Room을 사용하여 로컬 데이터베이스에 데이터 저장 Android Jetpack의 구성요소
상당한 양의 구조화된 데이터를 처리하는 앱은 데이터를 로컬에 유지하여 매우 큰 이익을 얻을 수 있습니다. 가장 일반적인 사용 사례는 기기가 네트워크에 액세스할 수 없을 때도 사용자가 오프라인 상태로 계속 콘텐츠를 탐색할 수 있도록 관련 데이터를 캐시하는 것입니다.
Room 지속성 라이브러리는 SQLite를 완벽히 활용하면서 원활한 데이터베이스 액세스가 가능하도록 SQLite의 추상화 계층을 제공합니다. 특히 Room을 사용하면 다음과 같은 이점이 있습니다.
- SQL 쿼리의 컴파일 시간 확인
- 반복적이고 오류가 발생하기 쉬운 상용구 코드를 최소화하는 편의 주석
- 간소화된 데이터베이스 이전 경로
이러한 점을 고려할 때 SQLite API를 직접 사용하는 대신 Room을 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
설정
앱에서 Room을 사용하려면 앱의 build.gradle 파일에 다음 종속 항목을 추가합니다.
Kotlin
dependencies { val room_version = "2.8.4" implementation("androidx.room:room-runtime:$room_version") // If this project uses any Kotlin source, use Kotlin Symbol Processing (KSP) // See Add the KSP plugin to your project ksp("androidx.room:room-compiler:$room_version") // If this project only uses Java source, use the Java annotationProcessor // No additional plugins are necessary annotationProcessor("androidx.room:room-compiler:$room_version") // optional - Kotlin Extensions and Coroutines support for Room implementation("androidx.room:room-ktx:$room_version") // optional - RxJava2 support for Room implementation("androidx.room:room-rxjava2:$room_version") // optional - RxJava3 support for Room implementation("androidx.room:room-rxjava3:$room_version") // optional - Guava support for Room, including Optional and ListenableFuture implementation("androidx.room:room-guava:$room_version") // optional - Test helpers testImplementation("androidx.room:room-testing:$room_version") // optional - Paging 3 Integration implementation("androidx.room:room-paging:$room_version") }
Groovy
dependencies { def room_version = "2.8.4" implementation "androidx.room:room-runtime:$room_version" // If this project uses any Kotlin source, use Kotlin Symbol Processing (KSP) // See KSP Quickstart to add KSP to your build ksp "androidx.room:room-compiler:$room_version" // If this project only uses Java source, use the Java annotationProcessor // No additional plugins are necessary annotationProcessor "androidx.room:room-compiler:$room_version" // optional - RxJava2 support for Room implementation "androidx.room:room-rxjava2:$room_version" // optional - RxJava3 support for Room implementation "androidx.room:room-rxjava3:$room_version" // optional - Guava support for Room, including Optional and ListenableFuture implementation "androidx.room:room-guava:$room_version" // optional - Test helpers testImplementation "androidx.room:room-testing:$room_version" // optional - Paging 3 Integration implementation "androidx.room:room-paging:$room_version" }
기본 구성요소
Room에는 다음 3가지 주요 구성요소가 있습니다.
- 데이터베이스 클래스: 데이터베이스를 보유하고 앱의 영구 데이터와의 기본 연결을 위한 기본 액세스 포인트 역할을 합니다.
- 데이터 항목: 앱 데이터베이스의 테이블을 나타냅니다.
- 데이터 액세스 객체(DAO): 앱이 데이터베이스의 데이터를 쿼리, 업데이트, 삽입, 삭제하는 데 사용할 수 있는 메서드를 제공합니다.
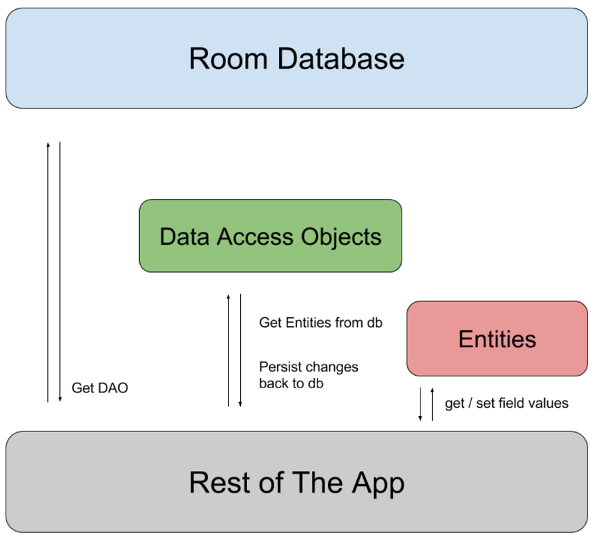
데이터베이스 클래스는 데이터베이스와 연결된 DAO 인스턴스를 앱에 제공합니다. 그러면 앱은 DAO를 사용하여 데이터베이스의 데이터를 연결된 데이터 항목 객체의 인스턴스로 검색할 수 있게 됩니다. 앱은 정의된 데이터 항목을 사용하여 상응하는 테이블의 행을 업데이트하거나 삽입할 새 행을 만들 수도 있습니다. 그림 1은 다양한 Room 구성요소 간 관계를 보여줍니다.
샘플 구현
이 섹션에서는 단일 데이터 항목과 단일 DAO가 있는 Room 데이터베이스의 구현 예를 보여줍니다.
데이터 항목
다음 코드는 User 데이터 항목을 정의합니다. 각 User 인스턴스는 앱 데이터베이스의 user 테이블에 있는 행 하나를 나타냅니다.
Kotlin
@Entity data class User( @PrimaryKey val uid: Int, @ColumnInfo(name = "first_name") val firstName: String?, @ColumnInfo(name = "last_name") val lastName: String? )
자바
@Entity public class User { @PrimaryKey public int uid; @ColumnInfo(name = "first_name") public String firstName; @ColumnInfo(name = "last_name") public String lastName; }
Room의 데이터 항목에 관한 자세한 내용은 Room 항목을 사용하여 데이터 정의를 참고하세요.
데이터 액세스 객체(DAO)
다음 코드는 UserDao라는 DAO를 정의합니다. UserDao는 앱의 나머지 부분이 user 테이블의 데이터와 상호작용하는 데 사용하는 메서드를 제공합니다.
Kotlin
@Dao interface UserDao { @Query("SELECT * FROM user") fun getAll(): List<User> @Query("SELECT * FROM user WHERE uid IN (:userIds)") fun loadAllByIds(userIds: IntArray): List<User> @Query("SELECT * FROM user WHERE first_name LIKE :first AND " + "last_name LIKE :last LIMIT 1") fun findByName(first: String, last: String): User @Insert fun insertAll(vararg users: User) @Delete fun delete(user: User) }
자바
@Dao public interface UserDao { @Query("SELECT * FROM user") List<User> getAll(); @Query("SELECT * FROM user WHERE uid IN (:userIds)") List<User> loadAllByIds(int[] userIds); @Query("SELECT * FROM user WHERE first_name LIKE :first AND " + "last_name LIKE :last LIMIT 1") User findByName(String first, String last); @Insert void insertAll(User... users); @Delete void delete(User user); }
DAO에 관한 자세한 내용은 Room DAO를 사용하여 데이터 액세스를 참고하세요.
데이터베이스
다음 코드는 데이터베이스를 보유할 AppDatabase 클래스를 정의합니다.
AppDatabase는 데이터베이스 구성을 정의하고 영구 데이터에 대한 앱의 기본 액세스 포인트 역할을 합니다. 데이터베이스 클래스는 다음 조건을 충족해야 합니다.
- 클래스에는 데이터베이스와 연결된 데이터 항목을 모두 나열하는
entities배열이 포함된@Database주석이 달려야 합니다. - 클래스는
RoomDatabase를 확장하는 추상 클래스여야 합니다. - 데이터베이스와 연결된 각 DAO 클래스에서 데이터베이스 클래스는 인수가 0개이고 DAO 클래스의 인스턴스를 반환하는 추상 메서드를 정의해야 합니다.
Kotlin
@Database(entities = [User::class], version = 1) abstract class AppDatabase : RoomDatabase() { abstract fun userDao(): UserDao }
자바
@Database(entities = {User.class}, version = 1) public abstract class AppDatabase extends RoomDatabase { public abstract UserDao userDao(); }
참고: 앱이 단일 프로세스에서 실행되면 AppDatabase 객체를 인스턴스화할 때 싱글톤 디자인 패턴을 따라야 합니다. 각 RoomDatabase 인스턴스는 리소스를 상당히 많이 소비하며 단일 프로세스 내에서 여러 인스턴스에 액세스해야 하는 경우는 거의 없습니다.
앱이 여러 프로세스에서 실행되는 경우 데이터베이스 빌더 호출에 enableMultiInstanceInvalidation()을 포함하세요. 이렇게 하면 각 프로세스에 AppDatabase 인스턴스가 있을 때 한 프로세스에서 공유 데이터베이스 파일을 무효화할 수 있으며 이 무효화는 다른 프로세스 내의 AppDatabase 인스턴스로 자동 전파됩니다.
사용
데이터 항목과 DAO, 데이터베이스 객체를 정의한 후에는 다음 코드를 사용하여 데이터베이스 인스턴스를 만들 수 있습니다.
Kotlin
val db = Room.databaseBuilder( applicationContext, AppDatabase::class.java, "database-name" ).build()
자바
AppDatabase db = Room.databaseBuilder(getApplicationContext(), AppDatabase.class, "database-name").build();
그런 다음 AppDatabase의 추상 메서드를 사용하여 DAO 인스턴스를 가져올 수 있습니다. 결과적으로 DAO 인스턴스의 메서드를 사용하여 데이터베이스와 상호작용할 수 있습니다.
Kotlin
val userDao = db.userDao() val users: List<User> = userDao.getAll()
Java
UserDao userDao = db.userDao(); List<User> users = userDao.getAll();
추가 리소스
Room에 관한 자세한 내용은 다음 추가 리소스를 참고하세요.

