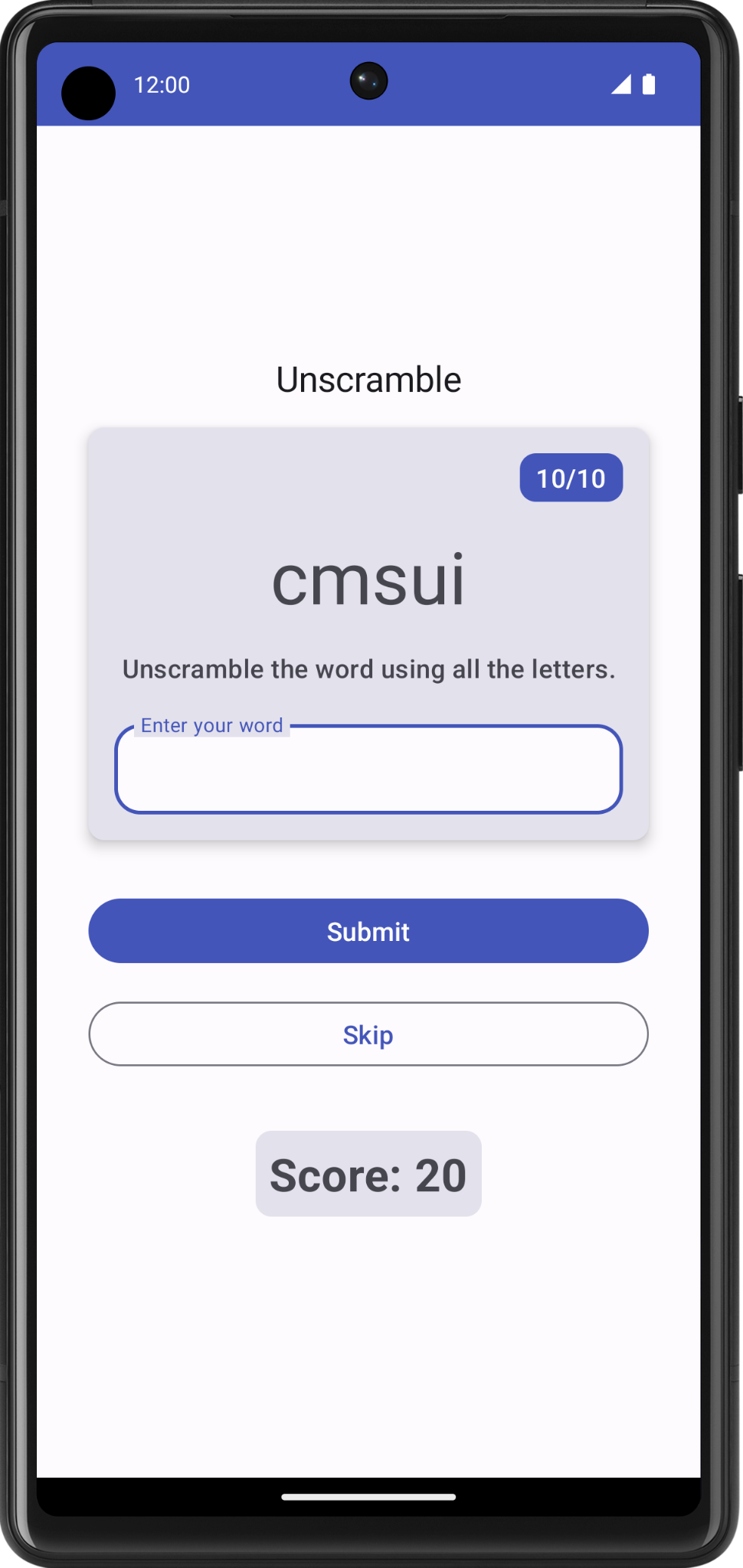
Unscramble 应用是一款猜乱序词的单人游戏。应用显示一个乱序词,玩家必须根据显示的所有字母猜出这个单词。如果猜出的单词正确,玩家就会得分。否则,玩家可以重新猜,次数不限。此外,应用还提供了一个跳过当前单词的选项。应用会在右上角显示单词数,即当前这一局游戏中猜过的乱序词数量。每一局游戏有 10 个乱序词。
|
|
|
获取起始代码
首先,请下载起始代码:
或者,您也可以克隆该代码的 GitHub 代码库:
$ git clone https://github.com/google-developer-training/basic-android-kotlin-compose-training-unscramble.git $ cd basic-android-kotlin-compose-training-unscramble $ git checkout starter
您可以在 Unscramble GitHub 代码库中浏览该起始代码。
3. 起始应用概览
若要熟悉起始代码,请完成以下步骤:
- 在 Android Studio 中打开包含起始代码的项目。
- 在 Android 设备或模拟器上运行应用。
- 点按 Submit 和 Skip 按钮以测试应用。
您会发现,应用中存在一些 bug。乱序词未显示,但已硬编码为“scrambleun”,而且当您点按按钮时,也没有任何反应。
在此 Codelab 中,您将使用 Android 应用架构来实现游戏功能。
起始代码演示
起始代码已为您预先设计了游戏屏幕布局。在本在线课程中,您将实现游戏逻辑。您将使用架构组件来实现推荐的应用架构并解决上述问题。下面简要介绍了一些文件,以帮助您上手。
WordsData.kt
此文件包含游戏中所用单词的列表,以及表示每局游戏最多单词数和玩家每猜对一个单词所得分数的常量。
package com.example.android.unscramble.data
const val MAX_NO_OF_WORDS = 10
const val SCORE_INCREASE = 20
// Set with all the words for the Game
val allWords: Set<String> =
setOf(
"animal",
"auto",
"anecdote",
"alphabet",
"all",
"awesome",
"arise",
"balloon",
"basket",
"bench",
// ...
"zoology",
"zone",
"zeal"
)
MainActivity.kt
此文件主要包含模板生成的代码。您可以在 setContent{} 代码块中显示 GameScreen 可组合函数。
GameScreen.kt
所有界面可组合函数都在 GameScreen.kt 文件中进行定义。以下部分对一些可组合函数进行了演示。
GameStatus
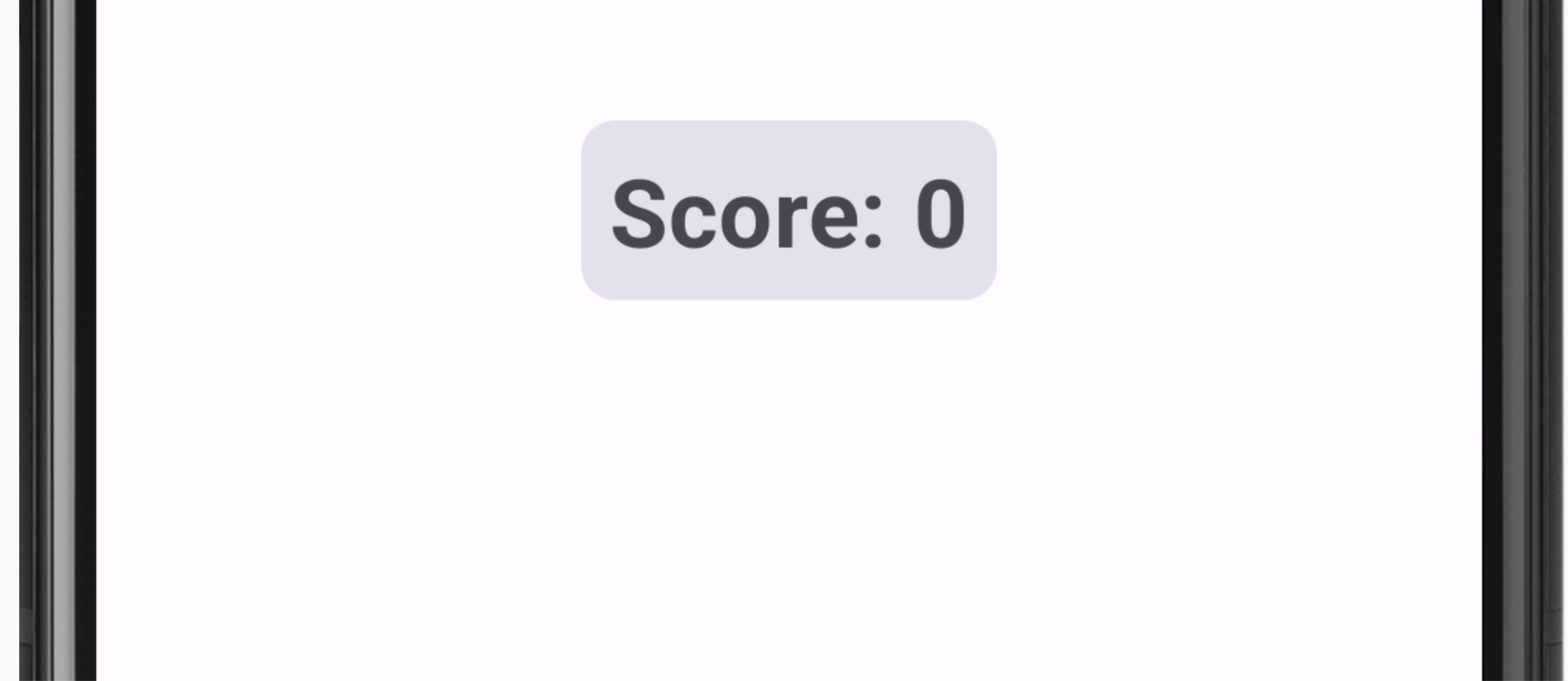
GameStatus 可组合函数会在屏幕底部显示游戏得分。可组合函数在 Card 中包含文本可组合函数。目前,得分已硬编码为 0。
// No need to copy, this is included in the starter code.
@Composable
fun GameStatus(score: Int, modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
Card(
modifier = modifier
) {
Text(
text = stringResource(R.string.score, score),
style = typography.headlineMedium,
modifier = Modifier.padding(8.dp)
)
}
}
GameLayout
GameLayout 可组合函数会显示主要游戏功能,包括乱序词、游戏说明以及用于接受用户猜测内容的文本字段。

请注意,以下 GameLayout 代码在 Card 中包含一个列,其中有三个子元素:乱序词文本、说明文本和供用户输入所猜单词的文本字段 OutlinedTextField。目前,乱序词硬编码为 scrambleun。您稍后将在此 Codelab 中实现显示 WordsData.kt 文件中的单词的功能。
// No need to copy, this is included in the starter code.
@Composable
fun GameLayout(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
val mediumPadding = dimensionResource(R.dimen.padding_medium)
Card(
modifier = modifier,
elevation = CardDefaults.cardElevation(defaultElevation = 5.dp)
) {
Column(
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(mediumPadding),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
modifier = Modifier.padding(mediumPadding)
) {
Text(
modifier = Modifier
.clip(shapes.medium)
.background(colorScheme.surfaceTint)
.padding(horizontal = 10.dp, vertical = 4.dp)
.align(alignment = Alignment.End),
text = stringResource(R.string.word_count, 0),
style = typography.titleMedium,
color = colorScheme.onPrimary
)
Text(
text = "scrambleun",
style = typography.displayMedium
)
Text(
text = stringResource(R.string.instructions),
textAlign = TextAlign.Center,
style = typography.titleMedium
)
OutlinedTextField(
value = "",
singleLine = true,
shape = shapes.large,
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(),
colors = TextFieldDefaults.textFieldColors(containerColor = colorScheme.surface),
onValueChange = { },
label = { Text(stringResource(R.string.enter_your_word)) },
isError = false,
keyboardOptions = KeyboardOptions.Default.copy(
imeAction = ImeAction.Done
),
keyboardActions = KeyboardActions(
onDone = { }
)
)
}
}
}
OutlinedTextField 可组合函数类似于在之前的 Codelab 中应用所使用的 TextField 可组合函数。
文本字段有两种类型:
- 已填充文本字段
- 框状文本字段

框状文本字段的强调效果在视觉上要弱于已填充文本字段。当在表单等有许多文本字段放在一处的位置使用框状文本字段时,其相对较弱的强调效果有助于简化布局。
在起始代码中,当用户输入所猜单词时,OutlinedTextField 不会更新。您将在此 Codelab 中更新该功能。
GameScreen
GameScreen 可组合函数包含 GameStatus 和 GameLayout 可组合函数、游戏名称、单词数,以及 Submit 和 Skip 按钮的可组合函数。
@Composable
fun GameScreen() {
val mediumPadding = dimensionResource(R.dimen.padding_medium)
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.verticalScroll(rememberScrollState())
.padding(mediumPadding),
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center,
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
Text(
text = stringResource(R.string.app_name),
style = typography.titleLarge,
)
GameLayout(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.wrapContentHeight()
.padding(mediumPadding)
)
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(mediumPadding),
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(mediumPadding),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
Button(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(),
onClick = { }
) {
Text(
text = stringResource(R.string.submit),
fontSize = 16.sp
)
}
OutlinedButton(
onClick = { },
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()
) {
Text(
text = stringResource(R.string.skip),
fontSize = 16.sp
)
}
}
GameStatus(score = 0, modifier = Modifier.padding(20.dp))
}
}
起始代码中未实现按钮点击事件。您将在此 Codelab 中实现这些事件。
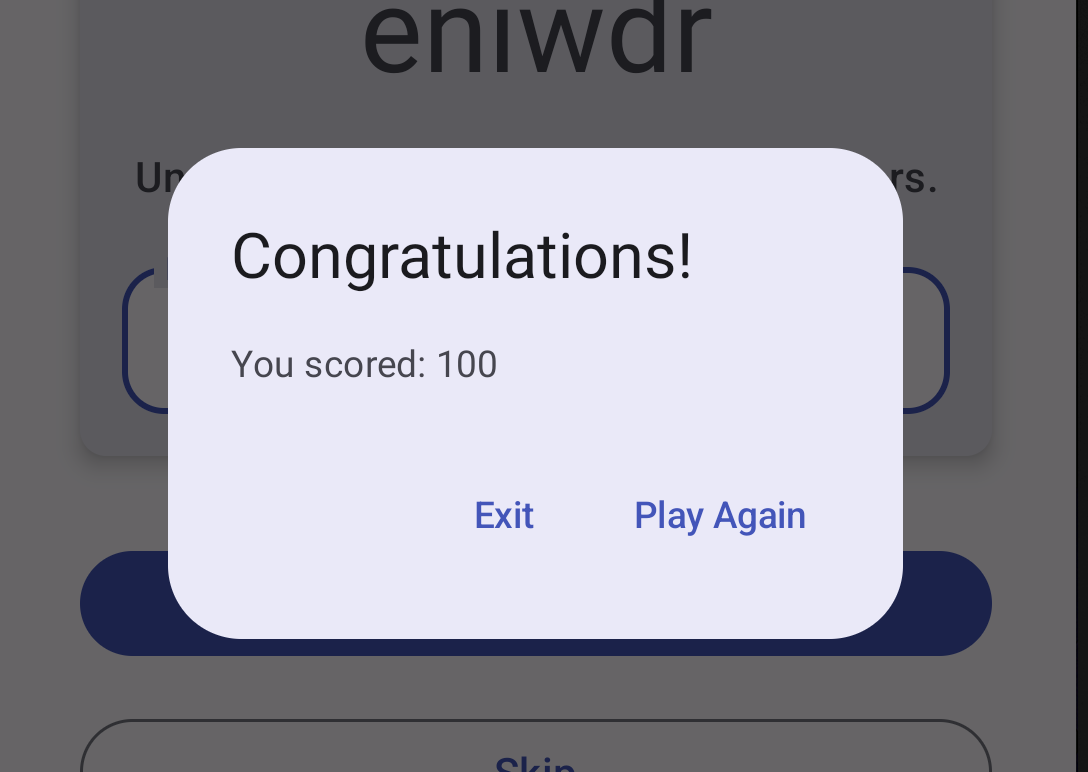
FinalScoreDialog
FinalScoreDialog 可组合函数用于显示一个对话框(即提示用户执行操作的小窗口),其中包含 Play Again 或 Exit 游戏选项。在此 Codelab 后面的内容中,您将实现在游戏结束时显示此对话框的逻辑。
// No need to copy, this is included in the starter code.
@Composable
private fun FinalScoreDialog(
score: Int,
onPlayAgain: () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier
) {
val activity = (LocalContext.current as Activity)
AlertDialog(
onDismissRequest = {
// Dismiss the dialog when the user clicks outside the dialog or on the back
// button. If you want to disable that functionality, simply use an empty
// onDismissRequest.
},
title = { Text(text = stringResource(R.string.congratulations)) },
text = { Text(text = stringResource(R.string.you_scored, score)) },
modifier = modifier,
dismissButton = {
TextButton(
onClick = {
activity.finish()
}
) {
Text(text = stringResource(R.string.exit))
}
},
confirmButton = {
TextButton(onClick = onPlayAgain) {
Text(text = stringResource(R.string.play_again))
}
}
)
}
4. 了解应用架构
应用架构提供了在应用中的类之间分配责任时应遵循的准则。精心设计的应用架构可以帮助您扩缩应用,以及用更多功能对应用进行扩展。架构还可以简化团队协作。
最常用的架构原则包括:分离关注点和通过模型驱动界面。
分离关注点
分离关注点设计原则指出,应将应用分为函数类,每个类都有各自的责任。
通过模型驱动界面
通过模型驱动界面原则指出,应该通过模型驱动界面,最好是通过持久性模型。模型是负责处理应用数据的组件。它们独立于应用中的界面元素和应用组件,因此不受应用的生命周期以及相关的关注点的影响。
推荐的应用架构
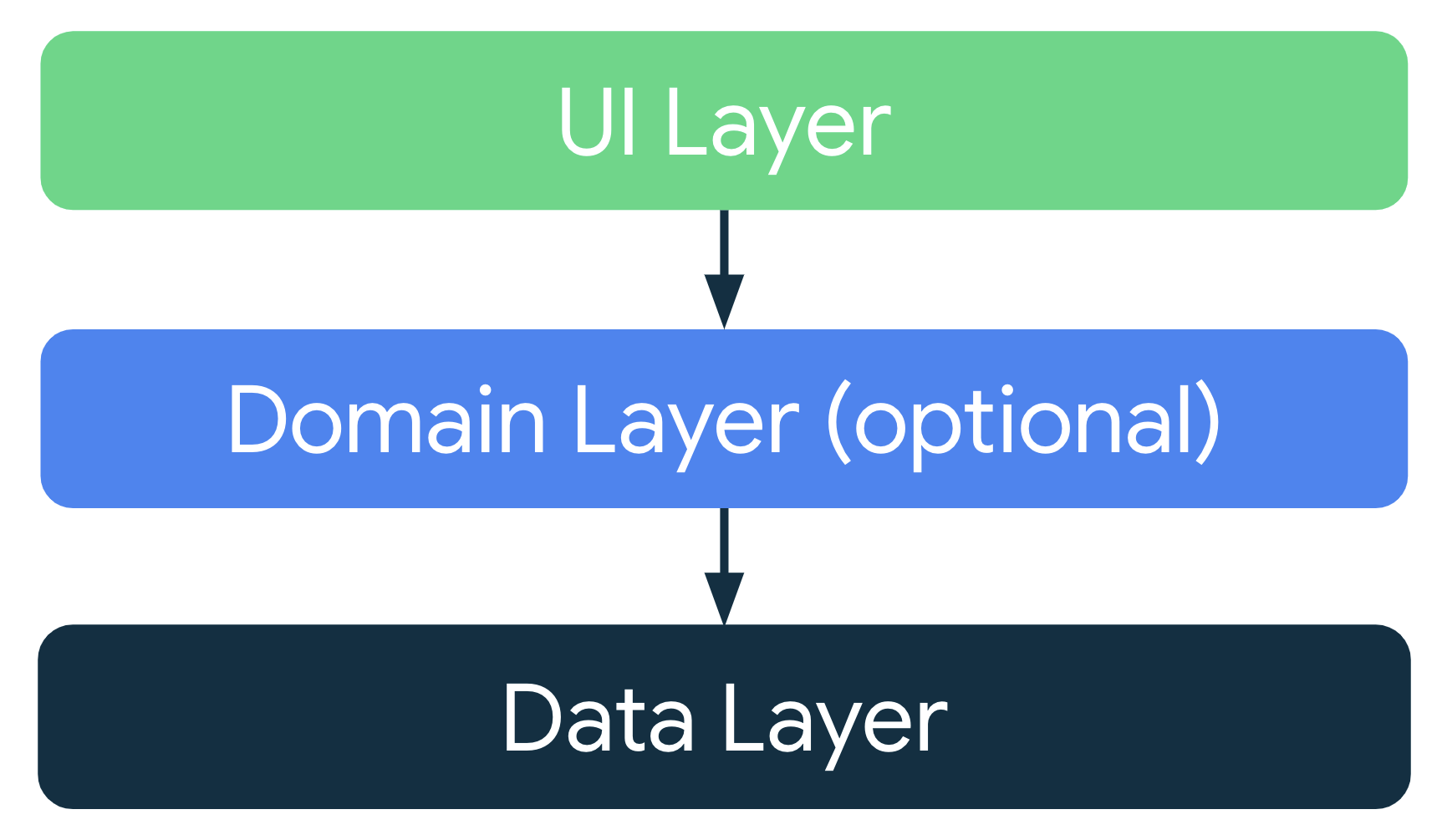
基于上一部分提到的常用架构原则,每个应用应至少有两个层:
- 界面层:在屏幕上显示应用数据但独立于数据的层。
- 数据层:用于存储、检索和提供应用数据的层。
您可以另外添加一个名为“网域层”的架构层,以简化和重复使用界面层与数据层之间的交互。该层是可选的,不在本课程的范围之内。
界面层
界面层(或表示层)的作用是在屏幕上显示应用数据。每当数据因用户互动(例如按了某个按钮)而发生变化时,界面都应随之更新,以反映这些变化。
界面层由以下组件组成:
- 界面元素:用于在屏幕上呈现数据的组件。您将使用 Jetpack Compose 构建这些元素。
- 状态容器:用于保存数据、向界面提供数据以及处理应用逻辑的组件。状态容器的一个示例为 ViewModel。
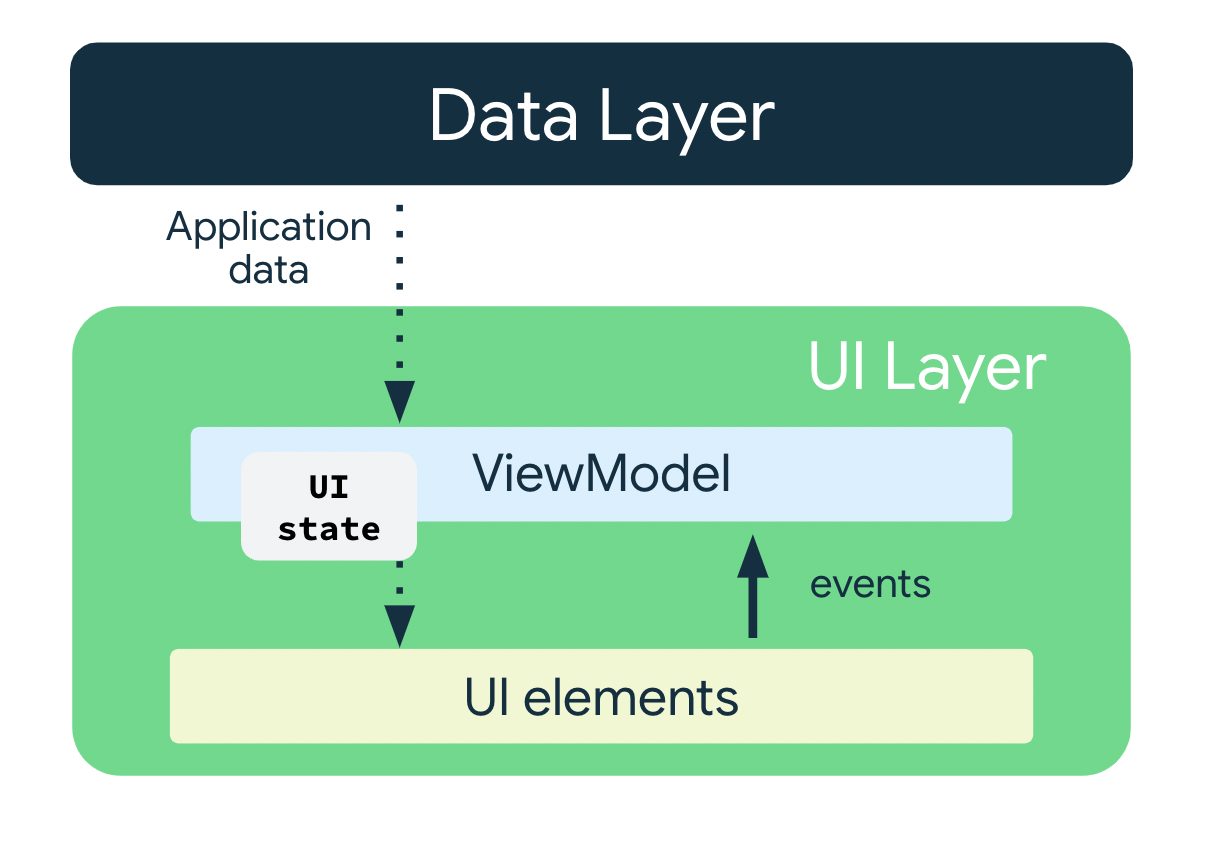
ViewModel
ViewModel 组件用于存储和公开界面所使用的状态。界面状态是经过 ViewModel 转换的应用数据。ViewModel 可让您的应用遵循通过模型驱动界面的架构原则。
ViewModel 会存储应用相关的数据,这些数据不会在 Android 框架销毁并重新创建 activity 时销毁。与 activity 实例不同,ViewModel 对象不会被销毁。应用会在配置更改期间自动保留 ViewModel 对象,以便它们存储的数据在重组后立即可用。
如需在应用中实现 ViewModel,请扩展架构组件库中提供的 ViewModel 类,并将应用数据存储在该类中。
界面状态
界面是相对用户而言的,而界面状态是相对应用而言的。界面是界面状态的直观呈现。对界面状态所做的任何更改都会立即反映在界面中。

界面是将屏幕上的界面元素与界面状态绑定在一起的结果。
// Example of UI state definition, do not copy over
data class NewsItemUiState(
val title: String,
val body: String,
val bookmarked: Boolean = false,
...
)
不可变性
以上示例中的界面状态定义是不可变的。不可变对象可保证多个来源不会即时更改应用的状态。这种保护机制让界面可以专注于发挥单一作用:读取状态并相应地更新其界面元素。因此,切勿直接在界面中修改界面状态,除非界面本身是其数据的唯一来源。违反这个原则会导致同一条信息有多个可信来源,从而导致数据不一致和轻微的 bug。
5. 添加 ViewModel
在此任务中,您将向应用添加 ViewModel,以存储游戏界面状态(乱序词、单词数和得分)。如要解决您在上一部分中注意到的起始代码中的问题,您需要将游戏数据保存在 ViewModel 中。
- 打开
build.gradle.kts (Module :app),滚动到dependencies代码块,然后为ViewModel添加以下依赖项。此依赖项用于向 Compose 应用添加生命周期感知型 ViewModel。
dependencies {
// other dependencies
implementation("androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-compose:2.6.1")
//...
}
- 在
ui软件包中,创建一个名为GameViewModel的 Kotlin 类/文件,然后从ViewModel类扩展它。
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
class GameViewModel : ViewModel() {
}
- 在
ui软件包中,为状态界面添加一个名为GameUiState的模型类。将其设为数据类,并为当前的乱序词添加变量。
data class GameUiState(
val currentScrambledWord: String = ""
)
StateFlow
StateFlow 是一个数据容器式可观察数据流,可发出当前状态更新和新状态更新。其 value 属性反映了当前状态值。如需更新状态并将其发送到数据流,请为 MutableStateFlow 类的 value 属性分配一个新值。
在 Android 中,StateFlow 适用于必须维护可观察的不可变状态的类。
可以从 GameUiState 公开 StateFlow,以便可组合函数能够监听界面状态更新,并使屏幕状态在配置更改后继续有效。
在 GameViewModel 类中,添加以下 _uiState 属性。
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.MutableStateFlow
// Game UI state
private val _uiState = MutableStateFlow(GameUiState())
后备属性
使用后备属性,可以从 getter 返回确切对象之外的某些其他内容。
Kotlin 框架会为 var 属性生成 getter 和 setter。
对于 getter 和 setter 方法,您可以替换其中一个方法或同时替换这两个方法,并提供您自己的自定义行为。为了实现后备属性,您需要替换 getter 方法以返回只读版本的数据。以下示例展示了后备属性:
//Example code, no need to copy over
// Declare private mutable variable that can only be modified
// within the class it is declared.
private var _count = 0
// Declare another public immutable field and override its getter method.
// Return the private property's value in the getter method.
// When count is accessed, the get() function is called and
// the value of _count is returned.
val count: Int
get() = _count
再举一个例子,假设您希望应用数据仅对 ViewModel 可见:
在 ViewModel 类之内:
_count属性设置为private且可变。因此,只能在ViewModel类中对其访问和修改。
在 ViewModel 类之外:
- Kotlin 中的默认可见性修饰符为
public,因此count是公共属性,可从界面控制器等其他类对其进行访问。val类型不能包含 setter。它不可变且处于只读状态,因此您只能替换get()方法。当外部类访问此属性时,它会返回_count的值且其值无法修改。此后备属性可以防止外部类擅自对ViewModel内的应用数据进行不安全的更改,但允许外部调用方安全地访问该应用数据的值。
- 在
GameViewModel.kt文件中,向名为_uiState的uiState添加后备属性。将该属性命名为uiState,其类型为StateFlow<GameUiState>。
现在,只能在 GameViewModel 中对 _uiState 进行访问和修改。界面可以使用只读属性 uiState 读取其值。您可以在下一步中修复初始化错误。
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.StateFlow
// Game UI state
// Backing property to avoid state updates from other classes
private val _uiState = MutableStateFlow(GameUiState())
val uiState: StateFlow<GameUiState>
- 将
uiState设为_uiState.asStateFlow()。
asStateFlow() 会使此可变状态流成为只读状态流。
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.StateFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.asStateFlow
// Game UI state
private val _uiState = MutableStateFlow(GameUiState())
val uiState: StateFlow<GameUiState> = _uiState.asStateFlow()
显示随机乱序词
在此任务中,您将添加辅助方法,以从 WordsData.kt 中随机选择一个单词并打乱单词的字母顺序。
- 在
GameViewModel中,添加一个名为currentWord且类型为String的属性,以保存当前的乱序词。
private lateinit var currentWord: String
- 添加一个辅助方法,以从列表中随机选择一个单词并打乱单词的字母顺序。将其命名为
pickRandomWordAndShuffle()(不带输入参数),并使其返回String。
import com.example.unscramble.data.allWords
private fun pickRandomWordAndShuffle(): String {
// Continue picking up a new random word until you get one that hasn't been used before
currentWord = allWords.random()
if (usedWords.contains(currentWord)) {
return pickRandomWordAndShuffle()
} else {
usedWords.add(currentWord)
return shuffleCurrentWord(currentWord)
}
}
Android Studio 会针对未定义的变量和函数标记错误。
- 在
GameViewModel中的currentWord属性之后添加以下属性,以用作可变集来存储游戏中用过的单词。
// Set of words used in the game
private var usedWords: MutableSet<String> = mutableSetOf()
- 再添加一个名为
shuffleCurrentWord()的辅助方法,以打乱当前单词的字母顺序,该方法会接受String并返回已打乱字母顺序的String。
private fun shuffleCurrentWord(word: String): String {
val tempWord = word.toCharArray()
// Scramble the word
tempWord.shuffle()
while (String(tempWord).equals(word)) {
tempWord.shuffle()
}
return String(tempWord)
}
- 添加一个辅助函数,以初始化名为
resetGame()的游戏。稍后您将使用此函数来启动和重启游戏。在此函数中,清除usedWords集中的所有单词,初始化_uiState。使用pickRandomWordAndShuffle()为currentScrambledWord选择一个新单词。
fun resetGame() {
usedWords.clear()
_uiState.value = GameUiState(currentScrambledWord = pickRandomWordAndShuffle())
}
- 向
GameViewModel添加init代码块,并从中调用resetGame()。
init {
resetGame()
}
现在,在构建应用时,您仍然不会看到界面有任何变化。您没有将 ViewModel 中的数据传递给 GameScreen 中的可组合函数。
6. 构建 Compose 界面
在 Compose 中,更新界面的唯一方式是更改应用的状态。您可以控制的是界面状态。每当界面的状态发生变化时,Compose 都会重新创建界面树中已更改的部分。可组合函数可以接受状态并公开事件。例如,TextField/OutlinedTextField 接受值并公开请求回调处理程序更改值的回调 onValueChange。
//Example code no need to copy over
var name by remember { mutableStateOf("") }
OutlinedTextField(
value = name,
onValueChange = { name = it },
label = { Text("Name") }
)
由于可组合函数接受状态并公开事件,因此单向数据流模式非常适合 Jetpack Compose。本部分将重点介绍如何在 Compose 中实现单向数据流模式,如何实现事件和状态容器,以及如何在 Compose 中使用 ViewModel。
单向数据流
单向数据流 (UDF) 是一种设计模式,在该模式下,状态向下流动,事件向上流动。通过遵循单向数据流,您可以将在界面中显示状态的可组合函数与应用中存储和更改状态的部分解耦。
使用单向数据流的应用的界面更新循环如下所示:
- 事件:界面的某一部分生成一个事件,并将其向上传递,例如将按钮点击传递给 ViewModel 进行处理;或者从应用的其他层传递事件,如指示用户会话已过期。
- 更新状态:事件处理脚本可能会更改状态。
- 显示状态:状态容器向下传递状态,而界面会显示此状态。
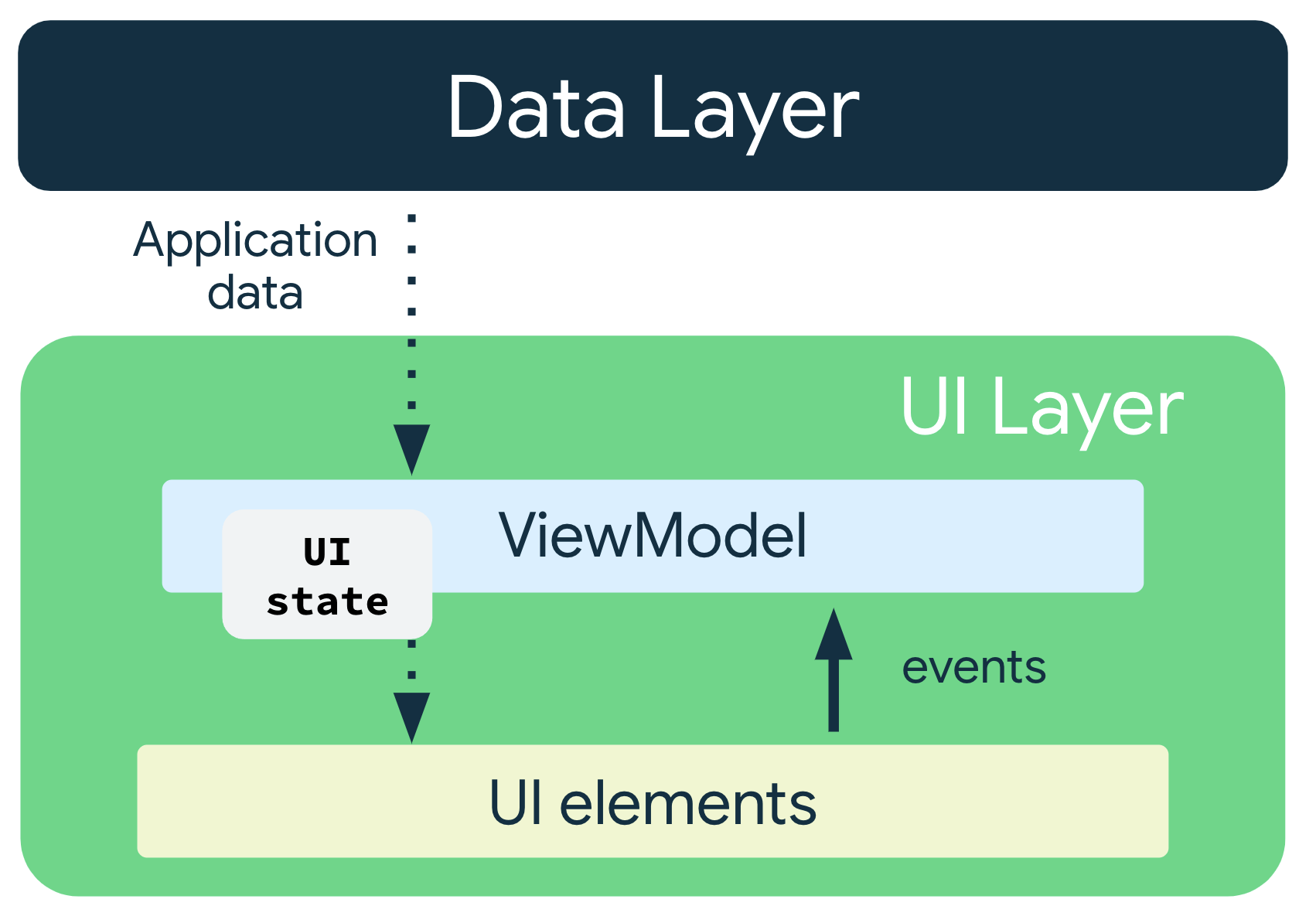
在应用架构中使用 UDF 模式会产生以下影响:
ViewModel会存储并公开界面所使用的状态。- 界面状态是经过
ViewModel转换的应用数据。 - 界面会向
ViewModel发送用户事件通知。 ViewModel会处理用户操作并更新状态。- 更新后的状态将反馈给界面以进行呈现。
- 系统会对导致状态更改的所有事件重复此流程。
传递数据
将 ViewModel 实例传递给界面,即从 GameViewModel 传递到 GameScreen.kt 文件中的 GameScreen()。在 GameScreen() 中,使用 ViewModel 实例通过 collectAsState() 访问 uiState。
collectAsState() 函数会从此 StateFlow 收集值,并通过 State 表示其最新值。StateFlow.value 用作初始值。每次向 StateFlow 发布一个新值时,返回的 State 都会更新,这会导致所有 State.value 用法重组。
- 在
GameScreen函数中,传递第二个参数,其类型为GameViewModel,默认值为viewModel()。
import androidx.lifecycle.viewmodel.compose.viewModel
@Composable
fun GameScreen(
gameViewModel: GameViewModel = viewModel()
) {
// ...
}
- 在
GameScreen()函数中,添加一个名为gameUiState的新变量。使用by委托并对uiState调用collectAsState()。
此方法可确保每当 uiState 值发生变化时,使用 gameUiState 值的可组合函数都会重组。
import androidx.compose.runtime.collectAsState
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
@Composable
fun GameScreen(
// ...
) {
val gameUiState by gameViewModel.uiState.collectAsState()
// ...
}
- 将
gameUiState.currentScrambledWord传递给GameLayout()可组合函数。您将在后续步骤中添加此参数,因此请暂时忽略该错误。
GameLayout(
currentScrambledWord = gameUiState.currentScrambledWord,
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.wrapContentHeight()
.padding(mediumPadding)
)
- 将
currentScrambledWord作为另一个参数添加到GameLayout()可组合函数中。
@Composable
fun GameLayout(
currentScrambledWord: String,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier
) {
}
- 更新
GameLayout()可组合函数以显示currentScrambledWord。将列中第一个文本字段的text参数设置为currentScrambledWord。
@Composable
fun GameLayout(
// ...
) {
Column(
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(24.dp)
) {
Text(
text = currentScrambledWord,
fontSize = 45.sp,
modifier = modifier.align(Alignment.CenterHorizontally)
)
//...
}
}
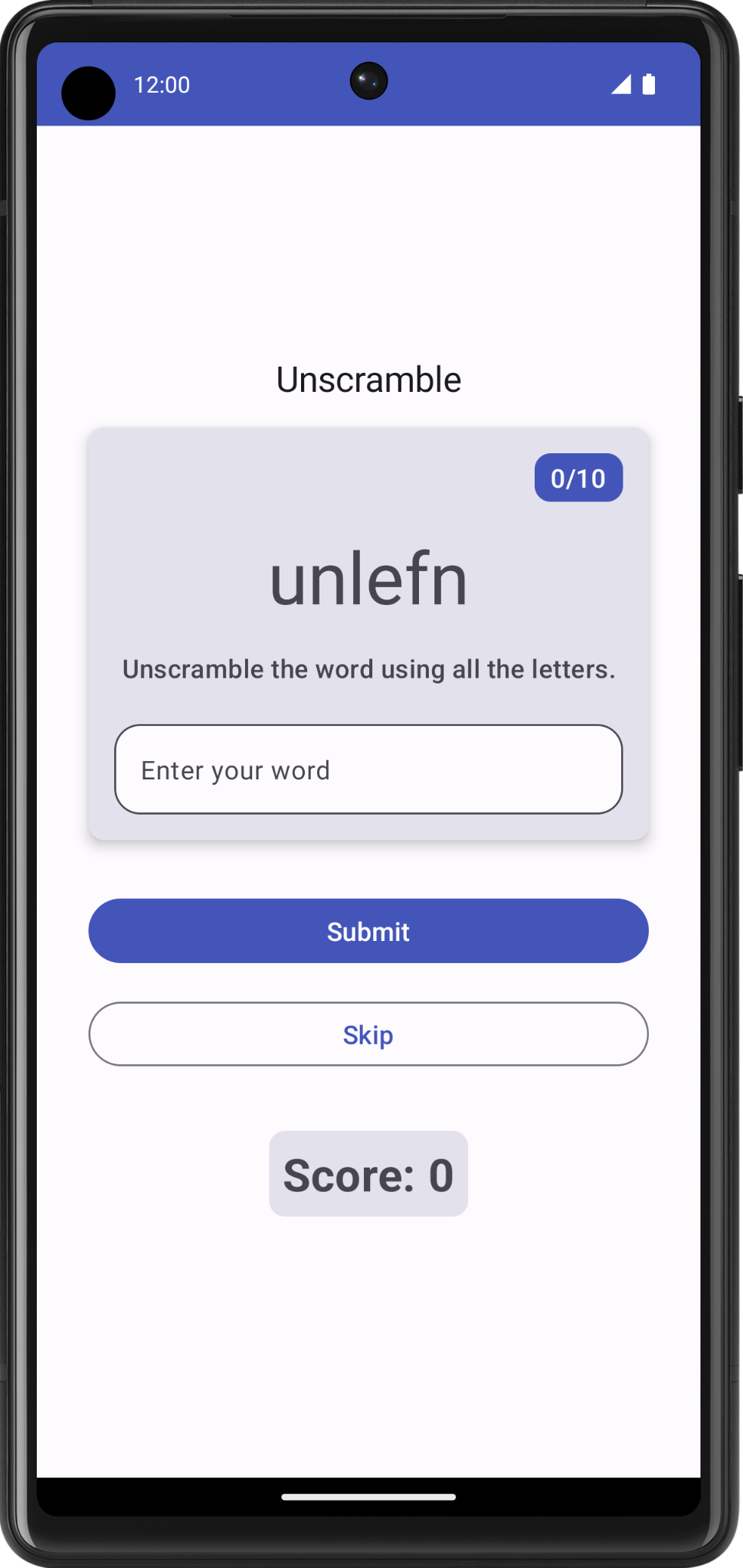
- 运行并构建应用。此时,您应该会看到乱序词。
显示猜出的单词
在 GameLayout() 可组合函数中,更新用户猜出的单词是从 GameScreen 向上流向 ViewModel 的事件回调之一。数据 gameViewModel.userGuess 将从 ViewModel 向下流向 GameScreen。
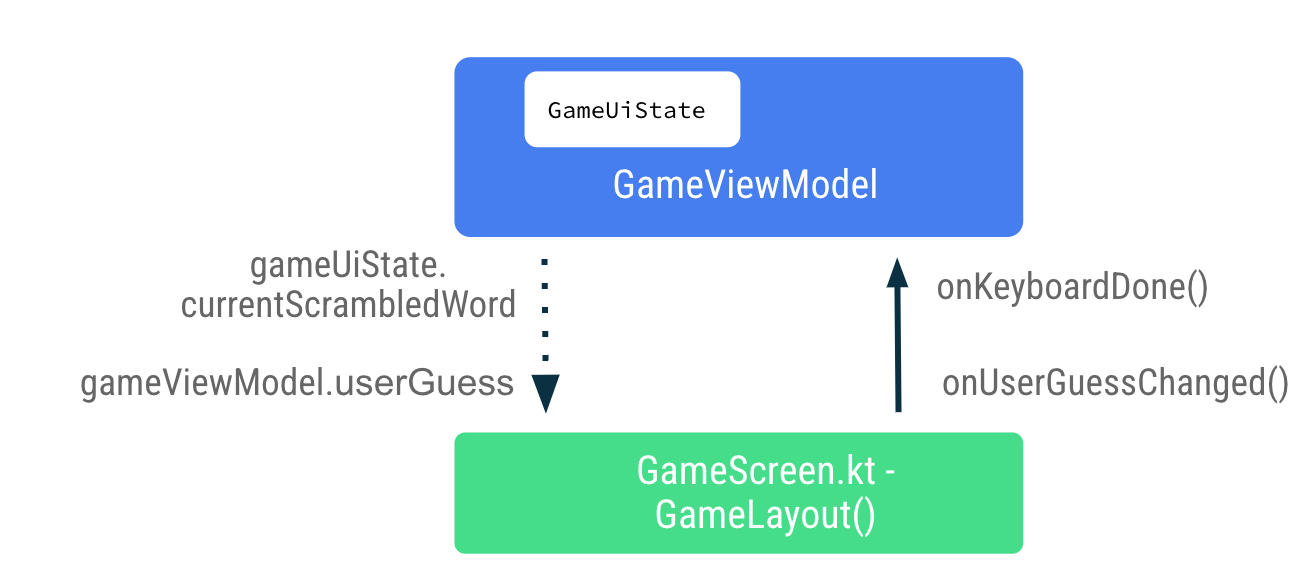
- 在
GameScreen.kt文件的GameLayout()可组合函数中,将onValueChange设置为onUserGuessChanged,并将onKeyboardDone()设置为onDone键盘操作。您将在下一步中修复错误。
OutlinedTextField(
value = "",
singleLine = true,
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(),
onValueChange = onUserGuessChanged,
label = { Text(stringResource(R.string.enter_your_word)) },
isError = false,
keyboardOptions = KeyboardOptions.Default.copy(
imeAction = ImeAction.Done
),
keyboardActions = KeyboardActions(
onDone = { onKeyboardDone() }
),
- 在
GameLayout()可组合函数中,再添加两个参数:onUserGuessChangedlambda 接受String参数,但不返回任何内容;onKeyboardDone不接受任何内容也不返回任何内容。
@Composable
fun GameLayout(
onUserGuessChanged: (String) -> Unit,
onKeyboardDone: () -> Unit,
currentScrambledWord: String,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
) {
}
- 在
GameLayout()函数调用中,为onUserGuessChanged和onKeyboardDone添加 lambda 参数。
GameLayout(
onUserGuessChanged = { gameViewModel.updateUserGuess(it) },
onKeyboardDone = { },
currentScrambledWord = gameUiState.currentScrambledWord,
)
您很快会在 GameViewModel 中定义 updateUserGuess 方法。
- 在
GameViewModel.kt文件中,添加一个名为updateUserGuess()的方法,用于接受String参数(用户猜出的单词)。在该函数内,使用传入的guessedWord更新userGuess。
fun updateUserGuess(guessedWord: String){
userGuess = guessedWord
}
在接下来的 ViewModel 中添加 userGuess。
- 在
GameViewModel.kt文件中,添加一个名为userGuess的 var 属性。使用mutableStateOf(),以便 Compose 观察此值,并将初始值设置为""。
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
var userGuess by mutableStateOf("")
private set
- 在
GameScreen.kt文件的GameLayout()内,再为userGuess添加一个String参数。将OutlinedTextField的value参数设置为userGuess。
fun GameLayout(
currentScrambledWord: String,
userGuess: String,
onUserGuessChanged: (String) -> Unit,
onKeyboardDone: () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier
) {
Column(
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(24.dp)
) {
//...
OutlinedTextField(
value = userGuess,
//..
)
}
}
- 在
GameScreen函数中,更新GameLayout()函数调用以包含userGuess参数。
GameLayout(
currentScrambledWord = gameUiState.currentScrambledWord,
userGuess = gameViewModel.userGuess,
onUserGuessChanged = { gameViewModel.updateUserGuess(it) },
onKeyboardDone = { },
//...
)
- 构建并运行您的应用。
- 尝试猜测并输入一个单词。文本字段可以显示用户猜出的单词。
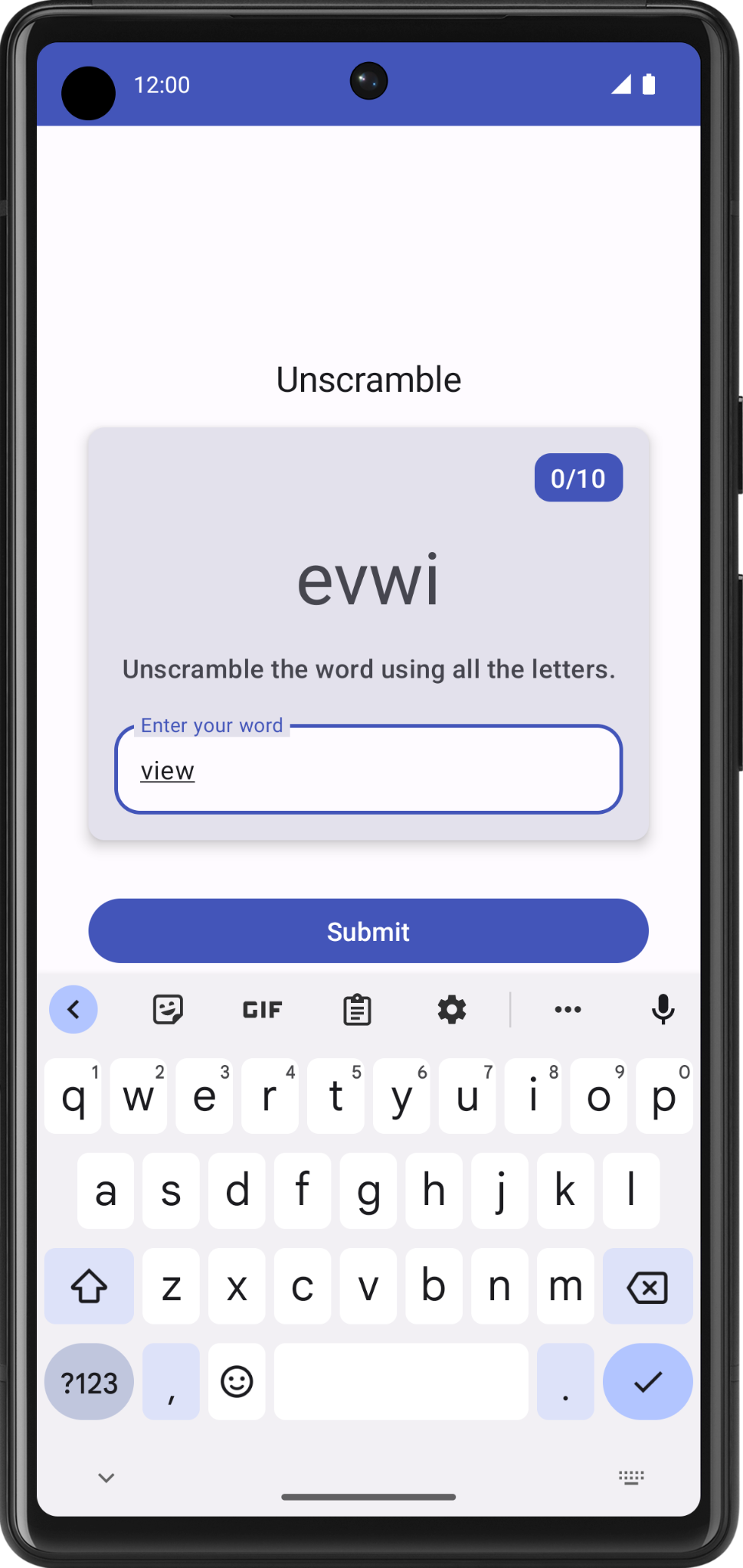
7. 验证猜出的单词并更新得分
在此任务中,您将实现一种方法来验证用户猜出的单词,然后更新游戏得分或显示错误。之后,您将用新得分和新单词来更新游戏状态界面。
- 在
GameViewModel中,再添加一个名为checkUserGuess()的方法。 - 在
checkUserGuess()函数中,添加一个if else代码块,以验证用户的猜测是否与currentWord一样。将userGuess重置为空字符串。
fun checkUserGuess() {
if (userGuess.equals(currentWord, ignoreCase = true)) {
} else {
}
// Reset user guess
updateUserGuess("")
}
- 如果用户的猜测有误,将
isGuessedWordWrong设为true。MutableStateFlow<T>.update()会使用指定的值更新MutableStateFlow.value。
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.update
if (userGuess.equals(currentWord, ignoreCase = true)) {
} else {
// User's guess is wrong, show an error
_uiState.update { currentState ->
currentState.copy(isGuessedWordWrong = true)
}
}
- 在
GameUiState类中,添加一个名为isGuessedWordWrong的Boolean,并将其初始化为false。
data class GameUiState(
val currentScrambledWord: String = "",
val isGuessedWordWrong: Boolean = false,
)
接下来,在用户点击 Submit 按钮或按键盘中的“Done”键时,您将事件回调 checkUserGuess() 从 GameScreen 向上传递至 ViewModel。将数据 gameUiState.isGuessedWordWrong 从 ViewModel 向下传递至 GameScreen,以设置文本字段中显示的错误。
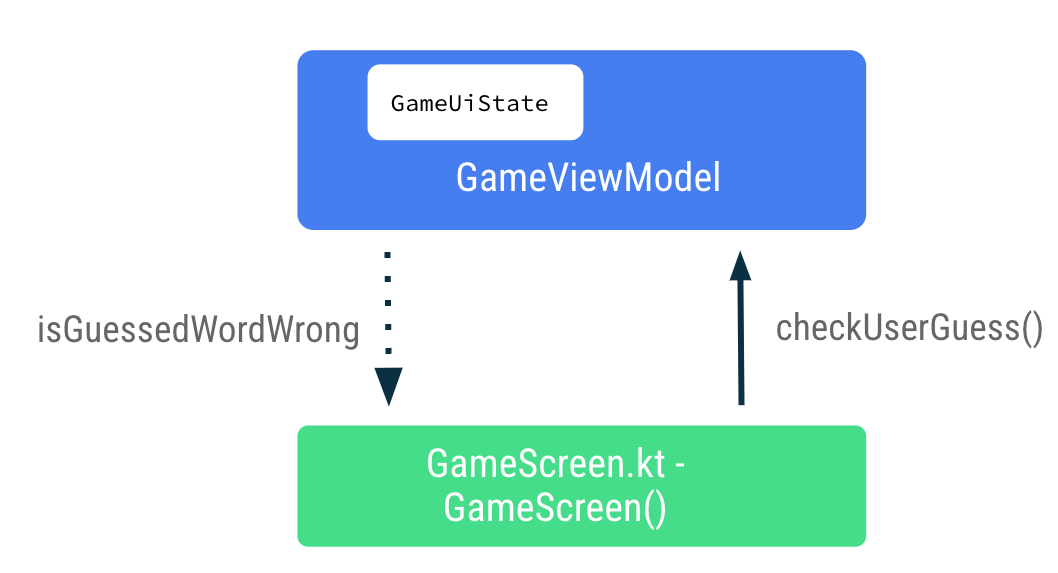
- 在
GameScreen.kt文件中的GameScreen()可组合函数末尾,在 Submit 按钮的onClicklambda 表达式内调用gameViewModel.checkUserGuess()。
Button(
modifier = modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.weight(1f)
.padding(start = 8.dp),
onClick = { gameViewModel.checkUserGuess() }
) {
Text(stringResource(R.string.submit))
}
- 在
GameScreen()可组合函数中,更新GameLayout()函数调用,以在onKeyboardDonelambda 表达式中传递gameViewModel.checkUserGuess()。
GameLayout(
currentScrambledWord = gameUiState.currentScrambledWord,
userGuess = gameViewModel.userGuess,
onUserGuessChanged = { gameViewModel.updateUserGuess(it) },
onKeyboardDone = { gameViewModel.checkUserGuess() }
)
- 在
GameLayout()可组合函数中,为Boolean添加一个函数参数isGuessWrong。将OutlinedTextField的isError参数设置为isGuessWrong,以便在用户猜错时在文本字段中显示错误。
fun GameLayout(
currentScrambledWord: String,
isGuessWrong: Boolean,
userGuess: String,
onUserGuessChanged: (String) -> Unit,
onKeyboardDone: () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier
) {
Column(
// ,...
OutlinedTextField(
// ...
isError = isGuessWrong,
keyboardOptions = KeyboardOptions.Default.copy(
imeAction = ImeAction.Done
),
keyboardActions = KeyboardActions(
onDone = { onKeyboardDone() }
),
)
}
}
- 在
GameScreen()可组合函数中,更新GameLayout()函数调用以传递isGuessWrong。
GameLayout(
currentScrambledWord = gameUiState.currentScrambledWord,
userGuess = gameViewModel.userGuess,
onUserGuessChanged = { gameViewModel.updateUserGuess(it) },
onKeyboardDone = { gameViewModel.checkUserGuess() },
isGuessWrong = gameUiState.isGuessedWordWrong,
// ...
)
- 构建并运行您的应用。
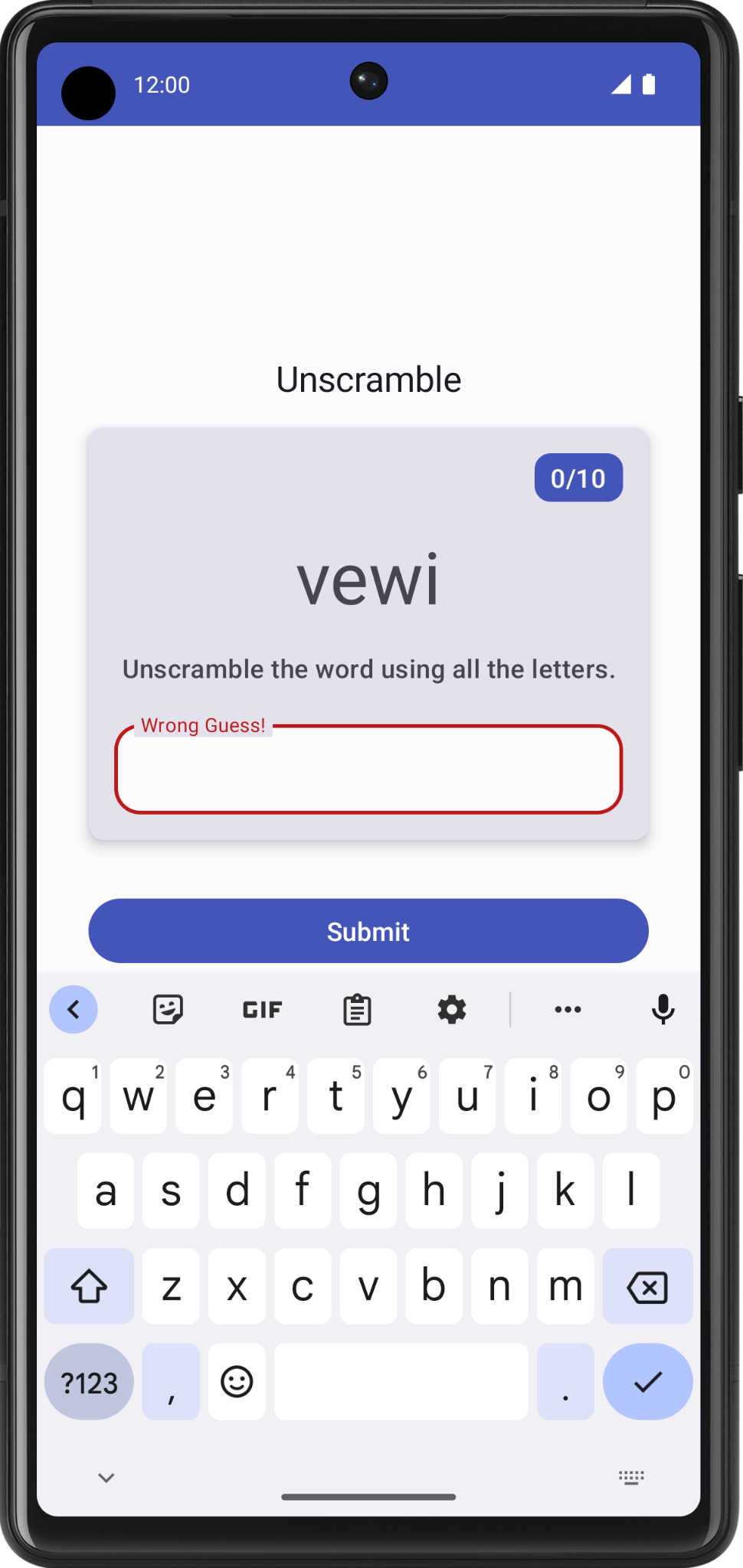
- 输入错误的猜测,然后点击 Submit。请注意,文本字段会变为红色,指明猜测有误。
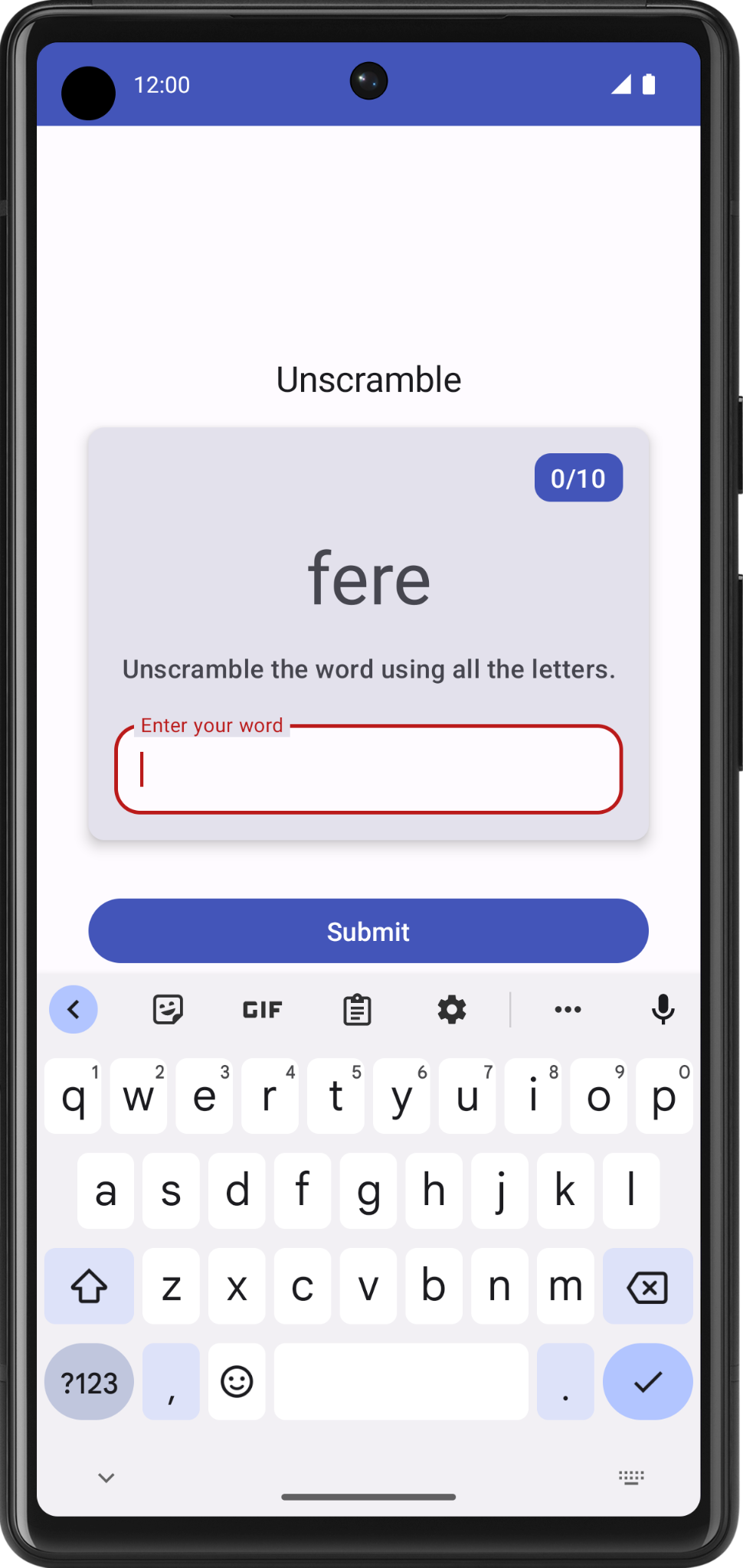
请注意,文本字段标签仍然显示“Enter your word”。为使应用简单易用,您需要添加一些错误文本,指明所猜的单词不对。
- 在
GameScreen.kt文件的GameLayout()可组合函数中,根据isGuessWrong上的文本字段更新标签参数,如下所示:
OutlinedTextField(
// ...
label = {
if (isGuessWrong) {
Text(stringResource(R.string.wrong_guess))
} else {
Text(stringResource(R.string.enter_your_word))
}
},
// ...
)
- 在
strings.xml文件中,向错误标签添加一个字符串。
<string name="wrong_guess">Wrong Guess!</string>
- 再次构建并运行您的应用。
- 输入错误的猜测,然后点击 Submit。请注意错误标签。
8. 更新得分和单词数
在此任务中,您将在用户玩游戏时更新得分和单词数。得分必须成为 _ uiState 的一部分。
- 在
GameUiState中,添加一个score变量并将其初始化为零。
data class GameUiState(
val currentScrambledWord: String = "",
val isGuessedWordWrong: Boolean = false,
val score: Int = 0
)
- 如要更新得分值,请在
GameViewModel的checkUserGuess()函数中,将if条件设置为当用户猜测正确时提高score值。
import com.example.unscramble.data.SCORE_INCREASE
fun checkUserGuess() {
if (userGuess.equals(currentWord, ignoreCase = true)) {
// User's guess is correct, increase the score
val updatedScore = _uiState.value.score.plus(SCORE_INCREASE)
} else {
//...
}
}
- 在
GameViewModel中,再添加一个名为updateGameState的方法来更新得分,增加当前单词数,并从WordsData.kt文件中选择一个新单词。添加一个名为updatedScore的Int作为参数。更新游戏状态界面变量,如下所示:
private fun updateGameState(updatedScore: Int) {
_uiState.update { currentState ->
currentState.copy(
isGuessedWordWrong = false,
currentScrambledWord = pickRandomWordAndShuffle(),
score = updatedScore
)
}
}
- 在
checkUserGuess()函数中,如果用户的猜测正确,请用更新后的得分调用updateGameState,为下一轮游戏做好准备。
fun checkUserGuess() {
if (userGuess.equals(currentWord, ignoreCase = true)) {
// User's guess is correct, increase the score
// and call updateGameState() to prepare the game for next round
val updatedScore = _uiState.value.score.plus(SCORE_INCREASE)
updateGameState(updatedScore)
} else {
//...
}
}
完成后的 checkUserGuess() 应如下所示:
fun checkUserGuess() {
if (userGuess.equals(currentWord, ignoreCase = true)) {
// User's guess is correct, increase the score
// and call updateGameState() to prepare the game for next round
val updatedScore = _uiState.value.score.plus(SCORE_INCREASE)
updateGameState(updatedScore)
} else {
// User's guess is wrong, show an error
_uiState.update { currentState ->
currentState.copy(isGuessedWordWrong = true)
}
}
// Reset user guess
updateUserGuess("")
}
接下来,与更新得分类似,您需要更新单词数。
- 在
GameUiState中针对计数再添加一个变量。将其命名为currentWordCount,并初始化为1。
data class GameUiState(
val currentScrambledWord: String = "",
val currentWordCount: Int = 1,
val score: Int = 0,
val isGuessedWordWrong: Boolean = false,
)
- 在
GameViewModel.kt文件的updateGameState()函数中,增加单词数,如下所示。系统会调用updateGameState()函数,为下一轮游戏做好准备。
private fun updateGameState(updatedScore: Int) {
_uiState.update { currentState ->
currentState.copy(
//...
currentWordCount = currentState.currentWordCount.inc(),
)
}
}
及格分数和单词数
完成以下步骤,以便将得分和单词数数据从 ViewModel 向下传递至 GameScreen。
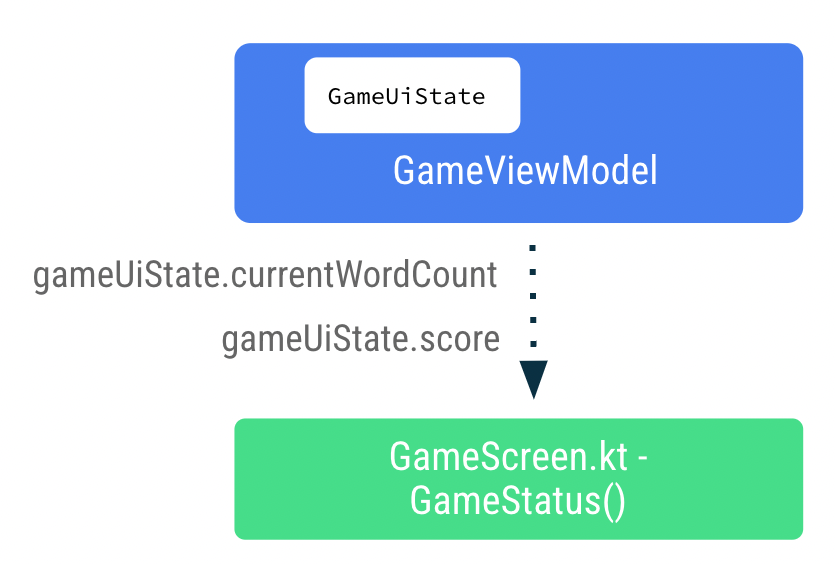
- 在
GameScreen.kt文件的GameLayout()可组合函数中,将单词数添加为参数,并将wordCount格式参数传递给文本元素。
fun GameLayout(
onUserGuessChanged: (String) -> Unit,
onKeyboardDone: () -> Unit,
wordCount: Int,
//...
) {
//...
Card(
//...
) {
Column(
// ...
) {
Text(
//..
text = stringResource(R.string.word_count, wordCount),
style = typography.titleMedium,
color = colorScheme.onPrimary
)
// ...
}
- 更新
GameLayout()函数调用以包含单词数。
GameLayout(
userGuess = gameViewModel.userGuess,
wordCount = gameUiState.currentWordCount,
//...
)
- 在
GameScreen()可组合函数中,更新GameStatus()函数调用以包含score参数。从gameUiState传递得分。
GameStatus(score = gameUiState.score, modifier = Modifier.padding(20.dp))
- 构建并运行应用。
- 输入猜出的单词,然后点击 Submit。请注意,得分和单词数更新了。
- 点击 Skip,您会发现没有任何反应。
如要实现跳过功能,您需要将跳过事件回调传递给 GameViewModel。
- 在
GameScreen.kt文件的GameScreen()可组合函数中,在onClicklambda 表达式中调用gameViewModel.skipWord()。
Android Studio 会显示错误,因为您尚未实现该函数。您将在下一步中通过添加 skipWord() 方法来修正此错误。当用户跳过某个单词时,您需要更新游戏变量并为下一轮游戏做好准备。
OutlinedButton(
onClick = { gameViewModel.skipWord() },
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()
) {
//...
}
- 在
GameViewModel中,添加方法skipWord()。 - 在
skipWord()函数内,调用updateGameState(),从而传递得分并重置用户猜测。
fun skipWord() {
updateGameState(_uiState.value.score)
// Reset user guess
updateUserGuess("")
}
- 运行应用并玩游戏。现在,您应该可以跳过单词了。
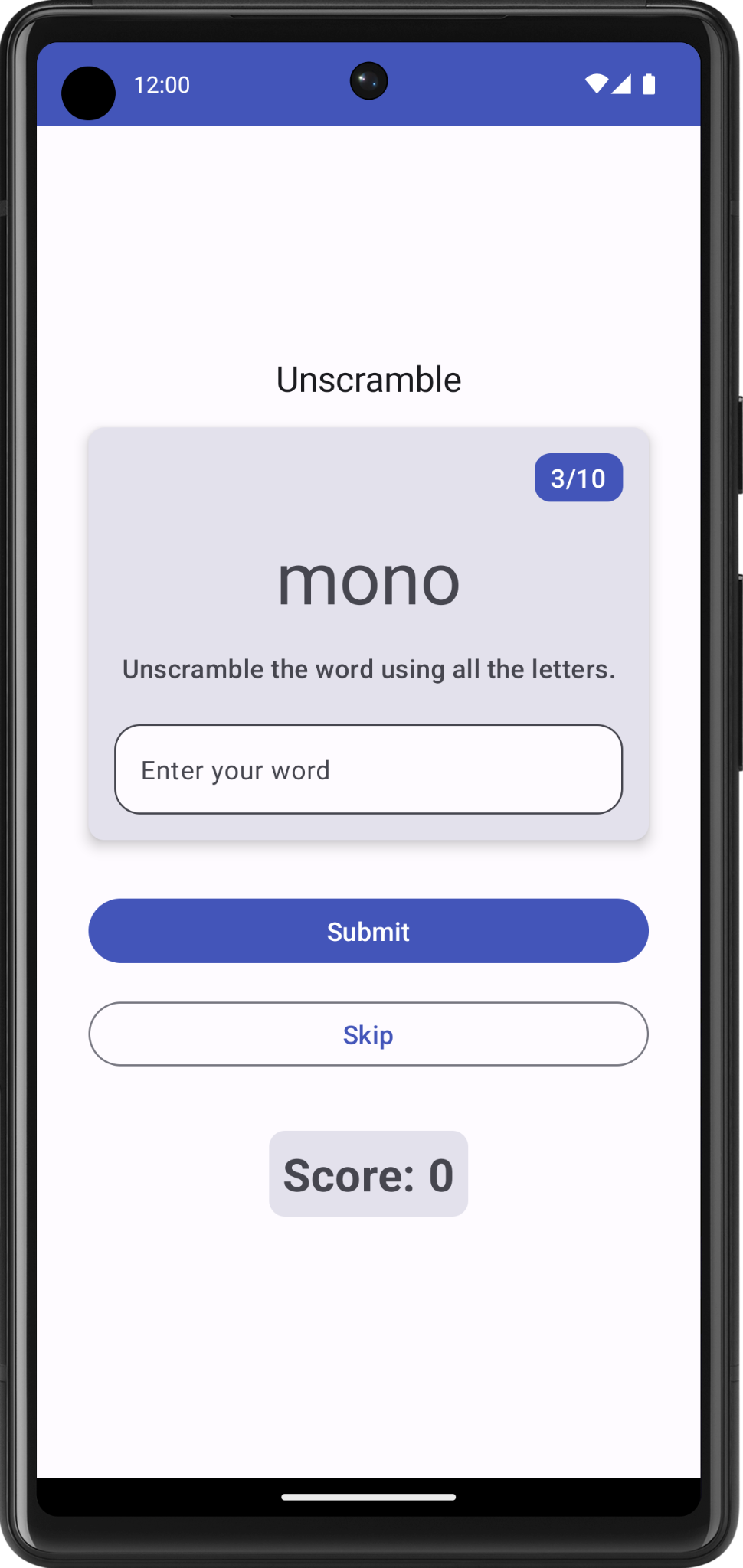
即使您猜完 10 个单词,也仍可以继续玩游戏。在下一个任务中,您将处理游戏的最后一轮。
9. 处理游戏的最后一轮
在当前实现中,用户可以跳过 10 个以上的单词,或者在猜完 10 个单词后继续玩游戏。在此任务中,您将添加用于结束游戏的逻辑。
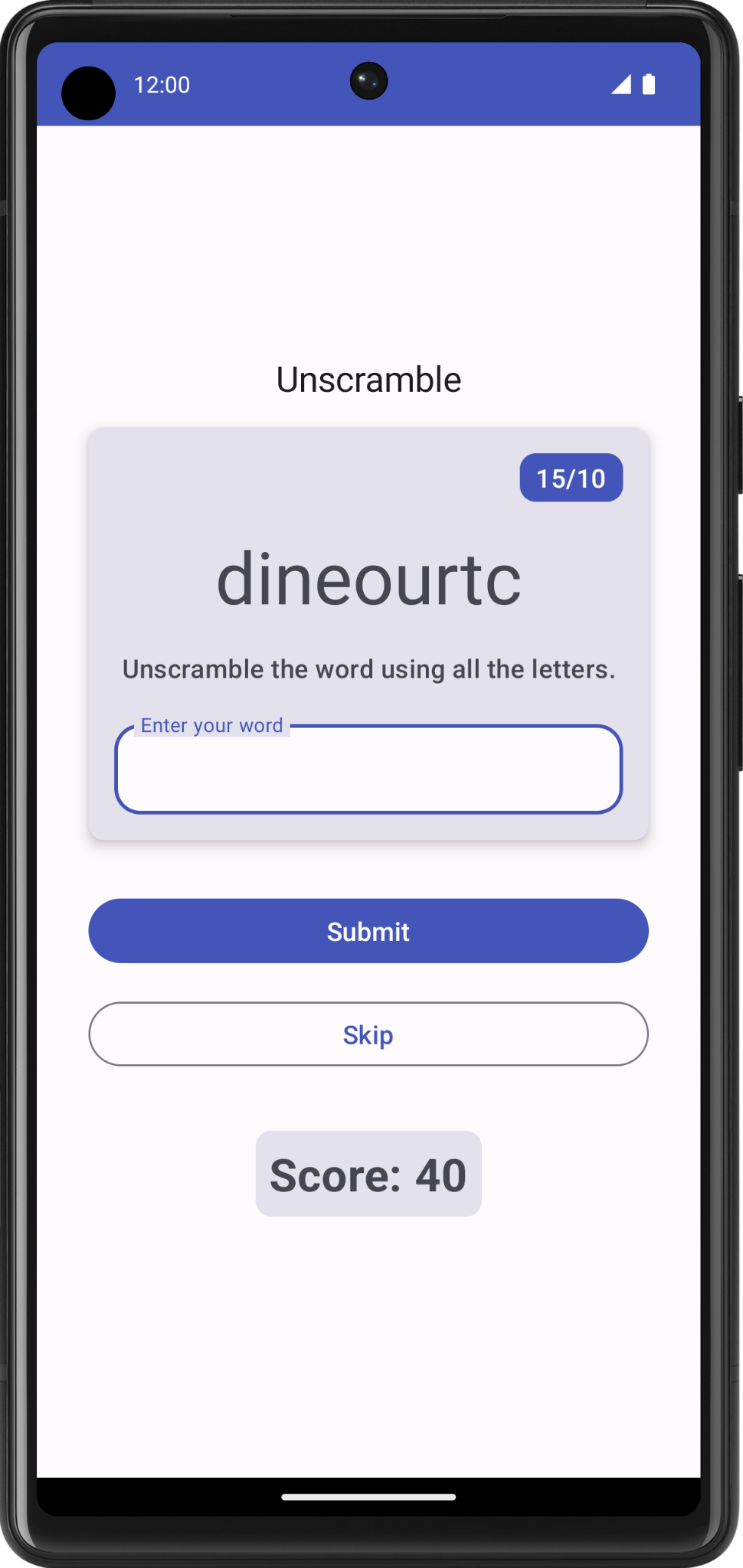
若要实现游戏结束逻辑,您首先需要检查用户是否已达到单词数上限。
- 在
GameViewModel中,添加一个if-else代码块,并将现有函数正文移至else代码块内。 - 添加一个
if条件,以检查usedWords数是否等于MAX_NO_OF_WORDS。
import com.example.android.unscramble.data.MAX_NO_OF_WORDS
private fun updateGameState(updatedScore: Int) {
if (usedWords.size == MAX_NO_OF_WORDS){
//Last round in the game
} else{
// Normal round in the game
_uiState.update { currentState ->
currentState.copy(
isGuessedWordWrong = false,
currentScrambledWord = pickRandomWordAndShuffle(),
currentWordCount = currentState.currentWordCount.inc(),
score = updatedScore
)
}
}
}
- 在
if代码块内,添加Boolean标志isGameOver,并将该标志设置为true来指示游戏结束。 - 在
if代码块内,更新score并重置isGuessedWordWrong。您的函数应该如以下代码所示:
private fun updateGameState(updatedScore: Int) {
if (usedWords.size == MAX_NO_OF_WORDS){
//Last round in the game, update isGameOver to true, don't pick a new word
_uiState.update { currentState ->
currentState.copy(
isGuessedWordWrong = false,
score = updatedScore,
isGameOver = true
)
}
} else{
// Normal round in the game
_uiState.update { currentState ->
currentState.copy(
isGuessedWordWrong = false,
currentScrambledWord = pickRandomWordAndShuffle(),
currentWordCount = currentState.currentWordCount.inc(),
score = updatedScore
)
}
}
}
- 在
GameUiState中,添加Boolean变量isGameOver并将其设置为false。
data class GameUiState(
val currentScrambledWord: String = "",
val currentWordCount: Int = 1,
val score: Int = 0,
val isGuessedWordWrong: Boolean = false,
val isGameOver: Boolean = false
)
- 运行应用并玩游戏。猜完 10 个单词之后,您将无法继续玩游戏。
游戏结束后,最好告知用户并询问他们是否想要再玩一次。您将在下一个任务中实现此功能。
显示游戏结束对话框
在此任务中,您会将 isGameOver 数据从 ViewModel 向下传递到 GameScreen,并使用它来显示一个提醒对话框,其中包含用于结束游戏或重玩游戏的选项。
对话框是提示用户做出决定或输入更多信息的小窗口。通常,对话框不会填满整个屏幕,而且需要用户执行操作后才能继续。Android 提供不同类型的对话框。在此 Codelab 中,您将学习提醒对话框。
提醒对话框详解
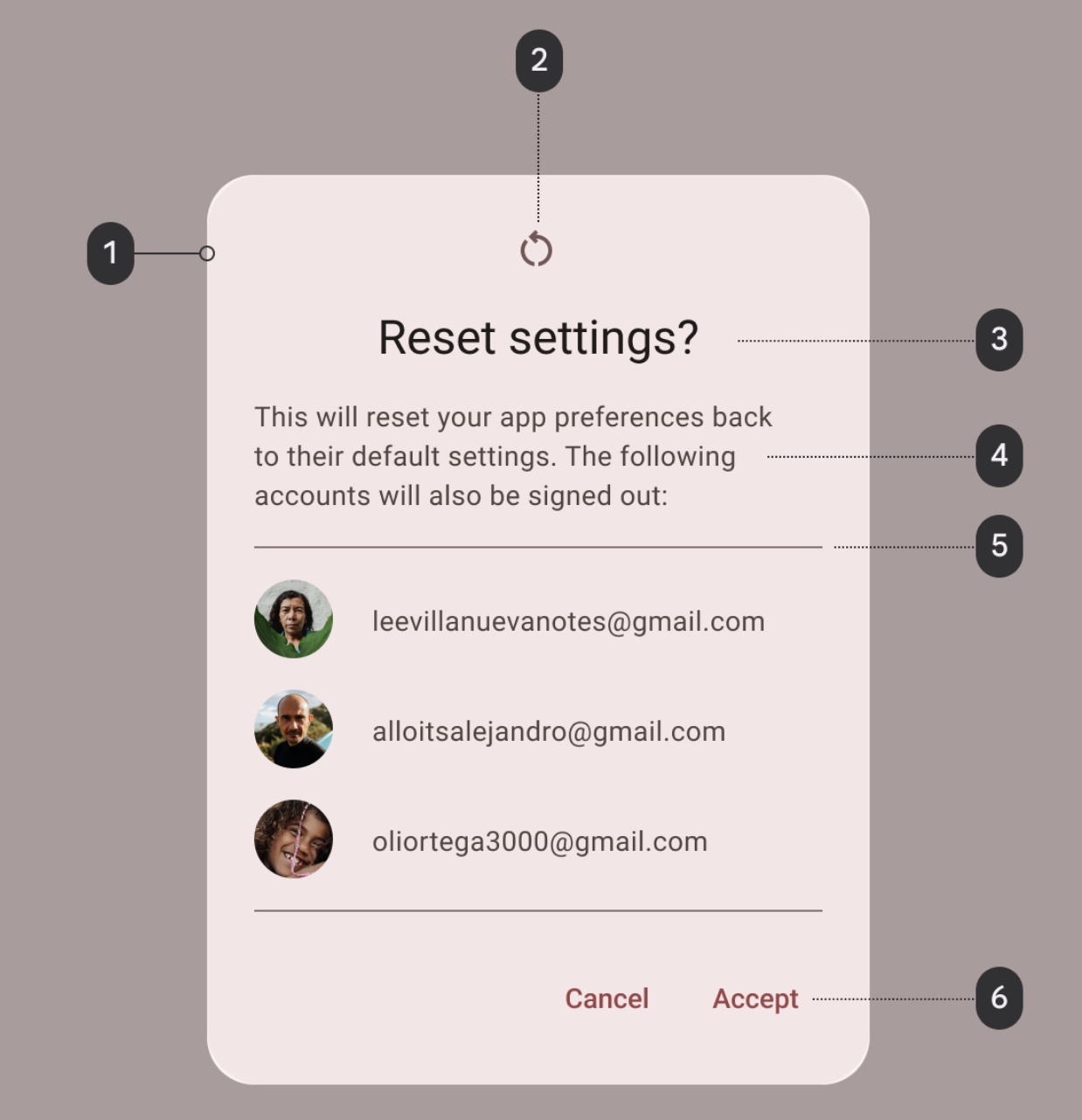
- 容器
- 图标(可选)
- 标题(可选)
- 辅助文本
- 分隔线(可选)
- 操作
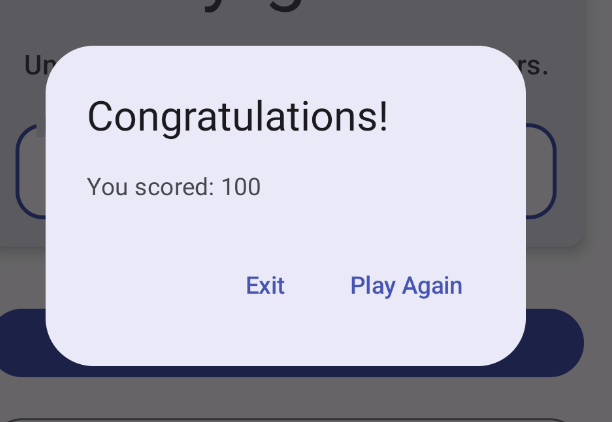
起始代码中的 GameScreen.kt 文件已提供一个函数来显示提醒对话框,其中包含用于退出游戏或重玩游戏的选项。
@Composable
private fun FinalScoreDialog(
onPlayAgain: () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier
) {
val activity = (LocalContext.current as Activity)
AlertDialog(
onDismissRequest = {
// Dismiss the dialog when the user clicks outside the dialog or on the back
// button. If you want to disable that functionality, simply use an empty
// onDismissRequest.
},
title = { Text(stringResource(R.string.congratulations)) },
text = { Text(stringResource(R.string.you_scored, 0)) },
modifier = modifier,
dismissButton = {
TextButton(
onClick = {
activity.finish()
}
) {
Text(text = stringResource(R.string.exit))
}
},
confirmButton = {
TextButton(
onClick = {
onPlayAgain()
}
) {
Text(text = stringResource(R.string.play_again))
}
}
)
}
在此函数中,title 和 text 参数用于在提醒对话框中显示标题和辅助文本。dismissButton 和 confirmButton 是文本按钮。在 dismissButton 参数中,您显示文本 Exit,并通过结束 activity 来终止应用。在 confirmButton 参数中,您重玩游戏并显示文本 Play Again。
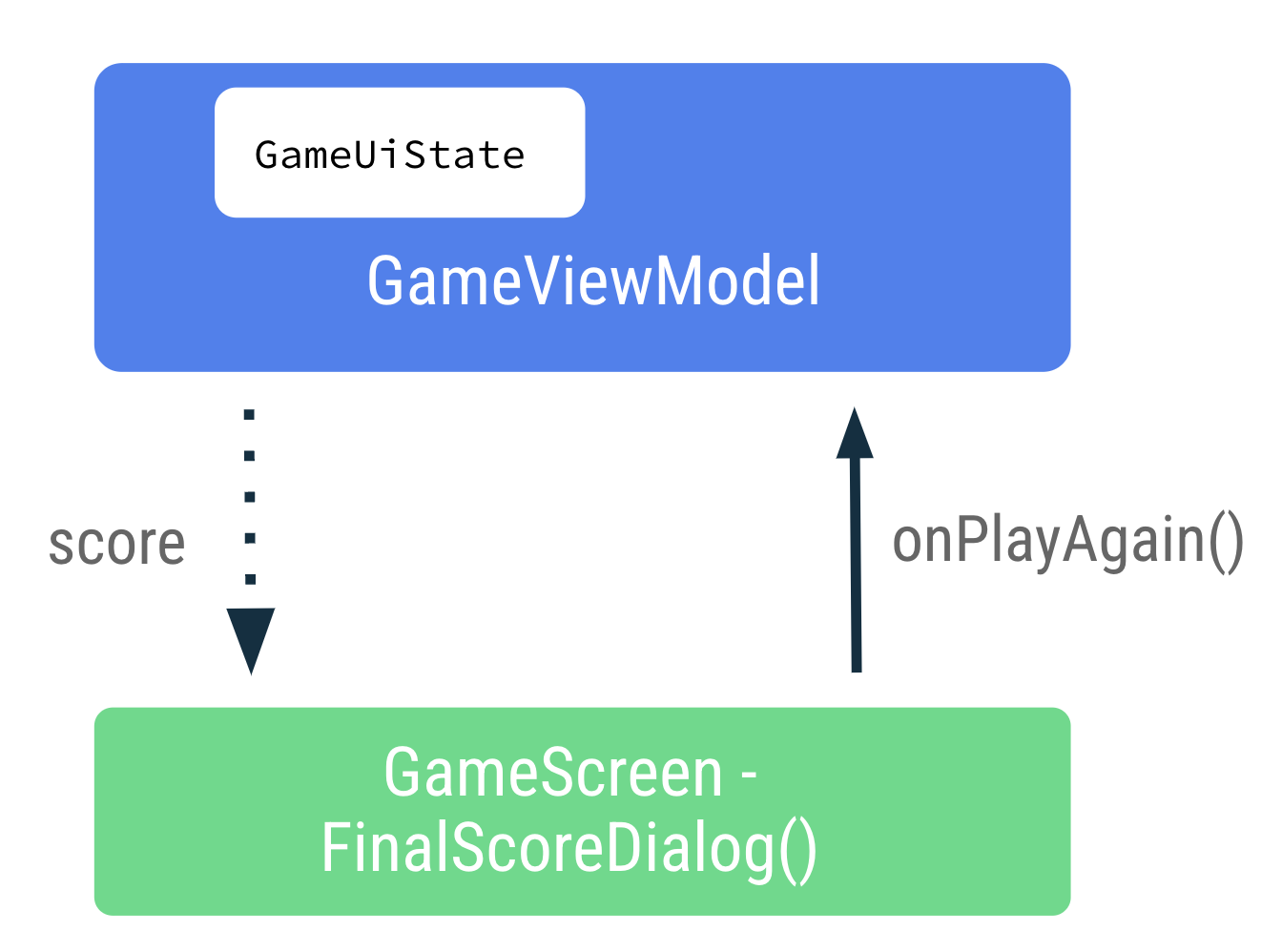
- 在
GameScreen.kt文件的FinalScoreDialog()函数中,请注意用于在提醒对话框中显示游戏得分的得分参数。
@Composable
private fun FinalScoreDialog(
score: Int,
onPlayAgain: () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier
) {
- 在
FinalScoreDialog()函数中,请注意如何使用text形参 lambda 表达式将score用作对话框文本的格式参数。
text = { Text(stringResource(R.string.you_scored, score)) }
- 在
GameScreen.kt文件中GameScreen()可组合函数末尾的Column代码块后,添加if条件以检查gameUiState.isGameOver。 - 在
if代码块中,显示提醒对话框。调用FinalScoreDialog(),从而传入onPlayAgain事件回调的score和gameViewModel.resetGame()。
if (gameUiState.isGameOver) {
FinalScoreDialog(
score = gameUiState.score,
onPlayAgain = { gameViewModel.resetGame() }
)
}
resetGame() 是从 GameScreen 向上传递给 ViewModel 的事件回调。
- 在
GameViewModel.kt文件中,调用resetGame()函数,初始化_uiState,然后选择一个新单词。
fun resetGame() {
usedWords.clear()
_uiState.value = GameUiState(currentScrambledWord = pickRandomWordAndShuffle())
}
- 构建并运行您的应用。
- 玩游戏,直到游戏结束,可以看到包含用于退出游戏或重玩游戏的 Exit 或 Play Again 选项的提醒对话框。尝试提醒对话框中显示的选项。
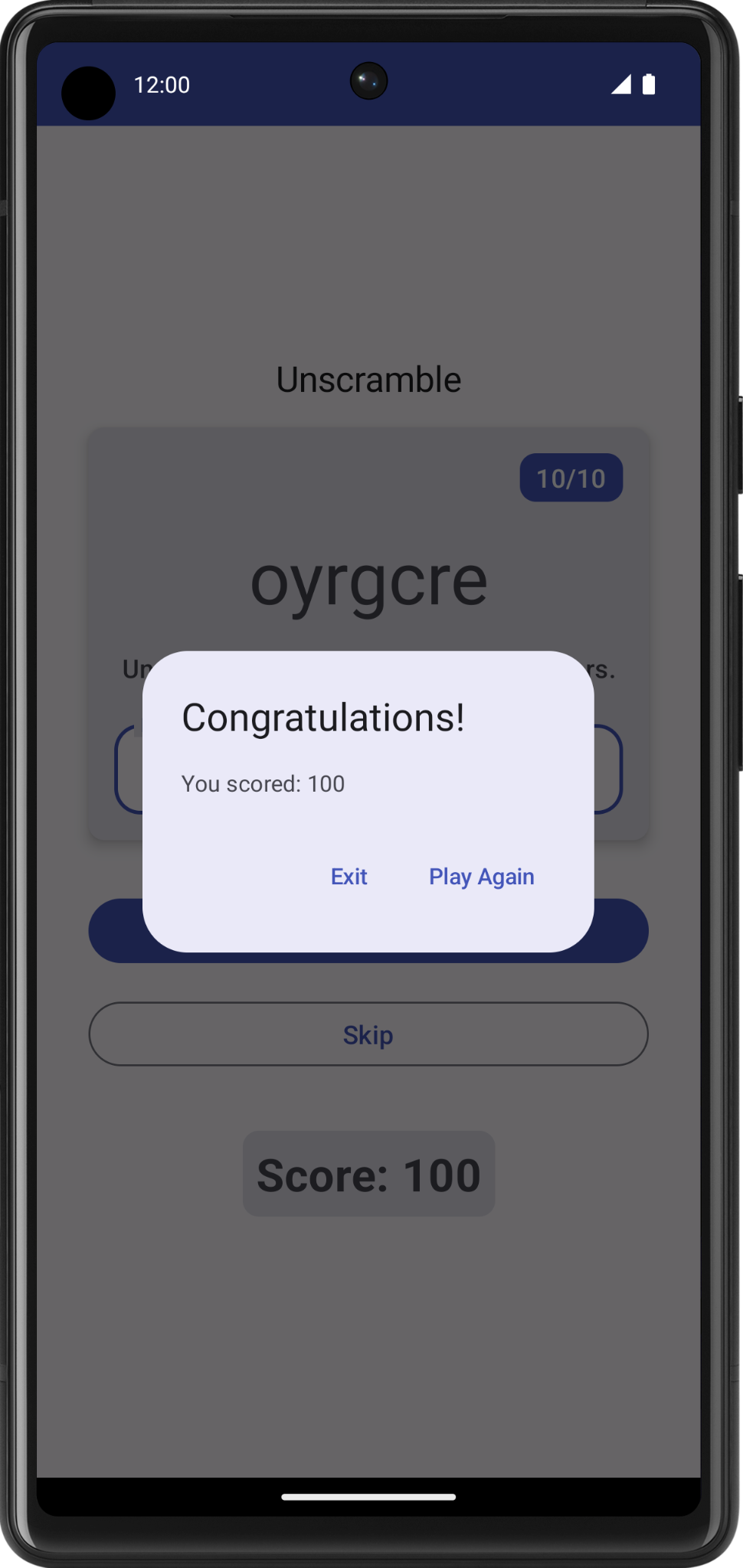
10. 设备旋转状态
在之前的 Codelab 中,您已了解了 Android 中的配置更改。发生配置更改时,Android 会从头开始重启相应 activity,同时运行所有生命周期启动回调。
ViewModel 存储应用相关的数据,这些数据不会在 Android 框架销毁并重新创建 activity 时销毁。在配置更改期间会自动保留 ViewModel 对象,不会像销毁 activity 实例一样将其销毁。它们存储的数据在重组后会立即可用。
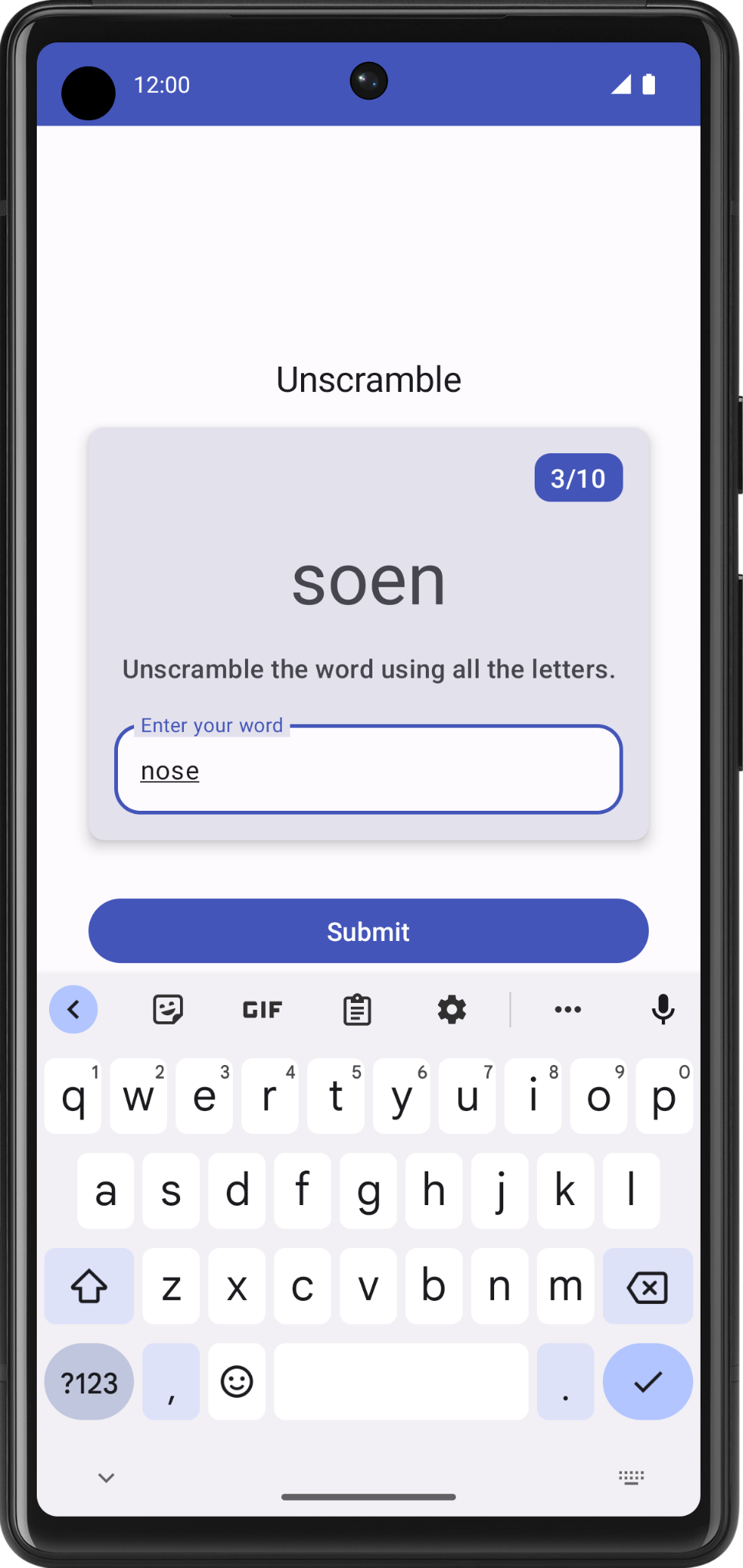
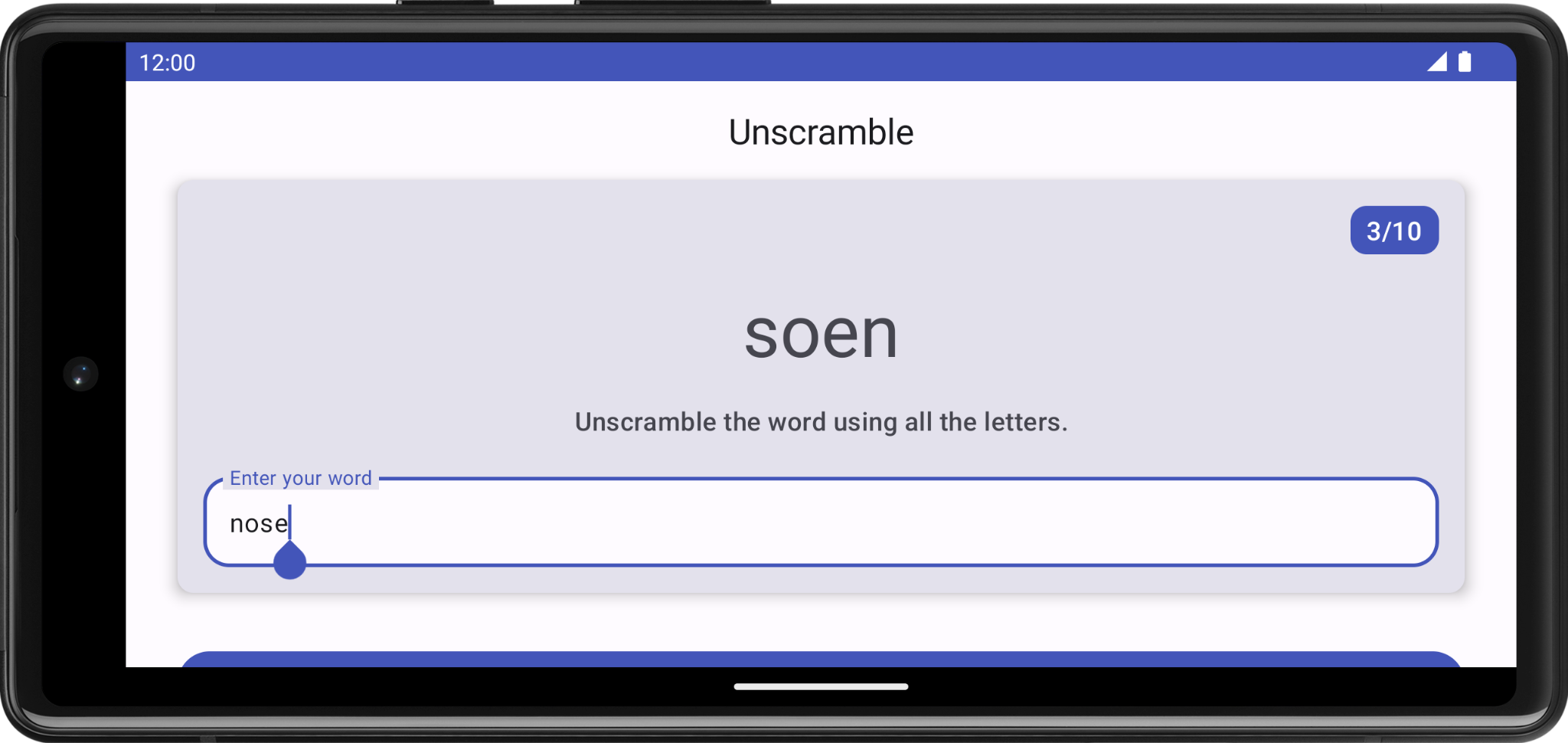
在此任务中,您将检查应用是否在配置更改期间保留状态界面。
- 运行应用并玩一下游戏,猜几个单词。将设备配置从竖屏模式更改为横屏模式,或者从横屏模式更改为竖屏模式。
- 可以看到,
ViewModel的状态界面中保存的数据在配置更改期间会保留。
11. 获取解决方案代码
如需下载完成后的 Codelab 代码,您可以使用以下 Git 命令:
$ git clone https://github.com/google-developer-training/basic-android-kotlin-compose-training-unscramble.git $ cd basic-android-kotlin-compose-training-unscramble $ git checkout viewmodel
或者,您也可以下载 ZIP 文件形式的代码库,将其解压缩并在 Android Studio 中打开。
如果您想查看此 Codelab 的解决方案代码,请前往 GitHub 查看。
12. 总结
恭喜!您已完成此 Codelab。现在,您已经了解了 Android 应用架构准则如何建议将具有不同责任的类分离并通过模型驱动界面。
别忘了使用 #AndroidBasics 标签在社交媒体上分享您的作品!