1. Before you begin
Introduction
In previous codelabs, you learned how to get data from a web service using a repository pattern and parse the response into a Kotlin object. In this codelab, you build on that knowledge to load and display photos from a web URL. You also revisit how to build a LazyVerticalGrid and use it to display a grid of images on the overview page.
Prerequisites
- Knowledge of how to retrieve JSON from a REST web service and the parsing of that data into Kotlin objects using the Retrofit and Gson libraries
- Knowledge of a REST web service
- Familiarity with Android architecture components, such as a data layer and repository
- Knowledge of dependency injection
- Knowledge of
ViewModelandViewModelProvider.Factory - Knowledge of coroutine implementation for your app
- Knowledge of the repository pattern
What you'll learn
- How to use the Coil library to load and display an image from a web URL.
- How to use a
LazyVerticalGridto display a grid of images. - How to handle potential errors as the images download and display.
What you'll build
- Modify the Mars Photos app to get the image URL from the Mars data, and use Coil to load and display that image.
- Add a loading animation and error icon to the app.
- Add status and error handling to the app.
What you'll need
- A computer with a modern web browser, such as the latest version of Chrome
- Starter code for the Mars Photos app with REST web services
2. App overview
In this codelab, you continue working with the Mars Photos app from a previous codelab. The Mars Photos app connects to a web service to retrieve and display the number of Kotlin objects retrieved using Gson. These Kotlin objects contain the URLs of real-life photos from the Mars surface captured from NASA's Mars Rovers.
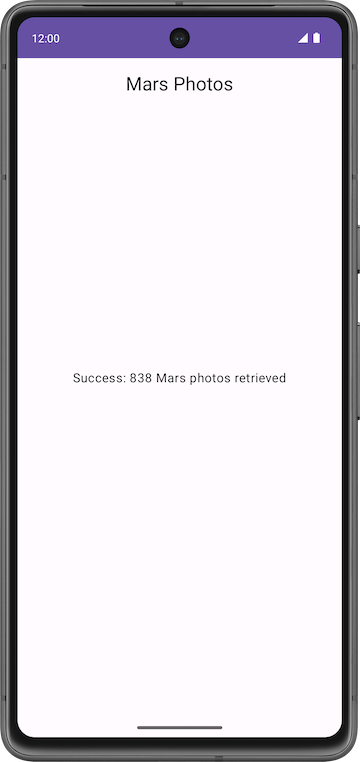
The version of the app you build in this codelab displays Mars photos in a grid of images. The images are part of the data that your app retrieves from the web service. Your app uses the Coil library to load and display the images and a LazyVerticalGrid to create the grid layout for the images. Your app will also handle network errors gracefully by displaying an error message.

Get the starter code
To get started, download the starter code:
Alternatively, you can clone the GitHub repository for the code:
$ git clone https://github.com/google-developer-training/basic-android-kotlin-compose-training-mars-photos.git $ cd basic-android-kotlin-compose-training-mars-photos $ git checkout coil-starter
You can browse the code in the Mars Photos GitHub repository.
3. Display a downloaded image
Displaying a photo from a web URL might sound straightforward, but there is quite a bit of engineering to make it work well. The image has to be downloaded, internally stored(cached), and decoded from its compressed format to an image that Android can use. You can cache the image to an in-memory cache, a storage-based cache, or both. All this has to happen in low-priority background threads so the UI remains responsive. Also, for the best network and CPU performance, you might want to fetch and decode more than one image at once.
Fortunately, you can use a community-developed library called Coil to download, buffer, decode, and cache your images. Without the use of Coil, you would have much more work to do.
Coil basically needs two things:
- The URL of the image you want to load and display.
- An
AsyncImagecomposable to actually display that image.
In this task, you learn how to use Coil to display a single image from the Mars web service. You display the image of the first Mars photo in the list of photos that the web service returns. The following images display the before and after screenshots:


Add Coil dependency
- Open the Mars Photos solution app from the Add repository and Manual DI codelab.
- Run the app to confirm that it shows the count of Mars photos retrieved.
- Open build.gradle.kts (Module :app).
- In the
dependenciessection, add this line for the Coil library:
// Coil
implementation("io.coil-kt:coil-compose:2.4.0")
Check and update the latest version of the library from the Coil documentation page.
- Click Sync Now to rebuild the project with the new dependency.
Display the Image URL
In this step, you retrieve and display the URL of the first Mars photo.
- In
ui/screens/MarsViewModel.kt, inside thegetMarsPhotos()method, inside thetryblock, find the line that sets the data retrieved from the web service tolistResult.
// No need to copy, code is already present
try {
val listResult = marsPhotosRepository.getMarsPhotos()
//...
}
- Update this line by changing
listResulttoresultand assigning the first Mars photo retrieved to the new variableresult. Assign the first photo object at index0.
try {
val result = marsPhotosRepository.getMarsPhotos()[0]
//...
}
- In the next line, update the parameter passed to the
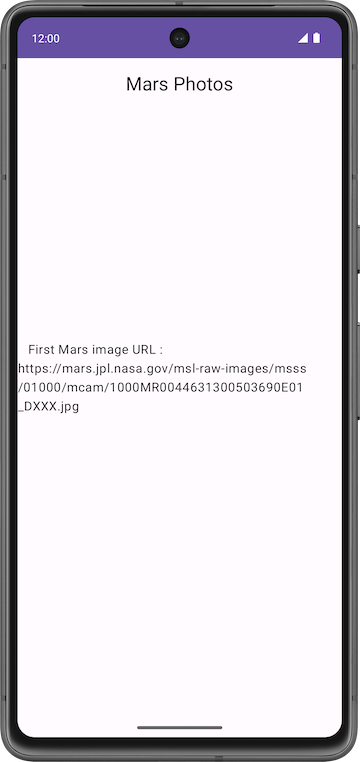
MarsUiState.Success()function call to the string in the following code. Use the data from the new property instead oflistResult. Display the first image URL from the photoresult.
try {
...
MarsUiState.Success("First Mars image URL: ${result.imgSrc}")
}
The complete try block now looks like the following code:
marsUiState = try {
val result = marsPhotosRepository.getMarsPhotos()[0]
MarsUiState.Success(
" First Mars image URL : ${result.imgSrc}"
)
}
- Run the app. The
Textcomposable now displays the URL of the first Mars photo. The next section describes how to make the app display the image in this URL.
Add AsyncImage composable
In this step, you'll add an AsyncImage composable function to load and display a single Mars photo. AsyncImage is a composable that executes an image request asynchronously and renders the result.
// Example code, no need to copy over
AsyncImage(
model = "https://android.com/sample_image.jpg",
contentDescription = null
)
The model argument can either be the ImageRequest.data value or the ImageRequest itself. In the preceding example, you assign the ImageRequest.data value—that is, the image URL, which is "https://android.com/sample_image.jpg". The following example code shows how to assign the ImageRequest itself to the model.
// Example code, no need to copy over
AsyncImage(
model = ImageRequest.Builder(LocalContext.current)
.data("https://example.com/image.jpg")
.crossfade(true)
.build(),
placeholder = painterResource(R.drawable.placeholder),
contentDescription = stringResource(R.string.description),
contentScale = ContentScale.Crop,
modifier = Modifier.clip(CircleShape)
)
AsyncImage supports the same arguments as the standard Image composable. Additionally, it supports setting placeholder/error/fallback painters and onLoading/onSuccess/onError callbacks. The preceding example code loads the image with a circle crop and crossfade and sets a placeholder.
contentDescription sets the text used by accessibility services to describe what this image represents.
Add an AsyncImage composable to your code to display the first Mars photo retrieved.
- In
ui/screens/HomeScreen.kt, add a new composable function calledMarsPhotoCard(), which takesMarsPhotoandModifier.
@Composable
fun MarsPhotoCard(photo: MarsPhoto, modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
}
- Inside the
MarsPhotoCard()composable function, add theAsyncImage()function as follows:
import coil.compose.AsyncImage
import coil.request.ImageRequest
import androidx.compose.ui.platform.LocalContext
@Composable
fun MarsPhotoCard(photo: MarsPhoto, modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
AsyncImage(
model = ImageRequest.Builder(context = LocalContext.current)
.data(photo.imgSrc)
.build(),
contentDescription = stringResource(R.string.mars_photo),
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()
)
}
In the preceding code, you build an ImageRequest using the image URL (photo.imgSrc) and pass it to the model argument. You use contentDescription to set the text for accessibility readers.
- Add
crossfade(true)to theImageRequestto enable a crossfade animation when the request completes successfully.
@Composable
fun MarsPhotoCard(photo: MarsPhoto, modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
AsyncImage(
model = ImageRequest.Builder(context = LocalContext.current)
.data(photo.imgSrc)
.crossfade(true)
.build(),
contentDescription = stringResource(R.string.mars_photo),
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()
)
}
- Update the
HomeScreencomposable to display theMarsPhotoCardcomposable instead of theResultScreencomposable when the request successfully completes. You fix the type mismatch error in the next step.
@Composable
fun HomeScreen(
marsUiState: MarsUiState,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier
) {
when (marsUiState) {
is MarsUiState.Loading -> LoadingScreen(modifier = modifier.fillMaxSize())
is MarsUiState.Success -> MarsPhotoCard(photo = marsUiState.photos, modifier = modifier.fillMaxSize())
else -> ErrorScreen(modifier = modifier.fillMaxSize())
}
}
- In the
MarsViewModel.ktfile, update theMarsUiStateinterface to accept aMarsPhotoobject instead of aString.
sealed interface MarsUiState {
data class Success(val photos: MarsPhoto) : MarsUiState
//...
}
- Update
getMarsPhotos()function to pass the first Mars photo object toMarsUiState.Success(). Delete theresultvariable.
marsUiState = try {
MarsUiState.Success(marsPhotosRepository.getMarsPhotos()[0])
}
- Run the app and confirm that it displays a single Mars image.

- The Mars photo is not filling the entire screen. To fill available space on screen, in
HomeScreen.ktinAsyncImage, set thecontentScaletoContentScale.Crop.
import androidx.compose.ui.layout.ContentScale
@Composable
fun MarsPhotoCard(photo: MarsPhoto, modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
AsyncImage(
model = ImageRequest.Builder(context = LocalContext.current)
.data(photo.imgSrc)
.crossfade(true)
.build(),
contentDescription = stringResource(R.string.mars_photo),
contentScale = ContentScale.Crop,
modifier = modifier,
)
}
- Run the app and confirm that the image fills the screen both horizontally and vertically.

Add loading and error images
You can improve the user experience in your app by showing a placeholder image while loading the image. You can also display an error image if the loading fails due to an issue, such as a missing or corrupt image file. In this section, you add both error and placeholder images using AsyncImage.
- Open
res/drawable/ic_broken_image.xmland click the Design or Split tab on the right. For the error image, use the broken-image icon that's available in the built-in icon library. This vector drawable uses theandroid:tintattribute to color the icon gray.

- Open
res/drawable/loading_img.xml. This drawable is an animation that rotates an image drawable,loading_img.xml, around the center point. (You don't see the animation in the preview.)

- Return to the
HomeScreen.ktfile. In theMarsPhotoCardcomposable, update the call toAsyncImage()to adderrorandplaceholderattributes as shown in the following code:
import androidx.compose.ui.res.painterResource
@Composable
fun MarsPhotoCard(photo: MarsPhoto, modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
AsyncImage(
// ...
error = painterResource(R.drawable.ic_broken_image),
placeholder = painterResource(R.drawable.loading_img),
// ...
)
}
This code sets the placeholder loading image to use while loading (the loading_img drawable). It also sets the image to use if image loading fails (the ic_broken_image drawable).
The complete MarsPhotoCard composable now looks like the following code:
@Composable
fun MarsPhotoCard(photo: MarsPhoto, modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
AsyncImage(
model = ImageRequest.Builder(context = LocalContext.current)
.data(photo.imgSrc)
.crossfade(true)
.build(),
error = painterResource(R.drawable.ic_broken_image),
placeholder = painterResource(R.drawable.loading_img),
contentDescription = stringResource(R.string.mars_photo),
contentScale = ContentScale.Crop
)
}
- Run the app. Depending on the speed of your network connection, you might briefly see the loading image as Coil downloads and displays the property image. But you won't see the broken-image icon yet, even if you turn off your network—you fix that in the last task of the codelab.
4. Display a grid of images with a LazyVerticalGrid
Your app now loads a Mars photo from the internet, the first MarsPhoto list item. You've used the image URL from that Mars photo data to populate an AsyncImage. However, the goal is for your app to display a grid of images. In this task, you use a LazyVerticalGrid with a Grid layout manager to display a grid of images.
Lazy grids
The LazyVerticalGrid and LazyHorizontalGrid composables provide support to display items in a grid. A lazy vertical grid displays its items in a vertically scrollable container, spanned across multiple columns, while a lazy horizontal grid has the same behavior on the horizontal axis.
From a design perspective, Grid Layout is best for displaying Mars photos as icons or images.
The columns parameter in LazyVerticalGrid and rows parameter in LazyHorizontalGrid control how cells are formed into columns or rows. The following example code displays items in a grid, using GridCells.Adaptive to set each column to be at least 128.dp wide:
// Sample code - No need to copy over
@Composable
fun PhotoGrid(photos: List<Photo>) {
LazyVerticalGrid(
columns = GridCells.Adaptive(minSize = 150.dp)
) {
items(photos) { photo ->
PhotoItem(photo)
}
}
}
LazyVerticalGrid lets you specify a width for items, and the grid then fits as many columns as possible. After calculating the number of columns, the grid distributes any remaining width equally among the columns. This adaptive way of sizing is especially useful for displaying sets of items across different screen sizes.
In this codelab, to display Mars photos, you use the LazyVerticalGrid composable with GridCells.Adaptive, with each column set to 150.dp wide.
Item keys
When the user scrolls through the grid (a LazyRow within a LazyColumn), the list item position changes. However, due to an orientation change or if the items are added or removed, the user can lose the scroll position within the row. Item keys help you maintain the scroll position based on the key.
By providing keys, you help Compose handle reorderings correctly. For example, if your item contains a remembered state, setting keys allows Compose to move this state together with the item when its position changes.
Add LazyVerticalGrid
Add a composable to display a list of Mars photos in a vertical grid.
- In the
HomeScreen.ktfile, create a new composable function namedPhotosGridScreen(), which takes a list ofMarsPhotoand amodifieras arguments.
@Composable
fun PhotosGridScreen(
photos: List<MarsPhoto>,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
contentPadding: PaddingValues = PaddingValues(0.dp),
) {
}
- Inside the
PhotosGridScreencomposable, add aLazyVerticalGridwith the following parameters.
import androidx.compose.foundation.lazy.grid.LazyVerticalGrid
import androidx.compose.foundation.lazy.grid.GridCells
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxWidth
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.PaddingValues
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
@Composable
fun PhotosGridScreen(
photos: List<MarsPhoto>,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
contentPadding: PaddingValues = PaddingValues(0.dp),
) {
LazyVerticalGrid(
columns = GridCells.Adaptive(150.dp),
modifier = modifier.padding(horizontal = 4.dp),
contentPadding = contentPadding,
) {
}
}
- To add a list of items, inside the
LazyVerticalGridlambda, call theitems()function passing in the list ofMarsPhotoand an item key asphoto.id.
import androidx.compose.foundation.lazy.grid.items
@Composable
fun PhotosGridScreen(
photos: List<MarsPhoto>,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
contentPadding: PaddingValues = PaddingValues(0.dp),
) {
LazyVerticalGrid(
// ...
) {
items(items = photos, key = { photo -> photo.id }) {
}
}
}
- To add the content displayed by a single list item, define the
itemslambda expression. CallMarsPhotoCard, passing in thephoto.
items(items = photos, key = { photo -> photo.id }) {
photo -> MarsPhotoCard(photo)
}
- Update the
HomeScreencomposable to display thePhotosGridScreencomposable instead of theMarsPhotoCardcomposable on completing the request successfully.
when (marsUiState) {
// ...
is MarsUiState.Success -> PhotosGridScreen(marsUiState.photos, modifier)
// ...
}
- In the
MarsViewModel.ktfile, update theMarsUiStateinterface to accept a list ofMarsPhotoobjects instead of a singleMarsPhoto. ThePhotosGridScreencomposable accepts a list ofMarsPhotoobjects.
sealed interface MarsUiState {
data class Success(val photos: List<MarsPhoto>) : MarsUiState
//...
}
- In the
MarsViewModel.ktfile, update thegetMarsPhotos()function to pass a list of Mars photo objects toMarsUiState.Success().
marsUiState = try {
MarsUiState.Success(marsPhotosRepository.getMarsPhotos())
}
- Run the app.

Notice there is no padding around each photo, and the aspect ratio is different for different photos. You can add a Card composable to fix these issues.
Add card composable
- In the
HomeScreen.ktfile, in theMarsPhotoCardcomposable, add aCardwith8.dpelevation around theAsyncImage. Assign themodifierargument to theCardcomposable.
import androidx.compose.material.Card
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.aspectRatio
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding
@Composable
fun MarsPhotoCard(photo: MarsPhoto, modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
Card(
modifier = modifier,
elevation = CardDefaults.cardElevation(defaultElevation = 8.dp)
) {
AsyncImage(
model = ImageRequest.Builder(context = LocalContext.current)
.data(photo.imgSrc)
.crossfade(true)
.build(),
error = painterResource(R.drawable.ic_broken_image),
placeholder = painterResource(R.drawable.loading_img),
contentDescription = stringResource(R.string.mars_photo),
contentScale = ContentScale.Crop,
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()
)
}
}
- To fix the aspect ratio, in
PhotosGridScreen()update the modifier for theMarsPhotoCard().
@Composable
fun PhotosGridScreen(photos: List<MarsPhoto>, modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
LazyVerticalGrid(
//...
) {
items(items = photos, key = { photo -> photo.id }) { photo ->
MarsPhotoCard(
photo,
modifier = modifier
.padding(4.dp)
.fillMaxWidth()
.aspectRatio(1.5f)
)
}
}
}
- Update the result screen preview to preview
PhotosGridScreen(). Mock data with empty image URLs.
@Preview(showBackground = true)
@Composable
fun PhotosGridScreenPreview() {
MarsPhotosTheme {
val mockData = List(10) { MarsPhoto("$it", "") }
PhotosGridScreen(mockData)
}
}
Since the mock data has empty URLs, you see loading images in the photo grid preview.
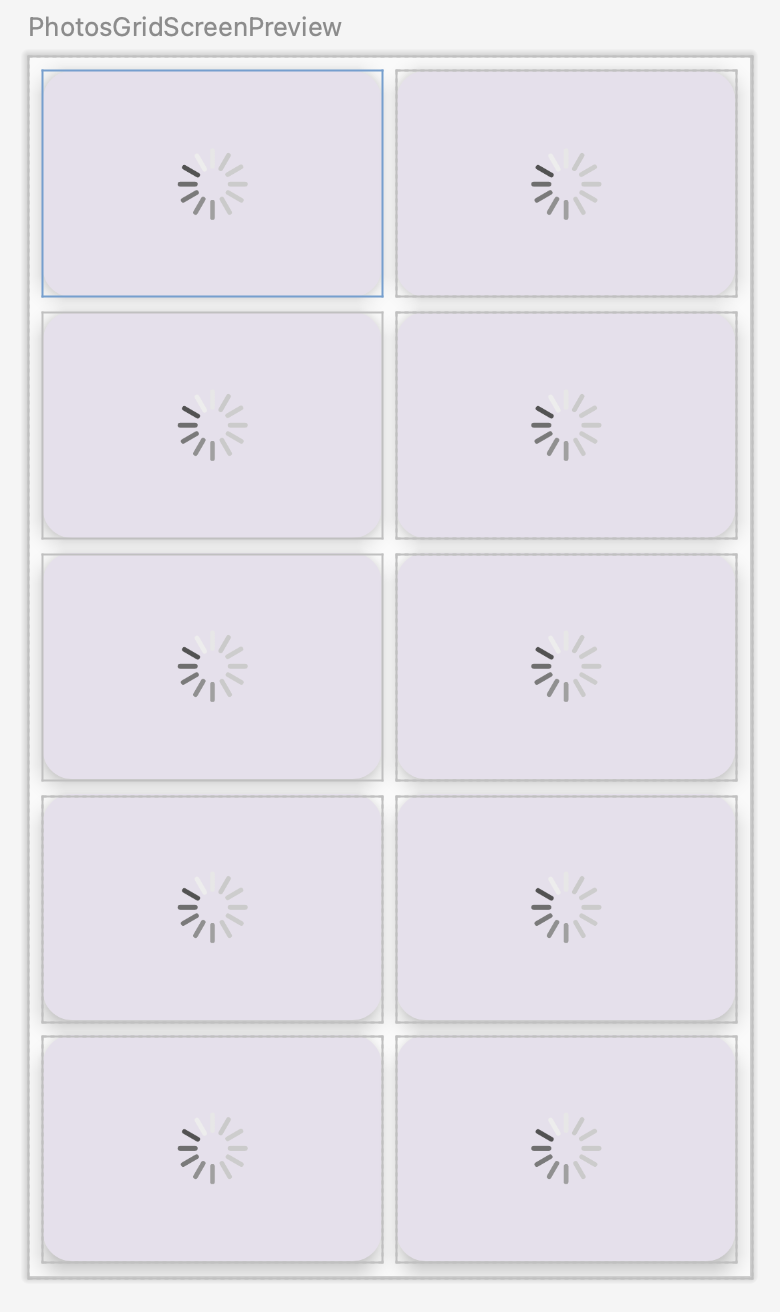
- Run the app.

- While the app is running, turn on Airplane Mode.
- Scroll the images in the emulator. Images that have not yet loaded appear as broken-image icons. This is the image drawable that you passed to the Coil image library to display in case any network error or image cannot be fetched.

Good job! You simulated the network connection error by turning on Airplane Mode in your emulator or device.
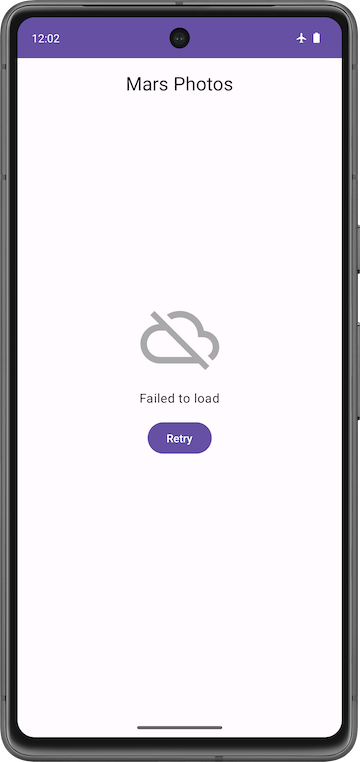
5. Add retry action
In this section you will add a retry action button and retrieve the photos when the button is clicked.
- Add a button to the error screen. In the
HomeScreen.ktfile, update theErrorScreen()composable to include aretryActionlambda parameter and a button.
@Composable
fun ErrorScreen(retryAction: () -> Unit, modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
Column(
// ...
) {
Image(
// ...
)
Text(//...)
Button(onClick = retryAction) {
Text(stringResource(R.string.retry))
}
}
}
Check the preview
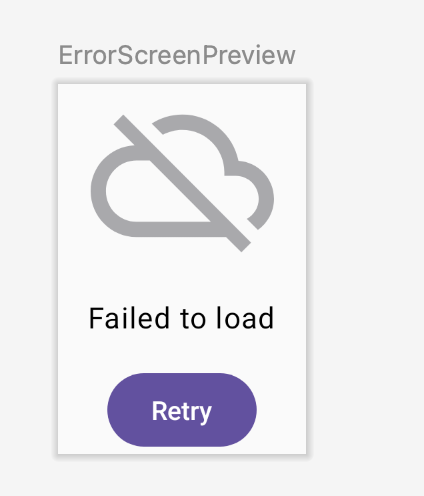
- Update the
HomeScreen()composable to pass in retry lambda.
@Composable
fun HomeScreen(
marsUiState: MarsUiState, retryAction: () -> Unit, modifier: Modifier = Modifier
) {
when (marsUiState) {
//...
is MarsUiState.Error -> ErrorScreen(retryAction, modifier = modifier.fillMaxSize())
}
}
- In the
ui/theme/MarsPhotosApp.ktfile, update theHomeScreen()function call to set theretryActionlambda parameter tomarsViewModel::getMarsPhotos. This will retrieve the mars photos from the server.
HomeScreen(
marsUiState = marsViewModel.marsUiState,
retryAction = marsViewModel::getMarsPhotos
)
6. Update the ViewModel test
The MarsUiState and the MarsViewModel now accommodate a list of photos instead of a single photo. In its current state, the MarsViewModelTest expects the MarsUiState.Success data class to contain a string property. Therefore, the test does not compile. You need to update the marsViewModel_getMarsPhotos_verifyMarsUiStateSuccess() test to assert that the MarsViewModel.marsUiState is equal to the Success state that contains the list of photos.
- Open the
rules/MarsViewModelTest.ktfile. - In the
marsViewModel_getMarsPhotos_verifyMarsUiStateSuccess()test, modify theassertEquals()function call to compare aSuccessstate (passing the fake photos list to the photos parameter) to themarsViewModel.marsUiState.
@Test
fun marsViewModel_getMarsPhotos_verifyMarsUiStateSuccess() =
runTest {
val marsViewModel = MarsViewModel(
marsPhotosRepository = FakeNetworkMarsPhotosRepository()
)
assertEquals(
MarsUiState.Success(FakeDataSource.photosList),
marsViewModel.marsUiState
)
}
The test now compiles, runs, and passes!
7. Get the solution code
To download the code for the finished codelab, you can use this git command:
$ git clone https://github.com/google-developer-training/basic-android-kotlin-compose-training-mars-photos.git
Alternatively, you can download the repository as a zip file, unzip it, and open it in Android Studio.
If you want to see the solution code for this codelab, view it on GitHub.
8. Conclusion
Congratulations on completing this codelab and building out the Mars Photos app! It's time to show off your app with real life Mars pictures to your family and friends.
Don't forget to share your work on social media with #AndroidBasics!
9. Learn more
Android developer documentation:
- Lists and grids | Jetpack Compose | Android Developers
- Lazy grids | Jetpack Compose | Android Developers
- ViewModel Overview
Other:

